Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endorine System
Uploaded by
Michaela Shianne E. Matitu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesThe endocrine system regulates homeostasis through the secretion of hormones directly into the bloodstream from various glands. The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" as it controls the functions of other endocrine glands by producing hormones. Some key glands and hormones include the thyroid (thyroxine), parathyroid (parathyroid hormone), pancreas (insulin and glucagon), adrenals (cortisol, aldosterone), and pineal gland (melatonin). Endocrine diseases can result from too little or too much secretions of hormones.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe endocrine system regulates homeostasis through the secretion of hormones directly into the bloodstream from various glands. The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" as it controls the functions of other endocrine glands by producing hormones. Some key glands and hormones include the thyroid (thyroxine), parathyroid (parathyroid hormone), pancreas (insulin and glucagon), adrenals (cortisol, aldosterone), and pineal gland (melatonin). Endocrine diseases can result from too little or too much secretions of hormones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesEndorine System
Uploaded by
Michaela Shianne E. MatituThe endocrine system regulates homeostasis through the secretion of hormones directly into the bloodstream from various glands. The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" as it controls the functions of other endocrine glands by producing hormones. Some key glands and hormones include the thyroid (thyroxine), parathyroid (parathyroid hormone), pancreas (insulin and glucagon), adrenals (cortisol, aldosterone), and pineal gland (melatonin). Endocrine diseases can result from too little or too much secretions of hormones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
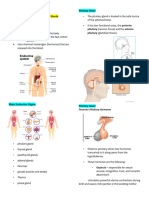
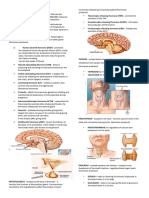
Structure and Function of -response hormones Pineal body
Endocrine System -metabolism hormones -Produces the hormone
Exocrine vs. Endocrine -and more…. melatonin which regulate daily
Exocrine – release products sleep-wake cycle or seasonal
(enzymes) into ducts rhythms associated with
-e.g.) Sweat, tears, digestive existing light conditions.
juices -Melatonin:
-Target tissues: hypothalamus
Endocrine – directly to -Functions: plays a role in
bloodstream; NO DUCTS onset of puberty and controls
-e.g) Hormones circadian rhythms. Light affects
its function.
Endocrine System
Glands – release products to
the bloodstream directly.
Hormones – products deliver
messages to body
-Chemical messengers
secreted by
endocrine glands, and
transported by the
Structure and Functions The
bloodstream.
Endo. System
Target cells – have specific
receptors for specific
hormones
The Endo. System GENERAL
FUNCTIONS
Homeostasis exists when
-Maintains homeostasis by there
regulating the production of is a
chemicals that affect most
functions of the body.
-Secretes substances that aid
the nervous system.
balance of
-Important regulator of growth Hypothalamus
substances. Endo. conditions
and development. -Structure located above the
are due to either hypo (too
pituitary gland that translates
little) or hyper (too much)
Endocrine system releases nervous system impulses into
secretions of substances
hormones endocrine
(hormones).
-growth hormones system messages.
-sex hormones -Controls pituitary secretions.
Glands and Their Hormones
ANTERIOR (front) -Secretes parathyroid
PITUITARY GLAND hormone, which affects the
1.Growth Hormone – amount of calcium in the
stimulates growth and blood.
metabolic function. -Raises blood calcium level.
2.Prolactin – stimulates milk
production and PARAthyroid Glands
secretion. -PTH-Parathyroid hormones
3.Follicle Stimulating -Increases the making of
Hormone – stimulates Vitamin D in the body.
the production of ova and -Causes bones to release
sperm. calcium and phosphate
4.Luteinizing Hormone – -PARATHORMONE – raises
stimulates ovaries and the blood calcium level.
testes.
Pituitary Gland 5.Thyroid- Stimulating Pancreas
Master gland Hormone–stimulates -Produces the hormones
-Controls the other endocrine thyroid gland. insulin and glucagon. Insulin
glands regulates transportation of
Growth Hormone (GH) Thyroid sugar, fatty acids, and amino
-Too much – gigantism -Produces hormones that acids into the cells.
-Too little – dwarfism regulate body metabolism -Insulin lowers blood sugar
Antidiuretic (ADH) (thyroxin). level.
-Stimulates kidneys to keep -Lowers blood calcium level -Glucagon raises the blood
water (calcitonin). sugar level.
