Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Guia Mdulo 12 Mi 444812 Downloadable 2447503
Uploaded by
charlyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Guia Mdulo 12 Mi 444812 Downloadable 2447503
Uploaded by
charlyCopyright:
Available Formats
Accede a apuntes, guías, libros y más de tu carrera
Mi vida en otra lengua
pag.
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
PREPARATORIA
ABIERTA
MATERIAL DE
APOYO
MÓDULO 12
“MI VIDA EN OTRA LENGUA”
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
GRAMMAR REFERENCE AND WORD LIST
UNIT 1 What are you doing?
SECTION 1 I'm planning a trip
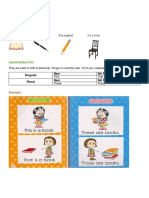
Present progressive
Affirmative
Subject Be + verb with -ing Complement
I am reading a book.
You, we, they are reading a book.
He, she, it is reading a book.
Negative
Subject Be + not + verb with -ing or Contraction Complement
(pronoun + be) + not + -ing
I am not reading a book.
I'm not reading a book.
You, we, they are not reading a book.
You're/We're/They're not reading a book.
He, she, it is not reading a book.
He's/She's/It's not reading a book.
Interrogative
Be Subject Verb with –ing Complement
Am I reading a book?
Are You, we, they reading a book?
Is He, she, it reading a book?
Present progressive short answers (yes / no answer)
Yes, subject + be No, subject + be + not Contraction (pronoun + be) + not
Yes, I am. No, I am not. No, I'm not.
Yes, you, we, they are. No, you , we, they are not. No, you’re, we're, they're not.
Yes, he, she, it is. No, he, she, it is not. No, he's, she's, it's not.
Personal pronoun and forms of the verb to be in present
Personal pronoun Verb to be in present
I am
You are
He is
She is
It is
We are
They are
Rules to add -ing to a verb
When a verb ends in -e, you drop the -e before adding –ing: make - making
When a one syllable verb ends in a vowel and consonant, you
double the consonant before adding –ing: run - running
When a verb ends with -y you just add –ing: lay – laying
When a verb ends in -ie, you change the -ie to -y and add –ing: die - dying
In all other cases you just add –ing: work - working
2
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Wh- questions
Where indicates place: Where are you going? To the library.
When indicates time: When are you leaving? Tomorrow night.
Who indicates person: Who are you? I'm a worker
Why indicates reason: Why are you sad? Because I can't find my pet.
What indicates thing or reason: What is this? It's a magazine.
What are you doing? I'm studying.
How indicates way to do or state of being:
How can I help you? Giving me a ride to my house.
How are you? Fine, thank you.
Wh- questions interrogative form
Wh- question Auxiliary verb Subject Verb Complement
Present:
What does he like most?
Present Progressive:
When are you talking to?
Past:
Where did you go yesterday?
Past Progressive:
How was he feeling last week?
Future:
When will you visit me?
Word list
Time and Dates The Natural Clothes Accessories Celebrations
Weather Disasters
Spring Rainy earthquake Dress Watch custom
Summer sunny ice break Jacket wallet tradition
Fall cloudy tornado blue jeans scarf handbag ceremony
winter Monday snowing hurricane shirt earrings Christmas
Tuesday foggy thunderstorm shoes socks bracelet Christmas Eve
Wednesday windy volcanic skirt ring Independence
Thursday Friday dry eruption flood tie sunglasses of Mexico
Saturday cold avalanche belt necklace Day of the
Sunday January ice storm tsunami suit portfolio Dead
February warm droughts pants hat
March hot blouse cap
April mild T-shirt
May high heeled shoes
June low heeled shoes
July sneakers
August September boots
October November bathing suit
December sandals trousers
turtle neck
sweater coat
short sleeved
blouse
3
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
SECTION 2 What did you do?
Auxiliary do / does / did
Present Tense: Auxiliary Do / Does Past Tense: Auxiliary Did.
Affirmative I open the door. I opened the door.
He opens the door. He opened the door.
Negative I don't open the door. I didn't open the door.
He doesn't open the door. He didn't open the door.
Interrogative Do I open the door? Did I open the door?
Yes. I do. / No, I don't. Yes, I did. / No, I didn't
Does he open the door? Did he open the door?
Yes, he does. / No, he doesn't. Yes, He did. / No, he didn't
Past tense
Affirmative
Subject Regular Verb (-ed) Complement
I, you, he, she, it, we, they played in the park.
Negative
Subject Auxiliary past didn't / did not Simple Verb (without –ed) Complement
I, you, he, she, it, we, they didn't or did not play in the park.
Interrogative
Auxiliary Did Subject Simple Verb (without -ed) Complement
Did I, you, he, she, it, we, they play In the park?
Past tense short yes / no answers
Yes / No Subject Auxiliary did / didn't
Yes I, you, he, she, it, we, they did
No I, you, he, she, it, we, they didn't
Adding -ed ending to regular verbs
When the simple form of the verb ends in e, you only add -d. change-changed
When the simple form of the verb ends in -y, you change it to i before study - studied.
adding -ed.
When a one-syllable verb ends in one vowel + consonant, you double the plan - planned
consonant (excepting c,w,x or y) before adding -ed. (Exception: allow -
allowed.)
When a verb of more than one syllable ends in vowel + consonant, the omit - omitted (the last
consonant is doubled before adding -ed if the last syllable is stressed. syllable sounds
stronger)
If the last syllable is unstressed, the consonant is not doubled (the last visit - visited
syllable doesn't sound strong).
Verb be past tense: was / were
Personal pronouns Affirmative Negative was + not or contraction Example
I, he, she, it was was not / wasn't I was hungry
I was not hungry.
I wasn't hungry.
(the same for he, she, it)
We, you, they were were not / weren't We were hungry.
We were not hungry.
We weren't hungry.
(the same for you, they)
4
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Past progressive
Affirmative
Subject Be + verb in -ing Complement
I, he, she. it was reacting a book.
You, we, they were reading a book.
Negative
Subject Be + not + verb in -ing or Contraction (wasn't / weren't) + -ing Complement
I, he, she, itwas not reading a book.
wasn't reading a book.
You, we, they were not reading a book.
weren't readin a book.
Interrogative
Be Subject Verb -ing Complement
Was I, he, she, it reading a book?
Were you, we, they reading a book?
Past progressive short answers (yes / no answer)
Yes, subject + be Yes, I / he / she / it was.
