Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine
Uploaded by
prettyfriends 050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesEndocrine
Uploaded by
prettyfriends 05Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
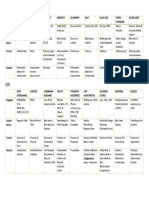
Anatomy and Physiology Lab (MT 632)
3rd Shifting Period
Endocrine System
Gland Hormone Target Cell Functions
Pineal Melatonin Brain & Helps regulate daily biological
Hypothalamus rhythms; inhibits GnRH
production.
Hypothalamus GnRH (gonadotropin- Anterior Pituitary Stimulates secretion of FSH & LH
releasing hormone)
CRH (corticotropin- Stimulates secretion of ACTH
releasing hormone)
TRH (thyrotropin- Stimulates secretion of TSH
releasing hormone)
GHRH (growth Stimulates secretion of GH
hormone-releasing
hormone)
Anterior TSH (thyroid- Thyroid Stimulates secretion of thyroid
Pituitary stimulating hormone hormone and growth of thyroid
ACTH Adrenal Cortex Stimulates secretion of
(adrenocorticotropic glucocorticoids and growth of
hormone) adrenal cortex
FSH (follicle- 1. Ovaries Stimulates secretion of estrogen
stimulating hormone) 2. Testes Stimulates sperm production
LH (luteinizing 1. Ovaries Stimulates ovulation
hormone) 2. Testes Stimulates secretion of
testosterone
GH (growth hormone) Liver, bone, Stimulates widespread tissue
cartilage, mucles, growth
adipose tissue
Posterior ADH (antidiuretic Kidneys Increases water retention
Pituitary hormone)
Oxytocin 1. Uterus Stimulates uterine contractions
2. Lactating breasts Stimulates release of milk
Thyroid T3 & T4 (thyroid Most tissues Elevates metabolic rate; increases
hormone) heart and respiration rates;
stimulates appetite
Calcitonin Osteoblasts Stimulates bone deposition
Parathyroid PTH (parathyroid 1. Osteoclasts Stimulates bone reabsorption to
hormone) increase blood calcium levels
2. Kidneys Stimulates reabsorption of
calcium by the kidneys to maintain
blood calcium levels
3. Small intestine Stimulates calcium absorption
Pancreas Insulin Most tissues, liver Stimulates cells to take in glucose
to lower blood glucose levels; tells
liver to store glucose as glycogen.
Glucagon Liver Stimulates glycogen conversion to
glucose and then the secretion to
raise blood glucose levels.
Adrenal Mineralocorticoids Kidneys Promote Na+ and water
Cortex (aldosterone) reabsorption; K+ excretion;
maintain blood volume and
pressure.
Glucocorticoids Most tissues Stimulates the breakdown of
(cortisol) protein & fat to make glucose;
suppress the immune system;
reduce inflammation
Androgens Most tissues Precursors to testosterone,
(dehydroepiandrosterone responsible for male secondary
[DHEA]) sex characteristics and for sex
drive in both sexes.
