Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine PDF
Uploaded by
Regina SantosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine PDF
Uploaded by
Regina SantosCopyright:
Available Formats
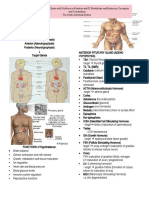
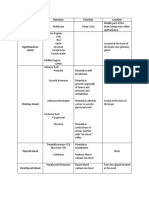
11 - Hormones and Endocrine Gland
Monday, October 14, 2019 7:53 AM
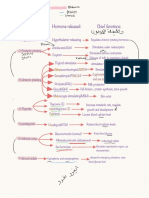
Glands Hormone Where Where Responses requested Results of Results of
hormone is hormone is undersecretion oversecretion
produced to be used (hyposecretion) (hypersecretion)
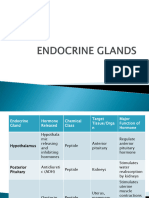
Hypothalamus
(Releasing Thyrotropin- Neuroendocrine anterior Increases secretion of thyroid- Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism
Hormones) releasing neurons pituitary stimulating hormone (TSH)
hormone (TRH)
Corticotropin- Neuroendocrine anterior Increases secretion of Addison disease Cushing syndrome,
releasing neurons pituitary adrenocorticotropic hormone androgenital syndrome
hormone (CRH) (ACTH)
Gonadotropin- Neuroendocrine anterior Increases secretion of follicle- Kallman syndrome Precocious puberty
releasing neurons pituitary stimulating hormone (FSH) and
hormone (GnRH) luteinizing hormone (LH)
Growth Neuroendocrine anterior Increases secretion of growth Pituitary dwarfism Gigantism, acromegaly
hormone- neurons pituitary hormone (GH)
releasing
hormone
(GHRH), aka
somatocrinin
Prolactin- Hypothalamus anterior Increases secretion of prolactin Menstrual disorders, Reduced menstruation,
releasing pituitary (PRL) delayed puberty, male anovulatory infertility,
hormone (PRF) infertility male impotence
(Inhibiting Growth Neuroendocrine anterior Decreases secretion of growth Gigantism, acromegaly Pituitary dwarfism
hormones) hormone– neurons pituitary hormone (GH)
inhibiting
hormone
(GHIH); also
called
somatostatin
Prolactin- Neuroendocrine anterior Decreases secretion of prolactin Reduced menstruation, Menstrual disorders,
inhibiting neurons pituitary (PRL) anovulatory infertility, delayed puberty, male
hormone (PIH) male impotence infertility
also called
dopamine
Neurohypophysis
(posterior-pituitary
gland)
Antidiuretic hypothalamu Kidneys, Conserves water by stimulating its Diabetes insipidus, Water retention, SIADH,
hormone (ADH) s smooth muscle reabsorption polyuria, polydipsia brain edema, weight gain
also called in arteriole from urine; stimulates vasoconstriction
vasopressin walls in arterioles of body, thereby raising
blood pressure
Oxytocin (OT) hypothalamu Female: Female: Stimulates smooth muscle Reduced milk release Rarely a problem
also called s Uterus, contraction in uterine wall; stimulates from mammary glands
vasopressin mammary milk ejection from mammary glands
glands
Male: Stimulates contraction of smooth
Male: Smooth muscle of male reproductive tract
muscle of male
reproductive
tract
BIO 110 Lecture Page 1
Adenohypophysis
(anterior-pituitary
gland)
Adrenocorticotro Corticotropic Adrenal cortex Stimulates secretion of adrenal cortical Addison disease Cushing syndrome,
pic hormone cells of pars hormones androgenital syndrome
(ACTH) distalis such as cortisol
Melanocyte- Cells of pars Skin Stimulates synthesis of melanin and abnormally light skin abnormally dark skin
stimulating intermedia Melanocytes dispersion of melanin granules in pigment pigment
hormone epidermal cells Obesity
(MSH)
Growth hormone Somatotropic Almost every Stimulates increased growth and Dwarfism Gigantism (child)
(GH) cells of pars cell in the body metabolism in target cells; stimulates Acromegaly (adult)
distalis synthesis of somatomedin in the
liver to stimulate growth at epiphyseal
plate
Prolactin (PRL) Mammotropic Receptors on Female: Stimulates milk production in Menstrual disorders, Reduced menstruation,
cells of pars organs mammary glands delayed puberty, male female infertility, male
distalis throughout the infertility impotence
body Male: May play a role in the sensitivity
of the interstitial cells to LH
Female:
Mammary
glands
Male:
Interstitial
cells in testes
Thyroid- Thyrotropic Thyroid gland Stimulates thyroid hormone synthesis Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism
stimulating cells of pars and secretion
hormone distalis
(TSH) also
called
thyrotropin
Luteinizing Gonadotropic Gonads Female: Stimulates ovulation, estrogen Menstrual problems, Hypergonadism, precocious
hormone (LH) cells of pars and progesterone synthesis in corpus impotence, infertility puberty
distalis Female: luteum of ovary
Ovaries
Male: Stimulates androgen synthesis in
Male: Testes testes
Follicle- Gonadotropic Gonads Female: Stimulates growth of ovarian Menstrual problems, Hypergonadism,
stimulating cells of pars follicles impotence, infertility precocious puberty
hormone distalis Female:
(FSH) Ovaries Male: Stimulates sperm production
Male: Testes
