Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes
Uploaded by
Gerard Jamero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageOriginal Title
notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageNotes
Uploaded by
Gerard JameroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
WALLBERG
THEORY OF CANCER • Non-Coding Regulatory RNA
• Warburg Effect aka Aerobic Glycolysis o Micro-RNA (miRNA) & Silencing RNA (siRNA) inhibit Gene Expression
o Long Non-Coding Regulatory RNA (lncRNA)
• Mitochondrial insult à insufficient Cellular Respiration à Tumorigenesis
• Cancer Cells exhibit Glucose Fermentation even when enough Oxygen is present to properly respire
(Glycolysis with Lactate secretion & Mitochondrial Respiration) MUTATIONS
• Permanent heritable DNA mRNA Base & AA Sequence changes
ADENOMATOUS POLYPOSIS COLI (APC) GENE • Point Mutations
o Transition – Purine à Purine/Pyrimidine à Pyrimidine
• Antagonizes WNT-b signaling à stimulating enhanced stimulating growth
o Transversion – Purine à Pyrimidine/Pyrimidine à Purine
• Negative regulator controlling b-Catenin concentrations
o Silent Mutation – New Codon, Same AA (No effect)
o b-Catenin – CHON in Adherent Junctions (Epithelial Tissue integrity)
o Missense Mutation – New Codon, Different AA (Variable effects)
• Interacts with E-Cadherin
o Non-Sense Mutation – New Codon is a STOP Codon (Shorter, Non-Functional)
• Mutations à Adenoma formation à Colorectal Cancer
• Frameshift Mutations – Base Deletion/Addition that should NOT be multiples of 3 (Shorter, Non-
• KRAS – Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Functional CHON)
• BAX – induces Cell Death (Apoptosis) • Large Segment Deletion – large Chromosomal Area loss during unequal Meiotic Crossover (Loss of
Function, Shorter/Entirely Missing)
XENOBIOTICS • Splice Donor/Acceptor – Slice Site loss à AA Addition/Deletion or Exon Deletion (e.g. Tay Sachs
• Phase I – Hydroxylation Reactions catalyzed by Cytochrome P450 Species Disease, Gaucher Disease, b-Thalassemia)
• Phase II – Conjugation Reactions catalyzed by various Enzymes • Triple Repeat Expansion – Coding Region Expansions cause longer & unstable CHON; shows Pedigree
o Glucuronidation (most frequent conjugated reaction) similar to Bilirubin using UDP- Anticipation (e.g. Huntington Disease, Fragile X Syndrome, Myotonic Dystrophy)
Glucuronic Acid catalyzed by Glucuronyl Transferases
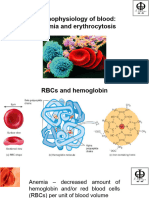
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA
NUCLEOTIDES • HbS Point (Missense) Mutation
• Nucleic Acid Building Blocks • b-Chain AA replacement (Glutamic Acid substituted with Valine)
• Purine/Pyrimidine Base + Ribose/Deoxyribose Sugar = NucleoSIDE • Extravascular & Intravascular Hemolysis
o D-Ribose/2-Deoxy-D-Ribose linked to N-1 (Pyrimidine)/N-9 (Purine) by b-N-Glycosidic Bonds • ¯ O2, High Altitudes, Acidosis precipitate Sickling (Deoxygenated HbS Polymerizes) à Anemia
o Purine Nucleosides: Adenosine, Guanosine • Sickle Cell Trait have resistance to Malaria
o Pyrimidine Nucleosides: Thymidine, Uridine, Cytidine • Crescent-Shaped RBCs
• Nucleoside + Phosphate = NucleoTIDE • Skull X-Ray: Crew Cut Sign ( Erythropoiesis à Marrow Expansion)
o Phosphoryl Group (5’-Phosphate) attached to Pentose C5 by Phosphodiester Bonds • Newborns initially Asymtpomatic ( HbF, ¯ HbS)
o Purine Nucleotides: Adenine, Guanine • Complications:
o Pyrimidine Nucleotides: Tymine, Uracil, Cytosine o Aplastic Crisis 2° to Parvovirus B19
o Autosplenectomy (Howell Jolly Bodies à Risk of infection from Encapsulated Organisms)
