Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System CBSE Class XI NEET
Uploaded by
Angelin Jacob0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views3 pageschemical control and coordination, endocrine system, CBSE class 11. NEET
The file is about different endocrine glands in the human body, the hormones secreted by each gland, and the functions of each hormone secreted. Everything is in a tabular form.!! Enjoy reading
Original Title
Endocrine system CBSE Class XI NEET
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchemical control and coordination, endocrine system, CBSE class 11. NEET
The file is about different endocrine glands in the human body, the hormones secreted by each gland, and the functions of each hormone secreted. Everything is in a tabular form.!! Enjoy reading
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views3 pagesEndocrine System CBSE Class XI NEET
Uploaded by
Angelin Jacobchemical control and coordination, endocrine system, CBSE class 11. NEET
The file is about different endocrine glands in the human body, the hormones secreted by each gland, and the functions of each hormone secreted. Everything is in a tabular form.!! Enjoy reading
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
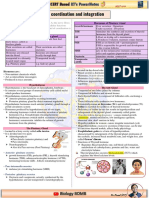
S.
No ENDOCRINE GLANDS HORMONES SECRETED FUNCTIONS
1. Hypothalamus • Releasing Hormones: Eg. GnRH Regulate the synthesis and secretion
• Inhibiting hormone: Eg. of Pituitary hormones.
Somatosatin
2. Pituitary gland • Growth Hormone (GH) Over-secretion and low secretion
leads to gigantism and dwarfism
respectively.
• Prolactin (PRL) Regulates the growth of the
mammary glands and formation of
milk.
• Thyroid stimulating hormone Stimulates the synthesis and
(TSH) secretion of thyroid hormones from
the thyroid gland.
• Adrenocorticotrophic hormone Stimulates the synthesis and
(ACTH) secretion of steroid hormones called
glucocorticoids from the adrenal
cortex.
• Luteinizing hormone (LH) Stimulate gonadal activity. Also
known as Gonadotrophins.
Stimulates the synthesis and
secretion of androgens. LH and
androgens regulate
spermatogenesis.
• Follicle stimulating hormone Induces ovulation of fully mature
(FSH) follicles and maintains the corpus
luetum. Stimulates growth and
development of the ovarian follicles
in females.
• Melanocyte stimulating Acts on melanocytes and regulates
hormone (MSH) pigmentation of the skin.
• Oxytocin Acts on smooth muscles and
stimulates contraction. Stimulates a
vigorous contraction of uterus at the
time of child birth and milk ejection
from the mammary gland.
• Vasopressin or Anti-diuretic Stimulates reabsorption of water
hormone (ADH) and electrolytes by the distal
tubules. Reduces loss of water
through urine (diuresis)
3. Pineal Gland • Melatonin Regulation of a 24-hour (diurnal)
rhythm of our body. Influences
metabolism, pigmentation,
menstrual cycle and defense
capacity.
4. Thyroid Gland • Tetraiodothyronine or thyroxine Regulation of the basal metabolic
(T4) rate. Support the process of RBC
• Triiodothyronine (T3) formation. Control metabolism of
carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Maintenance of water and
electrolyte balance.
• Thyrocalcitonin (TCT) Regulates the blood calcium levels.
5. Parathyroid Gland • Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Increases Ca+2 levels in blood.
Stimulates the process of bone
resorption.
6. Thymus • Thymosins Differentiation of T-lymphocytes,
which provide cell-mediated
immunity. Promote production of
antibodies.
7. Adrenal Gland • Adrenal medulla- adrenaline, Increases alertness, pupillary
noradrenaline dilation, piloerection, sweating etc.
Increases the heartbeat, the
strength of heart contraction and
the rate of respiration. Stimulate
breakdown of glycogen, lipids and
proteins.
• Adrenal cortex- Corticoids Stimulate gluconeogenesis, lipolysis
and proteolysis. Inhibit cellular
uptake and utilization of amino
acids. Maintains cardio-vascular
system as well as kidney functions.
Stimulates RBC production.
Aldosterone helps in the
maintenance of electrolytes, body
fluid volume, osmotic pressure and
blood pressure.
8. Pancreas • Glucagon Acts on liver cells (hepatocytes) and
stimulates glycogenolysis resulting
in an increased blood sugar.
Reduces cellular glucose uptake and
utilization.
• Insulin Regulation of glucose homeostasis.
Acts mainly on hepatocytes and
adipocytes. Enhances cellular
glucose uptake and utilization.
Stimulates conversion of glucose to
glycogen
9. Testis • Androgens Regulate the development,
maturation and functions of the
male accessory organs. Influence
the male sexual behavior.
Stimulatory role in the process of
spermatogenesis. Produces anabolic
effects on protein and carbohydrate
metabolism.