POSTERIOR (back) THYROXIN
PITUITARY GLAND 1. Too little thyroxine – Thymus Gland
-releases neurohormones hypothyroidism -The thymus gland, located
made in hypothalamus behind your sternum and
1. Oxytocin – stimulates the a. Depression, attention, between your lungs, is only
contraction of uterus and memory problems, weight active until puberty.
mammary gland gain.
cells. -After puberty, the thymus
-The hormone involved in 2. Too much thyroxine – starts to slowly shrink and
inducing labor during hyperthyroidism become replaced by fat.
childbirth. a. Agitation, irritability, &
-Hormone involved in bonding. weight loss. -Your thymus gland reaches its
-Hormone involved in maximum size when you're a
relationships. *Goiters – Growths on thyroid teenager. Then, it starts to
-Might be deficient in Autism. gland shrink slowly. By the time you
2. ADH – promotes retention turn 75 years old, your thymus
of water by kidneys. Parathyroid gland turns to fat.
-Thymosin is the hormone of 2. Aldosterone regulates Acromegaly
the thymus, and it stimulates mineral such as Na, Ca, and - hyper GH during
the development of Water balance in the adulthood
disease-fighting T cells. blood. - gradual enlargement or
-helps regulate your blood pH elongation of facial
(how acidic or basic it is) by bones and extremities,
controlling the levels of hands, feet, and jaws.
electrolytes in your blood.
3. Androgens such as Pituitary Dwarfism
Testosterone - Hypo GH before 25
-influence the development of - aka proportional
male secondary characteristics dwarfism
- Usually normal mental
-Adrenal Medulla (inner) & sexual functions
1. Adrenaline &
Noradrenaline both help to Thyroxine – increases
trigger physiological changes metabolic rate
to improve the “fight or flight” Overactive
response - Goiter
to stress and emergency. - Hyperthyroidism
- Grave’s Disease
Underactive
- Goiter
- Hypothyroidism
- Myxoedema (adults)
Adrenal glands
(top of the kidney) - Cretinism (kids)
-Produce about 30 hormones 1. )Calcitonin – lowers blood
-Adrenal Cortex (outer) Ca level
1. Cortisol helps control your Overactive
body’s use of fats, proteins - Tetany
and Underactive
carbohydrates. It also - Kidney Stones
suppresses inflammation, - Osteoporosis
regulates your blood
pressure, increases blood DISEASES: 2.)Parathormone (PTH) –
sugar and helps control your raises blood Ca level
sleep-wake cycle. Your Gigantism Overactive
adrenal glands release cortisol - An excessive growth of - Kidney Stones
during times of stress to help the long bones caused - Osteoporosis
your body get an energy boost by hypersecretion of the Underactive
and better handle an GH hormone before 25. - Tetany
emergency - extreme skeletal size
situation.
3.) Insulin – decrease blood - sluggish, weight gain;
sugar - slowing of body Diabetes Mellitus
levels function - Insulin allows glucose
Overactive to transfer into cell
- Hypoglycemia Cretinism - Hypo insulin OR target
- Hyperinsulinism (insulin - hypo thyroid hormone cell insensitivity to
shock) during early insulin
Underactive development - Lack of insulin
- Hyperglycemia -aka deformed dwarfism
- Diabetes - retarded mental INDICATIONS!
development; facial puffiness; - Polyuria
HYPERTHYROIDISM lack of muscle coordination Over urinating
- hyper thyroid hormone - Polydipsia
- nervous, tremor, weight Goiter Thirsty asf
loss, excessive hunger; - lack of iodine in diet - Polyphagia
fatigue; irritability - enlargement of thyroid Hungry af
Tetany Myxoedema
- hyper thyroid hormone - Puffiness (swelling) ASSESSMENT:
- painful muscle spasms, - Fatigue - List activities that contribute
tremors, or muscular - Obesity to the endocrine system
contractions - Dry, thickened skin diseases.
