Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrinology Table
Uploaded by
William Parton0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesEndocrinology cheat sheet for HUBS191.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEndocrinology cheat sheet for HUBS191.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesEndocrinology Table
Uploaded by
William PartonEndocrinology cheat sheet for HUBS191.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
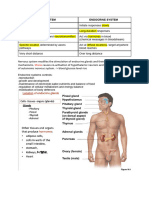
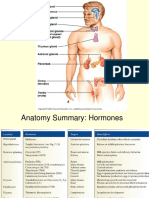
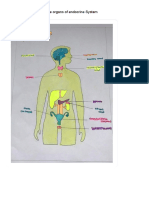
Place
Pancreas Pituitary Gland (Posterior Lobe)
Stimulus ↑blood glucose ↓blood glucose Child birth Low water potential
concentration concentration of the blood
Metabolic Fed state: Fasting state:
State anabolic catabolic
metabolism metabolism
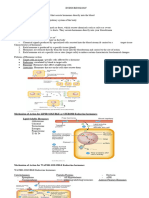
Hormones Pancreatic islet Pancreatic islet Posterior pituitary ADH (antidiuretic
beta cells secrete alpha cells secrete experiences an hormone) is released
insulin into glucagon increased AP frequency from the axon
bloodstream Alpha cells are the to release oxytocin— endings having been
sensor and control from the axon endings made in the
centre of neurons that connect hypothalamus (done
the hypothalamus to the by neural
posterior lobe. communication.
Hormones are made in
the hypothalamus.
Effects Liver cells: Liver cells: Stimulates contraction Stimulates kidneys to
Prevents glucose ↑glycogenolysis of uterine muscles reabsorb water (they
outputs so↑ net (breakdown of during child birth conserve water when
glucose uptake glycogen) (positive feedback) the body
—> glycogen and ↑glucogenesis dehydrates).
fat synthesis. (glucose synthesis) Stimulates milk release
Muscle and ↑ketone synthesis in breast feeding (milk
adipose cells: ejection reflex)
↑glucose uptake
—> fat synthesis,
amino acid
uptake, glycogen
and protein
synthesis
Response ↓blood glucose ↑blood glucose Positive feedback loop Negative feedback
concentration concentration and loop
reduces stimulus ↑blood ketones
concentration
reduce stimulus
Other –Only hormone –Glucagon is a –Peptide hormone –Peptide hormone
that lowers the peptide hormone
blood glucose –Target cells have
concentration membrane
–Insulin is a receptors
peptide hormone –Growth hormone,
–Target cells adrenaline and
have membrane cortisol can↑blood
receptors glucose
concentration
Place Liver (anterior pituitary Thyroid glands (anterior Parathyroid glands
hormone) pituitary hormone)
Stimulus Neural input: somatostatin External and internal stimuli ↓blood calcium
neurons & GHRH neurons lead to neural CNS input. concentration
Hormones Somatostatin neurons Hypothalamus secretes TRH Parathyroid gland secretes
stimulate the release of GH- (thyrotropin-releasing PTH
IH (growth hormone hormone) into the blood
inhibiting which…
hormone/somatostatin),
GHRH neurons stimulate Stimulates the secretion of
the release of GHRH TSH (thyroid-stimulating
(growth hormone releasing hormone) in the anterior
hormone). Both into the pituitary…
anterior pituitary gland
binding to a membrane Stimulates secretion of
receptor of a specific cell thyroid hormones into the
type. Leads to… blood (T3 (active), T4) from
thyroid glands.
Release of growth hormone
in the anterior pituitary Also releases calcitonin which
gland. is involved in calcium
homeostasis but rarely
Stimulates release of produced naturally.
somatomedin C (IGF-1) in
the liver.
