Professional Documents
Culture Documents
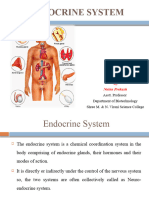
Pituitary Gland
Uploaded by
Allyza Marie Peña0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesThe pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, regulates many other endocrine glands through the hormones it secretes. It is divided into the anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior lobe secretes hormones that control growth, metabolism, and reproduction. These secretions are regulated by hormones from the hypothalamus. The posterior lobe stores and releases oxytocin and vasopressin, which are produced in the hypothalamus. Growth hormone stimulates growth and cell reproduction. It works through negative feedback loops to prevent overactivity. Disorders of the pituitary can cause dwarfism or excessive tissue growth.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, regulates many other endocrine glands through the hormones it secretes. It is divided into the anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior lobe secretes hormones that control growth, metabolism, and reproduction. These secretions are regulated by hormones from the hypothalamus. The posterior lobe stores and releases oxytocin and vasopressin, which are produced in the hypothalamus. Growth hormone stimulates growth and cell reproduction. It works through negative feedback loops to prevent overactivity. Disorders of the pituitary can cause dwarfism or excessive tissue growth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesPituitary Gland
Uploaded by
Allyza Marie PeñaThe pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, regulates many other endocrine glands through the hormones it secretes. It is divided into the anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior lobe secretes hormones that control growth, metabolism, and reproduction. These secretions are regulated by hormones from the hypothalamus. The posterior lobe stores and releases oxytocin and vasopressin, which are produced in the hypothalamus. Growth hormone stimulates growth and cell reproduction. It works through negative feedback loops to prevent overactivity. Disorders of the pituitary can cause dwarfism or excessive tissue growth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
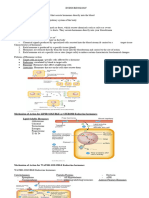
PITUITARY GLAND -Pituitary gland is controlled by hormones
produced by the Hypothalamus
-An oval, pear-shaped organ weighing about 0.4 to -Almost all secretions by the Pituitary is controlled
0.9 gms by either Hormonal or Nervous signals from the
-Located in the Hypophyseal fossa in the Sella Hypothalamus
Turcica (Pituitary Fossa)
-Divided into: Anterior Pituitary:
1. Anterior Lobe (Adenohypophysis) -Secretions by the Anterior Pituitary is controlled
2. Posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis) by hormones called Hypothalamic Releasing
Hormones or Inhibitory Hormones
Hypophyseal System:
-A portal system of veins that connect the Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary:
hypothalamus to the anterior lobe of the Pituitary
1.Growth Hormone- Stimulates protein synthesis
gland
and overall growth of most cells and tissues
-The HT secretes Hypothalamic Releasing
2.Adrenocorticotropin (Corticotropin)-
Hormones & Inhibitory Hormones that control the
Stimulates synthesis and secretion of adrenocortical
secretions of the anterior pituitary hormones.
hormones (cortisol, androgens, and aldosterone)
3.Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (Thyrotropin)-
Important Hypothalamic Hormones:
Stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyroid
1.Thyroid releasing hormone – causes release of
hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine)
TSH
4. Follicle stimulating hormone- Causes growth
2.Corticotropin releasing hormone – causes
of follicles in the ovaries and sperm maturation in
release of adrenocorticotropin
Sertoli cells of testes
3.GHRH – growth hormone release
4.GH Inhibitory Hormone – inhibits GH 5.Luteinizing Hormone- Stimulates testosterone
5.GnRH – LH & FSH synthesis in Leydig cells of testes; stimulates
6.Prolactin Inhibitory Hormone ovulation, formation of corpus luteum, and
<take note, if inhibit or releasing gani kay sa estrogen and progesterone synthesis in ovaries
hypothalamus a siya gikan> 6.Prolactin- - Promotes development of the female
breasts and secretion of milk
Embryology:
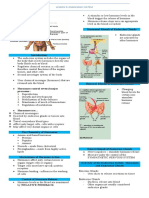
The two portions of the pituitary originate from Posterior Pituitary:
different sources Hormones of the Post. Pit.:
Anterior Pituitary Posterior Pituitary 1.Oxytocin- Stimulates milk ejection from breasts
Gland Gland and uterine contractions
anterior pituitary from posterior pituitary from a 2.Antidiuretic hormone or Vasopressin-
Rathke’s pouch, which neural tissue outgrowth
Increases water reabsorption by the kidneys and
is an embryonic from the hypothalamus
invagination of the causes vasoconstriction and increased blood
pharyngeal epithelium pressure
origin of the anterior origin of the posterior
pituitary from the pituitary from neural
pharyngeal epithelium tissue explains the
explains the epithelioid presence of large numbers
nature of its cells of glial-type cells in this
gland
Control Of The Pituitary Secretion By The
Hypothalamus
-The Pituitary gland is called the “Master gland”
as it controls many other endocrine glands
Negative Feedback Prevents Overactivity of
Hormone Systems
Although the plasma concentrations of many
hormones fluctuate in response to various stimuli
that occur throughout the day, all hormones studied
thus far appear to be closely controlled. In most
instances, this control is exerted through negative
feedback mechanisms that ensure a proper level of
hormone activity at the target tissue. After a
stimulus causes release of the hormone, conditions
or products resulting from the action of the
hormone tend to suppress its further release. In
other words, the hormone (or one of its products)
has a negative feedback effect to prevent
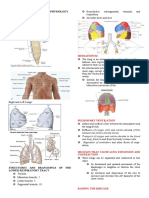
Hormones Of The Anterior Pituitary & Their Major oversecretion of the hormone or overactivity at the
Target Organ target tissue.