Yes, You / We / They were.
No, subject + be + not No, I / he / she / it was not.
No, You / We / They were not.
Subject + contraction (wasn't / weren't) No, I / he / she / it wasn't.
No, You / We / They weren't.
Connectors while and when
While gives more emphasis to the time, the When refers to a specific or punctual action.
duration of the action. While is used in past Its meaning changes if used in past or past
progressive and simple past to say that progressive.
something happened in the middle of
something else.
While I was reading, my mother came. When Tom arrived, we had dinner. (Past: Tom
arrived, then we had dinner)
When Tom arrived, we were having dinner.
(Past Progressive: Tom arrived, we already
started dinner)
Word list
Pastimes Expressions of time
Indoor dice games Nature at the moment a long time ago
Outdoor drawing painting every day yesterday
adventure golf paper craft next last
board hide and go rappelling now night/week/month/year
games seek sailing right now tomorrow
camping hiking tennis this next
canoeing hill walking valley morning/afternoon/evening day/week/month/year
card jewelry making video games this week day after tomorrow
games jogging water sports an hour ago in three days
climbing knitting zip-wire
cooking mountain bike
darts
5
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
SECTION 3 We had fun!
Irregular verbs
Simple Form Past Simple Form Past Simple Form Past
be was / were grow grew set set
beat beat hang hung shine shone
become became hear had shoot shot
begin began have heard shrink shrank
bend bent hit hit sing sang
bet bet hold held sink sank
bite bit hurt hurt sit sat
bleed bled keep kept sleep slept
break broke know knew slide slid
bring brought laid lay speak spoke
build built lead led spend spent
buy bought leave left spring sprang
can could lend lent stand stood
catch caught let let stick stuck
choose chose light lit sting stung
come came lose lost strike struck
cost cost leave left string strung
cut cut make made sweep swept
dig dug mean meant swim swam
do did meet met swing swung
drink drank pay paid take took
drive drove put put teach taught
eat ate quit quit tell told
fall fell read read think thought
feed fed ride rode throw threw
feel felt ring rang understand understood
fight fought run ran wake woke
find found say said weep wept
fly flew see saw wet wet
get got sell sold win won
give gave send sent write wrote
Simple past irregular verbs
Affirmative
Subject Irregular Verb Complement
I, you, he, she, it, we, they wrote a letter.
Negative
Subject Auxiliary past didn't / did not Simple Verb Complement
I, you, he, she, it, we, they didn't or did not write a letter.
Interrogative
Auxiliary Did Subject Simple Verb Complement
Did I, you, he, she, it, we, they write a letter?
Simple past irregular verbs short yes / no answers
Yes / No Subject Auxiliary did / didn't
Yes, I, you, he, she, it, we, they did.
No, I, you, he, she, it, we, they didn't / did not.
6
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Word list
Food drink and meals Health and Well Being Aches and diseases
Eggs Grease Rice good habits stomach ache
Beef grilled Roast beef bad habits headache
Bread meal salad exercise back ache
Breakfast meat Sauce smoking sore throat
calorie milk Shrimp drinking rash
carrot mushrooms Snack drugs earache
cereal water Soda doctor cough
chicken oil Sugar dentist fever
chili onion sweet balanced diet cold
cilantro pasta tea sleeping
fish peach tomato hygiene
Fried pepper vegetable energy
Fruit pizza yoghurt
garlic potato
UNIT 2 I’ didn't know about it!
SECTION 1 Talking about the past
Comparative and superlative forms
Rule Adjective Comparative Superlative
When the adjective is one syllable, you Cheap Cheaper than The Cheapest
just add -er or-est.
When the adjective ends in -y, you Pretty Prettier than The Prettiest
change it to -i before adding -er or -est.
When the adjective ends in vowel +
consonant, you double the consonant Big Bigger than The Biggest
before adding -er or -est.
When the adjective is two or more
syllables, you use more / less or most / intelligent more intelligent than The most intelligent
least. less intelligent than The least intelligent
Irregular adjectives
Irregular adjective comparative superlative
Good better best
Bad worse worst
Far further furthest
Little less least
Regular plural forms
Rules Examples
Add -s after words ending in consonant and –e. nose- noses cheek –cheeks
Add -es after words ending in -s,-ss,-x,- sh,- ch z and -o.
glass - glasses wish - wishes
tomato - tomatoes box – boxes
buzz - buzzes beach – beaches
bush – bushes
Change the -y to -i and add -es if there is a consonant baby – babies
before the -y.
Add -s after the -y if there is a vowel before it. toy – toys
Change -f or -fe to -v and add -es. calf - calves wife - wives
7
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Irregular plural forms
Man – men child – children
Woman – women foot – feet
louse – lice tooth – teeth
bacterium – bacteria mouse – mice
goose – geese louse – lice
Always plural
Scissors, trousers, pants, tongs, binoculars, jeans, shoes, earrings, glasses.
Deer, sheep and fish are always the same in singular and plural form.
Foreign plural forms
A few nouns of Greek or Latin origin retain their original plurals.
analysis – analyses, basis – bases, crisis – crises, datum – data, curriculum – curricula.
Expressions of time
Use AT with times and Use ON with days and dates. Use IN for months, years,
expressions. seasons and periods of time.
at 5 o’clock, On March in April in 2012
at lunch, On 12 December in winter
at lunch, On Saturday in the 201h century
at the age of..., On Friday evening in a few minutes
at the same time...,
at the moment...,
at Christmas / at Easter
at night
at the weekend
Word list
Family Stages of Life
great grandparents Baby
great grandmother Toddler
great grandfather Child
grandparents Adolescent
grandmother Young Adult
grandfather Adult
parents middle age
mother senior adult
father birth
uncle childhood
aunt adolescence
cousin adulthood
niece
daughter
son
brother
sister
SECTION 2 Let's talk about celebrations
Uncountable nouns
Rules Example
Is a word or an abstract idea that you can't Money, news, coffee, information, water.
count. Knowledge, etc.
Uncountable nouns don't have plural form. They luggage - luggages (wrong)
are not preceded by a or an. Ana needs information. (correct) Ana needs an
information (wrong)
8
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Uncountable nouns use how much, much, a lot How much information do you need? Ana needs
of, some or any. a lot of information. Ana needs some
information. Ana doesn't need any information.