Effects Liver cells (direct): Metabolism: Bone:
Stimulates gluconeogensis ↑BMR by ↑synthesis and ↑bone breakdown —> ↑
(short term) activity of Na+/K+ pump calcium release into blood
Muscle cells (direct): ↑body heat production (↑ (bone Ca2+ resorption)
Stimulates protein synthesis oxygen consumption and ATP
(long term) and ↓glucose hydrolysis) Kidneys:
uptake (short term) Fatty acid oxidation ↑calcium reabsorption —>
Adipose cells (direct): Increases proteolysis ↓urinary excretion of
↑increases triglyceride Enhances insulin depend calcium
breakdown (short term) entry of glucose into cells
Indirect effects: ↑gluconeogenesis and Vitamin D —> calcitriol
Somatomedin C promotes glycogenolysis. ↑ calcium absorption from
cell division (long term) and Other: food in intestine
so promotes growth. Stimulates growth
Contributes to normal
alertness and reflexes.
Response Somatomedin C (IGF-1) in T3 and T4 secretion inhibits ↑blood calcium
the liver. TRH and TSH. concentration reduces
Negative feedback: stimulus
Stimulation of GH-IH.
Limit GH-RH release.
Other GH has long-term effect on Fasting state: catabolic PTH, calcitriol and calcitonin
growth and short-term metabolism. are involved in calcium
effects on metabolism. T3 and T4 travel bound to a homeostasis.
Anterior pituitary carrier protein (thyroid-
connected to hypothalamus binding globulin, TBG).
by blood vessels.
Place Adrenal Glands (Medulla) Adrenal Glands (Cortex) (anterior
pituitary hormone)
Stimulus Stress Stress Non-stress
neural inputs
Hormones Sympathetic preganglionic fibre Hypothalamus secretes CRH
propagates an AP and ACh binds (corticotropin releasing
to receptors in adrenal medulla hormone)…
secretory cells. Secretes
adrenaline (80%) and Anterior pituitary secretes ACTH
noradrenaline (20%) into the (adrenocorticotropic hormone)…
blood stream, which takes the
hormones to the sympathetic Adrenal cortex synthesises and
target/effector cell. secretes cortisol. Binds to
receptors in cytoplasm of target
cells and activates gene
transcription to produce the
above responses.
Effects Skeletal muscle & liver: Muscle:
↑breakdown of glycogen to ↓glucose uptake
glucose (glycogenolysis) ↑protein breakdown
Fat: (gluconeogenesis in liver so need
↑breakdown of fat to fatty acids building blocks)
Fat:
↑fat breakdown
↓glucose uptake
Liver:
↑glucose synthesis
Other:
Helps one to cope with stress
Anti inflammatory (long-term)
Essential for maintaining normal
blood pressure
Response Makes fuel more readily available Cortisol secretion reduces
to cells. No negative feedback for secretion of CRH and ACTH.
stress response. Negative feedback. No negative
feedback for stress response.
Other Water soluble (amino acid Catabolic metabolism.
derivative) Increases:
Cell membrane receptor so uses a Blood glucose levels
secondary messenger pathway Blood pressure
Fast Heart rate
Amplification of cellular response Antiinflammatory actions.
