Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine Hormones
Uploaded by
Joe Sanone0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe document outlines various endocrine glands and their hormone productions and targets. The pituitary gland produces growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, gonadotropic hormones, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and anti-diuretic hormone. The thyroid gland produces T3 and T4 which regulate metabolism. The adrenal glands produce glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and sex hormones. The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone which regulates calcium and phosphorus balance.
Original Description:
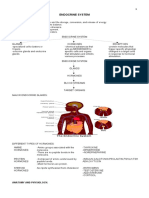
ENDOCRINE HORMONES
Original Title
ENDOCRINE HORMONES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines various endocrine glands and their hormone productions and targets. The pituitary gland produces growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, gonadotropic hormones, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and anti-diuretic hormone. The thyroid gland produces T3 and T4 which regulate metabolism. The adrenal glands produce glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and sex hormones. The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone which regulates calcium and phosphorus balance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesEndocrine Hormones
Uploaded by
Joe SanoneThe document outlines various endocrine glands and their hormone productions and targets. The pituitary gland produces growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, gonadotropic hormones, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and anti-diuretic hormone. The thyroid gland produces T3 and T4 which regulate metabolism. The adrenal glands produce glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and sex hormones. The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone which regulates calcium and phosphorus balance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
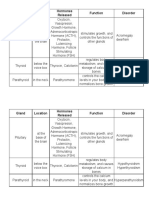
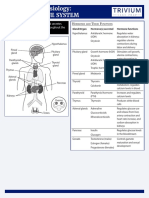
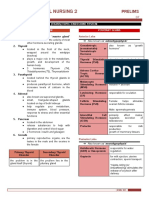
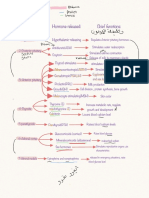
Source Hormone Target/Effect
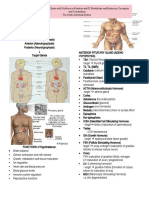
PITUITARY GLAND - GROWTH HORMONE concerned with growth of cells
ANTERIOR affects Carbohydrates, protein & fat metabolism
Icreased blood glucose lvl
PROLACTIN Breast development and lactation
THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE controls functions of the Thyroid Glands
GONADOTROPIC HORMONES OR Follicle Stimulation Hormone
GONADOTROPIN Luteinizing Hormone
Affects secondary sex characteristics
Sex steroids production in males and females
ADRENOCORTICOTROPI C HORMONE Controls adrenal glands
(ACTH
MELANOCYTES -STIMULATING HORMONE Pigmentation of the skin , Retina.
PITUITARY GLAND - ANTI-DIURETIC HORMONE Aka VASOPRESSIN
POSTERIOR Major control the osmolality (concentration) and body
water of volume.
Increase water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the
kidneys
OXYTOCIN Promotes milk-let down in lactating breast
Increased uterine contraction after labor has begun
THYROID GLAND T3 and T4 Regulate metabolic rate of cells
Regulate protein, fat, carbs. metabolism
Acts as insulin atagonist
affect cardia rate and force and output
Affect O2 utilization
THYROCALCITONIN It lowers serum calcium levels
Inhibits osteoclastic activity
Thyrocalcitonin HIGH - CA+ is LOW Lowers phosphates Level
Thyrocalcitonin LOW - CA+ is HIGH Dec. Calcium and Phospurous absorption in the GI tract
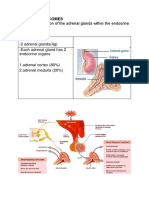
ADRENAL GLANDS ADRENAL CORTEX HORMONES 3S ; Sugar - Salt - Sex
1. GLUCOCORTICOIDS -
Maintain blood glucose levels (Sugar)
2. MINERALOCORTICOIDS (e.g. Aldosterone)
Maintain Sodium and Volume Status (Salt)
Increases Potassium and hydrogen excretion in distal
tubes
Aldosterone is “Pro-Sodium” (Retain)- Anti
Potassium (Excretes)
Aldosterone results to:
Increased – Hypernatremia –Hypokalemia
Decreased – Hyponatremia – Hyperkalemia
ddd
ddd
3. SEX HORMONES - (Androgen & Estrogen)
PARATHYROID PARATHORMONE (PTH) Regulates calcium and phosphorous balance
GLANDS Elevates serum calcium lvls by withdrawal from the bones
Low serum calcium levels stimulate PTH release
Hypersecretion of PTH –Hypercalcemia–
Hypophosphatemia
Hyposecretion of PTH –Hypocalcemia–
Hyperphosphatemia
You might also like
- Endocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioDocument5 pagesEndocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Adenohypophysis: HormonesDocument4 pagesAdenohypophysis: HormonesTomilynjan GarpaNo ratings yet
