Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HRM - 1st Week - Lecture Notes
Uploaded by
Prof. Jomar MariquitCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HRM - 1st Week - Lecture Notes
Uploaded by
Prof. Jomar MariquitCopyright:
Available Formats
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT BBC 1109
1ST WEEK
LECTURE HANDOUTS
PART I. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING
What Is HRM?
Human resource management (HRM) is the process of employing people, training them,
compensating them, developing policies relating to them, and developing strategies to retain
them. As a field, HRM has undergone many changes over the last twenty years, giving it an even
more important role in today’s organizations. In the past, HRM meant processing payroll,
sending birthday gifts to employees, arranging company outings, and making sure forms were
filled out correctly—in other words, more of an administrative role rather than a strategic role
crucial to the success of the organization. Jack Welch, former CEO of General Electric and
management guru, sums up the new role of HRM: “Get out of the parties and birthdays and
enrollment forms.… Remember, HR is important in good times, HR is defined in hard times”
(Frasch, et. al., 2010).
The Role of HRM
Keep in mind that many functions of HRM are also tasks other department managers perform,
which is what makes this information important, despite the career path taken. Most experts
agree on seven main roles that HRM plays in organizations. These are described in the following
sections.
1. Staffing
2. Development of Workplace Policies
3. Compensation and Benefits Administration
4. Retention
5. Training and Development
6. Dealing with Laws Affecting Employment
7. Worker Protection
8. Communication
Human Resource Planning
Human resource planning (HRP) describes an ongoing, data-driven process in which a company
systematically plans for the future in terms of human resources to ensure that available jobs are
suited with appropriately skilled employees. It identifies key HR initiatives for the time period
ahead that will help the organization achieve its strategic goals and maintain its competitive
advantage without staffing shortages or excesses.
Importance of human resource planning
Organizations must be able to adapt their human capital to sustain the continuous shifts in
technology, local and global economics, product innovation, and culture. Human resource
planning is integral to maximizing a well-equipped workforce, and it offers other advantages that
assist in accomplishing your organization’s mission.
Here are some of the objectives HRP can achieve:
Foreseeing and being prepared for cultural shifts and evolutions of the business environment.
Anticipating and identifying job and skill changes to meet labor demands.
Hiring the right talent on a timely basis to support expanded, decreased, or diversified
organizational plans.
Adapting hiring techniques and benefits to source and hire the best candidates.
Ensuring your workforce has optimal technical and soft skills to increase productivity.
Developing career paths for employees to increase their satisfaction and value.
Building and maintaining effective key HR processes. (Recruitment and selection, training
and development, compensation and benefits planning, performance management.)
Making good use of your HR budget.
Maintaining compliance with company policies and government regulations.
5 Steps In The Human Resource Planning Process
The actual process of human resource planning involves five general phases. Listed below is a
summary of each step to help you navigate the process:
1. Analyze organizational objectives and plans
2. Evaluate the current state of your workforce and uncover gaps
There are tools that can help you make a road map for this step of the HR planning process.
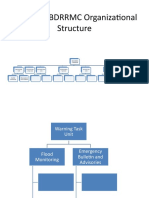
An organizational chart is a visual description of a company’s staff structure that designates
roles and reporting relationships. Below you can see an example of an HR organization chart in a
mid-sized organization
A replacement chart is a diagram of potential candidates and their readiness to step into certain
roles upon employee departures.
A skills inventory looks at the availability and preparedness of current employees to move into
either lateral or higher-level roles. It allows you to identify which employees have the ability to
take on new positions as the needs of the company change. It also helps you uncover any skills
deficiencies.