News, traffic, weather, work, luggage, chaos,
Most common uncountable nouns used in advice, behavior, trouble, bread, permission,
English. information, furniture, etc.
Countable nouns
Rules Example
Is a word that you can count and are preceded A newspaper, a car, an animal, an idea.
by a or an.
Countable nouns have plural form. Trees, children, women, boats, fish, shoes, etc.
How many apples do you need? I need a lot of
Countable nouns use how many, many, a lot of, apples. I need some apples. I don't need any
some or any. apples.
Some / any / a lot of
Some is used in affirmative sentences and means a little, a few, a I have some bread.
small number or amount.
Any is used in negative sentences or questions and means one, some I don't have any bread.
or all.
A lot of means many or much. I have a lot of bread.
Word list
Celebrations Parties Holidays
Celebrate Funeral Birthday cake Invitations Battle of Puebla
Firework bridal shower candles host Mexican
new year baby shower Balloons food Independence
baptism birthday fireworks drinks Mexican
First communion anniversary guests music Revolution
confirmation golden wedding anniversary presents dance floor 1985 earthquake
marriage silver wedding anniversary live music
SECTION 3 Talking about world's events
Word list
Discoverers and Inventors World's events Inventions and discoveries
Thomas Alva Edison Olympic Games car gasoline
Brothers Wright World Cups light bulb
Alexander Graham Bell World War II telephone
Alexander Fleming polonium and radiation
John L. Baird cinematographic projector
Karl Benz television
Augusto and Louis Lumiere relativity theory
Albert Einstein penicillin
J. Samuel Morse flight in aircraft
Charles Darwin telegraph
theory of evolution
9
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
UNIT 3. What happened to you?
SECTION 1. Where did we buy a present?
Subject and object pronouns
Singular Plural Singular Plural
Subject pronoun Subject pronoun Object pronoun Object pronoun
I We Me Us
You You You You
He They Him Them
She Her
It It
Word list
Public Places Beverages Snacks Plastic
computer game stores Japanese restaurant Juice Popcorns disposal plates
computing store ice cream parlor Tea peanuts disposal glasses
coffee shop pet store soft drinks fried potatoes plastic cutlery
shoe store book store water cheese trash bags
toy store stationery shop beer balloons
Italian restaurant music store wine
Mexican restaurant gym
bank cinemas
barber shop hospital
restrooms library
department store museum
Park bus station
Supermarket post office
theater markets
drugstore hotels
sports store landmarks
travel agency
SECTION 2 We had fun as tourists!
Adverbs of frequency
never Least Frequent
rarely
seldom
hardly ever
occasionally
sometimes
generally
often
regularly
frequently
usually
always
10
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Most Frequent
Expressions of frequency
Every day Twice a week / month / year
Once a week / month / year Three time a week / month / year
UNIT 4 I will be a lawyer!
SECTION 1 What am I going to do?
Future tense (will + verb)
Affirmative
Subject Will + Verb Complement
I, you, he, she, it, we, they will write a letter.
Negative
Subject Auxiliary won't / will not Simple Verb Complement
I, you, he, she, it, we, they won't or will not write A letter
Interrogative
Auxiliary will Subject Simple Verb Complement
Will I, you, he, she, it, we, they write a letter?
Future tense (will + verb) short yes / no answers
Yes / No Subject Auxiliary will /won't
Yes, I, you, he, she it, we, they will.
No, I, you, he, she it, we, they won't / will not.
Future tense (be+going to + verb)
Affirmative
Subject Contraction (pronoun + be form) or Be + going to + verb Complement
I I'm going to write a letter.
am going to write a letter.
You, we, they You're/ we're/ they're going to write a letter.
are going to write a letter.
He, she, it He's/she's/it's going to write a letter.
is going to write a letter.
Negative
Subject Contraction (pronoun + be form) or Be +not + going to + verb Complement
I I'm not going to write a letter.
am not going to write a letter.
You, we, they You're, we're, they're not going to write a letter.
are not going to write a letter.
He, she, it he's, she's, it's not going to write a letter.
is not going to write a letter.
Interrogative
Auxiliary am, is, are Subject Going to + verb Complement
Am I going to write a letter?
Are You, we, they going to write a letter?
is He, she, it going to write a letter?
11
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Future tense (be+going to + verb) short yes / no answers
Yes / No Subject Verb / Contraction + not
Yes, I am.
No, I'm not.
Yes, you, we, they Are.
No, you're not / you aren't.
(the same for we and they)
Yes, he, she, it is.
No, he's not / he isn't.
(the same for she and it)
Future forms: will or going to
You use will + verb when you decide to do something at the time of speaking. You have not
decided before. Example:
You look sick. I will call the doctor. (you decided at that moment)
You use be + going to + verb when you have already decided to do something. Example: Turn on
the TV. I'm going to watch the news. (you already decided to watch the T. V.)
Word list
Expressions in future
Soon A week from now The day after tomorrow
Later Next month In two years
Tomorrow I In two years Next year
Next week A year from now At noon
In a few minutes At three o'clock In a while
SECTION 2 I'm looking for a job
Would
Would is the past of will. He will go. He would go.
Would is used to express future but in past. He said he would go tomorrow.
Would is used to express repeated or habitual When he was a kid, he would always go to the beach.
actions in the past. If he didn't have a headache, he would be at the party.
Would is used as a conditional form using if.
Word list
Professions Trades and Jobs
Mathematician Plumber president assistant
Veterinarian policeman barber waitress
Lawyer painter actress waiter
Architect carpenter clerk secretary
Dentist fireman hairdresser steward
Archaeologist salesman President stewardess
Psychologist driver manager cashier
Journalist postman clerk businessman
Biologist gardener director businesswoman
Engineer waiter typist actor
SECTION 3 My personal life project
Word list
life project long term goals personal life project college
professional life project career short term goals employee
medium term goals
12
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
PREPARATORIA ABIERTA
MATERIAL DE APOYO
MÓDULO 12: MI VIDA EN OTRA LENGUA
_______________________________________________________________________
INSTRUCCIONES: Lea detenidamente cada uno de los párrafos e investigue por su
cuenta en internet los temas y conceptos más relevantes. Asimismo, puede
consultar con su asesor lo que no entienda.
1.- Choose a connector for the sentence.
Elige un conector para la frase.
“When I play soccer, everybody shouts.”
"Cuando juego al fútbol , todo el mundo grita ".