10. Ovaries • Estrogen Stimulation of growth and activities
of female secondary sex organs,
development of ovarian follicles,
appearance of female secondary sex
characters. Regulate female sexual
behavior.
• Progesterone Supports pregnancy. Acts on
mammary glands and stimulates the
formation of alveoli and milk
secretion.
11. Atrium • Atrial natriuretic factor Dilation of blood vessels. Reduction
of blood pressure.
12. Juxtaglomerular cells • Erythropoietin Erythropoiesis (formation of RBC)
13. Gastro-intestinal • Gastrin Acts on gastric glands and stimulate
tract the secretion of hydrochloric acid
and pepsinogen.
• Secretin Acts on exocrine pancreas and
stimulates the secretion of water
and bicarbonate ions.
• Cholecystokinin (CCK) Acts on both pancreas and gall
bladder and stimulates the secretion
of pancreatic enzymes and bile juice
respectively.
• Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) Inhibits gastric secretion and
motility.
You might also like
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Chemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: An Overview of Key Hormones and Their FunctionsDocument38 pagesThe Endocrine System: An Overview of Key Hormones and Their FunctionsAngelika ButaslacNo ratings yet
- Full Human Physiology Short NotesDocument11 pagesFull Human Physiology Short Notesseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Chemical Control and Integration Final ReviewedDocument78 pagesMind Map Chemical Control and Integration Final Reviewed09 Krishna TrivediNo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Padlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesPadlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Lect 4Document78 pagesEndocrine Lect 4Wajiha IffatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Part 1 and 2Document51 pagesEndocrine System Part 1 and 2Wajiha IffatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration by - Dr. Sunita SaxenaDocument66 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration by - Dr. Sunita SaxenaDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Endo AnaphysioDocument9 pagesEndo AnaphysioShelley Jade MenorNo ratings yet
- Hormones Secreted by Anterior and Posterior PituitaryDocument12 pagesHormones Secreted by Anterior and Posterior Pituitaryfarwafurqan1No ratings yet
- Chart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12Document2 pagesChart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12andrewy888No ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument4 pagesEndocrineSaumyaNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lecture Activity 10 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecture Activity 10 Endocrine SystemJohnNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Class 11 H ChapterDocument7 pagesBiology Notes For Class 11 H Chapterᴘᴀᴘɪᴛʜᴀ ᴋᴀɴɴᴀɴNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Hormone Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesHormone Coordination and IntegrationVinayNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument5 pagesEndocrineShem DelolaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesEndocrine Systemlee bon hukNo ratings yet
- Animal HormonesDocument16 pagesAnimal HormonesMaria Theresa HerreroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument14 pagesEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- Endocrinology: Glands, Hormones, FunctionsDocument22 pagesEndocrinology: Glands, Hormones, FunctionscimyNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- 22 Chemical Co-OrdinationDocument47 pages22 Chemical Co-OrdinationRachna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3Document4 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Human physiology lecture on endocrine system coordinationDocument12 pagesHuman physiology lecture on endocrine system coordinationPoorva NaikNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument25 pagesEndocrine System Feedback SystemsEthan Miles VigilanciaNo ratings yet
- Science Inquiry (Chapter 1)Document50 pagesScience Inquiry (Chapter 1)Nancy HastingNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: A Guide to Hormones and Glandular RegulationDocument19 pagesThe Endocrine System: A Guide to Hormones and Glandular RegulationJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- HormoneDocument18 pagesHormoneWorld now ??No ratings yet
- TICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 15Document14 pagesTICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 15Abram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Signals in AnimalsDocument60 pagesChemical Signals in AnimalsAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands Group 1Document15 pagesEndocrine Glands Group 110 - St. Hyacint Keziah Shane R. NazNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument34 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationBiju Mylachal100% (9)
- General Concept of Endocrine Glands and HormonesDocument51 pagesGeneral Concept of Endocrine Glands and HormonesTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIDocument9 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- 2.0 HormonesDocument5 pages2.0 HormonesHry WkNo ratings yet
- Points To RememberDocument4 pagesPoints To RememberkrNo ratings yet