3. Forecast future HR requirements
4. Develop and implement a plan
5. Monitor, review, and reassess your plan
You might also like
- Recuritment and Selction ProcessDocument127 pagesRecuritment and Selction ProcessVelmuruganKNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Chapter 1-3Document28 pagesHuman Resource Chapter 1-3Danae CaballeroNo ratings yet
- PWC M&A Integration - Change ManagementDocument10 pagesPWC M&A Integration - Change ManagementShuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HR and HR DepartmentDocument8 pagesIntroduction To HR and HR DepartmentNira SinhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 1 HR PlanningDocument11 pagesUnit 2 1 HR PlanningAsfawosen DingamaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument17 pagesHuman Resource ManagementOanaa ComanNo ratings yet
- Difference Between HRD and HRMDocument8 pagesDifference Between HRD and HRMSarath SNo ratings yet
- Abstract - HR ManagementDocument6 pagesAbstract - HR Managementfinal yearNo ratings yet
- Syeda Sabiiha Ahmed CHAPTER 2 After CorrectionDocument28 pagesSyeda Sabiiha Ahmed CHAPTER 2 After CorrectionFahimul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Strategic HR Case Study: Bounceback for InfosysDocument12 pagesStrategic HR Case Study: Bounceback for Infosysabhishek0% (1)
- Chapter 2, Leadership For TQMDocument32 pagesChapter 2, Leadership For TQMRameez Ramzan Ali88% (24)
- Human Resource ManagementDocument218 pagesHuman Resource ManagementJithin SajanNo ratings yet
- Rule 105 Special ProceedingDocument3 pagesRule 105 Special ProceedingTiger KneeNo ratings yet
- Mannu Kumar Singh - BBA - TalentServeDocument72 pagesMannu Kumar Singh - BBA - TalentServeMr XNo ratings yet
- HR NotesDocument26 pagesHR NotesIsha DhumalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Literature ReviewDocument39 pagesChapter 2 Literature ReviewArmanlover ArmanNo ratings yet
- HR Metrics and Outsourcing: Factors to ConsiderDocument35 pagesHR Metrics and Outsourcing: Factors to ConsiderUma Devi AnanthNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Resource Management 11th Edition Rue Byars and Ibrahim 0078112796 9780078112799Document36 pagesTest Bank For Human Resource Management 11th Edition Rue Byars and Ibrahim 0078112796 9780078112799TerryRandolphdsec100% (24)
- Steps in The Human Resource Planning ProcessDocument7 pagesSteps in The Human Resource Planning ProcessMaleeha AkbarNo ratings yet
- HRM CH-5Document13 pagesHRM CH-5MD. AL HossainNo ratings yet
- Task 2Document6 pagesTask 2Fatima ShakeelNo ratings yet
- NOTES - What Is Human Resource PlanningDocument3 pagesNOTES - What Is Human Resource PlanningMae DicdiquinNo ratings yet
- All Lesson 1-4Document69 pagesAll Lesson 1-4Trisha LawasNo ratings yet
- HRM2L2 HumanResPlanningDocument15 pagesHRM2L2 HumanResPlanningGloria Compound Youth OrganizationNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Prepared By: Teresa DimaculanganDocument8 pagesHuman Resource Management: Prepared By: Teresa Dimaculangansoyoung kimNo ratings yet
- Kashif AssignmentDocument4 pagesKashif AssignmentMuzzamil JanjuaNo ratings yet
- HR Planning VaretaDocument7 pagesHR Planning VaretaRam MathurNo ratings yet
- 08_EMILIANO-ZIDRICK-B_BSBA-MM-1ST-YEAR_HUMAN-RESOURCES-PLANNING-HRP-_20240322_134255_0000Document15 pages08_EMILIANO-ZIDRICK-B_BSBA-MM-1ST-YEAR_HUMAN-RESOURCES-PLANNING-HRP-_20240322_134255_0000ROMAR ANGELO ALONZONo ratings yet
- HR Package - Final Version (2.1)Document19 pagesHR Package - Final Version (2.1)Thanh MaiNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument26 pagesHuman Resource PlanningSushant GaikwadNo ratings yet
- HRM's Role in Business SuccessDocument13 pagesHRM's Role in Business SuccessTaarikNo ratings yet