_______________________________________________________________________________________
2.- Choose a connector for the sentence.
Elige un conector para la frase
“He sings along to the music on the radio When he takes a shower.”
"Canta junto a la música en la radio Cuando toma una ducha".
______________________________________________________________________________________
3.- Choose a verb for the sentence.
Elige un verbo de la frase
“Susan and Peter wake up very early.”
"Susan y Peter se despierta muy temprano".
_____________________________________________________________________________________
4.- Look at this poster:
Mira este cartel:
What is the purpose of the poster?
¿Cuál es el propósito del póster?
The store sells jewels at a lower price this week.
La tienda vende joyas a un precio menor esta semana.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
5.-Choose the gramatically correct negative form of the following sentence:
Elija la forma negativa gramaticalmente correcta de la siguiente frase:
“I'm taking care of Mary's pet.”
"Estoy cuidando de la mascota de María. "
“I'm not taking care of Mary's pet.”
"No voy a cuidar de la mascota de María. "
______________________________________________________________________________________
¿Qué dinámica sigues para asistir a la asesoría de Módulo 3 "Mi vida en otra lengua" con respecto al uso de
los verbos irregulares?
Las programas conforme a un plan de trabajo.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
13
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Complete with the Word question.
English Español
Complete the following question: Complete la siguiente pregunta :
“When were you born?” "Cuando naciste?"
I was born in 1980. Nací en 1980 .
What's the gramatically correct answer to the ¿Cuál es la respuesta correcta gramaticalmente a la
following question? siguiente pregunta ?
"What were you doing yesterday at 3 PM?" " ¿Qué estabas haciendo ayer a las 15:00 ? "
I was working on my PC. Yo estaba trabajando en mi PC.
The following questions are grammatically correct. Las siguientes preguntas son gramaticalmente correcta .
1. What do you do? 1. ¿Qué hace usted ?
2. What is Lorenzo playing? 2. ¿Qué es jugar Lorenzo?
3. What are you doing? 3. ¿Qué estás haciendo ?
What do you consider is the best way to correct ¿Cuáles considera que es la mejor manera de corregir
spelling on your writings? la ortografía en sus escritos?
Looking up in books the words you aren´t sure Mirando hacia arriba en los libros de las palabras que
about. usted aren't seguro.
Complete the following sentence with the correct Complete la siguiente frase con la forma correcta del
verb form. verbo .
“We planted an apple-tree in the backyard; " Plantamos un árbol de manzanas en el patio trasero;
unfortunately it died. desafortunadamente murió .
Choose the correct form of the verb to be for the Elija la forma correcta del verbo ser para la sentencia
sentence in future. en el futuro.
“ I am going to eat hot chips.” "Me voy a comer patatas fritas calientes. "
Complete the following sentence: Complete la siguiente frase :
The simple past with regular or irregular verbs El pasado simple con verbos regulares e irregulares
indicates an action: completed or finished in the indica una acción: terminado o terminado en el
past. pasado.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Fills in the blanks with the correct words: at, on, in or after
Llena los espacios en blanco con las palabras correctas: a, sobre, dentro o después.
The telephone rang _ after _ the doorbell.
In the next sentence, do you need any of these prepositions: “in”-“on” or “at”? or nothing?
“All our relatives came for a celebration __ nothing __ last Christmas.”
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the next sentence with the correct object pronoun:
“I love Mary, I've just bought a nice bunch of flowers for__her___.”
___________________________________________________________________________________
Mark the following sentences as correct C, or if they have errors E.
1. María Felix was an actress. Everybody knows about she. E
2. Jane was aware that something special occurred to him. C
3. My brother and me left earlier than usual. E
____________________________________________________________________________________
Why is the following question incorrect?
“Why do you did that during last class?”
Because the auxiliary in past is "did", the verb should be in infinitive without "to".
_____________________________________________________________________________________
14
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Change the next sentence to past continuous. Cambie la siguiente frase al pasado continuo .
All of the reindeer are leaping around in the snow. Todos los renos están saltando en la nieve .
All of the reindeer were leaping around in the Todos los renos saltaban en la nieve .
snow.
Fill in the blanks with a superlative adjective for Llene los espacios en blanco con un adjetivo superlativo para
the next sentence. la siguiente frase.
“China's population is were leaping of all the "La población de China se saltaban de todos los países."
countries.”
Fill in the blanks with the comparative and superlative Llene los espacios en blanco con los adjetivos
adjetives. comparativos y superlativos.
Comparative or superlative: larger, the largest Comparativo o superlativo: más grande, el más
grande
a. Which state is __ larger _______, Chihuahua or Zacatecas? a. ¿Qué estado es -mayor- , Chihuahua o Zacatecas?
b. Michoacan is _ the largest __ than Hidalgo. b. Michoacán es el _más grande _ que Hidalgo.
c. Which city has the __ the largest __ population: Guadalajara, c. ¿Qué ciudad tiene el _la mayor_ población:
Mexico City or Monterrey? Guadalajara, Ciudad de México o Monterrey?
d. Mexico City has __ larger ______ population of the country. d. Ciudad de México tiene _ mayor_ población del país.
The following sentences have the plural pronoun. Las siguientes oraciones tienen el pronombre
1. These children are nice. plural.
2. I have some mice in my house. 1. Estos niños son agradables.
2. Tengo algunos ratones en mi casa.
Tu asesor de Módulo 3 “Mi vida en otra lengua”, te da material de un tema nuevo para que lo estudies sobre
"el uso de los plurales irregulares" , pero no logras entenderlo, ¿qué haces?
Buscas más referencias para entenderlo, si es necesario pides ayuda al asesor.
Indicate which of the following words is an uncountable Indique cuál de las siguientes palabras es un
noun: noise, street, star, bottle…. sustantivo incontable: ruido, calle, estrella, botella
Noise ....
ruido
Fill in the blanks with the correct words. Llene los espacios en blanco con las palabras
correctas.
Some or any Algunos o cualquier
a. We have one dog, two cats and _ Some _ fish. a. Tenemos un perro, dos gatos y _ Algunos_ peces.
b. There are Some chocolate biscuits in the cupboard. b. Hay _ Algunas_ galletas de chocolate en el armario.
c. I can't find _ any __ books about Mexican movies. c. No puedo encontrar ningunos libros sobre cine mexicano.
d. My daugther doesn't have __ any ____ friends in Jalisco. d. Mi hija no tiene _ ningún_ amigo en Jalisco.
e. Would you like __ Some ___ grapes? e. ¿Quieres __Algunas_ uvas?