- Result of low calcium - Mental impairment
levels in the blood - Thin, brittle hair Reasons why diabetes is a
- Leads to poor calcium Winter depression common disease to the
absorption; chronic - Hyper melatonin Filipinos at present.
diarrhea; repeated - Usually in winter when
vomiting of gastric acid; days are shorter Give two hormones that have
and hyperventilation, a (sunlight inhibits opposite effects.
hysterical form of over melatonin)
breathing - Aka Seasonal affective 4. Why are endocrine glands
disorder (SAD) also called ductless gland
Graves disease - sadness resulting from
- hyper thyroid hormone exaggerated melatonin 5. What will happen if you
- inherited or possibly effects eliminate / remove the entire
autoimmune - exposed to endocrine system in our
- weight loss, high-intensity light human
nervousness, body systems?
increased heart rate, Diabetes insipidus
exophthalmos goiter - hypo or insensitivity to 4. Factors that affect the
ADH functions of the endocrine
Hypothyroidism - decrease in kidney’s system.
retention of water
- hypo thyroid hormone - excessive urination 5. Why is adrenaline called
- excessive thirst emergency hormone?
You might also like
- Microscopio Olympus CX31 Serv PDFDocument36 pagesMicroscopio Olympus CX31 Serv PDFalejandra0% (1)
- The Endocrine Glands and The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine Glands and The Nervous SystemLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Endocrine SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System NotesDocument11 pagesThe Endocrine System NotesArce JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine SystemRenz Carlvince Butihen-Billones0% (1)
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemMikaella Viador100% (2)
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Script For Midterm VRDocument5 pagesScript For Midterm VRDanica MerinNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - q3 ReviewerDocument16 pagesScience 10 - q3 ReviewerNicole Lapu-osNo ratings yet
- ABT Endocrine PPDocument39 pagesABT Endocrine PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer LecDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer LecNOELLE LAURAINNE TANZONo ratings yet
- Ing - Sistem EndokrinDocument9 pagesIng - Sistem EndokrinWarman PurbaNo ratings yet
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument12 pagesEndocrine GlandMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Lesson 1Document44 pagesThe Endocrine System Lesson 1Heaven Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands and Their FunctionsDocument31 pagesEndocrine Glands and Their FunctionsAfrina Asmi MINo ratings yet
- Chap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesDocument11 pagesChap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Endocrine System: Hormones Because Lipids Fear Water That's WhyDocument7 pagesUnit 8: Endocrine System: Hormones Because Lipids Fear Water That's WhyFaoloPanganNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Midterm)Document6 pagesEndocrine System (Midterm)edceljero127No ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System NotesShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine - Feb12Document39 pagesEndocrine - Feb12cabilesrobilyn479No ratings yet
- MC1 REVIEWER (Endocrine System) - MIDTERMSDocument6 pagesMC1 REVIEWER (Endocrine System) - MIDTERMSFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine System NotesDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine System Notesvictoria skoubourisNo ratings yet
- 22 Chemical Co-OrdinationDocument47 pages22 Chemical Co-OrdinationRachna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Noteshannah pelonia100% (1)
- Somatic Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesSomatic Nervous SystemGuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LecDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecmelbertconag1973No ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesThe Endocrine Systemheyraheyra70No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Group 6Document43 pagesEndocrine System: Group 6Redona Audrey RoseNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Presented By: 5th Group Feby Amalia Hardianty Suryana Syuaib Andi Nurul Virninda Debby Trisia SariDocument24 pagesThe Endocrine System: Presented By: 5th Group Feby Amalia Hardianty Suryana Syuaib Andi Nurul Virninda Debby Trisia SariAndi Nurhidayah100% (1)
