Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Article and Table - Peptide Hormones
Uploaded by
ZEBINA PIE GENORINGCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Article and Table - Peptide Hormones
Uploaded by
ZEBINA PIE GENORINGCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME: Morta, Alliezza Jane DATE: June 10, 2022
PEPTIDE HORMONES: ARTICLE AND TABLE
PHBIOSCI 226R
Article
Title: Use of Polyethylene Glycol to Separate Free and Antibody-Bound Peptide Hormones in
Radioimmunoassays
Citation: BERNARD DESBUQUOIS, G. D. AURBACH, Use of Polyethylene Glycol to Separate Free and Antibody-
Bound Peptide Hormones in Radioimmunoassays, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Volume
33, Issue 5, 1 November 1971, Pages 732–738, https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-33-5-732
Summary
Aqueous polyethylene glycol causes precipitation of antibody-bound peptide hormones labeled with
radioactive iodine with little or no precipitation of free hormones. Based on this finding, a method of separation
has been developed and applied to radioimmunoassays of insulin, parathyroid hormone, growth hormone and
arginine vasopressin. The new method provides several advantages over the double-antibody precipitation
method. It appears particularly valuable in immunoassays of substances of low molecular weight.
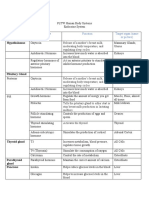
Table
Hormone Produced in Function
Adrenocorticotropic hormone Adrenal glands Stimulates the production of stress
(ACTH) hormones from the cortex, called cortisol
Amylin Pancreas A glucoregulatory hormone, regulator of
energy metabolism in health and disease
Angiotensin Liver Causes vasoconstriction and an increase in
blood pressure
Part of the renin-angiotensin system, which
regulates blood pressure
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) Myocytes of the heart Acts as an anti-hypertensive hormone
atria Dilates the blood vessels to reduce the
pressure
Helps in the reduction of reabsorption of
sodium by acting on several segments of the
nephron and other inner medullary
collecting ducts
Calcitonin Thyroid Reduces blood calcium, opposing the effects
of parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Cholecystokinin (CCK) Duodenum Facilitates digestion within the small
intestine
Gastrin Stomach Stimulates parietal cells of the stomach to
Duodenum secrete HCl
Pancreas Stimulates parietal cell maturation and
fundal growth
Ghrelin Stomach Stimulates appetite and growth hormone
release
Regulation of food intake, energy
metabolism, modulation of cardiovascular
function
Glucagon Pancreas Increase the blood glucose levels so that the
body has enough energy to function
properly
Supplies glucose to the body by promoting
glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
Growth hormone Anterior pituitary gland Regulates several physiological processes
such as metabolism and growth
Follicle-stimulating hormone Anterior pituitary gland Plays a role in the sexual development and
(FSH) reproduction in both males and females
Insulin Pancreas Regulates how the body uses and stores
glucose and fat
Leptin Hypothalamus Regulates energy homeostasis and
neuroendocrine function
Plays critical role in the adaptive response to
starvation
Luteinizing hormone (LH) Pituitary gland Stimulates the onset of puberty, regulates
menstruation, and contributes to sex drive
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone Pituitary gland Induces the synthesis and release of melanin
(MSH) hormone by melanocytes in the skin
Oxytocin Posterior pituitary gland Functions as a neurotransmitter in the brain
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Parathyroid Controls and regulates the levels of calcium
in the blood and raise their levels when they
are too low
Prolactin Pituitary gland Responsible for lactation, certain breast
tissue development and milk production
Renin Kidneys Regulates blood pressure
Somatostatin Pancreas Regulates gastric acid secretion
Thyroid-stimulating hormone Pituitary gland Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce
(TSH) thyroxine and then triiodothyronine which
stimulates the metabolism of almost every
tissue in the body
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone Hypothalamus Regulates thyroid gland growth and function
(TRH)
Vasopressin [arginine vasopressin Hypothalamus Plays an important role in the water balance
(AVP) or anti-diuretic hormone (osmoregulation) of the body
(ADH)] Maintains the proper osmotic concentration
of the blood plasma
Vasoactive intestinal peptide Immune cells Exerts a wide spectrum of immunological
(VIP) functions that control the homeostasis of
the immune system
You might also like
- CortisoneDocument3 pagesCortisonedb100067No ratings yet
- Steroid CyclesDocument5 pagesSteroid Cycleswatermelontaco75% (4)