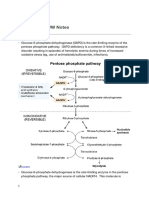
PURINE SYNTHESIS o Splenic Infarct/Sequestration Crisis
1 Ribose-5-P à Phosphoribosyl Pyrophosphate PRPP Synthase ATP o Salmonella Osteomyelitis
2 5-Phospho-b-o-Ribosylamine PRPP Glutamyl Amidotransferase -- o Painful Crises (Vasculo-Occlusive): Dactylitis, Priapism, Acute Chest Syndrome, Avascular
+ Glutamine Necrosis, Stroke
3 Glycinamide Ribosyl-5-Phosphate + Glycine -- o Renal Papullary Necrosis & Microhematuria
4 Formylglycinamide Ribosyl-5-Phosphate Formyltransferase + N10- -- • Treatment: Hydroxyurea ( HbF), Hydration
Formyltetrahydrofolate
5 Formylflycinamidine Ribosyl-5-Phosphate VI Synthetase --
6 Aminoimidazole Ribosyl 5-Phosphate VII Synthase ATP
7 Amimnoimidazole Carboxylate Ribosyl-5-P VII Carboxylase + CO2 --
8 Aminoimidazole Succinyl Carboxamide IX Synthase + Aspartate --
Ribosyl-5-Phosphate
9 Aminoimidazole Carboxamide Ribosyl-5-P Adenylosuccinase + Fumarate --
10 Formimidoimidazole Carboxamide Ribosyl-5-P Formyltransferase + N10- --
Formyltetrahydrofolate
11 Inosine Monophosphate (IMP) IMP Cyclohydrolase --
12 Adenylosuccinate Adenylosuccinate --
Xanthosine Monophosphate IMP Dehydrogenase --
13 Adenosine Monophosphate Adenylsuccinase --
Guanosine Monophosphate Transaminidase + Glutamine --
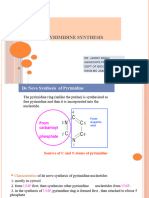
PYRIMIDINE SYNTHESIS
1 NH4 + CO2 à Carbamoyl Phosphate Carbamoyl-P Synthase 2 + --
Aspartic Acid
2 Carbamoyl Aspartic Acid Aspartate Transcarbamoylase --
3 Dihydroorotic Acid Dihydroorotase --
4 Orotic Acid Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase --
5 OMP Orotate Phosphoribosyltransferase --
6 UMP Orotidylic Acid Decarboxylase --
7 UDP ATP --
8 UTP à CTP ATP à CTP Synthase --
dUDP à TMP NADPH à Thymidylate Synthase --
DNA REPLICATION
• Occurs during S Phase
• DNA à DNA (Each Strand serves as a template for Complementary Daughter Strand)
1 Origin of Replication (ori) recognized by Origin Recognition Complex (ORC; DNA-A in E. Coli)
2 Helicase unwinds Double Helix (ATP)
3 ssDNA-Binding Proteins maintain Parent Strand Separation
Topoisomerase relieve Torsal Strain of Helicase-induced unwinding
4 • Type 1: Swivelase
• Type 2: Gyrase à Fluoroquinolones
5 Primase synthesizes short Complementary RNA Primer segments
DNA Polymerase III elongates DNA Strand (adds new Deoxyribonucleotides
6 • Lagging Strand (5’ à 3’ Direction) synthesized continuously & consists of Okazaki Fragments
• Proofreading: Mismatched Nucleotides removed via 3’ à 5’ Exonuclease
7 Another Primer reached à DNA Polymerase I removes Ribonucleotides by 5’ à 3’ Exonuclease
8 DNA Polymerase I fills gap with Deoxyribonucleotides
9 DNA Ligase seals nick (catalyzes formation of last Phosphodiester Bond; ATP)
TYPES OF RNA
• Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries Genetic Information from Nuclear DNA to Cytosol
o CHON Synthesis Template
o 5’ End: Methylguanosine Cap (prevents Digestion)
o 3’ End: Poly (A) Tail
o undergoes Modification in Eukaryotic Cells
• Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – MOST NUMEROUS (Rampant), Ribosome formation (CHON Synthesis site)
• Transfer RNA (tRNA) – SMALLEST (Tiny), translate mRNA Nucleotide Sequences into specific AAs
• Small Nuclear RNA (snRNA) – rRNA & mRNA Processing & Gene Regulation
You might also like
- Purine MetabolismDocument30 pagesPurine MetabolismSamarTharwatNo ratings yet
