Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Full Human Physiology Short Notes
Uploaded by
seetharaman8341Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Full Human Physiology Short Notes
Uploaded by
seetharaman8341Copyright:
Available Formats
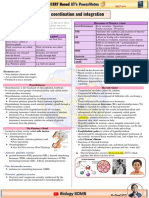
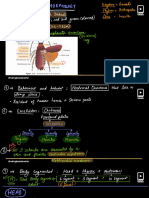
CHEMICAL COORDINATION AND INTEGRATION
1) THE HYPOTHALAMUS 3) Pineal gland
X
A hypothalamic hormone called Gonadotrophin
releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulates the The pineal gland is located on the dorsal side of
pituitary synthesis and release of forebrain. Pineal secretes a hormone called
gonadotrophins. melatonin.
On the other hand, somatostatin from the Melatonin plays a very important role in the
hypothalamus inhibits the release of growth regulation of a 24-hour (diurnal) rhythm of our
hormone from the pituitary body.
The posterior pituitary is under the direct neural
regulation of the hypothalamus
4) THYMUS
2) PITUITARY GLAND • The thymus gland is a lobular structure located
between lungs behind sternum on the ventral side
Aenohypophysis Neurohypophysis of aorta
Oxytocin
Pars Distalis Pars Intermedia Vasopressin • The thymus plays a major role in the
development of the immune system. This gland
secretes the peptide hormones called thymosins.
MSH
Growth hormone (GH), • Thymosins play a major role in the
Prolactin (PRL), differentiation of T-lymphocytes, which provide
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), cell-mediated immunity
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH),
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
5) THYROID 6) PARATHYROID
• The thyroid gland is composed of two lobes which are located • The parathyroid glands secrete a peptide hormone
on either side of the trachea. called parathyroid hormone (PTH). The secretion of
• Both the lobes are interconnected with a thin flap of PTH is regulated by the circulating levels of calcium
connective tissue called isthmus. ions
•Deficiency of iodine in our diet results in hypothyroidism and
enlargement of the thyroid gland, commonly called goitre. • Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases the Ca2+
levels in the blood. PTH acts on bones and
• Hypothyroidism during pregnancy causes defective stimulates the process of bone resorption
development and maturation of the growing baby leading to (dissolution/ demineralisation).
stunted growth (cretinism), mental retardation, low intelligence
quotient, abnormal skin, deaf-mutism, etc • PTH also stimulates reabsorption of Ca2+ by the
renal tubules and increases Ca2+ absorption from
• Exopthalmic goitre is a form of hyperthyroidism, the digested food. It is, thus, clear that PTH is a
characterised by enlargement of the thyroid gland, protrusion
hypercalcemic hormone, i.e., it increases the blood
of the eyeballs, increased basal metabolic rate, and weight loss,
Ca2+ levels
also called Graves’ disease
• Thyroid gland also secretes a protein hormone called
thyrocalcitonin (TCT) which regulates the blood calcium levels
7) ADRENAL GLAND 8) PANCREAS
A) Adrenal medulla – • The two main types of cells in the Islet of Langerhans
are called α-cells and β-cells. The α-cells secrete a
• The adrenal medulla secretes two hormones called adrenaline hormone called glucagon, while the β-cells secrete
or epinephrine and noradrenaline or norepinephrine. insulin.
• These are commonly called as catecholamines. Adrenaline and GLUCAGON INSULIN
noradrenaline are rapidly secreted in response to stress of any Glucagon acts mainly on Insulin acts mainly on
kind and during emergency situations and are called emergency the liver cells (hepatocytes) hepatocytes and
hormones or hormones of Fight or Flight. and stimulates adipocytes (cells of
glycogenolysis resulting in adipose tissue), and
B) Adrenal cortex – an increased blood sugar enhances cellular glucose
The adrenal cortex secretes many hormones, commonly called uptake and utilisation
as corticoids. Hyperglycemic hormone Hypoglycaemic Hormone
• The corticoids, which are involved in carbohydrate This hormone stimulates Insulin also stimulates
metabolism are called glucocorticoids. the process of conversion of glucose to
gluconeogenesis which also glycogen (glycogenesis) in
• In our body, cortisol is the main glucocorticoid. Corticoids,
contributes to the target cells
which regulate the balance of water and electrolytes in our hyperglycemia
body are called mineralocorticoids.
