Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mosaic Model Activity
Uploaded by
Larvin Andrei E. Bechayda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views4 pagesFluid Mosaic Model Activity
Uploaded by
Larvin Andrei E. BechaydaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Activity 1
CELL MEMBRANE
NAME: LARVIN ANDREI E. BECHAYDA
SECTION: 11- ANDRES BONIFACIO
I. Cytoplasmic Organelle: Membranous systems
a. Draw a plasma membrane (Fluid Mosaic Model) and Identify its parts and functions.
(Take a picture of your drawing and paste it in the box)
FUNCTIONS:
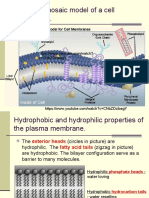
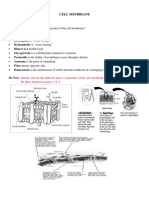
Hydrophilic head - Commonly known as “water-loving”, known for being polar, Hydrophilic
Heads faces outward and makes contact with fluids inside and outside of the cell.
Hydrophobic Tail – Commonly known as “water fearing”, known for being non-polar, protects
the cell parts from the water entering the cell.
Integral Protein – Responsible for the movement of the molecules across the phospholipid
bilayer and it extends through one or both layers.
Surface Protein – Plays the role in the cell communication
Cholesterol – Helps to regulate temperature and avoid the cell membrane from becoming stiffy.
Protein Channel- Acts as pores in which makes the water molecules enter.
Alpha Helix Protein – also known as “Transmembrane” which extends all the way across the
membrane.
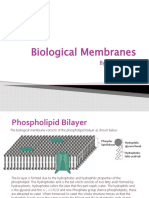
Phospholipid Bilayer- makes up the base or acts as the fabric of the membrane, has
hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.
Globular Protein - Acts as transport channels for certain molecules.
Glycolipid – Facilitates and maintains the stability of the cell-to-cell interactions of the
membrane.
Carbohydrate Chain – The chains recognize harmful bodies in cell-to-cell interaction.
Glycoprotein – Helps in binding on other cells (Cell Adhesion) and also helps in recognizing
harmful bodies.
II. Describe the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure as well as the models that preceded
it. Site evidences that either disproves or supports this model.
- In the Mid-19th Century, the development of colloidal chemistry and the
naming of the term “Osmosis”, then in 1855 two botanists named Naegeli
and Cramer stated that cell membrane plays role in the osmosis of cells.
Osmosis is the passage of water to a semipermeable membrane. After that,
in 1877 Botanist Wilhelm Pfeffer proposed that cells were entirely covered
by a thin surface that is called a plasma membrane which it contains cell
water and solutes. Next, in 1895-1899 Ernest Overton a British Physiologist
developed the concept of lipid membrane but it had a flaw in which the
explanation for the high permeability of water. Then, in 1904 Nathanson
proposed the Mosaic Model in which the Membrane is a mosaic with lipid
areas and areas with semipermeable gel which allows water in then in
refining the model Ruhland added that the membrane contains pores that
an additional passage for molecules. Next, in 1935 Hugh Davson and James
Danielli proposed that the Phospholipid Bilayer is surrounded by protein
layers on both sides and Lastly, It was then later proposed the Fluid Mosaic
Model by Singer-Nicholson in 1972 which explains that the Membrane is a
fluid structure with a mosaic of proteins embedded into the phospholipid
bilayer.
III. One of the main features of the cell surface membrane is that it is partially
permeable, so allowing the transfer of substance between its internal and external
environments. Using your knowledge of the fluid mosaic model, explain how the membrane
acts as a barrier to water-soluble molecules.
- It acts as a barrier to certain molecules especially to water-soluble
molecules to ensure the protection of the inside environment of the cell
and keep the outside materials selective which the term selectively
permeable comes from. Cell Membrane also has cholesterol that is
responsible for the regulation of temperature and helps in permeability and
cell fluidity. And based on the structure of the hydrophilic heads and
hydrophobic tails it allows the passage of water molecules that leads to the
hydrophobic tails immediately repels water to prevent water-soluble
molecules or polar materials from entering the membrane.