- Board Recall Must ReadDocument8 pagesBoard Recall Must ReadSarahSalvanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FADocument48 pagesBiochemistry FAJaankiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Midterm RecallsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Midterm Recallssuper novaNo ratings yet
- ANEMIADocument34 pagesANEMIAAkashNo ratings yet
- Cancer Chemotherapy: Acronym of RegimenDocument13 pagesCancer Chemotherapy: Acronym of RegimenVaibhav Bharat100% (1)
- Sketchy Antineoplastic DrugsDocument12 pagesSketchy Antineoplastic DrugsLinds GoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Handout 2019Document56 pagesBiochemistry Handout 2019Sai Charan100% (1)
- Blood BankingDocument8 pagesBlood Bankingadagay100% (1)
- Curs Nucleotide Sem 2Document58 pagesCurs Nucleotide Sem 2George PetreaNo ratings yet
- Pyrimidine SynthesisDocument35 pagesPyrimidine Synthesisdr.yogita.rajNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative Disorders PDFDocument52 pagesMyeloproliferative Disorders PDFBoneyJalgar100% (3)
- Anticancer Drugs: Nur PermatasariDocument67 pagesAnticancer Drugs: Nur Permatasari0910720085No ratings yet
- Clinical Enzymology: Enzyme Classification and NomenclatureDocument27 pagesClinical Enzymology: Enzyme Classification and NomenclaturePatrick DazaNo ratings yet
- Introductory Pharmacology - Cancer ChemotherapyDocument9 pagesIntroductory Pharmacology - Cancer ChemotherapyTyler Rosolowski100% (2)
- Table For Exam 2Document2 pagesTable For Exam 2raybuaNo ratings yet
- LMR Biochemistry - EnzymesDocument7 pagesLMR Biochemistry - EnzymesYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument38 pagesBiochemistryPrachiSinghNo ratings yet
- Physiology RenalDocument14 pagesPhysiology Renalahmedsalah565vvvNo ratings yet
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer EyeDocument2 pagesChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer EyenkivcNo ratings yet
- Renal Tubular Defects.Document20 pagesRenal Tubular Defects.HeforSheNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation Glycolysis: 2 Phosphates Krebs/citric/TCA Cycle: 1 PhosphateDocument17 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation Glycolysis: 2 Phosphates Krebs/citric/TCA Cycle: 1 PhosphatereeNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide Structure, Function, Metabolism and DNA Replication (New Curriculum) - StudentsDocument47 pagesNucleotide Structure, Function, Metabolism and DNA Replication (New Curriculum) - StudentsWing Yeng TanNo ratings yet
- Malarial RXDocument2 pagesMalarial RXalrainsNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle Disorders: DR CSN VittalDocument21 pagesUrea Cycle Disorders: DR CSN VittalWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- ACAWPurineand Pyrimindine Synthesis Presentationfor October 112010Document41 pagesACAWPurineand Pyrimindine Synthesis Presentationfor October 112010Ezekoko ChineseNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Chromosomal Abnormalities: Hi H I Ef e FDocument26 pages1.1 Chromosomal Abnormalities: Hi H I Ef e FGlupiaSprawaNo ratings yet
- AnticancerDocument27 pagesAnticancerLoreine Jane ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Hemostasis MF PortionDocument68 pagesMetabolic Hemostasis MF PortionTsegaye HailuNo ratings yet
- Anemia 2024Document50 pagesAnemia 2024b9p6vmfnc4No ratings yet
- Kuliah Pakar GlomerolopathyDocument114 pagesKuliah Pakar Glomerolopathypurnama baktiNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cancer Patients: Mona Shrestha MN (Adult Nursing)Document77 pagesDrugs For Cancer Patients: Mona Shrestha MN (Adult Nursing)sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Long Case 5Document7 pagesInternal Medicine Long Case 5RoshilNo ratings yet