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Follicular Most body cells Increases metabolism, oxygen use, Hypothyroidism, goiter Hyperthyroidism, Graves
hormones cells of growth, and energy use; supports and disease
(thyroxine and thyroid gland increases rate of development
triiodothyronine
)
Calcitonin Parafollicular Bone, kidney Reduces calcium levels in body fluids; No known problem Thyroid cancer; some
cells of decreases bone resorption and increases association with lung,
thyroid gland calcium deposition in bone breast, and pancreatic
cancers; chronic renal
failure
BIO 110 Lecture Page 2
Parathyroid Glands Parathyroid Chief cells of Bone, small Increases calcium levels Hypoparathyroidism Hyperparathyroidism
hormone (PTH) parathyroid intestine, in blood through bone resorption (so
gland kidney calcium
may be delivered to tissues needing
calcium ions, such as muscle tissue);
increases calcium absorption by small
intestine by calcitriol; decreases calcium
loss through the kidneys
Adrenal Glands
Epinephrine adrenal medulla Smooth Initiate stress responses; raise inconsequential Pheochromocytoma
(adrenaline) and muscle, heart rate, blood (benign tumor in adrenal
norepinephrine cardiac muscle, pressure, metabolic rate; dilate medulla)
(noradrenaline) blood vessels blood vessels;
mobilize fat; raise blood glucose
Various cells level
throughout the
body
Glucocorticoids adrenal cortex Many organs Stimulate lipid and protein Addison disease Cushing syndrome
(e.g., cortisol) metabolism; regulate blood
glucose levels
Mineralocorticoi adrenal cortex Kidney cells Regulate electrolyte composition Addison disease Hypertension, edema
ds (e.g., and concentration in body fluids
aldosterone)
Gonadocorticoids Zona reticularis of Sex organs Protein synthesis in sex organ cells Generally no effect: Adrenogenital syndrome
(e.g., androgens) adrenal cortex may see effect post-
menopause
Pancreas
Insulin Beta cells of Liver, skeletal Decreases glucose levels in body fluids, Hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia
pancreatic muscles, glucose transport into target cells;
islets adipose promotes glycogen and lipid formation
Tissue, body and storage
cells
Glucagon Alpha cells of Liver, adipose Increases blood glucose levels, glycogen Diabetes mellitus Hyperinsulism
pancreatic tissue breakdown in liver cells, lipid breakdown
islets in adipose cells
Somatostatin Delta cells of Alpha and beta Slows release of insulin and glucagon to Giantism, acromegaly Suppress insulin and
pancreatic cells of slow rate of nutrient absorption during glucagon release
islets pancreatic digestion
islets
Pancreatic F cells of Delta cells of Suppresses somatostatin secretion from Excessive pancreatic Inhibition of gallbladder
polypeptide pancreatic pancreatic delta cells enzyme secretion secretion; suppress
islets islets pancreas secretion;
overstimulates gastric
secretion
Gonads
Ovary Estradiol FSH and General Stimulates development of female Hypoestrogenism, or Precocious puberty
LH secondary estrogen deficiency,
sex characteristics infertility, menopause
Progesterone FSH and Uterus Completes preparation for pregnancy Sterility (can't make
LH kids)
BIO 110 Lecture Page 3
Mammary Stimulates development Lack of sexual Premature sexual
glands development development
Testis Testosterone FSH and Many organs Stimulates development of secondary sex Gynecomastia, Precocious puberty, muscle
LH characteristics in males and growth spurt Infertility hypertrophy
at
puberty
Male Stimulates development of sex organs; Lack of sexual Premature sex organs
reproductive stimulates development
structures spermatogenesis
Pineal Gland
Melatonin FSH and LH Gonads, brain, Regulates biological Difficulty sleeping, Fatigue, weight gain, depression, desire
pigment cells rhythms insomnia for good sleep
BIO 110 Lecture Page 4
BIO 110 Lecture Page 5
You might also like
- List of Hormones Hypersecretion and Hyposecretion PDFDocument11 pagesList of Hormones Hypersecretion and Hyposecretion PDFAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology PresentationDocument43 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and Physiology Presentationramoli1988No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocument144 pagesEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control Ch#17Document4 pagesCoordination and Control Ch#17Usman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Citation NeededDocument8 pagesEndocrine System: Citation NeededAsif Hassan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Document12 pagesWeek 1 - Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Jeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- Pituitary: Posterior PosteriorDocument4 pagesPituitary: Posterior PosteriorMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland Anatomy and Hormone RegulationDocument16 pagesPituitary Gland Anatomy and Hormone RegulationabdulNo ratings yet