- 22. Chemical Co Ordination and Integration_434dea34 f494 4704 a8c9 6876397e324eDocument53 pages22. Chemical Co Ordination and Integration_434dea34 f494 4704 a8c9 6876397e324epcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- The Endocrine System and Its Key HormonesDocument10 pagesThe Endocrine System and Its Key HormonesjoanneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System or Glandular SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine System or Glandular SystemchelzeacnayanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy SemiDocument14 pagesAnaphy SemipersonalimouNo ratings yet
- Big Picture F: MetalanguageDocument13 pagesBig Picture F: Metalanguagejohanna deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Science 9: Quarter 3: Role of HormonesDocument2 pagesScience 9: Quarter 3: Role of Hormonescrizlie enotNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRIONOLOGYDocument15 pagesENDOCRIONOLOGYmoepiNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument8 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYshaairatogleNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine and Metabolism SystemDocument8 pagesDiscussion 2.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine and Metabolism SystemAnjar AniNo ratings yet
- ABT Endocrine PPDocument39 pagesABT Endocrine PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System RevDocument3 pagesEndocrine System RevWena Grace NonanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - NURSINGDocument3 pagesEndocrine System - NURSINGFrancesca GraingerNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1 - 16 - 07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument32 pages10 Biology 1 - 16 - 07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- Female Repro AnatomyDocument19 pagesFemale Repro Anatomycyber secNo ratings yet
- Abortifacient - and - Antioxidant - Activities - of - A MarinaDocument16 pagesAbortifacient - and - Antioxidant - Activities - of - A MarinaDanang RaharjoNo ratings yet
- Efektifitas Senam Diabetes Terhadap Kadar Gula Darah Pada Pasien Diabetes Mellitus Di LamonganDocument6 pagesEfektifitas Senam Diabetes Terhadap Kadar Gula Darah Pada Pasien Diabetes Mellitus Di Lamonganfitrianingsih d4 kepNo ratings yet
- Definition - Cushing's Syndrome Is The Combination of Symptoms and SignsDocument4 pagesDefinition - Cushing's Syndrome Is The Combination of Symptoms and SignsSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Intercollegiate MRCS SyllabusDocument88 pagesIntercollegiate MRCS Syllabuskelly_ann23No ratings yet
- Ovulation TestingDocument5 pagesOvulation Testingpriya vermaNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Count and Biochemistry Panel ResultsDocument8 pagesComplete Blood Count and Biochemistry Panel Resultsgunjan pratapNo ratings yet
- 03 Na CB GuidelinesDocument152 pages03 Na CB GuidelinesPutri Zahra ArdiyanitaNo ratings yet
- Puberty Changes ExplainedDocument7 pagesPuberty Changes ExplainedLena Beth Tapawan Yap50% (4)
- Module 3Document20 pagesModule 3VENTURA, ANNIE M.No ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DDocument17 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DMekuriya BeregaNo ratings yet
- (John Andrews) Endocrinology and Iridology PDFDocument136 pages(John Andrews) Endocrinology and Iridology PDFpeter100% (1)
- Diabetes Cheat Sheet Copyright BNDocument2 pagesDiabetes Cheat Sheet Copyright BNJeshan Yanong BeltranNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic Cats With Long Acting InsulinDocument16 pagesManagement of Diabetic Cats With Long Acting Insulindia_dianneNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - Diabetes in Children2JDocument90 pagesUnit 8 - Diabetes in Children2Jkassaye tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Discuss Di Erence Between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and DM Type 2Document3 pagesDiscuss Di Erence Between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and DM Type 2DHANNILLIE JHAIRA NU�EZNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Endocrine, Pathology - Tumors - Endocrine Tumors PDFDocument7 pagesOsmosis Endocrine, Pathology - Tumors - Endocrine Tumors PDFYusril Marhaen0% (1)
- 2003, Vol.32, Issues 2, Consultative EndocrinologyDocument210 pages2003, Vol.32, Issues 2, Consultative Endocrinologyomar ramirezNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary HormonesDocument46 pagesAnterior Pituitary Hormonespramod bhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Reproductive SystemDocument180 pagesPhysiology of Reproductive Systemnirilib0% (1)
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument5 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Andrology BullDocument33 pagesAndrology Bulldahiphale1No ratings yet
- Anna's family health history genogramDocument1 pageAnna's family health history genogramAnnaMaeGacutanMarantanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Pediatric Reference Levels of Ft3, Ft4 and TSH Measured With Eclusys KitsDocument6 pagesDetermination of Pediatric Reference Levels of Ft3, Ft4 and TSH Measured With Eclusys KitsIan ChoongNo ratings yet
- Infertility IDocument36 pagesInfertility Idr_asaleh100% (1)
- A Computer Generated Number: Prepared By: Tawiah Bernice EbbiDocument2 pagesA Computer Generated Number: Prepared By: Tawiah Bernice EbbiAfia Tawiah100% (1)
- MudrasDocument30 pagesMudrasJorge HegelNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Medulla Hormones and the Fight or Flight ResponseDocument17 pagesAdrenal Medulla Hormones and the Fight or Flight ResponsehamidNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia - Schermerhorn, ThomasDocument2 pagesHypoglycemia - Schermerhorn, ThomasJuanMartínezNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Pre PDFDocument370 pagesThyroid Pre PDFLidijaNo ratings yet