Adrenal Epinephrine Most tissues Raises metabolic rate; increases
Medulla heart & respiration rates;
increases blood glucose levels
(complements SNS)
Ovaries Estrogen Most tissues Stimulates female secondary sex
characteristics; regulates
menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Testes Testosterone Most tissues Stimulates male secondary sex
characteristics; sex drive and
sperm production
Other tissues Prostaglandins Many tissues Have variety of functions, such as
relaxing smooth muscle in
respiratory airways and blood vessels
and causing contraction of
smooth muscle in the uterus
You might also like
- Chart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12Document2 pagesChart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12andrewy888No ratings yet
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliNo ratings yet
- Source Hormone Major Action: Adrenal CortexDocument3 pagesSource Hormone Major Action: Adrenal CortexReisha FungoNo ratings yet
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Ana EndoDocument2 pagesAna EndoFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Part 1 and 2Document51 pagesEndocrine System Part 1 and 2Wajiha IffatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Lect 4Document78 pagesEndocrine Lect 4Wajiha IffatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Endocrine Gland Hormone Target Cell/organ Main EffectsDocument2 pagesEndocrine System: Endocrine Gland Hormone Target Cell/organ Main EffectsJasmine LoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lecture Activity 10 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecture Activity 10 Endocrine SystemJohnNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseDocument2 pagesPituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseHiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument2 pagesHORMONESDa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument35 pagesEndocrine Systemmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument5 pagesEndocrine GlandSTEVEN OKURUTNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine and Metabolism SystemDocument8 pagesDiscussion 2.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine and Metabolism SystemAnjar AniNo ratings yet
- 4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionsDocument3 pages4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionssikaboaduaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NoteDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NoteFumzy AdelakunNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemCHIQUI JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Some Endocrine Glands and Their HormonesDocument3 pagesSome Endocrine Glands and Their HormonesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Endocrine Pituitary Gland: A.) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Document3 pagesChapter 10 - Endocrine Pituitary Gland: A.) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Reen BalbaguioNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine SystemKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionDocument1 pageChemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionNaman SinhaNo ratings yet
- Big Picture F: MetalanguageDocument13 pagesBig Picture F: Metalanguagejohanna deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDocument3 pagesEndocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Science Inquiry (Chapter 1)Document50 pagesScience Inquiry (Chapter 1)Nancy HastingNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemsDocument4 pagesHuman Body Systemsoiu7hjjs100% (15)
- Assignment MetabolismDocument10 pagesAssignment MetabolismCherrylyn RaytosNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Document1 page7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Rudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Estrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesDocument57 pagesEstrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Ch45 EndocrineSystemDocument3 pagesCh45 EndocrineSystemCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Handouts Topics (42-64)Document67 pagesPhysiology Handouts Topics (42-64)bc200411046No ratings yet
- Gland Hormone Function Target Organ (Name or Picture) : HypothalamusDocument2 pagesGland Hormone Function Target Organ (Name or Picture) : HypothalamusRoya ImaniNo ratings yet
- Hormone 4Document1 pageHormone 4Kehmily SucgangNo ratings yet
- Follicle Stimulating Ovaries/testes: Endocrine Gland MajorDocument2 pagesFollicle Stimulating Ovaries/testes: Endocrine Gland MajorPriyabrata PandaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Notes AnaphyDocument36 pagesDiscussion Notes Anaphyjade tanNo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NOTESDocument2 pagesEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNo ratings yet
- Term Paper : Isabela State UniversityDocument9 pagesTerm Paper : Isabela State UniversityFlor SagnipNo ratings yet
- TEAS 6 Science by KellyDocument22 pagesTEAS 6 Science by KellyLily GarciaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NotesSashaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer LecDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer LecNOELLE LAURAINNE TANZONo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKAUSTUBH SAWANTNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3Document4 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PresentationDocument231 pagesEndocrine System PresentationKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesAnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemReigh DakotaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. SevillenoDocument55 pagesAnatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. Sevillenocoral jade cuaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDocument5 pagesAnterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDevia OktaviandraNo ratings yet