- Personnel ManagementDocument5 pagesPersonnel ManagementRuzhy MufazirNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management (HRM) Is The Practice of Recruiting, Hiring, Deploying andDocument11 pagesHuman Resource Management (HRM) Is The Practice of Recruiting, Hiring, Deploying andAkash BdNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management BBA 1st YearDocument172 pagesHuman Resource Management BBA 1st Yearཟླ་བ་ ཆོས་སྒྲོན་་No ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument2 pagesHuman Resource PlanningSahil BaliNo ratings yet
- Project HRMDocument7 pagesProject HRMJava Spring Part 1No ratings yet
- The Impact of Human Resource Planning on Organizational PerformanceDocument13 pagesThe Impact of Human Resource Planning on Organizational Performancemusab100% (3)
- Chapter 1 HRDocument36 pagesChapter 1 HRVaishnavi SomaniNo ratings yet
- HRM PlaningDocument6 pagesHRM PlaningkrishnakumaribalakNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management (1) OneDocument148 pagesHuman Resource Management (1) OneMuhammad Anas KhanNo ratings yet
- HRP Ensures Right People for Right JobsDocument10 pagesHRP Ensures Right People for Right JobsTasnim RoufNo ratings yet
- (Topic) : Human Resource Function and PracticeDocument35 pages(Topic) : Human Resource Function and PracticeRachel CoutinhoNo ratings yet
- The Seven HR Basics: 1. Recruitment & SelectionDocument3 pagesThe Seven HR Basics: 1. Recruitment & Selectionphuong trangNo ratings yet
- What is HRP? Human Resource Planning ExplainedDocument5 pagesWhat is HRP? Human Resource Planning ExplainedSEEMA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Human Resource Planning (HRP)Document3 pagesHuman Resource Planning (HRP)Maria LeeNo ratings yet
- 2 Project HRM IntroductionDocument7 pages2 Project HRM IntroductionJava Spring Part 10% (1)
- Definition of Human Resource ManagementDocument29 pagesDefinition of Human Resource ManagementQamar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument15 pagesHuman Resource Planningabhishek chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument11 pagesHuman Resource PlanningJudy Achieng KuruNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument10 pagesHRMRajanNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument4 pagesHuman Resource ManagementcathyNo ratings yet
- HR Foundations: Functions and ApproachesDocument109 pagesHR Foundations: Functions and ApproachesPaula kelly100% (2)
- CH 1 HRMDocument12 pagesCH 1 HRMagragamidegree collegeNo ratings yet
- HRM - 1st WeekDocument27 pagesHRM - 1st WeekProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Importance of Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesUnderstanding the Importance of Human Resource ManagementSri HariNo ratings yet
- Manu BhaiDocument26 pagesManu Bhaijaygautam1710No ratings yet
- Future of Work: StrategyDocument10 pagesFuture of Work: StrategyMOHAMED BARHOMANo ratings yet
- Study On HR Operations ManagementDocument15 pagesStudy On HR Operations ManagementNavin Kumar100% (1)
- HRM PapDocument17 pagesHRM PapdpkjerryNo ratings yet
- Human ResourcesDocument7 pagesHuman Resourcesvidhya arunNo ratings yet
- Human Resource (HR)Document14 pagesHuman Resource (HR)Absar Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 IntroductionDocument37 pagesUnit 1 IntroductionAnonymous aXFUF6No ratings yet
- Emerging Issues in HRMDocument13 pagesEmerging Issues in HRMjemalne55120% (1)
- ACTIVITY #1 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT ANALYSISDocument6 pagesACTIVITY #1 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT ANALYSISRivera, Lord Angel AlagaseNo ratings yet
- HRM Google NotesDocument10 pagesHRM Google NotesDevansh JainNo ratings yet
