Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Clyde CapapasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Clyde CapapasCopyright:
Available Formats
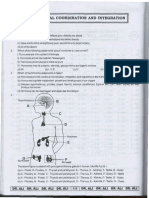
HORMONE
- Specialized chemical produced and
- Related to nervous system secreted by an endocrine cell or tissue
- Stimulation from Nervous System - Either in the bloodstream (target cells)
- Made up of tissues and organs called or fluids around cells
endocrine glands • Secreted for a short period of time
Ex: Adrenalin (epinephrine)
Hormones
- emergency cases
- Maintains homeostasis • Secreted for a long period of time
Ex: hormones from the ovaries
Glandular Epithelium
- Secreted over extended period of
- Used by nervous system and endocrine time to stimulate menstrual cycle
system
CLASSIFICATION OF HORMONE
FUNCTIONS:
1. Protein (peptide) hormone
1. Helps maintain homeostasis by regulating - Acts on the cell membrane
activities Ex: insulin, vasopressin, growth hormone,
- Controls chemical and water balance adrenocorticotropic hormone
- Controls growth and metabolism 2. Amide (Amino Acid derivative)
(chemical reactions that - Acts on the cell membrane
breakdowns/build ups substances Ex: epinephrine, norepinephrine
- controls embryonic development and 3. Steroids
preparation in nurturing new born - Acts intracellularly to modify
(prolactin) protein synthesis
- influences sexual behaviour - Penetrates the target cells
- stimulates the growth of the gonads membrane and interact directly
- feedback of the nervous system with the genes in the nucleus to
2. Its secretion act together with the nervous alter metabolism
system Ex: cortisol, estrogen, testosterone
- To help the body react to stress
properly ENDOCRINE GLANDS
3. Major regulator of growth and
development including sexual A. Pituitary Glands (hypophysis)
development and reproduction. - “Master Endocrine Glands”
- Below hypothalamus
COMPOSITION: - Controls several glands in the
1. Endocrine Glands body except adrenal glands
- Major glands in the body - Grape-size or pea-size
- Secrete products into interstitial fluid - Under the control of
surrounding secretory cells hypothalamus
- Pituitary gland, thyroid, parathyroid, - Located at the base of the brain in
pineal gland and adrenal glands the sella turcica of the sphenoid
2. Endocrine Organs bone
- Hormone secreting cells
- Contains cells that secrete hormones
- Thymus, hypothalamus, pancreas,
gonads, liver and other organs.
MOC: Prolactin RH
c. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
2 LOBES
(ACTH)
1. Anterior Pituitary Gland - Regulates the endocrine activity
(adenohypophysis) such as hormone production of
- Secrete hormones that regulate a the cortex portion of the adrenal
wide range of bodily activities gland (adrenal cortex: steroid)
from growth to reproduction. MOC: Corticotropic RH
a. Growth Hormone (GH)/ stimulates the release of
somatotropin/ somatotropic hormone
hormone (STH) d. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
- Stimulates the growth of the (TSH)/ Thyrotrophic hormone (TH)
bone and in the muscles - Stimulates the production and
• Muscles- stimulates the uptake of secretion of thyroid hormones
amino acids and the synthesis of e. Gonadotropic Hormone
protein - Regulates hormonal activity of
• Bones- stimulates the cell division the gonads
and protein synthesis which results - Influences the growth and
in the increase of the length and development such as the
width production of sperm cell and egg
MOC: - through the growth cell
hormone f. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
- growth hormone inhibiting (FSH)
hormone - As the follicle mature, they
produce estrogen and eggs are
FACTS ON GROWTH HORMONE prepared for ovulation
1. More growth hormone produced • Females:
during the growth phase the taller the - stimulates follicle development
healthier the person will be. in the ovaries
2. Secretion of growth hormones is at its • Males
highest peak during sleep and during - Stimulates sperm development
strenuous exercises. by the testes
3. Hyposecretion occurring during the MOC: Gonadotropin RH
growth phase of a child would result to g. Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
stunted growth and not dwarfism. - Stimulates corpus luteum to
4. Hypersecretion results in gigantism produce progesterone and some
5. If the pituitary begins producing estrogen
excess hormones after growth is • Yellow mass of tissue that
completed it results to acromegaly forms in the part of ovaries
- Thickening of jaw, nose hands after ovulation
- Enlargement of bone • Male’s LH is referred to as
- GH interstitial cell stimulating
b. Prolactin hormone (ICSH)
- Protein hormone - Stimulates the testosterone
- Promote breast development production in the interstitial cell
during pregnancy on the testes
- Secreted at the end of ➢ Hyposecretion of FSH and
pregnancy and acts on the LH leads to sterility in both
mammary gland males and females.