• Prolonged hyperglycemia leads to a complex disorder
• Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid in our body.
called diabetes mellitus which is associated with loss of
glucose through urine and formation of harmful
compounds known as ketone bodies
9) HORMONES OF OTHER ORGANS
Heart Kidney GI tract
Gastrin- stimulates the secretion of HCl & pepsinogen
ANF – decreases blood Erythropoietin- stimulates Secretin- stimulates secretion of water and
cccccccc pressure erythropoiesis bicarbonate ions
CCK - stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzymes
cccccccccccccccccccccccc and bile juice
GIP inhibits gastric secretion and motility
10) MECHANISM OF HORMONE ACTION
Protein hormone Steroid hormone
Insulin, glucagon, pituitary Cortisol, testosterone, estradiol
hormones, hypothalamic and progesterone
hormones, etc.
Water soluble Lipid soluble
Generate secondary messengers Do not generate secondary
(e.g., cyclic AMP, IP3 , Ca++ etc) messengers
after binding to receptors on
plasma membrane
X
X
C
You might also like
- Leifer Chapter 07 Study Guide Answer KeyDocument4 pagesLeifer Chapter 07 Study Guide Answer KeyTyler Finkle89% (18)
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocument5 pagesThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaRichard100% (1)
- All NBDE Questions 2008Document209 pagesAll NBDE Questions 2008Bonnie Seng100% (6)
- Endocrine SystemDocument96 pagesEndocrine SystemSandhya Kakkar100% (3)
- SEMINAR ON SCREENING of NootropicsDocument54 pagesSEMINAR ON SCREENING of Nootropicsrenukashukla8100% (10)
- Chemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration by - Dr. Sunita SaxenaDocument66 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration by - Dr. Sunita SaxenaDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Bio Notes CH 3Document7 pagesClass 11 Bio Notes CH 3VinayNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co - OrdinationDocument21 pagesChemical Co - OrdinationManinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFDocument8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFSaurav SoniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Signals in AnimalsDocument60 pagesChemical Signals in AnimalsAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System CBSE Class XI NEETDocument3 pagesEndocrine System CBSE Class XI NEETAngelin JacobNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co Ordination and Integration - 434dea34 f494 4704 A8c9 6876397e324eDocument53 pagesChemical Co Ordination and Integration - 434dea34 f494 4704 A8c9 6876397e324epcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Class 11 H ChapterDocument7 pagesBiology Notes For Class 11 H Chapterᴘᴀᴘɪᴛʜᴀ ᴋᴀɴɴᴀɴNo ratings yet
- Points To RememberDocument4 pagesPoints To RememberkrNo ratings yet
- BSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemDocument38 pagesBSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemAngelika ButaslacNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine Systemydnic alykPNo ratings yet
- 2.0 HormonesDocument5 pages2.0 HormonesHry WkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnshNo ratings yet
- "Endocrine System": Human Anatomy and Physiology IiDocument74 pages"Endocrine System": Human Anatomy and Physiology IiJethro JasneyNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document3 pages11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument53 pagesIntroduction To EndocrinologyAli ArainNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFDocument12 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration PDFSanjana SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- 22 Chemical Co-OrdinationDocument47 pages22 Chemical Co-OrdinationRachna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Signals in Animals: Egg Larva Pupa AdultDocument29 pagesChemical Signals in Animals: Egg Larva Pupa AdultMENWER ALJOHANINo ratings yet