- Diseases of the Pituitary GlandDocument10 pagesDiseases of the Pituitary Glandbalkrishna.narshaiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands in Human BeingsDocument6 pagesEndocrine Glands in Human Beingsrohityd2359No ratings yet
- Chemical Control and Coordination FinalDocument5 pagesChemical Control and Coordination Finalakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Mahayag Abuloc Labiste Sagayno VillaruelDocument32 pagesEndocrine System: Mahayag Abuloc Labiste Sagayno VillaruelJJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Activity Science - TableDocument4 pagesActivity Science - TableMiranda MirandaNo ratings yet
- Edson John C. Demayo BSN 1-ADocument1 pageEdson John C. Demayo BSN 1-AEdson John DemayoNo ratings yet
- GlandDocument2 pagesGlandsmith joeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument35 pagesEndocrine Systemmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliNo ratings yet
- 4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionsDocument3 pages4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionssikaboaduaNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland: Master Regulators of HormonesDocument5 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary Gland: Master Regulators of HormonesLiv LeysonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Navigation SearchDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Navigation SearchAnnagella De JesusNo ratings yet
- Chemical CoordinationDocument6 pagesChemical CoordinationAmalendhu MSNo ratings yet
- Hormones Updated ShortDocument72 pagesHormones Updated ShortAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Endocrine glands and their hormonesDocument2 pagesEndocrine glands and their hormonesHazel Mae TapiaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDocument3 pagesEndocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaNo ratings yet
- Follicle Stimulating Ovaries/testes: Endocrine Gland MajorDocument2 pagesFollicle Stimulating Ovaries/testes: Endocrine Gland MajorPriyabrata PandaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System GuideDocument2 pagesEndocrine System GuideJasmine LoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PresentationDocument231 pagesEndocrine System PresentationKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 9F. Endokrin 2Document53 pages9F. Endokrin 2Irfan Maulana AjiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Regulates Animal PhysiologyDocument9 pagesEndocrine System Regulates Animal PhysiologyFlor SagnipNo ratings yet
- Hormones Secreted by Anterior and Posterior PituitaryDocument12 pagesHormones Secreted by Anterior and Posterior Pituitaryfarwafurqan1No ratings yet
- 1892 Fdoc PDFDocument15 pages1892 Fdoc PDFLavender B MatjeleNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Presented By: 5th Group Feby Amalia Hardianty Suryana Syuaib Andi Nurul Virninda Debby Trisia SariDocument24 pagesThe Endocrine System: Presented By: 5th Group Feby Amalia Hardianty Suryana Syuaib Andi Nurul Virninda Debby Trisia SariAndi Nurhidayah100% (1)
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument14 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- The Role of Hormones in the Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesThe Role of Hormones in the Endocrine SystemAshly Santhosh KNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument23 pagesEndocrine Glandsumairabbasumar786No ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyDocument8 pagesEndocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees Endocrinologyzonia kilashNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument5 pagesEndocrine GlandSTEVEN OKURUTNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyDocument8 pagesEndocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyMohammad AlHamdanyNo ratings yet
- Ana EndoDocument2 pagesAna EndoFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Module 5Document9 pagesModule 5CamilleCalmaLenonNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 2Document22 pagesChapter1 2Thea NatacNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument41 pagesReproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryabdulNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDocument3 pagesENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDocument5 pagesAnterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDevia OktaviandraNo ratings yet
- Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical NatureDocument4 pagesGland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Naturernalfas100% (1)
- Chart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12Document2 pagesChart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12andrewy888No ratings yet
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Hormone Gland Functions ChartDocument2 pagesHormone Gland Functions ChartmNo ratings yet