➢ FSH and LH- stimulates - Secreted by the prevalent cells
maturation and release of called follicular cells
egg in the ovary -
2. Posterior Pituitary Gland a. Thyroxine (T4)
(Neurohypophysis) - 4 atoms of iodine
- Not an endocrine gland because - Major hormone secreted by the
it does not make the peptide thyroid follicles
hormone it releases - Regulates metabolism by
- Storage are by the hypothalamus speeding cellular respiration
a. Oxytocin b. Triiodothyronine (T3)
- Stimulates uterine contraction - Conversion of T4 to T3
during child birth and mammary - Regulates cellular metabolic
gland contraction activity
b. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)/ • TSH
Vasopressin • Both T3 and T4 is consist of iodine
- 2nd hormone release made from and amino acid tyrosine
the hypothalamus
- a peptide that helps regulate 1. Increases the energy rate from
fluid-balance → maintains water carbohydrates
balance →kidneys (distal renal 2. Increases the rate of protein synthesis
tubules to increase the water 3. Stimulates the activity of nervous
reabsorption system
• detected on the blood ▪ T3 is five times more potent than
T4 even though they have the
EFFECTS OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE
same function
1. haemorrhage
CONDITIONS:
- ADH secretion increases to
maintain the body’s fluid balance 1. Hyperthyroidism
2. Strenuous Exercise - Overactivity of thyroid gland
3. Nicotine which usually produce a goiter
4. Drugs 2. Goiter
5. Barbiturates - Enlargement of thyroid
- These 4 increases the secretion of - Iodine deficiency
ADH which results to the rise of 3. Cretinism
blood pressure and inhibition on - Mental retardation and irregular
the urine development of bones and
6. Alcohol or beer muscles
- Inhibits the ADH which results in - Underactive during prenatal
urine secretion 2. Calcitonin (CT)/ Thyrocalcitonin
- Polypeptide hormone produced
B. Thyroid Gland by parafollicular cells.
- Located at the neck anterior to - Acts on the bones, kidneys, and
trachea other cells
- 2 lobes - Lowers calcium concentration in
- ISTHMUS – bridge that connects the blood
the 2 lobes - As the calcium concentration
increases so as the calcitonin
1. Thyroid Hormone • Stops at elderly
C. Parathyroid Gland
- Body’s smallest endocrine gland 2. Forces cardiac contraction
- 2 pairs, one at each side 3. Increase breathing rate
a. Parathyroid Hormone/ Parathormone 4. Increase blood glucose level
(PTH) 5. Decrease digestive activity
- Regulates the concentration of
calcium and phosphate in the ▪ Instrumental in the fight or
blood. flight response
• Phosphate – build and ▪ Secreted in all kinds of stress
repair bones and teeth ▪ Nerve impulse travelling from
• Help the nerve function by the brain to the adrenal medulla
making the muscle trigger the release of adrenalin
contract and noradrenalin
• 85% of phosphorus can be
2. Adrenal Cortex
found on bones
- Surrounds the adrenal medulla
IMPROPER BALANCE OF CALCIUM AND
a. Glucocorticoids
PHOSPHATE - Affects the glucose metabolism
- Maintains blood glucose level in
1. Faulty transmission of nerve impulses blood, in response to injury,
to the brain stress or serious infections
b. Mineralocorticoids
2. Destruction of bone tissue
- Regulates the ionic
3. Delayed bone growth concentration of blood and
4. Tetany -uncontrollable muscle spasm tissue fluid
- Electrolyte or mineral salt
balance
D. Adrenal Glands - Regulates the concentration of
potassium and sodium in the
- Top of each kidney
body
c. Sex Steroids
2 ZONES
1. Adrenal Medulla E. Pineal Glands (Pineal Body)
- Central region - Produces melatonin
a. Adrenalin (Epinephrine) o Hormone that affects the
sleep/wake cycle
- 80% of the output of adrenal - Pea-size
medulla in human - Roof of the diencephalon, deep
- Synthesize from noradrenalin within the cerebral hemisphere
b. Noradrenalin (Norepinephrine) of the brain, posterior to the 3rd
- Principal transmitter of ventricle of the brain.