You might also like
- 1.3 Membrane StructureDocument6 pages1.3 Membrane StructureMukhammadaminkhon AnvarkhonovNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cell Membranes (Main)Document53 pages1.3 Cell Membranes (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Pre-ReadingDocument7 pagesCh. 5 Pre-ReadingDJ ISAACS50% (2)
- 1.3-4-Membrane Structure and TransportDocument33 pages1.3-4-Membrane Structure and TransportGiacomo Spinelli DonatiNo ratings yet
- Cell Membranes and Transport As BiologyDocument41 pagesCell Membranes and Transport As BiologyADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 Mod5 Transport Mechanisms EDITEDDocument21 pagesGenbio1 Mod5 Transport Mechanisms EDITEDmary gabrielle OrsuaNo ratings yet
- Once Upon A Time The Cell MembranesDocument35 pagesOnce Upon A Time The Cell Membranesjia wenNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell MembraneQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- 1985 Bretscher-MoleculesCellMembraneDocument11 pages1985 Bretscher-MoleculesCellMembraneAndreaNo ratings yet
- STD Ix Bio 1Document4 pagesSTD Ix Bio 1Sourav DasNo ratings yet
- 4 - Cell MembranesDocument23 pages4 - Cell Membraneswhether913No ratings yet
- Module 6 (GenBio)Document2 pagesModule 6 (GenBio)Christian Angel GomezNo ratings yet
- 2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDocument6 pages2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDuong TongNo ratings yet
- Course: PG-Pathshala Paper-12: Membrane Biophysics Content Writer: Dr. Jitendraa Vashistt, Jaypee University of Information & Technology, (H.P)Document8 pagesCourse: PG-Pathshala Paper-12: Membrane Biophysics Content Writer: Dr. Jitendraa Vashistt, Jaypee University of Information & Technology, (H.P)Tejinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane The Big PictureDocument4 pagesPlasma Membrane The Big PictureNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5Document373 pagesBiology Form 5shonotano71No ratings yet
- Fluid Mosaic Model of Plasma MembraneDocument16 pagesFluid Mosaic Model of Plasma MembraneNagaraj KallaiahNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 6Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 6JewelNo ratings yet
- Cells Basic Structure of LifeDocument41 pagesCells Basic Structure of LifeCleopatra NomathamsanqaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument6 pagesCell MembraneÖmer KhanNo ratings yet
- 2a-Membranes and Transport 2Document67 pages2a-Membranes and Transport 2kfy8vr7wtwNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Document7 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiNo ratings yet
- Biological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiDocument10 pagesBiological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiMariam El KhatibNo ratings yet
- Yasir 504Document20 pagesYasir 504Ehtisham ShahNo ratings yet
- Significance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismDocument10 pagesSignificance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismroshan khanNo ratings yet
- CMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadDocument24 pagesCMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Containing The Cell: Cell Membrane: Part I: Locating Physiology On The Web of KnowledgeDocument5 pagesContaining The Cell: Cell Membrane: Part I: Locating Physiology On The Web of KnowledgeEly TrajicoNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure and Function: Lecture OutlineDocument11 pagesMembrane Structure and Function: Lecture OutlineJohn Westly S. SabueroNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 4 CIE Biology A-Level PDFDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 4 CIE Biology A-Level PDFoqypooNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument1 pageTransport MechanismsJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Chemical Activity in The Cell: After You Have Finished Reading This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument21 pagesChemical Activity in The Cell: After You Have Finished Reading This Chapter, You Should Be Able TojohnnwakanmaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Q2W1Document3 pagesGen Bio 1 Q2W1Jasper BarlisNo ratings yet
- 2 4 Plasma MembraneDocument22 pages2 4 Plasma Membraneıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- C9e Answers Active Reading 07Document7 pagesC9e Answers Active Reading 07Daniel DHizzy Hizgilov83% (18)
- Chapter6 PDFDocument21 pagesChapter6 PDFsgw67No ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesCell MembranegrxcieeNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument30 pagesTransport MechanismsApril VeraNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane Student PPTDocument14 pagesPlasma Membrane Student PPTlube aguasNo ratings yet
- What Is The Fluid Mosaic ModelDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Fluid Mosaic ModelShnanca CarterNo ratings yet
- Cell Membranes and Transport 1Document28 pagesCell Membranes and Transport 1Rohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditDocument13 pagesq1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditInele Ellia AgReNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 2: Section 2.5Document20 pagesBiology Module 2: Section 2.5Nasteexo CaliNo ratings yet
- العملي 3Document8 pagesالعملي 3Mahmoud KhlifaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: Boundary LipidDocument18 pagesCell Biology: Boundary LipidVittal Athul RNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - Cell Structure and It's FunctionsDocument4 pages2.2 - Cell Structure and It's FunctionscarlNo ratings yet
- LSM1101 Notes LipidsDocument2 pagesLSM1101 Notes Lipidsgivena2ndchanceNo ratings yet