- Taree - The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesTaree - The Endocrine SystemLeomer Calderon jr.No ratings yet
- Abegail Joy B. Manlunas BS Psychology: Endocrine System Organ Hormone Function Disorder If Too High Disorder If Too LowDocument4 pagesAbegail Joy B. Manlunas BS Psychology: Endocrine System Organ Hormone Function Disorder If Too High Disorder If Too LowabegailmanlunasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Pituitary Gland (Endocrine SystemDocument37 pagesLesson Plan On Pituitary Gland (Endocrine SystemRosalyn Angcay Quintinita100% (1)
- Hormones Secreted by Endocrine GlandsDocument5 pagesHormones Secreted by Endocrine Glandsaditya7324100% (1)
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Making Babies: The Definitive Guide to Improving Your Fertility and Reproductive HealthFrom EverandMaking Babies: The Definitive Guide to Improving Your Fertility and Reproductive HealthNo ratings yet
- Study DesignsDocument11 pagesStudy DesignsRegina SantosNo ratings yet
- Weekly ScheduleDocument1 pageWeekly ScheduleRegina SantosNo ratings yet
- Fencing PDFDocument6 pagesFencing PDFRegina SantosNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory GlasswareDocument3 pagesCommon Laboratory GlasswareRegina SantosNo ratings yet
- Renal Calculi (NS Presentation)Document24 pagesRenal Calculi (NS Presentation)Norsyakira NawirNo ratings yet
- Resume NdetahDocument1 pageResume Ndetahapi-484395670No ratings yet
- Office of The Provincial Governor: Province of Oriental MindoroDocument1 pageOffice of The Provincial Governor: Province of Oriental MindoroZyreen Kate BCNo ratings yet
- Blepharoplasty: ExtendedDocument4 pagesBlepharoplasty: ExtendedBFF BotoxNo ratings yet
- Postoperative HypocalsemiaDocument6 pagesPostoperative HypocalsemiaAdinda PasaribuNo ratings yet
- A Student Manual of Clinical Skills 13 7 8Document194 pagesA Student Manual of Clinical Skills 13 7 8mofath100% (5)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument11 pagesCardiovascular SystemBSN 2-2 Espiritu Melody Mae DNo ratings yet
- 310-Article Text-582-1-10-20210312-1Document13 pages310-Article Text-582-1-10-20210312-1Ni Putu SwastyNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Ayurveda Project Concept Paper DR Palitha SerasingheDocument8 pagesCOVID 19 Ayurveda Project Concept Paper DR Palitha SerasingheRajeshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Aquagenic Palmoplantar Keratoderma With Dorsal Hand Involvement in An Adolescent FemaleDocument2 pagesAquagenic Palmoplantar Keratoderma With Dorsal Hand Involvement in An Adolescent FemaleTher RayNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefuroxime Drug Studymilkv93% (15)
- British Orthoptic Journal 2002Document9 pagesBritish Orthoptic Journal 2002roelkloosNo ratings yet
- Tetanus LectureDocument34 pagesTetanus LectureWonyenghitari GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Kit PDFDocument2 pagesBilirubin Kit PDFArasNo ratings yet
- Covid TestDocument1 pageCovid TestConcur ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- Attention and Executive Functions Conference Provides InsightsDocument5 pagesAttention and Executive Functions Conference Provides Insightsjonathan smithNo ratings yet
- Rosa 2014Document6 pagesRosa 2014Michal PerkowskiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDrug Study Dexamethasoneamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Vomiting and Diarrhea (Dogs)Document13 pagesVomiting and Diarrhea (Dogs)patjar jamalNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Basic Pharmacology For Nurses 17th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Basic Pharmacology For Nurses 17th Edition PDF Scribdcicely.smith712100% (38)
- Varicose VeinsDocument12 pagesVaricose Veinscheo sealyNo ratings yet
- Urinary Bladder MassDocument2 pagesUrinary Bladder Masskarl de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument7 pagesPulmonary Function Testspragna novaNo ratings yet
- First Aid Guide for WorkplacesDocument40 pagesFirst Aid Guide for WorkplaceswwwNo ratings yet
- Suspected Adverse Reactions To COVID 19 Vaccination and Safety of SoHODocument11 pagesSuspected Adverse Reactions To COVID 19 Vaccination and Safety of SoHOVevveNo ratings yet
- First Aid Skills Checklist PDFDocument2 pagesFirst Aid Skills Checklist PDFSridhar Tarai100% (1)
- Hiatal HerniaDocument9 pagesHiatal HerniaAnnJenn AsideraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0828282X22001271 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0828282X22001271 MainLilianne Mbengani LaranjeiraNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy EmbryologyDocument31 pagesRenal Anatomy EmbryologySnehal JayaramNo ratings yet
- Upper Midline CorrectionDocument5 pagesUpper Midline CorrectionmutansNo ratings yet