sympathetic nerve ending, - Under the control of post
supplying major organs and skin ganglion sympathetic fibers
- Increases blood pressure, - Influences by the amount of light
decreases intestine’s activity that enters the eye, where retina
signals the hypothalamus
▪ Recent studies states that
FUNCTIONS: RETINA produces
melatonin
1. Increases heart rate
• Circadian and Diurnal Rhythm of - Stimulates the secretion of
many tissue growth by somatotropic cells of
- Refers to day and night cycle of anterior pituitary gland
sleep B. Thymus
• Melatonin rises from mid-late evening - Lymphoid organ located behind
and drops at early morning hours. the sternum
- Jetlag, shifting - Processing of T cells (T
lymphocyte; WBC)
ENDOCRINE ORGANS
▪ Responsible for cellular
- Hormone secreting cells immunity
- Recognizes infected human cells
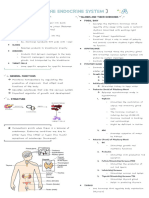
A. Hypothalamus and cancer cells and attacks
- Major endocrine gland these cells, then kills these cells
- Transmit impulses to pituitary → continue to search for more
gland to release hormone infected and cancer cells
- Integrating link - Superior to the mediastinum,
- Secrete hormones that control anterior to the aorta, posterior to
other endocrine glands the manubrium of the sternum
- Inhibiting and releasing
FUNCTION:
hormone
➢ Can change the function due to 1. Secretes the hormone thymosin that
stressful events/ emotions stimulates the T lymphocyte’s activity
FUNCTION:
C. Pancreas
1. Produce hormone which are send to - Abdominal cavity with its head
pituitary gland for release lying in the curve of the
2. Produces a releasing factor which duodenum and its tail stretches
trigger the release of hormone made to the left kidney
in the pituitary gland • Acini – tiny clumps of cells that
produce the digestive enzymes
HYPOTHALAMIC HORMONES • Islets of Langerhans
1. Inhibiting hormones - Small island of endocrine cells
a. Somatostatin scattered throughout
- Inhibits the secretion of both - Specialized tissue of pancreas
insulin and glucagon, also the 4 KINDS
gonadotropic hormone from
anterior pituitary gland 1. Alpha Cells- produces glucagon
b. Prolactin Inhibiting Hormone 2. Beta Cells- produces insulin (protein
(PIH) hormone)
2. Releasing Hormone 3. Delta Cells- produces somatostatin
a. Thyroprotein/ Thyroliberin - Inhibits glucagon and insulin
- Stimulates the release of
thyroprotein and prolactin from ➢ Liver breaks the insulin after
the anterior pituitary gland
b. Growth Releasing Hormone/
Somatocrinin
• Glucagon
- Polypeptide hormone
-
Stimulating the breakdown of Testosterone in Woman:
glycogen in the liver cells
- Bone strength and development
• Glycogenolysis
of limb muscle mass
- Process that helps maintain
- Found in the blood of normal
proper glucose levels in the
woman.
blood between meals.
- Responsible for the female’s
• Gluconeogenesis
sensitivity through nipples and
- Process by which the glucose is
clitoris associated for sexual
synthesize
response
➢ Takes place at the liver
Adrenal Androgens
• Glucose
- blood of woman and high
- Released from the liver and other
concentrated
storage sites in the body
- Normal: 70-110 mg/100 ml Male and Female
D. Gonads - production triggers the puberty
- Ovaries and testes - pubic hair
- Secretes hormones that helps
regulate reproductive functions 2. Female Sex Hormone
a. Estrogen (estrin, estrone,
1. Male Sex Hormones estradiol)
a. Testosterone - Primary sex hormone
- Most important cells in male - regulates menstrual cycle
- Interstitial cells of the testes - development of mammary
- Acts with LH and FSH to produce glands
or stimulates sperm production - female secondary characteristics
- Promotes the development and ▪ pubic hair
maintenance of ________ ▪ broadening of hips
behaviour ▪ mammary gland
- Stimulates growth of pubic hair b. Progesterone (progestins)
- Enlargement of larynx (voice to - Menstrual cycle
deepen) - Development of mammary
• Luteinizing Hormone gland
Female: - aids in the formation of placenta
- Target is ovaries and it triggers c. Relaxin
the ovulation - produce in small quantity
- Release the production of sex - during childbirth
hormones (estrogen, progestin) - uterus
- softens the cervix at the time of
Male: delivery for the baby to pass
easily.