- Hormones: Hormonal Control Nervous ControlDocument5 pagesHormones: Hormonal Control Nervous Controlvaibhav trivediNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration Handwriten Notes For Neet and JeeDocument5 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration Handwriten Notes For Neet and JeetechnosonicindiaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument26 pagesEndocrine Physiologysam bossaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Parathyroid GlandDocument29 pagesThe Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Parathyroid GlandRaed Abu HamadNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument48 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary GlandMohsin AbbasNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Chemical Control and Integration Final ReviewedDocument78 pagesMind Map Chemical Control and Integration Final Reviewed09 Krishna TrivediNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Sistem EndokrinDocument42 pagesAnatomi Sistem Endokrinnisya rafikoh100% (1)
- A&PII Test 1Document14 pagesA&PII Test 1Alyssa BattcockNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemDocument52 pagesEssentials of Anatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemMarrenSalvadorNo ratings yet
- Ila College of Health: Endocrine PhysiologyDocument40 pagesIla College of Health: Endocrine PhysiologyDaniel DendaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer LecDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer LecNOELLE LAURAINNE TANZONo ratings yet
- ABT Endocrine PPDocument39 pagesABT Endocrine PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 2Document50 pagesEndocrine System 2park jongseongNo ratings yet
- Endo AnaphysioDocument9 pagesEndo AnaphysioShelley Jade MenorNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument9 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAjay JamwalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument34 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationBiju Mylachal100% (9)
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument35 pages10 Endocrine SystemALICIA GOMEZNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument5 pagesEndocrineShem DelolaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument98 pagesEndocrine PhysiologyMohan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Physiology and Pathophysiology (Part 1)Document34 pagesEndocrine System Physiology and Pathophysiology (Part 1)ayaessam392002No ratings yet
- Module 22 HormonesDocument23 pagesModule 22 HormonesCrystal ManguneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System and Excretion WordDocument10 pagesEndocrine System and Excretion WordJoachim “Jayrz” MwambireNo ratings yet
- 09 - Endocrine System - AADocument39 pages09 - Endocrine System - AAMenalqueNo ratings yet
- Endocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationDocument4 pagesEndocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationCatherine Joy delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 CommunicationIII 1Document30 pagesLecture10 CommunicationIII 1Liana Rose MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- OT Endocrine SystemDocument53 pagesOT Endocrine SystemJei CorbesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System GlandsDocument40 pagesEndocrine System Glandsqty9jgkpnzNo ratings yet
- Ch45 EndocrineSystemDocument3 pagesCh45 EndocrineSystemCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CockroachDocument21 pagesCockroachseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Zoology TM Study Materials 2023 - R.padmanabanDocument86 pagesClass 12 Biology Zoology TM Study Materials 2023 - R.padmanabanDaily News100% (2)
- +2 Chap 11 TM ANUDocument28 pages+2 Chap 11 TM ANUseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Test-2 - 07 JAN., - FinalDocument31 pagesTest-2 - 07 JAN., - Finalseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Exception 20231120Document18 pagesException 20231120Lily AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Exception 20231120Document18 pagesException 20231120Lily AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Exception 20231120Document18 pagesException 20231120Lily AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Organic Problem EM-1Document10 pagesOrganic Problem EM-1seetharaman8341100% (1)
- 24012022070009 (2)Document832 pages24012022070009 (2)swetha poongodiNo ratings yet