Identify the object pronouns (me, you, him, her, it, us , you, them)
Which object form of the personal pronoun can substitute the underlined phrase in the sentence?
The boys are riding their bicycles.
them
___________________________________________________________________________________
Read this sentence: Mary works.
Change it to present progressive in the next forms:
1. Affirmative……. Mary is working
2. Negative……… Mary is not working
3. Interrogative….. Is Mary working?
___________________________________________________________________________________
15
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
¿Qué método utilizas para comprender temas como el uso de los pronombres y adjetivos?
Buscar datos que te remitan a la información relevante para aprenderla.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the sentences below with the appropriate word:
A. __ Did _ you go to Veracruz on Saturday?
B. No, we __ didn't._ We went to Acapulco.
____________________________________________________________________________________
Classify the following sentences as true (T) or false (F).
1. Negatives in the simple past tense are formed by adding DID NOT before the simple T
form of the verb.
2. The verb BE is not an exception to the previous sentence. F
3. YES / NO questions in the simple past are NOT created using the auxiliary DID. F
4. Questions with WH words in simple past are created by using the auxiliary DID before T
the subject.
Complete the following sentence in simple past using the correct verb form and auxiliary:
What time ___ did ___ the last train__ leave __?
____________________________________________________________________________________
Rewrite the sentence using the simple future tense.
"The team has a party".
The team will have a party.
____________________________________________________________________________________
What does this sentence express?
“It will probably rain tomorrow morning.”
A prediction about the future.
___________________________________________________________________________________
What does this sentence express?
“I'm fine now. When I get married, I'll have a lot of babies.”
Something the person believes will happen in the future.
¿Qué debes hacer si te encuentras en medio de una plática en inglés y,al estar hablando de los planes que
tienes para tu futuro, de pronto ya no sabes de que manera continuarla?
Reconocer que ya no sabes como seguir hablando del tema y solicitar le ayuda a alguien.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the sentence with the correct form of the verb “buy” and the form of future using “going
to”:
“I ___ am going to buy ___ a new car next year. I´m already saving money.”
___________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the sentence using idiomatic future: “going to”.
“Lupita and Lalo (rent) ___ are going to rent ___ a car to travel along the country.”
____________________________________________________________________________________
Si conocieras a una persona de habla inglesa a través de una red social ¿cómo intercambias información
con ella sobre tu proyecto de vida?
Expresarías de manera autónoma tus ideas utilizando las nociones gramaticales y vocabulario
propias para su formulación.
____________________________________________________________________________________
16
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
What's the right short answer for this?
“Would you like to go to the movies next weekend?”
No, I wouldn't.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Order the following words to make a coherent sentence.
1. would
2. he
3. not
4. the
5. organizing
6. be
7.evidence
8.?
Respuesta: would he not the organizing be evidence?
___________________________________________________________________________________
Al revisar la forma de formular preguntas en futuro, observas que hay distintas maneras para hacerlo. ¿Qué
opciones aprendes?
Todas para tener diferentes alternativas para preguntar.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Write the correct connector for the next sentence:
I was studying __ while __ Mom was making dinner.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Read the next sentence.
It`s not polite to make a lot of noise because you know that others are sleeping.
Now complete the same idea in a question of cause and effect:
Is it polite to make a lot of noise __ when __ you know that others are sleeping?
__________________________________________________________________________________
Choose a verb for the sentence.
“Peter _ watches _ TV in the evening “
_________________________________________________________________________________
The next sentences are in simple present.
Las siguientes frases están en presente simple.
1. I often write poems to my wife.
A menudo escribo poemas a mi esposa.
2. The sun barely shines with this weather.
El sol apenas brilla con este tiempo.
__________________________________________________________________________________
If I want to tell something that happened during the day and the person in front of me does not
understand when I speak in English, what happens to me?
Si yo quiero contar algo que pasó durante el día y la persona delante de mí no entiende cuando hablo en Inglés, ¿qué
me pasa?
I feel frustrated.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
the following sentence is gramatically correct.
La siguiente oración es gramaticalmente correcta.
Why is Julieta working as a hospital administrator this year?
¿Por qué es Julieta trabajando como administrador del hospital este año?
__________________________________________________________________________________
17
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Based on the picture, answer the following question:
Sobre la base de la imagen, responder a la siguiente pregunta:
What are they doing?
Qué están haciendo?
They are dancing.
Ellos están bailando.
__________________________________________________________________________________
The expressions and words below are in order. Is the logical sequence in present progressive.
Las expresiones y palabras de abajo están en orden. Es la secuencia lógica en el presente progresivo.
1. When you are
2. listening to
3. the radio
4. you can
5. hear his voice
R= When you are listening to the radio you can hear his voice
Cuando usted está escuchando la radio puede escuchar su voz
¿Qué aplicabilidad tiene el inglés en tu vida cotidiana?
Tratas de aplicarlo en todas las áreas de tu entorno donde sea posible.
____________________________________________________________________________________
Write a verb with the correct form of the verb to be for the sentence in past progressive.
Escribir un verbo con la forma correcta del verbo ser para la frase en pasado progresivo.
“ It _ was snowing _ last winter.”
"Estaba nevando el invierno pasado. "
___________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the next sentence using the correct tense and form of the verb:
Complete la siguiente frase con la forma del tiempo y correcta del verbo :
___________________________________________________________________________________
“When you rang me yesterday, I -was taking- a shower.”
" Cuando me llamó ayer, yo -estaba tomando- una ducha . "
___________________________________________________________________________________
Why do we use the verb in past form only in affirmative sentences?
¿Por qué usamos el verbo en forma pasada sólo en oraciones afirmativas ?
___________________________________________________________________________________
In negative and interrogative we have the auxiliary "did".
En negativas e interrogativas tenemos el auxiliar " hicimos ".
___________________________________________________________________________________
Change the sentence to simple past tense:
Cambie la sentencia a pasado simple :
___________________________________________________________________________________
"Paty is going to bake cookies for the guests".
" Paty va a hornear galletas para los huéspedes”.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Paty baked cookies for the guests.
Paty hornea galletas para los huéspedes.
___________________________________________________________________________________
18
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Choose a comparative adjective for the sentence.
Elegir un adjetivo comparativo para la frase.
