Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table For Exam 2
Uploaded by
raybua0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Table for Exam 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesTable For Exam 2
Uploaded by
raybuaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
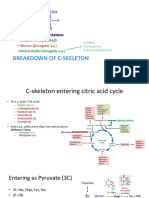
Folate B12-cobalamin (made w/ cobalt) B6
Food Sources Vegetables, Folic acid Animal foods -Animal foods
HOES -Destroyed: high heat, storage,
processing
Digestion -Polyglutamate form -B12 freed by HCl and Pepsin -Plant- pyridoxine (PN)
-Carboxypeptidases, zinc dep. -Attached to R-protein -Animal- pyridoxal (PL) &
-Diminish: Acidic, alcoholism, -Attached to IF (parietal cells from Pyridoxamine (PM)
legumes, lentils, cabbage, oranges, stomach) travel to Distal ileum -Broken down by alkaline
pancreatic exocrine insufficiency phosphatase-zinc dependent
Absorption -Proximal small intestine, colon -Distal ileum -Passive diffusion
-PCFT or passive -Passive -JEJUNUM
-Becomes THF -May be excreted in bile and -Goes into portal blood
-In cells exist as THF, 5-methyl THF, reabsorbed= long half-life -PMP and PNP become PLP with
5,10 formyl THF riboflavin help
Pathways -serves as methyl donors -Homocysteine and Methionine -AA metabolism- shiff base, unstable
-AA metabolism Serine-Glycine metabolism bond around a-carbon
-Choline Degradation -5-methyl THF becomes THF with -Transamination- synthesize
-Histidine Degradation help of cobalamin, nonessential aa
-Methionine and Homocysteine -methylcobalamin, homocysteine -AST and ALT
metabolism with help of methionine synthase -Deanimation -excrete ammonium
Methionine and SAM synthesis and B12 becomes methionine. -Decarboxylation-remove CO2
-DNA and RNA RBC -DNA and RNA RBC -Transsulfhydration- cysteine from
-gene expression -Propionyl-CoA-LmethylMalonyl-Coa- methionine (homocysteine-
- Pyrimidine synthesis and purine Succinyl-CoA (TCA) cystathionine-cysteine)
synthesis -accumulation of acid and L-malonyl -transSelenium metabolism
causes myelin abnormal -Glycogen degradation
-Tryptophan-niacin
-Heme
-Sphingolipids
-converts THF- 5,10methylene THF
-Gene expression
Special notes Methyl-folate trap Methyl-folate trap Homocysteine-cystathionine-
-deficiency in B12 keeps 5-methyl cysteine
THF trapped in that instead of
becoming THF
-creates higher homocysteine levels
(CVD)
-impaired DNA synthesis
-Folate can overcome B12 deficiency
by having enough Folic acid, can fix
the anemia
-RDA pregnant 400ug, 600DFE
(neuro tube defects)
Populations at risk Chronic alcoholism, malabsorptive Older people, vegetarians + vegans, Chronic alcoholism, older adults,
disorder, pregnant people, parietal cell destruction (pernicious systemic inflammation, L-dopa
malabsorptive disorder, MTHFR anemia and atrophic gastritis), Parkinsons, isoniazid
polymorphism, dialysis alkaline pH
Distal ileum resection, gastric bypass,
CROHNS and CELIAC
Deficiency Bright red tongue, glossitis, -Tired, fatigue, skin pallor, Rare, dermatitis, weakness, fatigue,
shortening of villi in GI tract, hematological and neurological cheilosis, glossitis, angular stoma,
megaloblastic, macrocytic, systems, neurological (unsteady gait)
hyperchromic -megaloblastic macrocytic anemia microcytic hypochromic anemia
-parietal cell destruction
Toxicity 1000ug none 100mg, >200-neurological problems
Excess folic acid can mask B12
deficiency
N-N Zinc deficiency 500mg Vit C and Cobalt deficiency Change in AA pool
Synergistic relationship with B12 Niacin dificiency
N-M Carbamazepine, metformin, oral Proton-pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, Isoniazid, oral contraceptives, L-dopa
contraceptives, furosemide oral contraceptives, metformin Parkinsons
You might also like
- 2anemiile MegaloblasticeDocument38 pages2anemiile MegaloblasticeAndreea DanielaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Ther 201Document2 pagesVitamins Ther 201Jenward HostalleroNo ratings yet
- Feline Hepatic LipidosisDocument46 pagesFeline Hepatic LipidosisAndre Suarez FarfanNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument38 pagesBiochemistryPrachiSinghNo ratings yet
- 5 6087101653624815826 PDFDocument3 pages5 6087101653624815826 PDFDijattx100% (1)
- Metabolic MRCPCHDocument11 pagesMetabolic MRCPCHJawwad Masood AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lipidosis HepaticaDocument45 pagesLipidosis HepaticaJojoa E WilNo ratings yet
- Vitamins TableDocument1 pageVitamins TableMicah Lou CalambaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism: Inborn ErrorsDocument18 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism: Inborn ErrorsAdedoyin BankoleNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument1 pageNotesGerard JameroNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument55 pagesWater Soluble VitaminsDr. M. Prasad Naidu100% (1)
