Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phần 2.1.2
Uploaded by
chuotchuot100720010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesPhần 2.1.2
Uploaded by
chuotchuot10072001Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
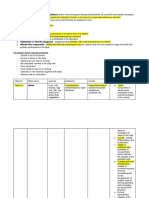
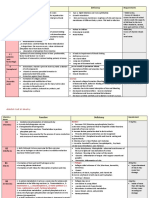
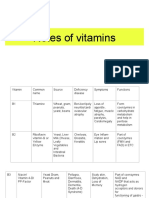
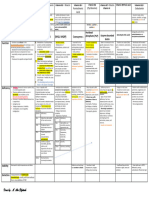
2.1.
2: Some common vitamins
named by named according main effect Vitamin deficiency
symbols to chemical disease
properties
A Axerophtol - plays a role in vision dry eyes, corneal
- keep the epithelium intact hypertrophy
D Calicferol Hypercalcemia, increased intestinal Rickets, soft bones
absorption of calcium and
phosphorus. Essential for bone
mineralization.
E Tocopherol Is the most important antioxidant. has reproductive
an effect on the reproductive system disorders
K Antihemorragias Participate in the blood clotting blood clotting
process through the role of disorders
synthesizing protrombin,
proconvertin, forming factors IX and
X.
B1 Thiamine Coenzyme decarboxylates a-ketone -Beriberi
acids. -
-Synthesis of acetyl choline Neuroinflammatory
disease
B2 Riboflavin Is the component that creates FMN - corneal disease
and FAD configuration - dermatitis
B3 Nicotinamide Plays a constitutive role in the - Vitamin PP
coenzyme NAD deficiency disease
B6 Pyridoxine Coenzyme of transaminase enzyme, -Epileptic disease
decarboxylation enzyme of tyrosine,
glutamic and some other amino acids.
Bc (M) Folicx acid - Participate in coenzyme transporting - Giant red blood
formyl and formimino groups. cells
- Plays an important role in cell - Anemia
growth and reproduction.
B5 Pentothenic acid - Structure of coenzyme A
- Transport of acyl radicals during -T/C Burning-Feet
fatty acid synthesis (ACP). - Gastritis, enteritis,
diarrhea, diarrhea,
hair loss...
B12 Cynocobalamin -Plays a role in stimulating
hematopoiesis Pernicious anemia
-Coenzyme isomerizes, reduces
formyl group, transfers methyl group.
C Ascorbic acid Participates in oxidation-reduction Vitamin C
processes, collagen synthesis, deficiency disease
tyrosine oxidation, adrenal steroid
metabolism.
You might also like
- Vitamins Ther 201Document2 pagesVitamins Ther 201Jenward HostalleroNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument3 pagesVITAMINSPCHS-REYES, Reyza Jane BNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument1 pageVitaminsmido_20067581No ratings yet
- Vitamins - It Must Be A Vital Organic Substance That Is Not An Energy-Producing Carbohydrate, Fat or Protein and Usually NecessaryDocument9 pagesVitamins - It Must Be A Vital Organic Substance That Is Not An Energy-Producing Carbohydrate, Fat or Protein and Usually NecessaryGia Espinosa OcbeñaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin's Name Function Deficiency Requirements: Retinal RetinolDocument4 pagesVitamin's Name Function Deficiency Requirements: Retinal RetinolAsem AlmeerabiNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A Carotenoids Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Vitamin CDocument2 pagesVitamin A Carotenoids Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Vitamin CNote MakerNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and VitaminsDocument3 pagesAmino Acids and Vitaminscathlynjoy.marsamoloNo ratings yet
- Notes of VitaminsDocument8 pagesNotes of VitaminsEllyNo ratings yet
- Vitamins NotesDocument8 pagesVitamins NotesEllyNo ratings yet
- (Characteristics, Classifications, Functions, and Updates) : Jessa C. Cabinan Jean Q. Calubayan Joyce E. TelloroDocument28 pages(Characteristics, Classifications, Functions, and Updates) : Jessa C. Cabinan Jean Q. Calubayan Joyce E. TelloroIvan Jhon AnamNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Vitamins: Vitamin-D (Calciferol)Document3 pagesShort Notes On Vitamins: Vitamin-D (Calciferol)Aastha WankhadeNo ratings yet
- Quick Nursing NotesDocument2 pagesQuick Nursing Notesgenelyn100% (1)
- Vitamin StudentDocument63 pagesVitamin Studentlethigialinhlop11a4No ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument2 pagesWater Soluble Vitaminsnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- BIO CHEM SeminarDocument28 pagesBIO CHEM SeminarBello Taofik InumidunNo ratings yet
- 4 VitaminsDocument2 pages4 VitaminsJessa MayNo ratings yet