- Endo EndoDocument45 pagesEndo EndomaoNo ratings yet
- BSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemDocument38 pagesBSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemAngelika ButaslacNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDocument3 pagesENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaNo ratings yet
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Document8 pagesOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Jhason John J. CabigonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
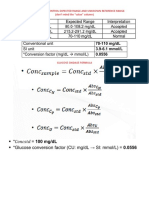
- Conventional Unit SI Unit Conversion Factor (MG/DL À Mmol/l)Document4 pagesConventional Unit SI Unit Conversion Factor (MG/DL À Mmol/l)prettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- Microtubules Which Occur On Exposed Membrane SurfacesDocument3 pagesMicrotubules Which Occur On Exposed Membrane Surfacesprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- Immunosero Qs 20ppDocument20 pagesImmunosero Qs 20ppprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- 3-PCR Gel ElectrophoresisDocument11 pages3-PCR Gel ElectrophoresiskuganatsukiNo ratings yet
- DNA Mutation and Repair PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Mutation and Repair PDFJULIA AUDREY PERALTANo ratings yet
- (Biochem Lab) Qualitest Carbs&lipidsDocument1 page(Biochem Lab) Qualitest Carbs&lipidsprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- (BIOCHEM LAB) LipidsDocument8 pages(BIOCHEM LAB) Lipidsprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- PMT Unit VDocument7 pagesPMT Unit Vprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- (BIOCHEM LAB) CarbohydratesDocument9 pages(BIOCHEM LAB) Carbohydratesprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- (Ethics) Nature of MoralityDocument5 pages(Ethics) Nature of Moralityprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- EthicsDocument3 pagesEthicsprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- IDSADocument8 pagesIDSAprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 12 The Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 12 The Endocrine Systemchirag mahidaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Endocrine System Part IDocument34 pagesTopic 6 Endocrine System Part IMahrokh DarabiNo ratings yet
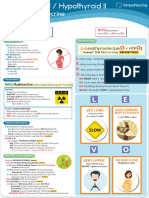
- Drug Study - LevothyroxineDocument1 pageDrug Study - LevothyroxineCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Rietz Thyroid Final PDFDocument50 pagesRietz Thyroid Final PDFRoberto CortezNo ratings yet
- Hormones in OrthodonticsDocument8 pagesHormones in OrthodonticsParameswaran ManiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument123 pagesEndocrine SystemZussette Corbita VingcoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Head and Neck - Student GuideDocument4 pagesAssessment of Head and Neck - Student GuideSherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- Hyper - Hypothyroid - PharmacologyDocument1 pageHyper - Hypothyroid - PharmacologyMa. Aira Jean PedroNo ratings yet
- Sustained Release T3 TherapyDocument10 pagesSustained Release T3 TherapyKARISHMA SHAIKHNo ratings yet
- Week-2 Anatomical Position Body Planes and Directional Terms For StudentsDocument29 pagesWeek-2 Anatomical Position Body Planes and Directional Terms For StudentsEnrique Camargo del MoralNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument4 pagesThyroidFemale calmNo ratings yet
- Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument2 pagesHormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsRenie Boy TabugonNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Activities Worksheet - PNS, ANS and Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesLab 9 Activities Worksheet - PNS, ANS and Endocrine SystemMareline MendietaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive Systemaye ayENo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LevothyroxineDocument1 pageDrug Study - LevothyroxineCarla Tongson Maravilla100% (1)
- Science10 - Q3 - Mod1 - The Endocrine System Glands and Their HormonesDocument23 pagesScience10 - Q3 - Mod1 - The Endocrine System Glands and Their HormonesFernadez Rodison100% (1)
- Thyroidectomy: 1. Brief Description of The ProcedureDocument4 pagesThyroidectomy: 1. Brief Description of The ProcedureAika CandadoNo ratings yet
- Lista SiemensDocument65 pagesLista SiemensAlexandraNo ratings yet
- MCQs On Anatomy of The Pelvis - Part 1Document3 pagesMCQs On Anatomy of The Pelvis - Part 1soban67% (3)
- Answer Sheets in Science 10 - Week 1 & 2 Hormones in Human ReprodcutionDocument4 pagesAnswer Sheets in Science 10 - Week 1 & 2 Hormones in Human ReprodcutionMa. Lourdes CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- TSH 2017-05 v23Document3 pagesTSH 2017-05 v23Yaser MNo ratings yet
- St. Alexius College, Inc.: Bs Pharmacy 1ADocument5 pagesSt. Alexius College, Inc.: Bs Pharmacy 1ABadajos Denise NickNo ratings yet
- 5,6-Thyroid HyperhypoDocument16 pages5,6-Thyroid Hyperhypomogesie1995No ratings yet
- Sankha Jee Medical Receipt-18.08.2022Document12 pagesSankha Jee Medical Receipt-18.08.2022saajnaNo ratings yet
- Althazar Score: Grading of PancreatitisDocument1 pageAlthazar Score: Grading of PancreatitisJuan GomezNo ratings yet
- 0001DD015401 1 Yf1Document1 page0001DD015401 1 Yf1Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Cite A Website in An Essay MlaDocument6 pagesHow To Cite A Website in An Essay Mlaafabfasaf100% (2)
- El Cateterismo Bilateral y Simultáneo de Los Senos Petrosos InferioresDocument8 pagesEl Cateterismo Bilateral y Simultáneo de Los Senos Petrosos InferioresPaoloNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment 10Document11 pagesHealth Assessment 10shannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- 41t3qpidtgztf1fevf4pneiyDocument4 pages41t3qpidtgztf1fevf4pneiyAdnan Rasheed ParimooNo ratings yet