Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VPHY 143 Parathyroid To Thyroid
Uploaded by
Regulus Fidelis SevillaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VPHY 143 Parathyroid To Thyroid
Uploaded by
Regulus Fidelis SevillaCopyright:
Available Formats
DLC VPHY 143 PARATHYROID AND THYROID GLANDS
PARATHYROID GLAND BONE PHYSIOLOGY Nasa fb yung pictures
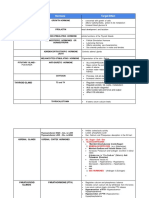
Chief cells – secretory cells of parathyroid gland - Stores 98-99% of Calcium
- Secretes Parathyroid hormone - Mineralization is needed because if it is ABNORMALITIES IN PARATHYROID HORMONE
deposited, it will provide the strength and SECRETION
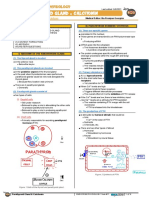
HORMONES REGULATING BLOOD CA LEVELS integrity of the bones
Hormone Secretory ▪ Otherwise, the bones will form PRIMARY HYPOPARATHYROIDISM IN DOGS
PTH (Parathormone Chief cells of the pores and become brittle - Rarely diagnosed in fogs
Parathyroid Gland making it prone to injuries - Sex predilection (65% of cases):
Vitamin D3 or calcitrol Renal tubular cells middle-aged spayed females
or 1-25 PARATHORMONE (PTH) - Age: as early as 6 weeks to 12 y/o
Thyrocalcitonin or Parafollicular cells of Stimulus for PTH secretion: Hypocalcemia (average age 4.8 y/o)
Calcitonin the thyroid gland Conditions that can lead to hypocalcemia - Breed predilection: toy poodles,
AIM: Maintain normal levels of blood calcium 1. Rickets, osteomalacia Labrador retriever, miniature schnauzers,
2. Low levels of Ca & Vitamin D in the diet German shepherds, Terrier breeds
- If the offspring cannot suckle enough milk,
FORMS OF CALCIUM IN PLASMA supplements are given, or the piglets are Etiology of Primary Hypoparathyroidism in Dogs
Form Amount in Functions transferred to other dam
Plasma 1. Accidental damage or destruction of
3. Pregnancy Parathyroid gland/s
Diffusible 50% of 2nd messenger 4. Lactation - Secondary to thyroidectomy
ionized Ca or total Muscle Action of PTH: Increase blood Ca levels 2. Removal of Parathyroid glands
Free Ca plasma contraction 3. Immune-mediated destruction of
calcium Nerve function Stimulus: Hypocalcemia activate Parathyroid parathyroid glands
Blood Chief Cells increase secretion & release of PTH 4. Hypomagnesemia – decreases secretion
coagulation blood stream bone, kidney, GIT and activity of PTH)
Non-diffusible 40% of Bound to plasma 5. Parathyroid agenesis
Ca or plasma total proteins – ACTION OF PTH
protein plasma albumin, Bone: osteoclasts PRIMARY HYPOPARATHYROIDISM IN CATS
bound Ca Ca globulins a. Mobilized Ca stores from the bone or - Occurs less frequently in cats
Diffusible 10% Bind w/ interstitial osteolysis (minerals will be freed and go - First reported case in cats in 1990
non-ionized substances to the bloodstream) - Sex predilection: male
Ca or Citrate: Calcium b. Formation of osteoclasts (more minerals) - Age: Just over 2 y/o
complexed citrate c. Activation of osteoclasts – osteoclastic or - Etiology: secondary to bilateral
Ca Phosphate: ca bone resorption parathyroidectomy
phosphate Kidney: distal tubules, collecting tubules,
HCO3: calcium collecting duct CLINICIALS SIGNS OF HYPOPARATHYROIDISM
bicarbonate a. Decrease excretion of Ca, Mg, H ions Neuromuscular abnormality – progressive
Calcium ions are filtered in the kidney, 90-98% of b. Increase renal excretion of PO4, K ions excitation of nervous system due to decrease in
filtered calcium is reabsorbed c. Production of Vitamin D3 Ca ions at myoneural junction
Intestine: Epithelial cells ⇨ Decreased myocardial contractility
NORMAL BLOOD/ PLASMA CALCIUM LEVELS a. Increase absorption of Ca and P ions ⇨ Hypocalcemic tetany due to increased
Species Mg/dL Species Mg/dL activity of motor nerve fibers
Dog 8.7-11.8 Cat 7.9-10.9 All of which would increase the plasma ⇨ Neuromuscular irritability
Cow 8.4-11 Horse 10.4-13.4 calcium levels o muscle twitching
Pig 9.3-11.5 Sheep 9.3-11.7 o tremors
Goat 9.0-11.6 o muscle cramps
SYNTHESIS OF VITAMIN D3 o convulsions
DLC VPHY 143 PARATHYROID AND THYROID GLANDS
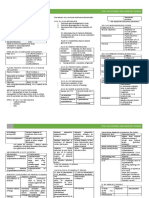
⇨ Tetanic spasms of respiratory muscles Etiology Feature Occurrence Ultimobranchial
⇨ Paralysis of respiratory muscles Parathyroid Functional More common glands (fish, birds,
o Laryngospasm adenoma tumor of males, solitary amphibians)
o Air obstruction parathyroid more common Stimulus Hypercalcemia
o Asphyxiation gland
Action Lower blood Ca level
o DEATH Parathyroid Increased # of More common
hyperplasia chief cells in males Inhibitor
- Increased body temp Parathyroid Malignant Rare 0 affect
carcinoma tumor middle to old Conditions that cause pypercalcemia
- Rapid breathing 1. Excess quantity of Ca in diet
are males (ave.