Supplements actions of Heart and blood vessel tone
sympathetic nervous system (contraction)
Catabolic
You might also like
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)From EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNo ratings yet
- Major endocrine glands and some of their hormonesDocument2 pagesMajor endocrine glands and some of their hormonesDa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Full Human Physiology Short NotesDocument11 pagesFull Human Physiology Short Notesseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Endocrine 2Document13 pagesEndocrine 2Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- endorine systemDocument27 pagesendorine systemBenjamin YickNo ratings yet
- Article and Table - Peptide HormonesDocument3 pagesArticle and Table - Peptide HormonesZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Document12 pagesWeek 1 - Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Jeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- 3.3-3.4 Coordination and ResponseDocument65 pages3.3-3.4 Coordination and ResponseathirahNo ratings yet
- Hormone regulation and the hypothalamus-pituitary axisDocument16 pagesHormone regulation and the hypothalamus-pituitary axisCal GoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Hormone RegulationDocument20 pagesEndocrine System: Hormone RegulationMark RamosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Endokrin S1 Non FKDocument68 pagesEndokrin S1 Non FKRirin DwiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Organ Hormone EffectDocument6 pagesEndocrine System: Organ Hormone EffectEmma KowalNo ratings yet
- 2009 John Wiley Sons Inc The Endocrine SystemDocument23 pages2009 John Wiley Sons Inc The Endocrine SystemnobodyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument8 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYshaairatogleNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Hormones and The Coordinating System of AnimalsDocument48 pagesHormones and The Coordinating System of AnimalsElaine MontealtoNo ratings yet
- Discussion Notes AnaphyDocument36 pagesDiscussion Notes Anaphyjade tanNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageNursing CS Endocrine SystemLia neNo ratings yet
- Chapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionDocument2 pagesChapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Regulates Animal PhysiologyDocument9 pagesEndocrine System Regulates Animal PhysiologyFlor SagnipNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Endocrine SystemnewDocument47 pagesEndocrine SystemnewKana KioshiNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NotesSashaNo ratings yet
- 7sistem EndokrinDocument72 pages7sistem EndokrinAlfianaNo ratings yet
- Chart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12Document2 pagesChart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12andrewy888No ratings yet
- Reproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument41 pagesReproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryabdulNo ratings yet
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Document8 pagesOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Jhason John J. CabigonNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesdenis_adigamovNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture 5 Hormone ChartDocument2 pagesBiology Lecture 5 Hormone Chartmark_pedersen_6No ratings yet
- Index CardsDocument6 pagesIndex CardsShanley SalemNo ratings yet
- Padlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesPadlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- Endocrine System NOTESDocument2 pagesEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System OverviewDocument39 pagesEndocrine System OverviewMenalqueNo ratings yet
- Chemical Signals in AnimalsDocument60 pagesChemical Signals in AnimalsAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PresentationDocument231 pagesEndocrine System PresentationKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument32 pagesEndocrine PhysiologyAziem ShazwanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Chapter SummaryDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Chapter SummaryShiny ChenNo ratings yet
- Growth Hormone (GH) All Over:: Hormone Origin Which 2 Messenger Target TissueDocument55 pagesGrowth Hormone (GH) All Over:: Hormone Origin Which 2 Messenger Target TissueJoe EpsteinNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument30 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYYou QiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System CBSE Class XI NEETDocument3 pagesEndocrine System CBSE Class XI NEETAngelin JacobNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Final TermDocument5 pagesAnaphy Final TermZoe DorothyNo ratings yet
- Hormones GlandsDocument1 pageHormones GlandsCHEN GAONo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument26 pagesEndocrine Physiologysam bossaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of the Pituitary GlandDocument10 pagesDiseases of the Pituitary Glandbalkrishna.narshaiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands and Their Major HormonesDocument11 pagesEndocrine Glands and Their Major HormonesAnisa JamitoNo ratings yet