The controlled variable is often not the secretory
rate of the hormone itself but the degree of activity
of the target tissue. Therefore, only when the target
tissue activity rises to an appropriate level will
feedback signals to the endocrine gland become
powerful enough to slow further secretion of the
hormone.
Feedback regulation of hormones can occur at all
levels, including gene transcription and translation
steps involved in the synthesis of hormones and
steps involved in processing hormones or releasing
Growth Hormone stored hormones.
-it is metabolized rapidly in part in the liver *** Somatostatin inhibits the Anterior Pituitary
IGF-1 : inhibits Ant. Pit. (direct)
Physiologic Actions: : stimulates SS secretion (indirect)
(a) Its major effects are directed to the growth of
skeletal muscles & long bones of the body & thus
plays a role in determining final body size
(b) It is a protein anabolic hormone and produces
positive nitrogen & phosphorus balance; a rise in
plasma phosphorus & a fall in BUN (blood urea
nitrogen); It increases protein synthesis
(c)Effects on CHO & Fat metabolism:
GH is a diabetogenic because it increases hepatic
glucose output & exerts an anti-insulin effect in
muscle
(d) Mineral metabolism
GH promotes a positive calcium, magnesium &
phosphate balance. It promotes growth of long
Physiology Of Growth:
bones at the epiphyseal plate in growing children &
-Growth is a complex phenomena that is affected
young adults
not only by GH but also by Thyroid hormones,
Androgens, Estrogens, Glucocorticoids & Insulin
Feedback Control of Hormone Secretion
-It is also affected by genetic factors & largely
dependent on adequate nutrition
-The food supply is the most important extrinsic A person of 20 has a body of 7-10 yrs. Old
factor affecting growth -A panhypopituitary dwarf does not pass through
-The diet must be adequate not only in CHON puberty & never secrete a sufficient quantity of
content but also in essential vitamins & minerals & Gonadotropic hormone to develop adult sexual
in calories so that ingested CHON is not burned for functions
energy 2.Acromegaly
-Increased GH secretion in adults
In humans, there are 2 periods of Rapid growth: -Occurs after adolescence, after the epiphysis of the
1.Infancy- this first period of rapid growth is partly long bone have fused with the shaft.
a continuation of the fetal growth period -The person can not grow taller but the soft tissue
2.Late Puberty-is the period just before growth continues to grow & the bone can grow thick.
stops -The bones of the hands, feet, forehead & jaw are
-Growth spurt is due to Protein anabolism enlarged
effect of Androgens & Estrogens -Soft tissues like the tongue, liver & kidneys are
-Although Androgens & Estrogens enlarged
initially stimulate growth, they ultimately 3.Gigantism
terminate growth by causing the epiphyses Increased GH secretion before adolescence when
to fuse to the long bones; Once the epiphyses of long bones are still open
epiphyses have closed, linear growth stops A person can grow as tall as 8 feet
Rate Of Growth Hormone Secretion Depends On:
1.Starvation especially with severe CHON
deficiency
2.Hypoglycemia
3.Exercise
4.Excitement
5.Trauma
6.During first 2 hours of deep sleep
Clinical Disorders Associated With GH:
1. Dwarfism:
-Results from generalized deficiency of Ant. Pit.
