Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orias DS Isoflurane
Uploaded by
Kyla OriasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orias DS Isoflurane
Uploaded by
Kyla OriasCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Student Nurse: Orias, Maria Kyla Joy B.
Date: May 26, 2023
Level/Block/Group:3BSN6 Hospital/Area: Operating Room Clinical instructor: Sir Jesus Cadaoas Rabe
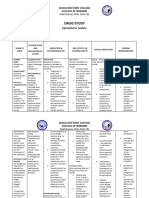
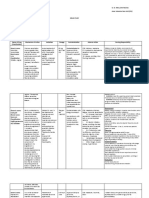
MECHANISM OF
NAME OF DRUG CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
ACTION
Isoflurane is a potent - Known or suspected CV: Ventricular, nodal, or General: Malignant hyperthermia Used with caution in patients with coronary
GENERIC NAME
volatile, halogenated genetic susceptibility atrial arrhythmia artery disease.
general inhalational to malignant CV: Torsades de pointes,
anesthetic that alters hyperthermia. perioperative hyperkalemia Monitor blood pressure and temperature to
Isoflurane the activity of neuronal - History of confirmed GI: Nausea, vomiting, resulting in cardiac arrhythmias detect residual hypotension and the
ion channels, hepatitis due to retching possibility of malignant hyperthermia.
specifically the fast halogenated GI: Hepatic dysfunction
BRAND NAME synaptic inhalational General: Chills ataxia, Must be given with a licensed
neurotransmitter anesthetic or asthenia, fatigue anesthesiologist
receptors. It may unexplained
Forane, Terrell depress myocardial moderate to severe Labs: Increase WBC count,
contractility, lower hepatic dysfunction. increased blood glucose,
blood pressure by increased serum creatinine,
CLASSIFICATION decreasing systemic decreased BUN.
vascular resistance, and
reduce sympathetic
nervous activity.
General Anesthetics
INDICATION
Induction and maintenance of
general anesthesia
DOSAGE AND
FREQUENCY
Inhalation induction: initial
0.5% v/v with oxygen or
oxygen and nitrous oxide
increase to 1.5 – 3 % v/v
Maintenance dose: 1- 2.5% v/v
with oxygen only.
You might also like
- Orias DS SevorfluraneDocument3 pagesOrias DS SevorfluraneKyla OriasNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therape Utic Actions Indica Tion Adverse Reaction Contraindi Cation Nursing Consider Ation Generic Name: Acetylcholine ChlorideDocument8 pagesDrug Name Therape Utic Actions Indica Tion Adverse Reaction Contraindi Cation Nursing Consider Ation Generic Name: Acetylcholine ChlorideFredie O HadjimudinNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-1st BatchDocument27 pagesDRUG STUDY-1st BatchCanny CańasNo ratings yet
- Gaborno Drug StudyDocument5 pagesGaborno Drug StudyShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- Isoflurane ThiopentalDocument13 pagesIsoflurane ThiopentalMr rawr100% (1)
- Drug Study orDocument5 pagesDrug Study orRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine DSDocument2 pagesHydralazine DSAntoniette Jane Martin PathayNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument1 pageAspirinJoshua KellyNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument1 pageAspirinJoshua KellyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name of Patient: Mrs. T. P. Diagnosis: Perineal Relaxation, Uterine Prolapse, With RectoceleDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Name of Patient: Mrs. T. P. Diagnosis: Perineal Relaxation, Uterine Prolapse, With RectoceleKristina Garces HuertasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Beta-Lactmase-Producing Strains of S. Aureus, or by Piperacillin Tazobactam SusceptibleDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Beta-Lactmase-Producing Strains of S. Aureus, or by Piperacillin Tazobactam SusceptibleKristine Young83% (6)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyadagayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Far Eastern UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Far Eastern UniversityChoy DacanayNo ratings yet
- TAMBALDocument4 pagesTAMBALVianca Kate MarquezNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY Update (Table 3)Document5 pagesDRUGSTUDY Update (Table 3)SONY MANDAPNo ratings yet
- Drug LordsDocument25 pagesDrug LordsGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument6 pagesDrug Study FinalJade HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- Naprex Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNaprex Drug StudyAngelica shane NavarroNo ratings yet
- Canine dx-1Document23 pagesCanine dx-1fereshte hszNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication /contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument10 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication /contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJohnmark PascuaNo ratings yet
- Patient'S Name: Chris Jhon Ruz Bed No: 155 DX: PneumoniaDocument5 pagesPatient'S Name: Chris Jhon Ruz Bed No: 155 DX: Pneumoniatanene08No ratings yet
- TelmisartanDocument2 pagesTelmisartanRea LynNo ratings yet
- David's Drug Guide Tenth Edition Judith Hopfer April Hazard Vallerand pg.558-560Document10 pagesDavid's Drug Guide Tenth Edition Judith Hopfer April Hazard Vallerand pg.558-560Justene PeñamoraNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting BPDocument13 pagesDrugs Affecting BPFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Epinephrine, Lidocaine, Diazepam)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Epinephrine, Lidocaine, Diazepam)Abigaile Operiano100% (2)