- Alkalosis 10.5 y/o) 2. X
- Impairment of bone 3. X
- Formation and bone remodeling Breed: Keeshond (40% of cases dx MSU
autosomal dominant gene)
- Fever MOA of Calcitonin in Lowering Blood Ca levels
- Tense or splinted abdomen
CLINICIAL SIGNS OF HYPERPARATHYROIDSIM 1. Promotes Ca deposition in bones
- Stiff gait - Lower osteoclasts activity
- Muscle tremors 1. Lameness due to its effect on the bones:
a. Softening and weakening of 2. Prevents bone resorption
- Muscle fasciculations - Decrease formation of new osteoclasts
- More bones – prone to deformities
b. Cysts formation in the bone 3. Decreases CA release from bones to the
blood
ELECTROLYTE ABNORMALITY IN (osteitis fibrosa cystica
c. Prone to - Lower blood Ca levels
HYPOPARATHYROIDISM 4. Something something…
1. Severe hypocalcemia Rubber Jaw Syndrome in Dogs
2. Ca deposition in various soft tissues
- Dogs with untreated primary
hypoparathyroidism is consistently below - Heart, stomach, intestines, kidneys
6.5 mg/dL 3. Formation of kidney stones (CaPO4, Ca
2. Mild to moderate hyperphosphatemia oxalate)
- Combined hypocalcemia and - Due to hypercalcemia
hyperphosphatemia + normal … 4. Decreased excitability of nerves
5. Faster coagulation time
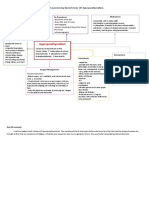
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS (LOW CA LEVELS) 6. Muscle weakness
7. Constipation and lack of appetite
Hypoalbuminemia Renal failure
- Due to depressed contractility of GIT
Puerperal tenay Acute pancreatitis muscles
Intestinal Starvation Management
malabsorption 1. Reduction of Ca in diet
Hypobitaminosis D Thyroid tumors 2. X
Cervical tumors 3. X
THYROID PARAFOLLICULAR CELLS
MANAGEMENT FOR HYPOPARATHYROIDSM - Big cells outside the thyroid follicles
1. Ca supplementation producing calcitonin
2. Vitamin D (D3) supplementation
3. PTH Treatment Calcitonin or Thyrocalcitonin
- Very expensive, elicit immune response Secretory cell TPC (mammals)
of animal
PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
DLC VPHY 143 PARATHYROID AND THYROID GLANDS
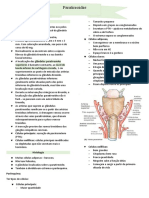
THYROID GLAND
- Located below the larynx and on either
side of & anterior to the trachea
Structure of Thyroid Gland
1. Thyroid Follicles
a. Lumen – filled with colloid
(follicular cells’ secretion)
▪ Colloid – consists of thyroglobulin, a
large glycoprotein which contains
the thyroid hormones
Stimulus for Thyroid Inhibitor for Thyroid
Hormone Secretion Hormone Secretion
Exposure of animal to low Conditions that
environmental stimulates sympathetic
temperature (cold) nervous system
A. Formation and secretion of Thyroglobulin
B. Oxidation of Iodide Ions
Excitement, anxiety C. Iodination of Tyrosine and Formation of Thyroid
Hormones or Organification Thyroglobulin
Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Secretion - Coupling Reaction
D. Storage of Thyroglobulin
- If not produced, will be stored
E. Release of T3 & T4 from Thyroid Gland
F. Binding with Plasma Proteins
Plasma Protein BindingAffinity
Thyroxine Binding High affinity for
Globulin (TBG) thyroxine
Thyroxine Binding Binds T3 and T4
Prealbumin
Albumin Binds T3 and T4
Can be measured in the blood
TSH Signaling Pathway
FORMATION OF THYROID HORMONE
You might also like
- PTH Regulation and Hyperparathyroidism GuideDocument39 pagesPTH Regulation and Hyperparathyroidism GuideAris josuaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Endocrinology Part 2: Pediatrics 2Document8 pagesPediatric Endocrinology Part 2: Pediatrics 2sarguss14No ratings yet
- ParathyroidDocument2 pagesParathyroiddhaineyNo ratings yet
- HypocalcemiaDocument4 pagesHypocalcemiaJezreel BonaNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Gland Anatomy and FunctionDocument3 pagesParathyroid Gland Anatomy and FunctionElla OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Hypocalcemia and Primary HypoparathyroidismDocument24 pagesChapter 16 - Hypocalcemia and Primary HypoparathyroidismSteffi AraujoNo ratings yet