- Stimulates the release of sex
E. Kidney
hormone (testosterone)
- Primary organ for the secretion
• FSH
of water
- Essential for pubertal
- Produce hormones and
development and function of the
substance
gonads of men and women
a. Erythropoietin
- Kidney hormone that stimulates
the production of RBC from bone
marrow.
b. Prostaglandins
- A substance that resembles a
hormone
- Controls the smooth muscle
during contraction, blood
pressure inflammation and body
temperature
- Autocrine – acting messenger
molecule
- Exert their effect locally where
they are produced
c. Medullipin
- Created by interstitial cells in the
renal papillae
- Converted to medullipin 2 in the
liver
- Results from vasodilation
d. Renin/ Angiotensinoginase
- A substance → enzyme
- Release in the kidney that
breakdowns protein
- Influences blood pressure
volume and the intake of salt
and water
e. Heart
- Considered as endocrine organ
- Atria contains secretory granules
that produce, store and secrete
atriopeptin (peptide hormone)
Atriopeptin
1. Helps maintain proper balance of fluid
and electrolytes by increasing the
output sodium urine
2. Release the blood vessels directly
- Lowers the blood pressure ny
blocking the hormone that tends
to increase the blood pressure
3. Reduces the blood volume by
stimulating the kidneys to filter more
blood and release more urine.
You might also like
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthFrom EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System NotesShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemMikaella Viador100% (2)
- AnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesAnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemReigh DakotaNo ratings yet
- Ing - Sistem EndokrinDocument9 pagesIng - Sistem EndokrinWarman PurbaNo ratings yet
- Endorine SystemDocument4 pagesEndorine SystemMichaela Shianne E. MatituNo ratings yet
- MC1 REVIEWER (Endocrine System) - MIDTERMSDocument6 pagesMC1 REVIEWER (Endocrine System) - MIDTERMSFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Chap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesDocument11 pagesChap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument12 pagesExcretory Products and Their EliminationPoorva NaikNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Animal ScienceDocument15 pagesEndocrine System Animal ScienceJairus LampanoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemDearly Niña OsinsaoNo ratings yet
- 6 Hormones Secreted by The AdenohypophysisDocument5 pages6 Hormones Secreted by The Adenohypophysischristine_8995No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology ReviewerDocument10 pagesGrade 10 Biology ReviewerNadine Victoria DizonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument12 pagesEndocrine GlandMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Endocrine SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer LecDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer LecNOELLE LAURAINNE TANZONo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument7 pagesANAPHYMary Joyce MejiaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System NotesDocument11 pagesThe Endocrine System NotesArce JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - q3 ReviewerDocument16 pagesScience 10 - q3 ReviewerNicole Lapu-osNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Glands and The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine Glands and The Nervous SystemLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesPituitary GlandAllyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pages10 Endocrine SystemMardy Martin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemsDocument4 pagesOrgan SystemsDenine Dela Rosa OrdinalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System TransesDocument5 pagesEndocrine System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- BSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemDocument38 pagesBSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemAngelika ButaslacNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Script For Midterm VRDocument5 pagesScript For Midterm VRDanica MerinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Quarter 3 - EndocrineDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Quarter 3 - Endocrinerafaelesguerra028No ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument5 pagesEndocrineShem DelolaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemIvy Jana BelenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Lesson 1 Grade 10Document3 pagesEndocrine Lesson 1 Grade 10Christine omaney MalagambaNo ratings yet
- 22 Chemical Co-OrdinationDocument47 pages22 Chemical Co-OrdinationRachna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Endo AnaphysioDocument9 pagesEndo AnaphysioShelley Jade MenorNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Zoology)Document3 pagesEndocrine System (Zoology)Cheska de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology2021Document19 pagesEndocrine Physiology2021saimon reyNo ratings yet
- Anaphy SemiDocument14 pagesAnaphy SemipersonalimouNo ratings yet
- hORmones in Plants Class Note Class 10 ...Document4 pageshORmones in Plants Class Note Class 10 ...AceHunterNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv Human Anatomy and Physiology: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument12 pagesUnit - Iv Human Anatomy and Physiology: Very Short Answer QuestionsRK YeleswarapuNo ratings yet
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemJames CastroNo ratings yet
- HormonyDocument3 pagesHormonya.dobjaszNo ratings yet