- Coagulants and Anti CoagulantsDocument22 pagesCoagulants and Anti Coagulantsdhainey100% (2)
- Biochemistry Exam 1 ReviewDocument37 pagesBiochemistry Exam 1 ReviewThomas B.100% (1)
- Pediatric Endocrinology Part 2: Pediatrics 2Document8 pagesPediatric Endocrinology Part 2: Pediatrics 2sarguss14No ratings yet
- User FileDocument10 pagesUser FileJoesph Franco FernandezNo ratings yet
- ANTICANCER DRUGS PalacpacDocument98 pagesANTICANCER DRUGS PalacpacMiguel C. Dolot100% (1)
- 9 Genetics Lecture - DNA Mutations and Molecular HematologyDocument48 pages9 Genetics Lecture - DNA Mutations and Molecular HematologyAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument81 pagesBiochemistryGlorivy E. Mora GonzalezNo ratings yet
- MIB 3 AnnotatedDocument78 pagesMIB 3 AnnotatedShekhar NandalNo ratings yet
- Ebr Hy CluesDocument16 pagesEbr Hy CluesStaporn KasemsripitakNo ratings yet
- SBRC General PrinciplesDocument51 pagesSBRC General Principlesdalia khamoNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Qus (T.me@uworld2021)Document33 pagesFrequently Asked Qus (T.me@uworld2021)saranya sankarNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Arpit BhattDocument42 pagesPresented By: Arpit BhattSiddharth JainNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 - ANEMIADocument45 pagesHema 2 - ANEMIARayana UbasNo ratings yet
- Podocyte Visceral Epithelial CellDocument78 pagesPodocyte Visceral Epithelial CellAJ PsychNo ratings yet
- Hyper Arg I Nine MiaDocument6 pagesHyper Arg I Nine MiaannyNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument48 pagesNucleic AcidsMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument24 pagesBio NotesIslam MansourNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)Document4 pagesMyeloproliferative Neoplasms: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)BONNA FAYE CHRISZEL HUI YING TANNo ratings yet
- Ascp StudyDocument18 pagesAscp StudyJamaica EstorninosNo ratings yet
- Pharma Cvs Endocrine RespDocument15 pagesPharma Cvs Endocrine RespYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- 3 - Clinical Pharmacology of ChemotherapyDocument111 pages3 - Clinical Pharmacology of ChemotherapyChinIsiangSocitoNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument65 pagesBiochemistryjosue gomezNo ratings yet
- OB Blood Transfusions PregnancyDocument37 pagesOB Blood Transfusions Pregnancykhadzx100% (2)
- USMLE Step 1 JournalDocument167 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Journalmed studentNo ratings yet
- Hematological Systems - Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesHematological Systems - Lecture NotesAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid GlandDocument3 pagesParathyroid GlandElla OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Leapotswe International School: Cambridge IGCSEDocument16 pagesLeapotswe International School: Cambridge IGCSEShepherd W NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Advances in Laparoscopy of The Abdominal Wall HerniaDocument215 pagesAdvances in Laparoscopy of The Abdominal Wall HerniaErlan SantosNo ratings yet
- Using Knockout and Transgenic Mice To Study Physiology and BehaviorDocument34 pagesUsing Knockout and Transgenic Mice To Study Physiology and Behaviorgülsüm önalNo ratings yet
- Adrenal MedullaDocument17 pagesAdrenal MedullahamidNo ratings yet
- Pedigree ChartsDocument12 pagesPedigree ChartsvaughanNo ratings yet