- SL paraDocument36 pagesSL parapurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Part 2 DRAFTDocument6 pagesEndocrine Part 2 DRAFTPreeti Joan BuxaniNo ratings yet
- Canonio t4 Calcium Magnesium Imbalances MedsurgDocument6 pagesCanonio t4 Calcium Magnesium Imbalances Medsurgchi kNo ratings yet
- Calcium, Phos, MGDocument27 pagesCalcium, Phos, MGRiya AktarNo ratings yet
- Calcium and PhosphateDocument35 pagesCalcium and PhosphateSULEIMAN OMARNo ratings yet
- Macrominerals: Calcium, Phosphorus, and Magnesium SupplementationDocument40 pagesMacrominerals: Calcium, Phosphorus, and Magnesium SupplementationFadli IlhamNo ratings yet
- Rickets and bone disease guideDocument25 pagesRickets and bone disease guideJames RatchanontNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Glands: Anatomy, Function and DisordersDocument28 pagesParathyroid Glands: Anatomy, Function and DisordersOmar Alruwaili100% (1)
- Milk FeverDocument78 pagesMilk FeverAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Calcium and phosphorus metabolism competency tableDocument8 pagesCalcium and phosphorus metabolism competency tableSaranNo ratings yet
- Hormon Parathyroid: Dr. Nanang Miftah F, SPPDDocument13 pagesHormon Parathyroid: Dr. Nanang Miftah F, SPPDFitri Nur DiniNo ratings yet
- 5 Minute Biochemistry PresentationDocument23 pages5 Minute Biochemistry PresentationPITAGAN, Galda Boy 1-FNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Hormone: Shahab Ullah Khan Ayub Medical CollegeDocument28 pagesParathyroid Hormone: Shahab Ullah Khan Ayub Medical CollegeDr KhanNo ratings yet
- Pathology IcsmDocument84 pagesPathology IcsmAlice TangNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument22 pagesMineralsLovely Pardilla TorillaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism and Disorders (Hanan)Document169 pagesCalcium Metabolism and Disorders (Hanan)drhananfathyNo ratings yet
- Apg ParatireoideDocument5 pagesApg ParatireoideGabriela RochaNo ratings yet
- Calcium HomeostasisDocument10 pagesCalcium Homeostasiszsf8m52ky4No ratings yet
- Ca N P MetaDocument71 pagesCa N P MetaJagadish S GowdaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System DR Yogesh Swami 3Document11 pagesEndocrine System DR Yogesh Swami 3chiragm1408No ratings yet
- Ca Phosphate MetaDocument77 pagesCa Phosphate MetanivethaseshaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Full NotesDocument30 pagesUnit 2 Full NotesLauren StamNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcaemia in Primary CareDocument2 pagesHypercalcaemia in Primary CareShazwani KKTSNo ratings yet
- The Veterinary JournalDocument8 pagesThe Veterinary JournalVichi Posse SilvaNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Hormone: DR Pramod Kumar Asstt. Professor Department of Veterinary Physiology Bihar Veterinary College, PatnaDocument19 pagesParathyroid Hormone: DR Pramod Kumar Asstt. Professor Department of Veterinary Physiology Bihar Veterinary College, PatnasanathNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Parathyroid DiseaseDocument11 pagesPediatric Parathyroid DiseaseLuis Ruelas SanchezNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism and Disorders ODocument14 pagesCalcium Metabolism and Disorders OvmdcabanillaNo ratings yet
- 047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland CalcitoninDocument4 pages047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland Calcitoninیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Table For Exam 2Document2 pagesTable For Exam 2raybuaNo ratings yet
- CalciumDocument77 pagesCalciumRhaffy RapaconNo ratings yet
- HyperparathyroidismDocument2 pagesHyperparathyroidismpsyNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Causes of Passive Cervical FlexionDocument7 pagesTop 5 Causes of Passive Cervical FlexionCabinet VeterinarNo ratings yet
