Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Note 17 Dec 2021
Uploaded by
mCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Note 17 Dec 2021
Uploaded by
mCopyright:
Available Formats
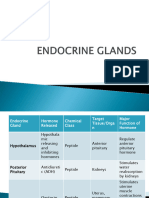
Gland: Hormone released: Chief functions:
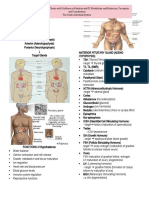
1-Hypothalamus Hypothalamic-releasing Regulates Anterior pituitary hormones
Antidiuretic(ADH) Stimulates water reabsorption
2-Posterior pituitary
• Stimulates uterine contraction
Oxytocin
• Release of milk by mammary glands
Thyroid-stimulates stimulates thyroid
Adrenocorticotropic(ACTH) Simulates adrenal cortex
Egg(ovaries) and sperm(testes)
Gonadotropic(FSH,LH)
3-Anterior pituitary and sex hormone production
Prolactin(PRL) Milk production
Growth(GH) Cell division , protein synthesis, bone growth
Melanocyte-stimulating(MSH) Skin color
Thyroxine (T) Increase metabolic rate, regulate.
4-Thyroide
triiodothyronine (T) growth and development
Calcitonin Lowers blood calcium level
5-parathyroids Parathyroid(PTH)
Raises blood calcium levels
Glucocorticoids (cortisol) Raise blood glucose
6-Adrenal cortex
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) reabsorbed sodium
Sex hormones Stimulates reproductive organs ,six
characteristics
7-Adrenal medulla Epinephrine and norepinephrine released in emergency situations, raise
blood glucose level
Insulin Lowers blood glucose ,glycogen formation
8-Pancreas
Glucagon
Raises blood glucose
9-Testes Androgens (testosterone)
Stimulates male sex characteristics
Estrogens, progesterone, small Stimulates female sex characteristics
10-ovaries
amount of testosterone
11-Thymus Thymosins Maturation of T lymphocytes
12-pineal gland
Controls circadian rhythms, possibly
Melatonin
involved in maturation of sexual organs
You might also like
- Module Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesModule Endocrine SystemVynz Morales CosepNo ratings yet
- Hormones Updated ShortDocument72 pagesHormones Updated ShortAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Assignment IN NutritionDocument5 pagesAssignment IN NutritionJasper SeeNo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument2 pagesHORMONESDa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 2: PrelimsDocument10 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 2: PrelimsjoanneNo ratings yet
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- 4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionsDocument3 pages4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionssikaboaduaNo ratings yet
- Padlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesPadlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- Follicle Stimulating Ovaries/testes: Endocrine Gland MajorDocument2 pagesFollicle Stimulating Ovaries/testes: Endocrine Gland MajorPriyabrata PandaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemZennith AngawaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands and Their Major HormonesDocument11 pagesEndocrine Glands and Their Major HormonesAnisa JamitoNo ratings yet
- Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical NatureDocument4 pagesGland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Naturernalfas100% (1)
- Endocrine GlandDocument5 pagesEndocrine GlandSTEVEN OKURUTNo ratings yet
- Ana EndoDocument2 pagesAna EndoFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NotesSashaNo ratings yet
- TEAS 6 Science by KellyDocument22 pagesTEAS 6 Science by KellyLily GarciaNo ratings yet
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Document8 pagesOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Jhason John J. CabigonNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Presented By: 5th Group Feby Amalia Hardianty Suryana Syuaib Andi Nurul Virninda Debby Trisia SariDocument24 pagesThe Endocrine System: Presented By: 5th Group Feby Amalia Hardianty Suryana Syuaib Andi Nurul Virninda Debby Trisia SariAndi Nurhidayah100% (1)
- Taree - The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesTaree - The Endocrine SystemLeomer Calderon jr.No ratings yet
- Chart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12Document2 pagesChart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12andrewy888No ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Prof - DR. Didik Tamtomo, DR PAK, MM, MKK Pakar Anatomi KedokteranDocument78 pagesEndocrinology: Prof - DR. Didik Tamtomo, DR PAK, MM, MKK Pakar Anatomi KedokteranAnnisaInayati-msNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PresentationDocument231 pagesEndocrine System PresentationKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliNo ratings yet
- Animal HormonesDocument2 pagesAnimal HormonesSameer Singh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Assignmnet 12Document3 pagesChapter 1 Assignmnet 12nabihazonabNo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionDocument1 pageChemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionNaman SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionDocument2 pagesChapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Endocrine in Animals (CBSE)Document3 pagesEndocrine in Animals (CBSE)Ashwani GahlotNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NOTESDocument2 pagesEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument23 pagesEndocrine Glandsumairabbasumar786No ratings yet
- Activity Science - TableDocument4 pagesActivity Science - TableMiranda MirandaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. SevillenoDocument55 pagesAnatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. Sevillenocoral jade cuaNo ratings yet
- Estrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesDocument57 pagesEstrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Notes AnaphyDocument36 pagesDiscussion Notes Anaphyjade tanNo ratings yet
- Endorine SystemDocument4 pagesEndorine SystemMichaela Shianne E. MatituNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Endocrine Gland Hormone Target Cell/organ Main EffectsDocument2 pagesEndocrine System: Endocrine Gland Hormone Target Cell/organ Main EffectsJasmine LoNo ratings yet
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document15 pagesBiology 1maielsherif2020No ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrineprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 13, 2024Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 13, 2024Abhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- Gland Hormone Function Target Organ (Name or Picture) : HypothalamusDocument2 pagesGland Hormone Function Target Organ (Name or Picture) : HypothalamusRoya ImaniNo ratings yet
- Endo EndoDocument45 pagesEndo EndomaoNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDocument5 pagesAnterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDevia OktaviandraNo ratings yet
- IOE Endocrine System 22-23Document13 pagesIOE Endocrine System 22-23genevievekearney04No ratings yet
- Endocrine PDFDocument5 pagesEndocrine PDFRegina SantosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesDocument18 pagesEndocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesAnkur HazraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocument144 pagesEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Making Babies: The Definitive Guide to Improving Your Fertility and Reproductive HealthFrom EverandMaking Babies: The Definitive Guide to Improving Your Fertility and Reproductive HealthNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Physiology of ENT For Paramedics - Dr. Fuad RidhaDocument52 pagesAnatomy, Physiology of ENT For Paramedics - Dr. Fuad Ridhafuadredza100% (1)
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- MTE Radionuclear THYROID FK UnandDocument44 pagesMTE Radionuclear THYROID FK UnandAmriyani OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- ENDO InhouseDocument29 pagesENDO Inhouseniczdelosreyes8No ratings yet
- Digestive System Worksheet 2013 2Document3 pagesDigestive System Worksheet 2013 2contessa padonNo ratings yet
- Insert - Elecsys Anti Tg.09005021500.V1.EnDocument4 pagesInsert - Elecsys Anti Tg.09005021500.V1.EnVegha NedyaNo ratings yet
- Treatment For Benign Thyroid Nodules With A CombinDocument7 pagesTreatment For Benign Thyroid Nodules With A CombindarthjesussithNo ratings yet
- Red Phoenix MeditationDocument3 pagesRed Phoenix MeditationAbel100% (1)
- Group (3) - Lab Report Fisvet 1 - P6 - Week 9Document20 pagesGroup (3) - Lab Report Fisvet 1 - P6 - Week 9NatAsyaNo ratings yet
- PdfText - 2022-12-15T172553.484Document1 pagePdfText - 2022-12-15T172553.484Himanshu MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- اسئلة فسلجة ثاني كورس ثانيDocument5 pagesاسئلة فسلجة ثاني كورس ثانيRad RYNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Tenth Edition: Seeley'sDocument10 pagesEssentials of Anatomy & Physiology Tenth Edition: Seeley'sRica Mae TingcoNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Endocrine Nursing: Muhammad Yaqoob Instructor Ion-DuhsDocument51 pagesUnit II: Endocrine Nursing: Muhammad Yaqoob Instructor Ion-DuhsyaqoobmdNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesDiseases of The Endocrine SystemJaeLene DacwagNo ratings yet
- RSLT An21100870 PDFDocument3 pagesRSLT An21100870 PDFMuhammed Ameen MoulaviNo ratings yet
- Neuro General Neuro: Proptosis/ Exophthalmos ChemosisDocument4 pagesNeuro General Neuro: Proptosis/ Exophthalmos ChemosisShakina FareedNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function Tests PPT of IMS BHUDocument74 pagesThyroid Function Tests PPT of IMS BHUPriyanshu Mandal100% (1)
- Thyroid DisorersDocument23 pagesThyroid DisorersBryan Lloyd RayatNo ratings yet
- OralcholecystographyDocument13 pagesOralcholecystographySuman PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Gonzalez Vs Stonegate Pharmacy 2Document11 pagesGonzalez Vs Stonegate Pharmacy 2Anonymous Pb39klJNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormone Profile in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument6 pagesThyroid Hormone Profile in Chronic Kidney DiseaserefaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 182: Biology II Assignment 1 - Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument4 pagesBIOL 182: Biology II Assignment 1 - Nervous and Endocrine SystemsMayaNo ratings yet
- Ref Ultrasoud of The Normal Thyroid 2020Document7 pagesRef Ultrasoud of The Normal Thyroid 2020Daniel Alejandro CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesClass 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine SystemDXN LUDHIANANo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function TestingDocument12 pagesThyroid Function TestingDewi Paramita YuniarahmiNo ratings yet
- Blood TestsDocument3 pagesBlood TestsMarycharinelle Antolin MolinaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Solved The Riddle of Illness 3Rd Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Solved The Riddle of Illness 3Rd Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFronald.kempker777100% (25)
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Document18 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Dayana Isabel Osorio LuxNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE FinalDocument68 pagesENDOCRINE FinalJerick Sevilla SearesNo ratings yet