___________________________________________________________________________________
“Sandy's hair is __ longer than __ Nancy's.”
"El pelo de Sandy es __ más largo que- el de Nancy ".
___________________________________________________________________________________
¿Si desconoces la manera en la que puede ser usado un comparativo en inglés, que opción te puede ayudar
a eliminar tu duda?
Buscar en un diccionario y verificar los usos de la palabra.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Form the correct plural form of the following word: Child
Formar el plural correcto de la siguiente palabra: Niño
Children
niños
___________________________________________________________________________________
Rewrite the sentence using plural nouns and change the number 1 for 100.
Vuelva a escribir la frase usando nombres plurales y cambiar el número 1 para 100.
___________________________________________________________________________________
"There is one mouse in the kitchen".
"Hay un ratón en la cocina".
___________________________________________________________________________________
There are one hundred mice in the kitchen.
Hay cien ratones en la cocina.
Determine which of the following sentences use the correct quantifier.
People should drink a lot of water.
I have a lot of work to do.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Después de leer un texto donde aparecen cuantificadores en una pregunta o información en inglés, qué
haces normalmente?
verificas haber entendido.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct preposition ( at, on, in or after) for the sentence:
Hidalgo was born _____ in ______Guanajuato ________ in ________1753.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct expressions "in-at-on" to complete the sentences:
1. “My mother's birthday is _ in _ April.”
2. “I always get up early _on__ Friday mornings”.
3. “Please, try to be home _at__ lunch time.”
___________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the following sentence with the corresponding pronoun.
Laura saw __them_____ (her friends) last week.
__________________________________________________________________________________
The next sentences are incorrect based on the grammar for simple past.
1. Where did you picked up your English?
2. When does she had the accident?
3. What time did the match was start?
____________________________________________________________________________________
What's the correct question to get this answer based on the grammar for simple past and the best
choice of a question word?
“The concert began at six o'clock”.
What time did the concert begin?
19
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Complete the question: “Will you please call me up when you _ arrive __ there?”
What's the correct and logical question for this answer?
"Beto is presenting his findings to Andres".
What is Beto doing?
____________________________________________________________________________________
Which object pronoun can substitute the Qué pronombre objeto puede sustituir la frase
underlined phrase in the sentence? subrayada en la oración ?
Can you tell the people the way to the train ¿Puedes decirle a la gente el camino a la estación
station? de tren ?
ellos
them
Which object pronoun can substitute the underlined Qué pronombre objeto puede sustituir la frase
phrase in the sentence? subrayada en la oración?
Can you help my sister and me to finish the homework, ¿Puedes ayudar a mi hermana ya mí para terminar la
please? tarea, por favor?
Us nosotros
Turn this statement into a question: Gire esta declaración en una pregunta:
"Molly buys gift certificates at the department store". "Molly compra certificados de regalo en la tienda por
Did Carla __buy___ gift certificates at the department departamentos".
store? Por favor, certificados de regalo Carla __compra___ en
los grandes almacenes?
What's the correct question to get this underlined ¿Cuál es la pregunta correcta para obtener esta
answer?: respuesta subrayada ?:
I went to the movies yesterday. Fui al cine ayer.
When did you go to the movies? ¿Cuándo te vas al cine?
The following phrases remember the things that you experienced as a kid.
1. On my first birthdays I was afraid of clowns.
2. When I see pictures from my childhood I feel nostalgic.
3. I still see some of my schoolmates from elementary school.
____________________________________________________________________________________
What would you do if you´re waiting for someone at the airport and a foreigner approaches you and asks you
this:
"Do you know what time the bank opens?"
I´d try to answer using my knowledge in English.
____________________________________________________________________________________
Choose a logical verb with the correct form of the verb to be for the sentence in future.
“ I _ am going to eat _ hot chips.”
You're invited to a wedding and the invitation says: "After the ceremony, there's a reception with family
and friends”.
Usted está invitado a una boda y la invitación dice: "Después de la ceremonia, hay una recepción con amigos y
familiares".
You understand that:
Usted entiende que:
There will be a reception after the end of the ceremony.
Habrá una recepción después de la final de la ceremonia.
Match the concepts in left column with their corresponding examples on the right column.
Relaciona los conceptos de la columna izquierda con sus correspondientes ejemplos en la columna de la
derecha.
20
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
We use the present continuous tense to Examples:
express:
Usamos el tiempo presente continuo para expresar
1.-Actions that are happening right now. a. My cousin is building his new house next
Acciones que están sucediendo en este momento. month.
2. Future plans. Mi primo construirá su nueva casa el próximo mes.
Los futuros planes. b. Liz is studying hard these days in Canada.
3. Actions that are happening around now or Liz está estudiando duro estos días en Canadá
are temporary. c. Two policemen are following the suspect...
Acciones que están sucediendo alrededor de ahora o watch them, right there!
son temporales. Dos policías están siguiendo al sospechoso ... míralos, justo
ahí!
d. They are starting samba lessons this evening.
Ellos empezaran las lecciones de samba esta noche.
1-c ; 2-a,d; 3-b
How do you offer a drink in a polite way?
¿Cómo ofrece una bebida de una manera cortés?
What would you like to drink?
Qué le gustaría beber?
__________________________________________________________________________________
What option complete the expression below:
¿Qué opción de completar la siguiente expresión:
“I'm a little worried. She's 2 hours late.
"Estoy un poco preocupado. Ella es 2 horas más tarde.
Why __ would __ she __ be __ so late?”
¿Por qué __ estaría ella __ tan tarde? "
___________________________________________________________________________________
Write a logical sentence with the given words:
Escribe una oración lógica con las palabras dadas:
Told / he/ me/ 10:00/ would/ after/ be/he/ here
Contada / él / Me / 10: 00 / se / después / ser / él / aquí
He told me he would be here after 10:00.
Él me dijo que iba a estar aquí después de las 10:00.
__________________________________________________________________________________
In the next sentence, identify the type of verb, not the tense.
En la frase siguiente, identificar el tipo de verbo, no el tiempo verbal.
The girl lives in Mexico.
La niña vive en México.
Regular verb
Verbo Regular
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Is it possible to distinguish irregular and regular verbs in a sentence in present? Why?
¿Es posible distinguir los verbos irregulares y regulares en una frase en presente? ¿Por qué?
No, because the verb in present has no indication of its conjugation.