- Tongue Diseases NDocument46 pagesTongue Diseases NhazeemmegahedNo ratings yet
- 108-Article Text-149-1-10-20180925Document5 pages108-Article Text-149-1-10-20180925AsihNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Vaccination Certificate: Vaccinee DetailsDocument1 pageCovid-19 Vaccination Certificate: Vaccinee DetailsSantiago A. de Guzman Elementary SchoolNo ratings yet
- Amylase and Lipase Tests PDFDocument7 pagesAmylase and Lipase Tests PDFMahendra BalarNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 1060) Herman Waldmann (Auth.), Michael Steinitz (Eds.) - Human Monoclonal Antibodies - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2014)Document367 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 1060) Herman Waldmann (Auth.), Michael Steinitz (Eds.) - Human Monoclonal Antibodies - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2014)KoaLa AyuNdhaNo ratings yet
- Oral Path PDFDocument367 pagesOral Path PDFAashka Desai100% (2)
- 2015 The Role of Probiotic TT For IbdDocument16 pages2015 The Role of Probiotic TT For Ibdsujata sharmaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument10 pagesSyllabusAnonymous KCtOAUZIyNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever: Assoc - Prof.Dr - Zurkurnai Yusof USMDocument25 pagesRheumatic Fever: Assoc - Prof.Dr - Zurkurnai Yusof USMfadlicardio100% (1)
- Bayot Si LanceDocument8 pagesBayot Si LanceCarl CadungogNo ratings yet
- Wa0008.Document8 pagesWa0008.Dany MorBenNo ratings yet
- Types and The Functions of WHITE BLOOD CELLSDocument3 pagesTypes and The Functions of WHITE BLOOD CELLSSakura UchihaNo ratings yet
- Identifying Unknown BacteriaDocument2 pagesIdentifying Unknown BacteriaCrystal GronholmNo ratings yet
- Cimetidine Anti Cancer Drug Reverses Tumor Immunity - Jeffrey Dach MDDocument26 pagesCimetidine Anti Cancer Drug Reverses Tumor Immunity - Jeffrey Dach MDnepretipNo ratings yet
- Ashkenazi Jewish ScreeningDocument10 pagesAshkenazi Jewish ScreeningJorge SHNo ratings yet
- Theories of Aging: Eva B. Jugador, RNDocument56 pagesTheories of Aging: Eva B. Jugador, RNEva Boje-JugadorNo ratings yet
- 1.5 ProkaryotesDocument17 pages1.5 ProkaryotesKate Rashell SevillaNo ratings yet
- Strengths Weaknesses of The Modern GSDDocument12 pagesStrengths Weaknesses of The Modern GSDapi-208346542100% (1)
- Concept of Health Disease and PreventionDocument33 pagesConcept of Health Disease and PreventionitdocNo ratings yet
- Resume Anurag Mani Tripathi: Career ObjectiveDocument4 pagesResume Anurag Mani Tripathi: Career Objectivekrishna16No ratings yet
- A Review of Lung Cancer Research in MalaysiaDocument9 pagesA Review of Lung Cancer Research in MalaysiaCahrun CarterNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestation in Sickle Cell Anemia: A Study in Chhattisgarh Institute of Medical Sciences (CIMS) Bilaspur, Chhattisgarh, India.Document4 pagesClinical Manifestation in Sickle Cell Anemia: A Study in Chhattisgarh Institute of Medical Sciences (CIMS) Bilaspur, Chhattisgarh, India.IOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Child Adolescent Development Notes and AnkiDocument3 pagesChild Adolescent Development Notes and AnkiVlad Vexillogist CarreroNo ratings yet
- Determination of Lethal Dose Ld50of Venom of Four Different Poisonous Snakes Found in PakistanDocument4 pagesDetermination of Lethal Dose Ld50of Venom of Four Different Poisonous Snakes Found in PakistanSutirtho MukherjiNo ratings yet
- Let - Reviewer: Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesLet - Reviewer: Multiple ChoiceRussiel DagohoyNo ratings yet