- Chemical Co Ordination and Integration - 434dea34 f494 4704 A8c9 6876397e324eDocument53 pagesChemical Co Ordination and Integration - 434dea34 f494 4704 A8c9 6876397e324epcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- Science: Endocrine & Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesScience: Endocrine & Nervous SystemLUISE DANIELLA DELOS REYES DOLOTALLASNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIDocument9 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- Hormones and Coordinating System of AnimalsDocument2 pagesHormones and Coordinating System of AnimalsLin ManahanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands Group 1Document15 pagesEndocrine Glands Group 110 - St. Hyacint Keziah Shane R. NazNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemynaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - NURSINGDocument3 pagesEndocrine System - NURSINGFrancesca GraingerNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument1 pageEndocrineDiwata DonatoNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemsDocument4 pagesOrgan SystemsDenine Dela Rosa OrdinalNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document3 pages11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: FunctionDocument24 pagesEndocrine System: FunctionCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Endocrine SystemDocument24 pages2018 - Endocrine SystemCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- Science - Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesScience - Endocrine SystemedieNo ratings yet
- Endrocrine NotesDocument5 pagesEndrocrine NoteskatNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledJhannyt Jyn BasaloNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Apllied ScienceDocument44 pagesEndocrinology Apllied ScienceAdam PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Science - LensDocument8 pagesScience - LensAte DannyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument13 pagesEndocrine SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- BSC NotesDocument9 pagesBSC NotesTayyaba ShahNo ratings yet
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthFrom EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesFourth Quarter Examjanice gumabao50% (4)
- Rugelach Recipe From Monday Morning Cooking ClubDocument2 pagesRugelach Recipe From Monday Morning Cooking ClubAnonymous W5F9r2b2hNo ratings yet
- My Family (Speaking Cards)Document1 pageMy Family (Speaking Cards)Maria Marynuch100% (1)
- The 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All TimeDocument4 pagesThe 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All Timeungku1No ratings yet
- Phase-Locked Loop Independent Second-Order Generalized Integrator For Single-Phase Grid SynchronizationDocument9 pagesPhase-Locked Loop Independent Second-Order Generalized Integrator For Single-Phase Grid SynchronizationGracella AudreyNo ratings yet
- Greyhound Free Patt.Document14 pagesGreyhound Free Patt.claire_garlandNo ratings yet
- IJETR022563Document5 pagesIJETR022563erpublicationNo ratings yet
- ADT Cat D400EDocument2 pagesADT Cat D400EEbran AndromedaNo ratings yet
- UNDP NP Dhangadhi SWM TOR FinalDocument4 pagesUNDP NP Dhangadhi SWM TOR FinalNirmal K.c.No ratings yet
- Sip Dissertation - Final - Final For CollegeDocument17 pagesSip Dissertation - Final - Final For Collegevikashirulkar922No ratings yet
- Welding Inspection Technology: Module 7 - Visual Inspection WorkshopDocument20 pagesWelding Inspection Technology: Module 7 - Visual Inspection Workshoprex valenciaNo ratings yet
- De Thi Vao 10 Chuyen Hoa Nguyen Trai Hai Duong 20212022Document2 pagesDe Thi Vao 10 Chuyen Hoa Nguyen Trai Hai Duong 20212022Trần Ngọc BíchNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument29 pagesElectricity and MagnetismNashrul HaqNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Worksheet - SHHSDocument3 pagesCatalyst Worksheet - SHHSNerd 101No ratings yet
- Astrophysics & CosmologyDocument2 pagesAstrophysics & CosmologyMarkus von BergenNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 7 (PDF)Document1 pageUnit Test 7 (PDF)emirelliucNo ratings yet
- MD 2 MidtermDocument31 pagesMD 2 MidtermRea Rebenque100% (1)
- Vision For Mobile Robot Navigation - A Survey PDFDocument31 pagesVision For Mobile Robot Navigation - A Survey PDFtes donlodNo ratings yet
- The Greek LettersDocument18 pagesThe Greek LettersSupreet GuptaNo ratings yet
- B2 - Effects of UV-C Treatment and Cold Storage On Ergosterol and Vitamin D2 Contents in Different Parts of White and Brown Mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus)Document6 pagesB2 - Effects of UV-C Treatment and Cold Storage On Ergosterol and Vitamin D2 Contents in Different Parts of White and Brown Mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus)Nadya Mei LindaNo ratings yet
- GP 24-21 - Fire Hazard AnalysisDocument53 pagesGP 24-21 - Fire Hazard AnalysisJohn DryNo ratings yet
- Site AnalysisDocument20 pagesSite AnalysisCarlo RosaioNo ratings yet
- Ryan's DilemmaDocument11 pagesRyan's DilemmaAkhi RajNo ratings yet
- HP Prodesk 400 G6 Microtower PC: Reliable and Ready Expansion For Your Growing BusinessDocument4 pagesHP Prodesk 400 G6 Microtower PC: Reliable and Ready Expansion For Your Growing BusinessPằngPằngChiuChiuNo ratings yet
- AT2H - Basics - Symbolism in HinduismDocument28 pagesAT2H - Basics - Symbolism in Hinduismapi-3764210No ratings yet
- P eDocument22 pagesP eKiks AshNo ratings yet
- Oplan Tumbler ProposalDocument3 pagesOplan Tumbler ProposalKay Tuppil ManzanillaNo ratings yet
- KRC1 Start-Up PDFDocument29 pagesKRC1 Start-Up PDFRafael50% (2)
- Conduit 5Document42 pagesConduit 5dediNo ratings yet