No, porque el verbo en presente no tiene ninguna indicación de su conjugación.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Is it possible to distinguish in the third person if the verb is regular or irregular?
¿Es posible distinguir en tercera persona si el verbo es regular o irregular?
It´s impossible to distinguish them, no matter what the form is.
Está imposible distinguirlos, no importa lo que la forma es.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
21
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Mayra has to do some homework about "subject pronouns" and "object pronouns". Instead of consulting a
book Mayra decided to check a forum on a website called "MiTarea . com". After asking her questions she
got several answers she has to analyze before she can take one as correct.
This is the dialogue:
Mayra Hello everyone: Can anyone tell me when we use a "subject pronoun" and when an "object
pronoun"?
sent 2 hours ago
Juan when the noun is in the position of the object and we don´t want to repeat the noun, bye
Miguel when we want to substitute a noun in a sentence. If the noun is before the verb we use the
"subject pronoun". If the noun is after the verb we use the "object pronoun".
1 person liked this answer
Ismy when the noun has the function of a subject and we don´t want to repeat it, oxoxo
1 person liked this answer
Jonás when we want to substitute a noun. If the noun is singular, we use a "subject pronoun"...if the
noun is plural we use the "object pronoun" ok?
Mayra Thank you everyone, all your answers are interesting but I think only one is correct.
1 hour ago
Who gave the right answer?
¿Quién le dio la respuesta correcta?
R= Miguel
___________________________________________________________________________________
Is this sentence correct? Why?
¿Es correcta esta frase? ¿Por qué?
“I does get amazed at Day of the Death offerings on November 2nd."
"Estoy sorprendido por el Día de las ofrendas de muertos del 2 de noviembre."
No, because you can use the auxiliary in affirmative, but "do" goes with the subject "I".
No, porque se puede utilizar el auxiliar en afirmativo, porque "hacer" va con el sujeto "I".
____________________________________________________________________________________________
The sentence “These days I'm sleeping a lot.” expresses:
La frase "En estos días me estoy durmiendo mucho." Expresa:
Temporary present, even though it´s not happening at the moment.
Presente temporal, a pesar de que no está sucediendo en el momento.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Indicate if the following sentences are in simple present (S) or present progressive (P):
Indique si las siguientes frases son en presente simple (S) o presente progresivo (P):
1.He reads the newspaper at mornings. S
Lee el periódico en la mañana.
2. I'm speaking English to you because you want to practice it. P
Le hablo en Inglés a usted porque usted quiere practicarlo.
3. They speak Italian and Chinese every day. S
Ellos hablan italiano y chino todos los días.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
__
Read the following sentence:
Lea la siguiente frase:
"Every word on that page is working hard to highlight your talents and skills."
"Cada palabra en esa página está trabajando duro para poner de relieve sus talentos y habilidades."
Now, change it to the gramatically correct interrogative form asking "why?"
22
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Ahora, cambie a la forma interrogativa gramaticalmente correcto preguntar "¿por qué?"
Why is every word on that page working hard to highlight your talents and skills?
¿Por qué cada palabra en esa página trabajando duro para poner de relieve sus talentos y habilidades?
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Relate the tenses on the left to their corresponding questions on the right.
Relaciona los tiempos de la izquierda para sus correspondientes preguntas a la derecha.
Tenses Questions
1. Simple Present b. What do you do?
d. Is your sister at school?
2. Present continuous a. What are you doing?
c. Where is Mexico playing?
e. Is Rafael working in the office, now?
[1-b,d] [2-a,c,e]
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct verb conjugation for the sentence in past continuous.
Choose the correct verb conjugation for the sentence in past continuous.
“ They ______ football at school."
“ They ______ football at school."
were playing
were playing
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Choose a correct verb conjugation for the sentence in past continuous.
Elija una conjugación del verbo correcto para la condena en pasado continuo.
“ We ___________ in a small town.”
"Nos _____________ en un pequeño pueblo."
were living
vivíamos
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the following sentence:
Complete la siguiente frase:
The simple past with regular or irregular verbs indicates an action:___________
El pasado simple con verbos regulares e irregulares indica una acción: ___________
completed or finished in the past.
completado o terminado en el pasado.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Turn the next sentence into a question.
Encienda la siguiente frase en una pregunta.
Pepe was sleeping because the Math class was boring.
Pepe estaba durmiendo porque la clase de Matemáticas era aburrido.
__________________ because the Math class was boring?
____________________ Porque la clase de Matemáticas era aburrido?
Was Pepe sleeping
Fue Pepe durmiendo
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Si tuvieras que presentar un examen de colocación de inglés en el ingreso a la universidad, ¿cuál crees que es tu
desempeño en el manejo de los tiempos en pasado y presente?
Bueno, porque tienes bastante vocabulario, conoces las estructuras y manejas los verbos en sus diferentes
conjugaciones.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
What is the tense for each sentence?
¿Cuál es el tiempo para cada oración?
The British Trevor Baylis invented in 1996 a wind-up radio. It doesn't need electricity or batteries. You wind it up by
hand. He got the idea for the radio while he was watching TV.
El británico Trevor Baylis inventó en 1996 una radio de cuerda. No necesita electricidad ni baterías. Usted enrolla para arriba con la
mano. Él tuvo la idea de la radio mientras él estaba viendo la televisión.
Past, present, present, past, past progressive.
Pasado, presente, presente, pasado, pasado progresivo.
23
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
____________________________________________________________________________________________
We call them regular verbs because the past tense of each is formed by adding "ed" to the end of the verb.
Los llamamos los verbos regulares porque el tiempo pasado de cada uno se forma añadiendo "ed" al final del verbo.
But some verbs have many different ways of forming the past tense, because there is no regular pattern, these
verbs are kown as irregular verbs. Pero algunos verbos tienen muchas maneras diferentes de formar el tiempo pasado, porque
no hay un patrón regular, estos verbos son kown como verbos irregulares.
Change to past tense the following verbs: choose, weep, like, beat, drive, fly
Cambio de tiempo pasado los siguientes verbos: elegir, llorar, como, batir, conducir, volar
chose, wept, liked, beat, drove, flew.
eligió, llorado, me gustó, golpe, condujo, voló.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
The following sentence:
La siguiente frase:
“Mi automóvil corre más rápido que el tuyo”, would be translated to English as:
"Mi automóvil corre Más rápido Que el tuyo", se traduciría a Inglés como:
My car runs faster than yours.