- Calcium and PhosphorusDocument34 pagesCalcium and Phosphorus075 Keerthighaa SNo ratings yet
- Parathormone, CalcitoninDocument14 pagesParathormone, CalcitoninIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Midterm RecallsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Midterm Recallssuper novaNo ratings yet
- HYPERPARATHYROIDISM On PPDocument26 pagesHYPERPARATHYROIDISM On PPSobia NaseemNo ratings yet
- Cc2 l7 Other GlandsDocument2 pagesCc2 l7 Other GlandsRose Denisse EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Hormone PDFDocument120 pagesParathyroid Hormone PDFLaura TapiaNo ratings yet
- Physiology, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) : Statpearls (Internet)Document10 pagesPhysiology, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) : Statpearls (Internet)chafeb febiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine HormonesDocument2 pagesEndocrine HormonesJoe SanoneNo ratings yet
- Calcium and Its Significance in The Bone MetabolismDocument26 pagesCalcium and Its Significance in The Bone MetabolismVamsi MurthyNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism: Dr. Yuliana Rahmah R, M.Kes, SPPDDocument28 pagesCalcium Metabolism: Dr. Yuliana Rahmah R, M.Kes, SPPDAhmad Jaelani Jayadi SiajengNo ratings yet
- Blgo. Cesar D. Quesquen Lopez: Sales MineralesDocument8 pagesBlgo. Cesar D. Quesquen Lopez: Sales MineralesIsai CubasNo ratings yet
- Calcium MetabolismDocument19 pagesCalcium MetabolismShabariNath R NairNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument14 pagesVitaminsnacot58559No ratings yet
- Macrominerals Sources Deficiency Toxicity FunctionsDocument3 pagesMacrominerals Sources Deficiency Toxicity FunctionsGia Espinosa OcbeñaNo ratings yet
- Physiology RenalDocument14 pagesPhysiology Renalahmedsalah565vvvNo ratings yet
- Wk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesDocument65 pagesWk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesPotato PceeNo ratings yet
- Calcium MetabolismDocument51 pagesCalcium MetabolismAlan ThomasNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia in Dogs Emergent Care Diagnostics and TreatmentsDocument8 pagesHypercalcemia in Dogs Emergent Care Diagnostics and Treatmentstarilubis277No ratings yet
- Parathyroid: Calcium and Vitamin DDocument135 pagesParathyroid: Calcium and Vitamin DPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Calcium Homeostasis: V.Yuvaraj ROLL NO.: 150 First Year MbbsDocument22 pagesCalcium Homeostasis: V.Yuvaraj ROLL NO.: 150 First Year MbbsYuvarajNo ratings yet
- Randomized Controlled Trials: Traditional Experimental DesignsDocument6 pagesRandomized Controlled Trials: Traditional Experimental DesignsRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Stud - OUTBREAK INVESTIGATIONDocument5 pagesStud - OUTBREAK INVESTIGATIONRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Stud2019 - Sampling Animal PopulationsDocument9 pagesStud2019 - Sampling Animal PopulationsRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Chain of Infection Lecture OutlineDocument5 pagesChain of Infection Lecture OutlineRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Stud2019 - Sampling Animal PopulationsDocument9 pagesStud2019 - Sampling Animal PopulationsRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Stud - OUTBREAK INVESTIGATIONDocument5 pagesStud - OUTBREAK INVESTIGATIONRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Chain of Infection Lecture OutlineDocument5 pagesChain of Infection Lecture OutlineRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Vphy 143 Lab Experiment 4Document12 pagesVphy 143 Lab Experiment 4Regulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Taphonomy of Hair A Study of PostmortemDocument8 pagesTaphonomy of Hair A Study of PostmortemRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- VPHY 143 CUSHING'S AND ADDISON'S DISEASEDocument6 pagesVPHY 143 CUSHING'S AND ADDISON'S DISEASERegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Aquagenic Palmoplantar Keratoderma With Dorsal Hand Involvement in An Adolescent FemaleDocument2 pagesAquagenic Palmoplantar Keratoderma With Dorsal Hand Involvement in An Adolescent FemaleTher RayNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0828282X22001271 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0828282X22001271 MainLilianne Mbengani LaranjeiraNo ratings yet