- Index CardsDocument6 pagesIndex CardsShanley SalemNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Notes On Endocrine DrugsDocument2 pagesPharmacology: Notes On Endocrine DrugsByron ChuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine in Animals (CBSE)Document3 pagesEndocrine in Animals (CBSE)Ashwani GahlotNo ratings yet
- Endocrine New EditionDocument150 pagesEndocrine New Editiondigracia manatigaNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureDocument153 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureAnthony Riggs100% (1)
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Hormone GroupDocument35 pagesHormone GroupNeph VargasNo ratings yet
- Review Endocrine Disorders FINALDocument166 pagesReview Endocrine Disorders FINALmeranith100% (10)
- Endo EndoDocument45 pagesEndo EndomaoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Lecture KayzardnDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry Lecture KayzardnHenry QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Endo ReviewerDocument5 pagesEndo ReviewerZIAN LABADIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument2 pagesHORMONESDa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cushing Syndrome Addisons 1Document6 pagesCushing Syndrome Addisons 1Czarena Ysabelle PayotNo ratings yet
- 2009 John Wiley Sons Inc The Endocrine SystemDocument23 pages2009 John Wiley Sons Inc The Endocrine SystemnobodyNo ratings yet
- GlandDocument2 pagesGlandsmith joeNo ratings yet
- General Biology Lesson 13Document13 pagesGeneral Biology Lesson 13GUCOR, LOVELY SHANE C.No ratings yet
- Thyrotropin-Releasing HormoneDocument8 pagesThyrotropin-Releasing HormoneBhagyaNo ratings yet
- CA 2 MOD 10 - Endocrine Disorders 2022-2023 PDFDocument16 pagesCA 2 MOD 10 - Endocrine Disorders 2022-2023 PDFAyen PaloNo ratings yet
- Assignment IN NutritionDocument5 pagesAssignment IN NutritionJasper SeeNo ratings yet
- Estrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesDocument57 pagesEstrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Effects Adrenal Hormones RegebDocument7 pagesEffects Adrenal Hormones RegebPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Prof - DR. Didik Tamtomo, DR PAK, MM, MKK Pakar Anatomi KedokteranDocument78 pagesEndocrinology: Prof - DR. Didik Tamtomo, DR PAK, MM, MKK Pakar Anatomi KedokteranAnnisaInayati-msNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Cortex - Corticosteroids Corticosteroids: GonadotrocorticoidsDocument13 pagesAdrenal Cortex - Corticosteroids Corticosteroids: GonadotrocorticoidsThierd Cañete IIINo ratings yet
- Endocrine System DrugsDocument66 pagesEndocrine System DrugsRania HamamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionDocument2 pagesChapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument39 pagesEndocrinologyJanelle RemorozaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 3: EndocrinologyDocument21 pagesClinical Chemistry 3: EndocrinologyRomie Solacito100% (3)
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemNovie Jane HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Steroids, GH, ProlactinDocument34 pagesAdrenal Steroids, GH, ProlactinMohammad Hazamyn Hazrul HamzahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemMark DimarucutNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Mahayag Abuloc Labiste Sagayno VillaruelDocument32 pagesEndocrine System: Mahayag Abuloc Labiste Sagayno VillaruelJJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument58 pagesEndocrine Systemfranzpersonal810No ratings yet
- Introduction To Endocrine Physiology: DR EvaDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Endocrine Physiology: DR EvaEmmanuel Julius ChalighaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Endocrine SystemDocument24 pages2018 - Endocrine SystemCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: FunctionDocument24 pagesEndocrine System: FunctionCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism and Disorders (Hanan)Document169 pagesCalcium Metabolism and Disorders (Hanan)drhananfathyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PharmaDocument10 pagesReviewer in Pharmark24zsyfmxNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet McatDocument16 pagesReview Sheet McatCal GoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NursingDocument5 pagesEndocrine NursingMiss GNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Endorine SystemDocument4 pagesEndorine SystemMichaela Shianne E. MatituNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument106 pagesEndocrine Systemloveseeker06No ratings yet