- BIOLS372. (21) Endocrinology SummaryDocument15 pagesBIOLS372. (21) Endocrinology SummaryNawaf Al.RiffaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co Ordination and Integration - 434dea34 f494 4704 A8c9 6876397e324eDocument53 pagesChemical Co Ordination and Integration - 434dea34 f494 4704 A8c9 6876397e324epcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- Sci ReviewerDocument3 pagesSci ReviewerIce SullezaNo ratings yet
- E N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryDocument3 pagesE N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document3 pagesChapter 10Zoe DorothyNo ratings yet
- Endokrinologi Reproduksi: Bayu Kurniawan, DRDocument48 pagesEndokrinologi Reproduksi: Bayu Kurniawan, DRdocbay100% (1)
- Pituitary Gland PDFDocument5 pagesPituitary Gland PDFLiv LeysonNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemCELLINA CLARISSE DE LEONNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIDocument9 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology - The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology - The Endocrine SystemKraig Andre RellegueNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemRoeisa SalinasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument12 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationdlotlikar767No ratings yet
- Somatic Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesSomatic Nervous SystemGuenNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine SystemThieza Mecca LucenaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationDocument4 pagesEndocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationCatherine Joy delos SantosNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 LEctureDocument3 pagesNCM 107 LEctureLee BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality Is The Capacity To HaveDocument74 pagesHuman Sexuality Is The Capacity To HaveKlaus AlmesNo ratings yet
- Self-Care Test Kits - PPT of HOSPITALDocument10 pagesSelf-Care Test Kits - PPT of HOSPITALbc070400339No ratings yet
- Sem.1 Revision HLDocument88 pagesSem.1 Revision HLRawanMazen SharifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (Maternal)Document47 pagesChapter 5 (Maternal)Veloria AbegailNo ratings yet
- Underlying Anomalies That May Contribute To Decreased Fertility in Patients With EndometriosisDocument11 pagesUnderlying Anomalies That May Contribute To Decreased Fertility in Patients With EndometriosisHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of The Male Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesAnatomy Physiology of The Male Female Reproductive SystemLilian JerotichNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Endocrine and Nervous Systems 2017Document169 pagesPhysiology of The Endocrine and Nervous Systems 2017Criss CristinaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination 1Document22 pagesChemical Coordination 1SureshNo ratings yet
- Your Hormone Levels (Estrogen and Progesterone) Usually Change Throughout The Menstrual Cycle and Can Cause Menstrual SymptomsDocument14 pagesYour Hormone Levels (Estrogen and Progesterone) Usually Change Throughout The Menstrual Cycle and Can Cause Menstrual SymptomsBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Functions of PlacentaDocument8 pagesFunctions of PlacentappsavidalandNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument16 pagesQuiz LetMohamed Y AbdallahNo ratings yet
- BbosbDocument6 pagesBbosbDaniella Natividad CeceNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemZander Ragasa GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 12bio Assignment ch123Document14 pages12bio Assignment ch123Krishna GovilNo ratings yet
- Normal Menstrual CycleDocument20 pagesNormal Menstrual CycleTrevor UratelNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control of GametogenesisDocument37 pagesHormonal Control of GametogenesisZeneishaNo ratings yet
- Finasteride 5mg PDFDocument18 pagesFinasteride 5mg PDFddandan_2No ratings yet
- Oxandrolone TabletsDocument5 pagesOxandrolone Tabletsfaqed ilzakiraNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document32 pagesModule 4Shaira Eve100% (1)
- 414 1801 1 PBDocument10 pages414 1801 1 PBAl AnzuhrafulNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Theoretical HandoutDocument153 pagesEndocrine System: Theoretical HandoutAmy AmyNo ratings yet
- HSB The Endocrine System Csec NotesDocument4 pagesHSB The Endocrine System Csec NotesGiaaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Meningiomas 2003Document18 pagesPathophysiology of Meningiomas 2003Klinik medan DeliNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture - Hypothalamus Pituitary Gonadal Axis - Reproductive PhysiologyDocument8 pages1st Lecture - Hypothalamus Pituitary Gonadal Axis - Reproductive PhysiologyBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- MCQs On Chemical Coordination and ControlDocument18 pagesMCQs On Chemical Coordination and ControlPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanNo ratings yet
- 1a ReproductiveAndSexualHealthDocument2 pages1a ReproductiveAndSexualHealthKenjie Palaganas CentenoNo ratings yet
- Why Sex Hormones Matter For NeuroscienceDocument10 pagesWhy Sex Hormones Matter For NeuroscienceМакар РогатковNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Class 12th ProjectsDocument35 pagesGuidelines For Class 12th ProjectsRitwik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences - Reproduction and Endocrine System and HomeostasisDocument83 pagesLife Sciences - Reproduction and Endocrine System and HomeostasisLusani NetshifhefheNo ratings yet