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument2 pagesWater Soluble Vitaminsnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Riazuddin (MS 210931)Document10 pagesRiazuddin (MS 210931)Mohona Rahman KhanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument91 pagesVitamins and MineralsPyaesone AungNo ratings yet
- RMS115 Lect 5 Fatty Acid MetDocument83 pagesRMS115 Lect 5 Fatty Acid Metdmutethia68No ratings yet
- Hematology SummaryDocument9 pagesHematology SummaryJovielle Hayden100% (1)
- 07 PDH and Tca CycleDocument23 pages07 PDH and Tca CyclePrincess Noreen SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of VitaminsDocument93 pagesPharmacology of VitaminsDelphine NjokuNo ratings yet
- Hypolipidemic DrugsDocument34 pagesHypolipidemic Drugsmrudul harneNo ratings yet
- Table For Exam 3Document3 pagesTable For Exam 3raybuaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDADocument4 pagesVitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDAAndy J. ReyesNo ratings yet
- N-Metabolism AA II 2018 HandoutDocument19 pagesN-Metabolism AA II 2018 HandoutlinNo ratings yet
- SGD Aa PDFDocument11 pagesSGD Aa PDFyasiraNo ratings yet
- Bca Protein Metab 2Document69 pagesBca Protein Metab 2Genina MaylemNo ratings yet
- Purine MetabolismDocument30 pagesPurine MetabolismSamarTharwatNo ratings yet
- Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument32 pagesWater-Soluble VitaminsHomed OpriNo ratings yet
- Calcium Phosphorus HandoutDocument8 pagesCalcium Phosphorus HandoutSaranNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble 1Document1 pageWater Soluble 1api-3742802No ratings yet
- Topic 9 - Anemia 4Document27 pagesTopic 9 - Anemia 4Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Biochem Quick Review by Haji MuhammadDocument7 pagesBiochem Quick Review by Haji Muhammadimran dilawarNo ratings yet
- IRONDocument48 pagesIRONSarthak RunkhNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Vitamin-Like Substances: PathwaysDocument12 pagesVitamins and Vitamin-Like Substances: PathwaysAdnan QureshiNo ratings yet
- CT StructureDocument8 pagesCT StructureMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cell Disorders I. AnemiaDocument11 pagesRed Blood Cell Disorders I. AnemiaGea MarieNo ratings yet
- Folate and B12 MechanismDocument6 pagesFolate and B12 MechanismFlowerNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry High Yield PointsDocument18 pagesBiochemistry High Yield PointsAnonymous S0H8cqgnfiNo ratings yet
- VPHY 143 Parathyroid To ThyroidDocument3 pagesVPHY 143 Parathyroid To ThyroidRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme B-12 and FolateDocument9 pagesMetabolisme B-12 and FolateYeniNo ratings yet
- Nutrition VitaminDocument7 pagesNutrition VitaminIsabella SupardiNo ratings yet
- Met Purin 28 OktDocument62 pagesMet Purin 28 OktXIID 67No ratings yet
- Role of Vitamins As Coenzymes: Riboflavin Pantothenic Acid Pyridoxine Folic AcidDocument34 pagesRole of Vitamins As Coenzymes: Riboflavin Pantothenic Acid Pyridoxine Folic AcidNeethu JohnNo ratings yet
- 081220190water Soluble Vit. (E.Sh) Lecture 2 - 2019 StudentsDocument22 pages081220190water Soluble Vit. (E.Sh) Lecture 2 - 2019 Studentsslmen1269No ratings yet
- Lecture 10. Basic Concepts of Vitaminology. Biochemistry of Water-Soluble and Fat-Soluble VitaminsDocument58 pagesLecture 10. Basic Concepts of Vitaminology. Biochemistry of Water-Soluble and Fat-Soluble VitaminsВіталій Михайлович НечипорукNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument14 pagesVitaminsAri RaharjaNo ratings yet
- Class Notes HMP Shunt Path WayDocument18 pagesClass Notes HMP Shunt Path WayShivanand MaliNo ratings yet
- KEMU Guide by Sheraz Ali SOLVEDDocument133 pagesKEMU Guide by Sheraz Ali SOLVEDdrmoazzinivyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - General and Characteristics. Water Soluble VitaminsDocument29 pagesLecture 6 - General and Characteristics. Water Soluble VitaminsEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- Anemia SDocument5 pagesAnemia SGps PandetteNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 2Document6 pagesClinical Chemistry 2Romie SolacitoNo ratings yet
- Folic AcidDocument10 pagesFolic AcidAl Mudassir7No ratings yet
- RBC Micro-Macro MeasurementsDocument11 pagesRBC Micro-Macro MeasurementsDingdongLopezNo ratings yet
- Abdon MelodyDocument4 pagesAbdon MelodyChirs Nicole CaguitlaNo ratings yet