- Article and Table - Peptide HormonesDocument3 pagesArticle and Table - Peptide HormonesZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 2: PrelimsDocument10 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 2: PrelimsjoanneNo ratings yet
- Group 9 (Module 22)Document24 pagesGroup 9 (Module 22)maba.zuniga.sjcNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PresentationDocument231 pagesEndocrine System PresentationKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Note 17 Dec 2021Document2 pagesNote 17 Dec 2021mNo ratings yet
- Presented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarDocument34 pagesPresented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarSohaib NasirNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionDocument1 pageChemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionNaman SinhaNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3Document4 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- ABT Endocrine PPDocument39 pagesABT Endocrine PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition PDF EbookDocument41 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition PDF Ebookjennifer.lawver532100% (44)
- Nutrition For Pregnant WomenDocument3 pagesNutrition For Pregnant WomenKeff MundaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank Health Assessment For Nursing Practice 6th Edition Wilson PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank Health Assessment For Nursing Practice 6th Edition Wilson PDF Full Chapterbeatermany.imubd2100% (19)
- Ob Osce.04 CTG ReadingDocument6 pagesOb Osce.04 CTG ReadingDasha VeeNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary AmenorrhoeaDocument72 pagesPrimary and Secondary Amenorrhoead clarkeNo ratings yet
- Examination of ElbowDocument18 pagesExamination of Elbowharmohit singhNo ratings yet
- Liver Pathology EMQDocument1 pageLiver Pathology EMQhazirmm100% (2)
- Narcissistic MothersDocument11 pagesNarcissistic MothersSeraph100% (7)
- Agc332 Lecture 10-Wheat DiseasesDocument33 pagesAgc332 Lecture 10-Wheat DiseasesSolomon MbeweNo ratings yet
- Arterial Line Analysis PresentationDocument35 pagesArterial Line Analysis PresentationLisa GilbertNo ratings yet
- Sanum Therapy Book Helios PDFDocument314 pagesSanum Therapy Book Helios PDFOscarNo ratings yet
- Splice PDFDocument5 pagesSplice PDFpedroNo ratings yet
- Caffein Intox PDFDocument3 pagesCaffein Intox PDFSejahtera SurbaktiNo ratings yet
- Aromatherapy For Professionals ENGDocument593 pagesAromatherapy For Professionals ENGcamelia100% (3)
- Yvonne Farrell Psycho Emotional NotesDocument10 pagesYvonne Farrell Psycho Emotional Notesபாலஹரிப்ரீதா முத்து100% (2)
- Pharmaceutical Market Europe - June 2020Document50 pagesPharmaceutical Market Europe - June 2020Areg GhazaryanNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Taiwan's Vaccination Services and Applications For Vaccine Injury CompensationsDocument15 pagesAn Analysis of Taiwan's Vaccination Services and Applications For Vaccine Injury CompensationsAnonymous FNZ3uR2AHsNo ratings yet
- J Potratz ResumeDocument3 pagesJ Potratz Resumeapi-216040679No ratings yet
- VBAC MCQsDocument3 pagesVBAC MCQsHanaNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis - PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesOsteoporosis - PathophysiologyMary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Essay On WaterDocument111 pagesEssay On WaterBlue StoneNo ratings yet
- Plan Training Session: Trainers Methodology Level I Templates Document No. Issued By: Ntta Page I of VIIDocument31 pagesPlan Training Session: Trainers Methodology Level I Templates Document No. Issued By: Ntta Page I of VIIBenevict L. IbañezNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health: Ekta Modi 2 MPT in RehabDocument368 pagesMaternal Health: Ekta Modi 2 MPT in RehabMihir_Mehta_5497100% (1)
- WelcomeDocument74 pagesWelcomeSagarRathodNo ratings yet
- HRCT in Diffuse Lung Diseases - II: Dr. Bhavin JankhariaDocument33 pagesHRCT in Diffuse Lung Diseases - II: Dr. Bhavin JankhariaAbdul QuyyumNo ratings yet
- Dermoscopy ReviewDocument28 pagesDermoscopy ReviewMarwa RagabNo ratings yet
- Non - Food Meher Final Report (2023)Document87 pagesNon - Food Meher Final Report (2023)atakltigebertsadikNo ratings yet
- Garcia. Act 1 and 2 NUR103Document4 pagesGarcia. Act 1 and 2 NUR103Frances Katherine GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Validity of Acupuncture in Veterinary MedicineDocument10 pagesThe Validity of Acupuncture in Veterinary MedicinePaolaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Marcelia Suryatenggara, Sp. S - How To Choose Your AnalgeticsDocument9 pagesDr. Marcelia Suryatenggara, Sp. S - How To Choose Your AnalgeticsFreade AkbarNo ratings yet