- Biochem Vitamins MineralsabsbbzDocument9 pagesBiochem Vitamins MineralsabsbbzYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- B-Complex VitaminsDocument1 pageB-Complex VitaminsIbrahim JamalNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDADocument4 pagesVitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDAAndy J. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vitamins TableDocument1 pageVitamins TableMicah Lou CalambaNo ratings yet
- Vit CDocument31 pagesVit CsatyadbaNo ratings yet
- Vit CDocument31 pagesVit CsatyadbaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument36 pagesVitamins & MineralsMarisha Christin TarihoranNo ratings yet
- Jashore University of Science and Technology: Presented by Presented ToDocument10 pagesJashore University of Science and Technology: Presented by Presented ToMohona Rahman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ramos - Activity VitaminsDocument7 pagesRamos - Activity VitaminsChristian Vonne B. RamosNo ratings yet
- Riazuddin (MS 210931)Document10 pagesRiazuddin (MS 210931)Mohona Rahman KhanNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Name Molecular FunctionDocument1 pageVitamin Name Molecular Functionajayterdal8471No ratings yet
- Tricks To Remember Vitamins and Their Deficiency 31Document5 pagesTricks To Remember Vitamins and Their Deficiency 31Cruel SatyaNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument5 pagesBiochemistrySer ReyesNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument17 pagesVitaminsnicholaschungu24No ratings yet
- Tricks To Remember Vitamins and Their Deficiency 31 1 76Document5 pagesTricks To Remember Vitamins and Their Deficiency 31 1 76Pussy catNo ratings yet
- Abdon MelodyDocument4 pagesAbdon MelodyChirs Nicole CaguitlaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM, Vit. & Blood (Reviewer)Document8 pagesBIOCHEM, Vit. & Blood (Reviewer)michaelamontanielNo ratings yet
- Nutri PrelimDocument1 pageNutri PrelimShekinah MaeNo ratings yet
- Summary On Vitamins: Vitamins Aka Category FunctionsDocument2 pagesSummary On Vitamins: Vitamins Aka Category FunctionsnivedbNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument2 pagesVitamins and MineralsMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Vitamin E & K-BdsDocument50 pagesVitamin E & K-BdsIsaiah JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Vitamin AsDocument4 pagesVitamin AsDiego Ramirez SiancasNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument5 pagesNoteSheena Mae SasanNo ratings yet
- BV300Document39 pagesBV300rajeevunnao100% (1)
- Vitamin統整表Document1 pageVitamin統整表黃河洛No ratings yet
- Vitamins N MSC 2019Document105 pagesVitamins N MSC 2019Shasha Reverse AgingNo ratings yet
- Table For Exam 2Document2 pagesTable For Exam 2raybuaNo ratings yet
- Printable Lecture On Enzymes and Vitamins Main 1Document37 pagesPrintable Lecture On Enzymes and Vitamins Main 1Izzy ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and VitaminDocument70 pagesNutrition and VitaminTob JurNo ratings yet
- Coenzima Función de La Coenzima Vitamina Relacionada Función de La Vitamina Fuente de La Vitamina DeficienciaDocument3 pagesCoenzima Función de La Coenzima Vitamina Relacionada Función de La Vitamina Fuente de La Vitamina DeficienciaCristian PulidoNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Oligoelements Abstract Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezDocument5 pagesVitamins and Oligoelements Abstract Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezCristhian LozanoNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Lec.1: Dr. NahidaDocument11 pagesVitamins: Lec.1: Dr. NahidaxxxdarknessNo ratings yet
- SGD Aa PDFDocument11 pagesSGD Aa PDFyasiraNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Metabolism Intro - BC I 2565-SheetDocument43 pagesVitamin and Metabolism Intro - BC I 2565-SheetWirawit SIWONGTRAKULNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: FGLM Success Is Not Final Failure Is Not FatalDocument16 pagesPediatrics: FGLM Success Is Not Final Failure Is Not FatalkrishNo ratings yet
- Vitamin For Final MCQDocument14 pagesVitamin For Final MCQSajia Abedin 1821432649No ratings yet
- Macrominerals Sources Deficiency Toxicity FunctionsDocument3 pagesMacrominerals Sources Deficiency Toxicity FunctionsGia Espinosa OcbeñaNo ratings yet