- 091220190vitamins B12, Folic, C (E.sh) Lecture 3 Students 2018Document32 pages091220190vitamins B12, Folic, C (E.sh) Lecture 3 Students 2018slmen1269No ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGY-LECTURE-NOTES FTP Lectures PDFDocument50 pagesHEMATOLOGY-LECTURE-NOTES FTP Lectures PDFkat100% (8)
- Approach To Anemia-Iron Deficiency, Megaloblastic and Hemolytic AnemiaDocument106 pagesApproach To Anemia-Iron Deficiency, Megaloblastic and Hemolytic Anemiasarath chandranNo ratings yet
- Phần 2.1.2Document2 pagesPhần 2.1.2chuotchuot10072001No ratings yet
- 111 - 1 Nutrition 13Document139 pages111 - 1 Nutrition 13Wei Liong SiaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism HW3 Antioxidants SP24Document6 pagesMetabolism HW3 Antioxidants SP24raybuaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism HW4 Fat Soluble Vitamins SP24Document6 pagesMetabolism HW4 Fat Soluble Vitamins SP24raybuaNo ratings yet
- ServSafe NotesDocument5 pagesServSafe NotesraybuaNo ratings yet
- ICU Step-Down Case Documentation and Questions - RayburnDocument3 pagesICU Step-Down Case Documentation and Questions - RayburnraybuaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument78 pagesCase Study - Diabetic KetoacidosisEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Material - ECG TestDocument26 pagesSupplementary Material - ECG TestSiraj AL sharifNo ratings yet
- Concise CardiologyDocument354 pagesConcise CardiologyAtish_Mathur_9874No ratings yet
- Neurocritical Care in The General Intensive Care UnitDocument17 pagesNeurocritical Care in The General Intensive Care UnitdanielNo ratings yet
- Mineralocorticoid Excess Syndromes: Ellen Marie Freel, Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, Glasgow, United KingdomDocument12 pagesMineralocorticoid Excess Syndromes: Ellen Marie Freel, Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, Glasgow, United KingdomRobby Paguh TariganNo ratings yet
- COPD Flow SheetDocument2 pagesCOPD Flow SheetSachin PillaiNo ratings yet
- GEC 103 Week 8 Activity and Home StudyDocument6 pagesGEC 103 Week 8 Activity and Home StudyLorenz Joy Ogatis BertoNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: Mitchell HorowitzDocument43 pagesCardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: Mitchell Horowitzionanic72No ratings yet
- CRT Exam Test QuestionsDocument4 pagesCRT Exam Test QuestionsDharlyn MungcalNo ratings yet
- Journal Club Presentation RPGN-1Document53 pagesJournal Club Presentation RPGN-1sagor9364No ratings yet
- Tesis PLT-WBC RatioDocument4 pagesTesis PLT-WBC RatioDanielMahendraNo ratings yet
- CPR Awareness TrainingDocument5 pagesCPR Awareness TrainingSayed SallamNo ratings yet
- Cha Ds - Vasc: Condition PointsDocument5 pagesCha Ds - Vasc: Condition PointsΑντώνιος ΧατζηγεωργίουNo ratings yet
- Ms By: Sir Greylando A. Hisu R.N.BSE.,MANDocument3 pagesMs By: Sir Greylando A. Hisu R.N.BSE.,MANCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- MCQ ChoDocument31 pagesMCQ Choامجد حسين جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument4 pagesAngina PectorisAnn CunananNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Respiratory System 1Document41 pagesBio1 Respiratory System 1Camela Kim Domider TenorioNo ratings yet
- AEBA QUESTIONS-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesAEBA QUESTIONS-WPS OfficeMarj Castor LisondraNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesBlood VesselsNeel GamiNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of ECGDocument53 pagesBasic Principles of ECGSmita Jain100% (1)
- Levin (1993) - Drowning and Near Drowning (Klasifikasi Tenggelam)Document16 pagesLevin (1993) - Drowning and Near Drowning (Klasifikasi Tenggelam)Filbert TandeanNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaWilmar Drilon IIINo ratings yet
- Istilah Kode Icd 9-10Document328 pagesIstilah Kode Icd 9-10Anonymous BFwZr77BNo ratings yet
- Final Estimation of SGOTDocument3 pagesFinal Estimation of SGOTshibsankar rakshitNo ratings yet
- ECIM 2024 Scientific ProgrammeDocument39 pagesECIM 2024 Scientific ProgrammeFenix RenaceNo ratings yet
- Surgery 4 - Answers v1 (Wide)Document55 pagesSurgery 4 - Answers v1 (Wide)Humzala BashamNo ratings yet
- STEP 2 CK New Free 120 (Q)Document59 pagesSTEP 2 CK New Free 120 (Q)M. Baidar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness and Outcomes of H-Isdn in Addition To Conventional Therapy in Acute Heart Failure Patients With Renal ImpairmentDocument10 pagesEffectiveness and Outcomes of H-Isdn in Addition To Conventional Therapy in Acute Heart Failure Patients With Renal ImpairmentIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Elisa Dal Canto 2019Document8 pagesElisa Dal Canto 2019Nikola Dragicka DragicevicNo ratings yet
- MRI WorksheetDocument2 pagesMRI WorksheetDilini WijesinghNo ratings yet