- 12maths V2 Important 5marks (EM)Document14 pages12maths V2 Important 5marks (EM)seetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Revision Test Time Table - 01022023 - 12 TH & 11 TH - 230203 - 164057Document3 pagesRevision Test Time Table - 01022023 - 12 TH & 11 TH - 230203 - 164057seetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Chemistry TM Special GuideDocument42 pagesChemistry TM Special Guideseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- +2 Slow Learner Questions (EM) - 2023 PDFDocument2 pages+2 Slow Learner Questions (EM) - 2023 PDFUdhayaNo ratings yet
- Palani-Ram 12th Physics Important Questions-2023Document6 pagesPalani-Ram 12th Physics Important Questions-2023seetharaman8341No ratings yet
- TN Lockdown GuidelinesDocument2 pagesTN Lockdown Guidelinesseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- 12th Maths MidtermDocument2 pages12th Maths Midtermseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Zoology TM Study Materials 2023 - R.padmanabanDocument86 pagesClass 12 Biology Zoology TM Study Materials 2023 - R.padmanabanDaily News100% (2)
- 12 TH TAMILDocument45 pages12 TH TAMILseetharaman8341100% (1)
- Eosinophilic DermatosesDocument15 pagesEosinophilic DermatosesmikelNo ratings yet
- OBAT Life Saving FixDocument2 pagesOBAT Life Saving FixDevi0% (1)
- Nrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: Zithromax, Zmax, Z-PakDocument2 pagesNrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: Zithromax, Zmax, Z-PakJanet Sheldon50% (2)
- 223 NotesDocument36 pages223 NotesNing BalderasNo ratings yet
- Choosing AEDs in Special SituationsDocument88 pagesChoosing AEDs in Special SituationsTristanNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Dental SedationDocument209 pagesA Guide To Dental SedationZilan MengütayNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Mscs in Pharmaceutical SciencesDocument77 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Mscs in Pharmaceutical SciencesObada Sibai100% (1)
- Drug Study (Decocon A)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Decocon A)MerielLouiseAnneVillamilNo ratings yet
- Beta Blockers Cheat Sheet: Happy Nursing!Document1 pageBeta Blockers Cheat Sheet: Happy Nursing!GloryJaneNo ratings yet
- Cintias AMC QUICK REVIEWDocument217 pagesCintias AMC QUICK REVIEWFlavin AmbroseNo ratings yet
- Cholera Kits 2021 Content 20.02.2024 Rev LabDocument37 pagesCholera Kits 2021 Content 20.02.2024 Rev LabElom Kokou ASSIGBLEY100% (1)
- WAJA CHP.5 Chemicals For ConsumersDocument20 pagesWAJA CHP.5 Chemicals For ConsumersSafwan Mazlan100% (2)
- Hyperuricemia XXXX XXXXX XxjeuneDocument32 pagesHyperuricemia XXXX XXXXX XxjeuneOziq Juga ReMa-eNo ratings yet
- Sub: Application For The Post of Executive, International BusinessDocument4 pagesSub: Application For The Post of Executive, International BusinessGaFf ArNo ratings yet
- Generic List - MOH PHCs-March-2023Document11 pagesGeneric List - MOH PHCs-March-2023drabdulrabbNo ratings yet
- Assignment:: Course Title Course Code:Bph-115Document14 pagesAssignment:: Course Title Course Code:Bph-115toushif ahmedNo ratings yet
- Export Data Obat 4 Satuan 20230103074944Document409 pagesExport Data Obat 4 Satuan 20230103074944adrianus andriNo ratings yet
- Clinical Treatment of Rabbits Experimentally Infected With Staphylococcus Aureus Using Different AntibioticsDocument4 pagesClinical Treatment of Rabbits Experimentally Infected With Staphylococcus Aureus Using Different Antibioticsarum pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Abc FSN PDFDocument6 pagesAbc FSN PDFRachel SinambanNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument3 pagesSulfonamidesMahdi DiabNo ratings yet
- Combivent Rimup Eng Aug 2018Document3 pagesCombivent Rimup Eng Aug 2018Xhexania LJWNo ratings yet
- Managing Pulmonary EmbolismDocument9 pagesManaging Pulmonary EmbolismBolívar IseaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cannabis Intoxication Case SeriesDocument8 pages2 - Cannabis Intoxication Case SeriesPhelipe PessanhaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Diabetes MelitusDocument7 pagesJurnal Diabetes MelitusNova RosalinaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Pain Management in Adults and Children: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pages4.2 Pain Management in Adults and Children: Learning ObjectivesINNOCENT KHULIWANo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii. Treatment Modalities of CancerDocument12 pagesChapter Iii. Treatment Modalities of CancerA. Lizette PabloNo ratings yet