- Act2 Bio SciDocument4 pagesAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- 4 BiomembranesDocument43 pages4 Biomembranesc3rberussNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Cell Membranes and Transport: SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Cell Membranes and Transport: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Theory - StructureDocument32 pagesBasic Cell Theory - StructureRuby SamarNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and PermeabilityDocument1 pageCell Membrane and PermeabilityJessell Makiputin 2No ratings yet
- Cell Biology - DissertationDocument7 pagesCell Biology - Dissertationprerana chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Cell MebraneDocument10 pagesCell MebraneChandra SihombingNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cells and Tissues NotesDocument33 pagesAnaphy Cells and Tissues NotesshannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument9 pages1 Cell Membrane Structure and Functionstrawberrysmoothy66No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Astrii LyNo ratings yet
- Answers To Prepare For The 1st Module ControlDocument2 pagesAnswers To Prepare For The 1st Module Controlazizirabia5No ratings yet
- Palm Oil: Processing, Characterization and Utilization in The Food Industry - A ReviewDocument17 pagesPalm Oil: Processing, Characterization and Utilization in The Food Industry - A Review19-032 Otniel Wahana Christian SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Cannizzaro ReactionDocument16 pagesCannizzaro ReactionEm NaNo ratings yet
- TDS Nitocote NT402 Saudi ArabiaDocument4 pagesTDS Nitocote NT402 Saudi ArabiaAdarsh PNo ratings yet
- 891-7 DOW CORNING Silicone HV Grease TNDocument2 pages891-7 DOW CORNING Silicone HV Grease TNRahila AlaviNo ratings yet
- Awt MCQ QuestionDocument81 pagesAwt MCQ QuestionSHUBHAM Yadav75% (4)
- Lecture 5 - Ultraviolet and Visible (UV-Vis) SpectrosDocument40 pagesLecture 5 - Ultraviolet and Visible (UV-Vis) SpectrosBelay HaileNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Industrial Processes For Cadmium Removal From Phosphoric Acid - A ReviewDocument26 pagesComparative Analysis of Industrial Processes For Cadmium Removal From Phosphoric Acid - A Reviewfatima ezzahraNo ratings yet
- Physicochemical Characterization of Traditionally Fermented Liquid Manure From Fish Waste (Gunapaselam)Document7 pagesPhysicochemical Characterization of Traditionally Fermented Liquid Manure From Fish Waste (Gunapaselam)ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Alloys Phase Diagrams Phase Transformations (Diffusion Controlled, Martensitic) Novel Alloys (Structural, SS, HEA)Document13 pagesStructure of Alloys Phase Diagrams Phase Transformations (Diffusion Controlled, Martensitic) Novel Alloys (Structural, SS, HEA)Parijat MitraNo ratings yet
- Topic II Basic Principles of Extraction of Metals From Ores & PurificationDocument31 pagesTopic II Basic Principles of Extraction of Metals From Ores & PurificationKing of KingsNo ratings yet
- Antinutritional Factors in Plant Foods: Potential Health Benefits and Adverse EffectsDocument6 pagesAntinutritional Factors in Plant Foods: Potential Health Benefits and Adverse EffectsVennyNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesLAB REPORT Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsSafwan Jamil62% (13)
- The Potentials of Henna (L) Leaves Extracts As Counter Stain in Gram Staining ReactionDocument5 pagesThe Potentials of Henna (L) Leaves Extracts As Counter Stain in Gram Staining ReactionAna Virginia MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Chemicals From LigninDocument13 pagesChemicals From LigninsaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Environmental Factors On Maxillofacial Elastomers: - Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesEffects of Environmental Factors On Maxillofacial Elastomers: - Literature ReviewpalliNo ratings yet
- Tools Reagents Recombinant Protein Purification BrochureDocument16 pagesTools Reagents Recombinant Protein Purification BrochureMeka SaimaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Proton Neutron Electron Grade 7 Proton, Neutron, ElectronDocument6 pagesAtomic Proton Neutron Electron Grade 7 Proton, Neutron, ElectronMaria Isabella HarsonoNo ratings yet
- Chem 345 Exam IIIOS KeyDocument9 pagesChem 345 Exam IIIOS KeyQuoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Rynite® 935 BK505-gb-Regulatory Information Sheet (RIS)Document13 pagesRynite® 935 BK505-gb-Regulatory Information Sheet (RIS)Quality teamNo ratings yet
- Membrane FoulingDocument8 pagesMembrane FoulingSushanta BeheraNo ratings yet
- USP-NF 621 ChromatographyDocument14 pagesUSP-NF 621 ChromatographyNur AcarNo ratings yet
- C5 Chemical Changes Exam Question Pack: 119 Minutes 119 MarksDocument28 pagesC5 Chemical Changes Exam Question Pack: 119 Minutes 119 MarksequakeroatsNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Silver SulphateDocument5 pagesElectrolysis of Silver SulphateJackson_de_Roz_6005100% (1)
- Seat No Fe 2022-23Document29 pagesSeat No Fe 2022-23gaurangghavate8No ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project Study of Constituent of AlloysDocument19 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project Study of Constituent of AlloysVaishnavi.V NathanNo ratings yet
- Michael L. Shuler, Fikret Kargi - Bioprocess Engineering - Basic Concepts-Prentice Hall (2001) (077-113)Document37 pagesMichael L. Shuler, Fikret Kargi - Bioprocess Engineering - Basic Concepts-Prentice Hall (2001) (077-113)Dome VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Marine Coatings Technical Modules: Module 0: IntroductionDocument4 pagesMarine Coatings Technical Modules: Module 0: IntroductionHung DinhNo ratings yet
- MDI Synonyms, Acronyms, and CAS Registry Numbers: November 2001, Diisocyanates PanelDocument4 pagesMDI Synonyms, Acronyms, and CAS Registry Numbers: November 2001, Diisocyanates Panelnur34No ratings yet
- Catalogue of Hubei Longsheng SihaiDocument12 pagesCatalogue of Hubei Longsheng SihaiDilip ParmarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.6Document4 pagesExperiment No.6alandanwar266No ratings yet