- Draw and Label The Organs of Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesDraw and Label The Organs of Endocrine SystemShainaChescaEvansNo ratings yet
- 15.09.2020 - Hormones of Protein NatureDocument40 pages15.09.2020 - Hormones of Protein NatureFaiz AkramNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co - OrdinationDocument21 pagesChemical Co - OrdinationManinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Activity Science - TableDocument4 pagesActivity Science - TableMiranda MirandaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Lesson 13Document13 pagesGeneral Biology Lesson 13GUCOR, LOVELY SHANE C.No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocument144 pagesEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Physiology Handouts Topics (42-64)Document67 pagesPhysiology Handouts Topics (42-64)bc200411046No ratings yet
- Introduction To Nerve Conduction StudiesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Nerve Conduction StudiesIngrid GomesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Psychology CourseDocument21 pagesFundamentals of Psychology CourseSalaguste Angelica MarieNo ratings yet
- Spinal AnesthesiaDocument7 pagesSpinal AnesthesiaHamdan afzalNo ratings yet
- dll-NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument8 pagesdll-NERVOUS SYSTEMLeny SantosNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain ManagementDocument31 pagesAcute Pain ManagementTherese Jane TiradorNo ratings yet
- Diffuser RecipesDocument11 pagesDiffuser RecipesAgus AzconaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breathing and Respiratory Control During SleepDocument8 pagesPhysiology of Breathing and Respiratory Control During SleepAchmad Hafidz BaraqbahNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid: Dr. Anupriya JDocument33 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid: Dr. Anupriya JVivek PatelNo ratings yet
- Universitas Tadulako, Palu, Sulawesi TengahDocument8 pagesUniversitas Tadulako, Palu, Sulawesi TengahMuhammad FauzanNo ratings yet
- Craniofacial PainDocument12 pagesCraniofacial PainJyothsna YelpulaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Exam for MS SignsDocument2 pagesClinical Exam for MS SignsssNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters &: Their Mode of ActionDocument45 pagesNeurotransmitters &: Their Mode of ActionAshani AaroraNo ratings yet
- The Physiology Excitable TissuesDocument71 pagesThe Physiology Excitable TissuesSalih ÇayırNo ratings yet
- Complex Systems Model of Fatigue: Integrative Homoeostatic Control of Peripheral Physiological Systems During Exercise in HumansDocument11 pagesComplex Systems Model of Fatigue: Integrative Homoeostatic Control of Peripheral Physiological Systems During Exercise in Humansok okNo ratings yet
- Fall Final Exam Concepts ReviewDocument9 pagesFall Final Exam Concepts ReviewColeton GNo ratings yet
- Science g10 LM q3Document131 pagesScience g10 LM q3Seiza MwaNo ratings yet
- Wedeen2012-Grid Structure of Brain PathwaysDocument9 pagesWedeen2012-Grid Structure of Brain Pathwaysiulia andreeaNo ratings yet
- Gut Feelings - The Emerging Biology of Gut-Brain Communication, Emeran A. MayerDocument15 pagesGut Feelings - The Emerging Biology of Gut-Brain Communication, Emeran A. Mayeraltemio100% (1)
- Module Chapter 1Document41 pagesModule Chapter 1Miz MiaNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Essentials of Anatomy Physiology 8th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Essentials of Anatomy Physiology 8th Edition PDF Scribdjune.thompson131100% (38)
- Overview of The Central Amygdala Role in Feeding BehaviourDocument23 pagesOverview of The Central Amygdala Role in Feeding Behaviourjefferson HiagoNo ratings yet
- Lozada, Adrian - CV 03.03.2023Document7 pagesLozada, Adrian - CV 03.03.2023Katrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Slow Deep BreathingDocument17 pagesSlow Deep BreathingpluigiaNo ratings yet
- Assessment - U19LA002 Emotional Intelligence & Stress Management May 2022Document16 pagesAssessment - U19LA002 Emotional Intelligence & Stress Management May 2022DheenadayalanNo ratings yet
- NTC The Pulse TestDocument2 pagesNTC The Pulse TestEvaNo ratings yet
- Case Report - SAHDocument41 pagesCase Report - SAHNeni NirmalaNo ratings yet
- A Nervous TripDocument12 pagesA Nervous TripMark Owen BaldoNo ratings yet
- Polyvagal Informed Therapy Master Class Modules 15Document27 pagesPolyvagal Informed Therapy Master Class Modules 15sorintichy100% (1)
- A Fully Endoscopic Occipital Transtentorial Approach To The Pineal RegionDocument11 pagesA Fully Endoscopic Occipital Transtentorial Approach To The Pineal Regionjoao alfredoNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Townsend Test BankDocument15 pagesEssentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Townsend Test Bankkimberlymorriscntsoqmyjw100% (6)