- HRM - 2nd Week - Lecture HandoutDocument14 pagesHRM - 2nd Week - Lecture HandoutProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- HRM - 4th Week - Lecture HandoutDocument16 pagesHRM - 4th Week - Lecture HandoutProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- BDRRMC PresentationDocument6 pagesBDRRMC PresentationProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- The Republic Act 10121Document31 pagesThe Republic Act 10121Prof. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- Proposed BDRRMC Organizational StructureDocument9 pagesProposed BDRRMC Organizational StructureProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- DRR Basic ConceptsDocument11 pagesDRR Basic ConceptsProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- Internal Memo: To: Through: Through: From: Date: SubjectDocument2 pagesInternal Memo: To: Through: Through: From: Date: SubjectDapo OrimoloyeNo ratings yet
- Laureen Odendo Mba 2018Document84 pagesLaureen Odendo Mba 2018Maria HauleNo ratings yet
- Sources of Recruitment External Vs Internal NotesDocument13 pagesSources of Recruitment External Vs Internal NotesAvijit DindaNo ratings yet
- Managers & Managing: Efficiency, Effectiveness, Tasks & SkillsDocument2 pagesManagers & Managing: Efficiency, Effectiveness, Tasks & SkillsDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Importance of Management: It Helps in Achieving Group Goals - It Arranges The Factors ofDocument10 pagesImportance of Management: It Helps in Achieving Group Goals - It Arranges The Factors ofBaqar MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Competency Mapping of Sales Staff in the Automotive IndustryDocument29 pagesCompetency Mapping of Sales Staff in the Automotive IndustryEkta Tractor Agency KhetasaraiNo ratings yet
- Topic Two Theories and History of ManagementDocument10 pagesTopic Two Theories and History of ManagementEli KagothoNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Development Thesis PDFDocument5 pagesHuman Resource Development Thesis PDFstacyjohnsonreno100% (2)
- HURIS Corporate Profile: Your Partner for Organizational EffectivenessDocument9 pagesHURIS Corporate Profile: Your Partner for Organizational EffectivenessNgọc HânNo ratings yet
- Acme HR BrochureDocument10 pagesAcme HR BrochureacmeNo ratings yet
- Unilever Case Study: Staff Training and DevelopmentDocument24 pagesUnilever Case Study: Staff Training and DevelopmentThảo NhiNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - Human ResourcesDocument74 pagesUnit 8 - Human ResourcesJoyNo ratings yet
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017 From ISO/IEC 17025:2005 LMS Transition Instructions / ChecklistDocument42 pagesISO/IEC 17025:2017 From ISO/IEC 17025:2005 LMS Transition Instructions / ChecklistGlobal Certification RegistrarNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Q1 Challengesto HRMDocument8 pagesModule 10 Q1 Challengesto HRMprabodhNo ratings yet
- HR-insights On NetflixDocument2 pagesHR-insights On NetflixAngel LocsinNo ratings yet
- HRM Case No. 7Document3 pagesHRM Case No. 7Movie 2UNo ratings yet
- Nature and Significance of Management: Unit-1 Worksheet-1Document74 pagesNature and Significance of Management: Unit-1 Worksheet-1GINNI BHULLARNo ratings yet
- Functions of CommunicationDocument1 pageFunctions of CommunicationMohitNo ratings yet
- HRM in Service Sector Management (Latest)Document8 pagesHRM in Service Sector Management (Latest)Devansh1 Bhatt2No ratings yet
- HRM - 1stDocument15 pagesHRM - 1stAnandhu AravindNo ratings yet
- HRM SEM III (2016, 2017, 2019) Question Papers St. Xavier's College, RanchiDocument4 pagesHRM SEM III (2016, 2017, 2019) Question Papers St. Xavier's College, RanchishivangiNo ratings yet
- TYBMS HRM GlobalPerspectiveDocument5 pagesTYBMS HRM GlobalPerspectiveSalil SarvagodNo ratings yet
- HR Planning Term PaperDocument28 pagesHR Planning Term PaperMd Zahirul IslamNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit 4 Part 3Document17 pagesHRM Unit 4 Part 3Ruhani AroraNo ratings yet