- Lyphochek Immunoassay Plus Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: Revision Date 2023-09-25 Indicates Revised InformationDocument2 pagesLyphochek Immunoassay Plus Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: Revision Date 2023-09-25 Indicates Revised InformationclinicalbiochemistryNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Organ Hormone EffectDocument6 pagesEndocrine System: Organ Hormone EffectEmma KowalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NoteDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NoteFumzy AdelakunNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument2 pagesHORMONESDa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Hormone GroupDocument35 pagesHormone GroupNeph VargasNo ratings yet
- Some Endocrine Glands and Their HormonesDocument3 pagesSome Endocrine Glands and Their HormonesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 1 M PhysiologyDocument10 pages1 M PhysiologyLorenz L. Llamas IIINo ratings yet
- Chart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12Document2 pagesChart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12andrewy888No ratings yet
- Sistema EndocrinoDocument31 pagesSistema EndocrinoJhon Alexis M ArgoteNo ratings yet
- Assignment MetabolismDocument10 pagesAssignment MetabolismCherrylyn RaytosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet McatDocument16 pagesReview Sheet McatCal GoNo ratings yet
- Gland Hormone Function Target Organ (Name or Picture) : HypothalamusDocument2 pagesGland Hormone Function Target Organ (Name or Picture) : HypothalamusRoya ImaniNo ratings yet
- Estrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesDocument57 pagesEstrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Term Paper : Isabela State UniversityDocument9 pagesTerm Paper : Isabela State UniversityFlor SagnipNo ratings yet
- Source Hormone Major Action: Adrenal CortexDocument3 pagesSource Hormone Major Action: Adrenal CortexReisha FungoNo ratings yet
- Activity Science - TableDocument4 pagesActivity Science - TableMiranda MirandaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology TableDocument3 pagesEndocrinology TableWilliam PartonNo ratings yet
- TEAS 6 Science by KellyDocument22 pagesTEAS 6 Science by KellyLily GarciaNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrineprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- Endocrine System NotesDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NotesSashaNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Document1 page7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Rudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Async Ina2 Medicalsurgicalnsg Midterm Usls Bsn4 Feb2023 v2 With Vids AsynchDocument156 pagesAsync Ina2 Medicalsurgicalnsg Midterm Usls Bsn4 Feb2023 v2 With Vids AsynchMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Science Inquiry (Chapter 1)Document50 pagesScience Inquiry (Chapter 1)Nancy HastingNo ratings yet
- Ms - Anu Sebastian: B.Pharm M.Pharm Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Nirmala College of Pharmacy Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam, KeralaDocument18 pagesMs - Anu Sebastian: B.Pharm M.Pharm Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Nirmala College of Pharmacy Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam, KeralaZzeba KhanNo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Full Human Physiology Short NotesDocument11 pagesFull Human Physiology Short Notesseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument25 pagesEndocrine System Feedback SystemsEthan Miles VigilanciaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture 5 Hormone ChartDocument2 pagesBiology Lecture 5 Hormone Chartmark_pedersen_6No ratings yet
- Endocrine System NOTESDocument2 pagesEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNo ratings yet
- Hormones BSN-1-mergedDocument24 pagesHormones BSN-1-mergedzahraNo ratings yet
- Assignment IN NutritionDocument5 pagesAssignment IN NutritionJasper SeeNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine and Metabolism SystemDocument8 pagesDiscussion 2.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine and Metabolism SystemAnjar AniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- SGD - DigestiveDocument4 pagesSGD - DigestiveSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ChartDocument1 pageEndocrine ChartKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesaddiekboringNo ratings yet
- 4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionsDocument3 pages4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionssikaboaduaNo ratings yet
- Animal Hormones and Their Functions: Balete, Berida, BorromeoDocument88 pagesAnimal Hormones and Their Functions: Balete, Berida, BorromeoRessabela Juniper FayneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Hormone RegulationDocument20 pagesEndocrine System: Hormone RegulationMark RamosNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and LactationDocument16 pagesPregnancy and LactationsukantaryNo ratings yet
- GLANDSDocument1 pageGLANDSJOEL BALAJADIANo ratings yet
- TICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 15Document14 pagesTICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 15Abram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 2Document13 pagesEndocrine 2Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. SevillenoDocument55 pagesAnatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. Sevillenocoral jade cuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionDocument2 pagesChapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System CBSE Class XI NEETDocument3 pagesEndocrine System CBSE Class XI NEETAngelin JacobNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- NURS 236 Management of Patients With Disorders of The Endocrine SystemDocument78 pagesNURS 236 Management of Patients With Disorders of The Endocrine Systemalmayasaalali66No ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine SystemKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesFrom EverandHealthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccination: From Interesting Agent To The Patient: Anis DaouDocument16 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccination: From Interesting Agent To The Patient: Anis DaouZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Qc2 SuspensionsDocument23 pagesQc2 SuspensionsZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Sterile Preparation-Practice ProblemDocument3 pagesSterile Preparation-Practice ProblemZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Powders Practice ProblemDocument4 pagesPowders Practice ProblemZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy ReviewerDocument6 pagesPharmacognosy ReviewerZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Androgen and AntiandrogenDocument18 pagesAndrogen and AntiandrogenIrma MarianyNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin, ADH Lecture For 2nd Year MBBS by DR Waeem KausarDocument28 pagesOxytocin, ADH Lecture For 2nd Year MBBS by DR Waeem KausarIMDCBiochemNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument3 pagesEndocrine Glandsdan 123No ratings yet
- 1.menstrual CycleDocument7 pages1.menstrual CycleAyenachew AyelikNo ratings yet
- Infographics of Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesInfographics of Endocrine System2086151No ratings yet
- Introduction - Functions of Aldosterone and GlucocorticoidsDocument19 pagesIntroduction - Functions of Aldosterone and GlucocorticoidssabaNo ratings yet
- Secondary Amenorrhea Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageSecondary Amenorrhea Testing AlgorithmpolygoneNo ratings yet
- K13-14 - Fisiologi Hormon Tiroid, Paratiroid, Dan AdrenalDocument62 pagesK13-14 - Fisiologi Hormon Tiroid, Paratiroid, Dan AdrenalMuhammad Ikhram Habib DaulayNo ratings yet
- ROCHE-LIVA Ready Reagent BECHAMN SYSMEXDocument9 pagesROCHE-LIVA Ready Reagent BECHAMN SYSMEXLimon Medikal Sistemleri Limon MedicalNo ratings yet
- MR NITIN PDFDocument2 pagesMR NITIN PDFVenkat Nitin GuttaNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Its Hormones, Hormones of The Pituitary GlandDocument28 pagesHypothalamus and Its Hormones, Hormones of The Pituitary GlandAnirudh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- UT Progestin PDFDocument10 pagesUT Progestin PDFLidyaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology MCQDocument9 pagesEndocrinology MCQWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- HypopituitarismDocument2 pagesHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract HormonesDocument10 pagesGastrointestinal Tract HormonesKevin SangNo ratings yet
- Endocrine: - Hilary MantelDocument33 pagesEndocrine: - Hilary MantelVictoria MorenoNo ratings yet
- Tosoh Bioscience Tosoh Bioscience: CL Aia-Pack ReagentsDocument2 pagesTosoh Bioscience Tosoh Bioscience: CL Aia-Pack ReagentsAleksandar MisicNo ratings yet
- Sistem Endokrin 2 - TugasDocument19 pagesSistem Endokrin 2 - TugasElrisa SalsabillaNo ratings yet
- Hypopituitarism: Group OneDocument22 pagesHypopituitarism: Group OneSAMMYNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Pharmacology Lecturio ReflectionDocument7 pagesReproductive Pharmacology Lecturio ReflectionNathaniel SolisNo ratings yet
- 1st Lec On Endo Physiology by DR RoomiDocument24 pages1st Lec On Endo Physiology by DR RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- AP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021Document11 pagesAP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021daleng subNo ratings yet
- COBAS 6000: E601 Reagent Inventory MONTH/YEAR: - AUGUST 2020Document3 pagesCOBAS 6000: E601 Reagent Inventory MONTH/YEAR: - AUGUST 2020Charmaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- IPF Sanction Registry 20220914Document3 pagesIPF Sanction Registry 20220914Ryan AuliaNo ratings yet
- Drug Acting On Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesDrug Acting On Reproductive SystemRoshann Marcus MamaysonNo ratings yet
- Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical NatureDocument4 pagesGland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Naturernalfas100% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The Endocrine SystemDocument90 pagesDrugs Acting On The Endocrine SystemKATHERINE GRACE JOSENo ratings yet