- Vitmin and MineralDocument1 pageVitmin and Mineralkero R.habibNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of VitaminsDocument64 pagesBiochemistry of VitaminsConrado CatimbangNo ratings yet
- Compiled By: C. Andres Bs Pharm 4ADocument4 pagesCompiled By: C. Andres Bs Pharm 4AOdyNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument10 pagesVITAMINSkerynne dyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Vitamins 2020Document99 pagesLecture Vitamins 2020Lawal Bello DanchadiNo ratings yet
- Bài Writing TestDocument1 pageBài Writing Testchuotchuot10072001No ratings yet
- Av Thi NóiDocument5 pagesAv Thi Nóichuotchuot10072001No ratings yet
- The Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument1 pageThe Peripheral Nervous Systemchuotchuot10072001No ratings yet
- Writing Test Bài MẫuDocument1 pageWriting Test Bài Mẫuchuotchuot10072001No ratings yet
- Q2-PPT-PE10-Module1.2 (Running As Exercise)Document30 pagesQ2-PPT-PE10-Module1.2 (Running As Exercise)Gericho MarianoNo ratings yet
- LH 11 180 190 220 230 270 280 390 400 Breaker Safety & Operating InstructionsDocument304 pagesLH 11 180 190 220 230 270 280 390 400 Breaker Safety & Operating InstructionshadensandorNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review AnswerDocument6 pagesFinal Exam Review AnswerJosh ClickNo ratings yet
- Epsom Salt ClassDocument7 pagesEpsom Salt ClassSofia marisa fernandesNo ratings yet
- Early Production ContainmentDocument2 pagesEarly Production Containmenttravi9580% (5)
- Upstream Marine Standard IBU ChevronDocument52 pagesUpstream Marine Standard IBU ChevronAndrew Hendy Indrakusuma50% (2)
- PETRODETAILSDocument2 pagesPETRODETAILSAlexanderNo ratings yet
- 5 - DystociaDocument43 pages5 - DystociaMara Medina - BorleoNo ratings yet
- MTCP Pamir Sector 2021 OCT07 R1.0Document19 pagesMTCP Pamir Sector 2021 OCT07 R1.0Derya KadikashNo ratings yet
- Whsms ManualDocument22 pagesWhsms ManualSayed AbbasNo ratings yet
- HSEQ-HQ-06-08-00 Transportation StandardDocument15 pagesHSEQ-HQ-06-08-00 Transportation StandardAHMED AMIRANo ratings yet
- Auto Fuel Policy Vision 2025Document294 pagesAuto Fuel Policy Vision 2025Rejith RajanNo ratings yet
- (D E Watt) Quantities For Generalized Dosimetry of (BookFi)Document388 pages(D E Watt) Quantities For Generalized Dosimetry of (BookFi)Νικος ΜατσαφλοκοςNo ratings yet
- Project Planning Template - Castillo JiselleDocument7 pagesProject Planning Template - Castillo Jiselleapi-692396370No ratings yet
- Roofing ActivitiesDocument2 pagesRoofing ActivitiesArnold Roy Coballes ManaloNo ratings yet
- LOTO-100 CompactoDocument3 pagesLOTO-100 CompactoRyan KaneNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin: CautionDocument8 pagesService Bulletin: CautiondfmolinaNo ratings yet
- PENC N BONDIDocument5 pagesPENC N BONDIYLND100% (1)
- Sf1 Cinderella JuneDocument60 pagesSf1 Cinderella JuneLaLa FullerNo ratings yet
- Handouts First Aid in MasonryDocument5 pagesHandouts First Aid in MasonryIvyNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Test - Q3 English 9Document6 pagesQuarterly Test - Q3 English 9Rodrigl BaiganNo ratings yet
- Toyota/Lexus U140E/F, U240E, U241E: Click On Part Numbers For Product Details or VisitDocument1 pageToyota/Lexus U140E/F, U240E, U241E: Click On Part Numbers For Product Details or Visitvipper king2012No ratings yet
- 2015 Pri XLDocument2 pages2015 Pri XLTimmyJuriNo ratings yet
- Classroom and Lab Area - Job Roles Wise2Document117 pagesClassroom and Lab Area - Job Roles Wise2Param ShikshaNo ratings yet
- Safety Health & Environment MethodologyDocument14 pagesSafety Health & Environment MethodologymusengemNo ratings yet
- (V) Disaster Management by Vaishali MamDocument7 pages(V) Disaster Management by Vaishali Mamnvn.2130No ratings yet
- People. Passion. Possibilities.: .30 .11 Thread Relief As RequiredDocument40 pagesPeople. Passion. Possibilities.: .30 .11 Thread Relief As RequiredFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Power of The Mind 2010 PDFDocument32 pagesPower of The Mind 2010 PDFTijana Morača Aćimović100% (3)
- C1 - C7 General Requirements For Equipment ErectionDocument24 pagesC1 - C7 General Requirements For Equipment ErectionephNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics A320Document101 pagesHydraulics A320KamalVirk100% (6)