- 9 Steam InhalationDocument2 pages9 Steam InhalationKen Morales Alcantara100% (1)
- Teenage and >35yrs preg have adverse outcomesDocument40 pagesTeenage and >35yrs preg have adverse outcomesJeyakumar MeyyappanNo ratings yet
- MorsDocument13 pagesMorsBSRT1A BERBANO, IAN JEWEL M.No ratings yet
- Holoxan Pi PDFDocument18 pagesHoloxan Pi PDFKarol IonasNo ratings yet
- Urinary Bladder MassDocument2 pagesUrinary Bladder Masskarl de guzmanNo ratings yet
- LP Vulnus Laceratum PDFDocument8 pagesLP Vulnus Laceratum PDFAlfrida Ade BunapaNo ratings yet
- BB Pheresis GuidelinesDocument190 pagesBB Pheresis GuidelinesBill ThomNo ratings yet
- Covid TestDocument1 pageCovid TestConcur ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ChartsDocument61 pagesAntibiotic Chartspempekplg100% (1)
- Polyomavirus LectureDocument60 pagesPolyomavirus Lecturerggefrm75% (4)
- Perineum RepairDocument5 pagesPerineum RepairYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- 2004 NEJM Photosensitivity NEJ 2004Document7 pages2004 NEJM Photosensitivity NEJ 2004Alma EscobarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Laser Dental EducationDocument5 pagesAdvanced Laser Dental EducationJulia KamenovaNo ratings yet
- Menopause - Digital ProgramDocument7 pagesMenopause - Digital ProgramU of T MedicineNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy and The Microcirculation in Health and Critical IllnessDocument11 pagesFluid Therapy and The Microcirculation in Health and Critical IllnessAdote DrmNo ratings yet
- Pedia History Taking (Oct9)Document5 pagesPedia History Taking (Oct9)fall autumnNo ratings yet
- 310-Article Text-582-1-10-20210312-1Document13 pages310-Article Text-582-1-10-20210312-1Ni Putu SwastyNo ratings yet
- Cervical SpondylosisDocument25 pagesCervical Spondylosisjeevan ghimireNo ratings yet
- Safety Assessment and Attenuation of Cisplatin Induced Nephrotoxicity by Tuberous Roots of Boerhaavia DiffusaDocument12 pagesSafety Assessment and Attenuation of Cisplatin Induced Nephrotoxicity by Tuberous Roots of Boerhaavia DiffusaRigotti BrNo ratings yet
- ABG BASICS YvonneDocument48 pagesABG BASICS Yvonneนีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Epidemiology:: A Clouded VisionDocument31 pagesOphthalmic Epidemiology:: A Clouded Visionnutrifmeal arifNo ratings yet
- Hla B27Document5 pagesHla B27Madhu Kunchi100% (1)
- Accupuncture and Induction of LaborDocument73 pagesAccupuncture and Induction of LaborMarisela Sereia NagôNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis: Clin. Immunol. / Lab. Work/ Renal Disorders/ Urine Analysis/ Dr. Batool Al-HaidaryDocument11 pagesUrinalysis: Clin. Immunol. / Lab. Work/ Renal Disorders/ Urine Analysis/ Dr. Batool Al-HaidaryIM CTNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Vaginitis and Vulvitis PDFDocument3 pagesTreatment of Vaginitis and Vulvitis PDFrendyNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lab Study ChartDocument2 pagesParasitology Lab Study ChartnoneyabuNo ratings yet
- (Helveston) Surgical Management of StrabismusDocument518 pages(Helveston) Surgical Management of StrabismusMarianaNo ratings yet
- Activity Notification and Consent Form (Under 18yrs) : Sensitive: Personnel (When Participant's Details Are Entered)Document2 pagesActivity Notification and Consent Form (Under 18yrs) : Sensitive: Personnel (When Participant's Details Are Entered)Alvin JacobNo ratings yet