Secretion during childhood (GRH, GH, IGF-I)
-Features of the body develop in appropriate
proportion to one another but the rate of
development is greatly reduced
e.g. A child of 10 yrs. Old has a bodily
development of 4-5 yrs. Old
You might also like
- MRA Project Milestone 2Document20 pagesMRA Project Milestone 2Sandya Vb69% (16)
- Castigliano's 2nd TheoremDocument29 pagesCastigliano's 2nd TheoremMiddle East100% (4)
- The Flowers of May by Francisco ArcellanaDocument5 pagesThe Flowers of May by Francisco ArcellanaMarkNicoleAnicas75% (4)
- Decretals Gregory IXDocument572 pagesDecretals Gregory IXDesideriusBT100% (4)
- Describe Hormones and Their CompositionDocument7 pagesDescribe Hormones and Their CompositionShahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)Document31 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)arun231187No ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIDocument9 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- Endocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Document61 pagesEndocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Farah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemDearly Niña OsinsaoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Part 1 (Robbins)Document28 pagesEndocrine System - Part 1 (Robbins)sarguss14100% (2)
- Ing - Sistem EndokrinDocument9 pagesIng - Sistem EndokrinWarman PurbaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine SystemThieza Mecca LucenaNo ratings yet
- Neuroendocrine System NotesDocument9 pagesNeuroendocrine System Notestara.mehrNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocument144 pagesEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRIONOLOGYDocument15 pagesENDOCRIONOLOGYmoepiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: EndocrinologyDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: EndocrinologyAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Endo Toxi Handouts RevisedDocument23 pagesEndo Toxi Handouts RevisedMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- hORmones in Plants Class Note Class 10 ...Document4 pageshORmones in Plants Class Note Class 10 ...AceHunterNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 20231110 222858 0000Document87 pagesDrugs Acting On The Endocrine System 20231110 222858 0000Sameera DahamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology ReviewerDocument10 pagesGrade 10 Biology ReviewerNadine Victoria DizonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction - CC3: Mechanism of Hormonal ActionDocument40 pagesIntroduction - CC3: Mechanism of Hormonal ActionAl-hadad AndromacheNo ratings yet
- Hormones (Short Version)Document80 pagesHormones (Short Version)Vivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesEndocrine SystemDioh EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- MC1 REVIEWER (Endocrine System) - MIDTERMSDocument6 pagesMC1 REVIEWER (Endocrine System) - MIDTERMSFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine Systempranutan739No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Pituitary Hormones and Their Control by The HypothalamusDocument39 pagesLecture 2 - Pituitary Hormones and Their Control by The HypothalamusHomeground entertainmentNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1 Patho 2 Kmu IhsanDocument33 pagesUnit 2 Part 1 Patho 2 Kmu IhsanRehan Khan RkNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: DR - Entissar Mansour 2O16-2017Document162 pagesEndocrine System: DR - Entissar Mansour 2O16-2017Zainab Alshamary100% (1)
- EndokrinDocument70 pagesEndokrinNur Hadi PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Lec 8-Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesLec 8-Endocrine SystemHarahap DarwisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine SystemrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland PDFDocument5 pagesPituitary Gland PDFLiv LeysonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System NotesShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Johanna Jane H. Macasero - Endocrine System TranscriptDocument13 pagesJohanna Jane H. Macasero - Endocrine System TranscriptJohanna MacaseroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ResonanceDocument51 pagesEndocrine ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Apllied ScienceDocument44 pagesEndocrinology Apllied ScienceAdam PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Endocrinedisorders Study 20session 201 1Document39 pagesEndocrinedisorders Study 20session 201 1Yehuda Gelar PamungkasNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument12 pagesEndocrinejamille consingNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument14 pagesEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- Structure and Function of The Endocrine SystemDocument53 pagesStructure and Function of The Endocrine Systemwalt65No ratings yet
- 11J Caybot Jashjovian Task12Document18 pages11J Caybot Jashjovian Task12JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- Unit IXDocument10 pagesUnit IXPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument74 pagesEndocrinologysyedahaleemajunaidsNo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyNo ratings yet
- 10 - Hormonal AgentsDocument64 pages10 - Hormonal Agentsnica velanoNo ratings yet
- Hormones:: Signaling MoleculesDocument20 pagesHormones:: Signaling MoleculesSangeeta DwivediNo ratings yet