- Tolleno Drug Study LONGDocument9 pagesTolleno Drug Study LONGHannah TollenoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyDocument2 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacologypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Levofloxac in (Levox)Document2 pagesLevofloxac in (Levox)jbespirituNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Review: Liver Dysfunction in Critical IllnessDocument17 pagesReview: Liver Dysfunction in Critical IllnessRoger Ludeña SalazarNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, OpioidsDocument3 pagesAntidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, Opioidskaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument5 pagesDrug NameSushiBaLNo ratings yet
- 50 Emergency DrugsDocument70 pages50 Emergency DrugsderizNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyNorjana Hadji WahabNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY PheumoniaDocument5 pagesCASE STUDY PheumoniaEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study-CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Synergy DrugDocument4 pagesSynergy DrugUDDE-E MARISABELNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: ER DrugsDocument5 pagesDrug Study: ER Drugsmaeca101No ratings yet
- Group-M9-A-Case-Study-1 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesGroup-M9-A-Case-Study-1 - Drug StudyRen Mark CanlasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument6 pagesDrug Study FinalAraw GabiNo ratings yet
- B. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsDocument12 pagesB. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsSienaNo ratings yet
- Beriso Drug StudyDocument5 pagesBeriso Drug StudyKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument27 pagesDrug StudyChan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument10 pagesEmergency DrugsEmMan80% (5)
- Drug Study: Anti-InfectiveDocument8 pagesDrug Study: Anti-InfectiveTri ShaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesStephen VillegasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: The Health Sciences CenterDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: The Health Sciences CenterAna Luisa Conejos ConeseNo ratings yet
- De Jesus, Lovelle Grace E. (Drug Study)Document7 pagesDe Jesus, Lovelle Grace E. (Drug Study)LOVELLE GRACE DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Annual Report of NHRC (2016-17)Document240 pagesAnnual Report of NHRC (2016-17)Shruti Nagvanshi100% (1)
- Fluoride Menace in OrissaDocument83 pagesFluoride Menace in OrissaProfessor PrabhatNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-11081506 (Ridhi) 11081524 (Khushboo) 11081560 (Shiny) 11081542 (Sakshi)Document17 pagesPresented By:-11081506 (Ridhi) 11081524 (Khushboo) 11081560 (Shiny) 11081542 (Sakshi)Akanksha KapoorNo ratings yet
- Effect of Safety Training On Risk ToleranceDocument22 pagesEffect of Safety Training On Risk Tolerancechamal IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Uganda Dental Association Journal November 2019Document36 pagesUganda Dental Association Journal November 2019Trevor T KwagalaNo ratings yet
- Tre Mad OdesDocument31 pagesTre Mad OdesmoosNo ratings yet
- Effective Leadership Towards The Star Rating Evaluation of Malaysian Seni Gayung Fatani Malaysia Organization PSGFMDocument10 pagesEffective Leadership Towards The Star Rating Evaluation of Malaysian Seni Gayung Fatani Malaysia Organization PSGFMabishekj274No ratings yet
- Individual CounselingDocument7 pagesIndividual CounselingCarla Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Analysis of GRIHA Certified BuildingsDocument26 pagesAnalysis of GRIHA Certified BuildingsAnshul Sharma100% (7)
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards: Ankur 2018-19Document10 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards: Ankur 2018-19Pubg GamerNo ratings yet
- SUPW SrimukhDocument15 pagesSUPW SrimukhsrimukhsaiNo ratings yet
- Im9 2002 PDFDocument89 pagesIm9 2002 PDFV1QT0RNo ratings yet
- Final Sheet MotalityDocument69 pagesFinal Sheet MotalityAshima GabgotraNo ratings yet
- Nexus Magazine AprilMay 2019Document100 pagesNexus Magazine AprilMay 2019Izzy100% (2)
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Industrial HygieneDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Industrial Hygienesiti zubaidahNo ratings yet
- Bertam ProfileDocument8 pagesBertam ProfilesadassanNo ratings yet
- Analytical ExpositionDocument10 pagesAnalytical ExpositionR E HandhitaNo ratings yet
- Attitude of EMPLOYEES in Terms of Compliance of Health and SafetyDocument6 pagesAttitude of EMPLOYEES in Terms of Compliance of Health and SafetyJanice KimNo ratings yet
- Playlist AssignmentDocument7 pagesPlaylist AssignmentTimothy Matthew JohnstoneNo ratings yet
- Bias, Confounding and Fallacies in EpidemiologyDocument68 pagesBias, Confounding and Fallacies in EpidemiologyShakir KhanNo ratings yet
- Bed Making LectureDocument13 pagesBed Making LectureYnaffit Alteza Untal67% (3)
- Vince Gironda 8x8 RoutineDocument10 pagesVince Gironda 8x8 RoutineCLAVDIVS0% (2)
- Draft HHP Informed Consent FormDocument7 pagesDraft HHP Informed Consent Formapi-589951233No ratings yet
- Sacrococcygeal TeratomaDocument21 pagesSacrococcygeal TeratomaEm VelascoNo ratings yet
- Valsalyacare Withprocuts....Document7 pagesValsalyacare Withprocuts....saumya.bsphcl.prosixNo ratings yet
- MMO Chat Filter Bad WordsDocument15 pagesMMO Chat Filter Bad WordsWilliam KravetsNo ratings yet
- Fetal Mummification in CowsDocument22 pagesFetal Mummification in CowsTahseen AlamNo ratings yet
- HSCA Vol10 RoseCheramieDocument9 pagesHSCA Vol10 RoseCheramiekanashane4794No ratings yet
- ApproachPerformance 01 PDFDocument6 pagesApproachPerformance 01 PDFAdam MazurekNo ratings yet
- ACSM - 2007 SpringDocument7 pagesACSM - 2007 SpringTeo SuciuNo ratings yet