- Chap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesDocument11 pagesChap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument12 pagesExcretory Products and Their EliminationPoorva NaikNo ratings yet
- Q3 Activity 2 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesQ3 Activity 2 Endocrine Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine SystemRishelle Mae Miñoza PilonesNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocument27 pagesThe Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemMikaella Viador100% (2)
- Under The Guidance Of:: Dr. Sandeep Tandon Professor and Head of Dept. of PedodonticsDocument79 pagesUnder The Guidance Of:: Dr. Sandeep Tandon Professor and Head of Dept. of PedodonticsMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument12 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationdlotlikar767No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Effects Caused by HormonesDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Effects Caused by HormonesMa. Pia Lorein JacintoNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument48 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary GlandMohsin AbbasNo ratings yet
- BIOLS372. (21) Endocrinology SummaryDocument15 pagesBIOLS372. (21) Endocrinology SummaryNawaf Al.RiffaiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System OutlineDocument17 pagesEndocrine System OutlineEsthermae PanadenNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument8 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYshaairatogleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReviewerDocument5 pagesEndocrine ReviewerAshley MalolotNo ratings yet
- Unit2-Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument80 pagesUnit2-Hypothalamus and Pituitarypranutan739No ratings yet
- Theories of AgingDocument1 pageTheories of AgingAllyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- OT Infograph 1Document1 pageOT Infograph 1Allyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- OT Infograph 2Document1 pageOT Infograph 2Allyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- Forearm Supination Rom MMTDocument4 pagesForearm Supination Rom MMTAllyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- Respi NotesDocument10 pagesRespi NotesAllyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- Heddeger STSDocument3 pagesHeddeger STSAllyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World: GlobalizationDocument4 pagesContemporary World: GlobalizationAllyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsDocument24 pagesBlood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsPaulo DanielNo ratings yet
- Speakout Language BankDocument7 pagesSpeakout Language BankСаша БулуєвNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Review QuestionsSouthernGurl99No ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument10 pagesAnxiety DisordersAhmed AntarNo ratings yet
- Summary of All Sequences For 4MS 2021Document8 pagesSummary of All Sequences For 4MS 2021rohanZorba100% (3)
- Energizing Your ScalesDocument3 pagesEnergizing Your ScalesjohnNo ratings yet
- X2ho LteDocument7 pagesX2ho LtePrasoon PuthuvattilNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Ppismp StudentsDocument6 pagesExercise and Ppismp StudentsLiyana RoseNo ratings yet
- Why I Want To Be An Army OfficerDocument1 pageWhy I Want To Be An Army OfficercmphalanNo ratings yet
- MagellansssdsaDocument2 pagesMagellansssdsaPrincess NaleNo ratings yet
- Subculture of Football HooligansDocument9 pagesSubculture of Football HooligansCristi BerdeaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Latin Course Book I Vocabulary Stage 1 Stage 2Document3 pagesCambridge Latin Course Book I Vocabulary Stage 1 Stage 2Aden BanksNo ratings yet
- HF CharactersDocument5 pagesHF CharactersAudri DebnathNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2: Project AdministrationDocument69 pagesChapter - 2: Project AdministrationRenish RanganiNo ratings yet
- 4complete The Min1Document3 pages4complete The Min1julia merlo vegaNo ratings yet
- Men Orr HagiaDocument8 pagesMen Orr HagiaAtika Bashirati IlmanNo ratings yet
- Chuyen de GerundifninitiveDocument7 pagesChuyen de GerundifninitiveThao TrinhNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument2 pagesCaseKimi Walia0% (2)
- WhatsApp Chat With MiniSoDocument28 pagesWhatsApp Chat With MiniSoShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- 07.03.09 Chest PhysiotherapyDocument10 pages07.03.09 Chest PhysiotherapyMuhammad Fuad MahfudNo ratings yet
- Abcs Booklet Kidney-Stones PDFDocument20 pagesAbcs Booklet Kidney-Stones PDFDendhy Dwi Handana SagitaNo ratings yet
- How You Are Programmed To Be POOR and THINK Small - The MAGIC of THINKING BIGDocument88 pagesHow You Are Programmed To Be POOR and THINK Small - The MAGIC of THINKING BIGOlegario S. Sumaya IIINo ratings yet
- Sec 25 HmaDocument3 pagesSec 25 HmaMukul BajajNo ratings yet
- How We Organize Ourselves-CompletedupDocument5 pagesHow We Organize Ourselves-Completedupapi-147600993No ratings yet
- Accenture 172199U SAP S4HANA Conversion Brochure US Web PDFDocument8 pagesAccenture 172199U SAP S4HANA Conversion Brochure US Web PDFrajesh2kakkasseryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Documentation Course 2020Document36 pagesNursing Documentation Course 2020Marianne Laylo100% (1)