Mi coche corre más rápido que el suyo.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Tu asesor de Módulo 3 “Mi vida en otra lengua”, te da material de un tema nuevo para que lo estudies sobre "el uso de
los plurales irregulares" , pero no logras entenderlo, ¿qué haces?
Buscas más referencias para entenderlo, si es necesario pides ayuda al asesor.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct words to complete the following sentence:
Elegir las palabras correctas para completar la siguiente frase:
Javier has ______ books on his desk, but Sandra doesn`t have _____ books on her desk.
Javier tiene _____________ libros sobre su escritorio, pero Sandra no tiene ___________ libros sobre su escritorio.
Some y any
Algunos y cualquier
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct preposition for the sentence:
Elegir la preposición correcta para la frase:
at, on, in or after
en, sobre, en o después
The telephone and the door bell rang ______________ the same time
El teléfono y sonó el timbre de la puerta ______________ mismo tiempo
At
en
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Analyzes time expressions on the left with the right phrases.
Analiza las expresiones de tiempo de la izquierda con las frases de la derecha.
Time expressions Sentences.
1. at a. They arrived ___ three o'clock in the afternoon.
d. I went to Saltillo _______ age five.
2. on b. Maradona was born ______ the 3rd of February.
c. My children got up ______ Sunday morning.
d. I went to Saltillo _______ age five.
Read the text and complete it with the correct pronouns :
Lea el texto y completarlo con los pronombres correctos:
1.He came to church with ____ (her/she), as ____ (him/he) always did.
Él vino a la iglesia con ____ (ella / ella), como ____ (él / ella) siempre lo hicieron.
2. ____ (her/she) took the precaution to place ____ (him/he) next to her.
____ (ella / ella) tomaron la precaución de colocar ____ (él / ella) a su lado.
her he she him
24
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
su (de ella) él ella su (de él)
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Observe the picture and complete the sentences with the correct pronoun:
Observa la imagen y completa las frases con el pronombre correcto:
1.Susana I'm so nervous! this is our first time in a contest!
Susana estoy tan nerviosa! esta es nuestra primera vez en un concurso!
2. Mateo: You are doing great, don't be afraid. People will notice it, as I do.
Mateo: Lo estás haciendo muy bien, no tengas miedo. La gente se dará cuenta que, como yo.
3. Mateo: _____ (they/them) will clap a lot.
Mateo: _____ (ellos / ellas) darán muchos aplausos.
4. Other competitors: Watch ____ (they/them), they are incredible!
Otros competidores: Mira ____ (ellos / ellas), que son increíbles!
5. Other competitors: Let's ask ____ (they/them) to teach ________ (we/us)!
Otros competidores: Pidámosle a ____ (ellos / ellas) nos enseñen a _______ (nosotros / nosotros)!
they them them us
ellos ellos ellos nos
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
¿Qué método utilizas para comprender temas como el uso de los pronombres y adjetivos?
Buscar datos que te remitan a la información relevante para aprenderla.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
Turn the first statement into a question:
Cambia la primera declaración en una pregunta:
"My sister and I needed to get up early the last month, because we didn't have a car".
"Mi hermana y yo teníamos que levantarnos temprano el último mes, debido a que no tenemos coche".
_____________ need to get up early last month?
__________ era necesario levantarnos temprano el mes pasado?
Did we
Hemos
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Change the statement below to the negative form in past tense:
Cambie la instrucción abajo para la forma negativa en tiempo pasado:
"She mixes the ingredients for the Thanksgiving stuffing".
"Ella Mezcla los ingredientes para el relleno de Acción de Gracias".
She __________the ingredients for the Thanksgiving stuffing this morning.
Ella __________ los ingredientes para el relleno de Acción de Gracias esta mañana.
didn´t mixed
No mexcló
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the sentences below with the appropriate word:
Completa las frases siguientes con la palabra adecuada:
A._____ you go to Veracruz on Saturday?
_______ vas a Veracruz el sábado?
B. No, we ______ We went to Acapulco.
No, nosotros ______ Fuimos a Acapulco.
Did y didn't.
Hizo y no lo hizo.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Classify the following sentences as true (T) or false (F).
Clasifica las siguientes frases como verdaderas (T) o falsas (F).
Sentences True (T) or false (F)
1. Negatives in the simple past tense are formed by adding DID NOT before the simple T
form of the verb.
2. The verb BE is not an exception to the previous sentence. F
25
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
3. YES / NO questions in the simple past are NOT created using the auxiliary DID. F
4. Questions with WH words in simple past are created by using the auxiliary DID T
before the subject.
Rewrite the sentence using the simple future tense.
Vuelva a escribir la frase con el futuro simple.
"The team has a party".
"El equipo tiene una de las partes".
The team will have a party.
El equipo tendrá una fiesta.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Rewrite the sentence using the simple future tense:
Vuelva a escribir la frase con el futuro simple:
"Juan is an expert on using computers".
"Juan es un experto en el uso de computadoras."
Juan will be an expert on using computers.
Juan va a ser un experto en el uso de computadoras.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Order the numbers of the following words to make a logical sentence in the conditional for future.
Orden los números de las siguientes palabras para formar una frase lógica en condicional para el futuro.
1. every day
2. your brain
3. read
4. work
5. better
6. if you
7. will
If you read every day your brain will work better.
Si usted lee todos los días su cerebro funcione mejor.
6 3 1 2 7 4 5
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Read the sentence and choose which answer is the correct one for this situation.
Lee la oración y elige qué respuesta es la correcta para esta situación.
You arranged to play tennis today.
Usted arregló para jugar al tenis hoy.
Now you decide that you don't want to play.
Ahora usted decide que no quiere jugar.
You say: ___________________________.
Usted dice: ___________________________.
I don't think I´ll play tennis today.
No creo que voy a jugar al tenis hoy.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Order the words to make a coherent sentence.
Ordenar las palabras para formar una frase coherente.
1. movies
2. the
3. I
4. to
5. am
6. going
I am going to the movies.
Voy al cine
356421
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the sentences using the correct form of “going to”.
26
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Completa las frases usando la forma correcta de "ir a".
Choose afirmative, interrogative or negative.
Elija afirmativas, interrogativas o negativas.
1. Pedro's sweater is dirty. He (wash) _________________ it.
2. I've decided to pick up some eggs. I (fry) _______________ them.
3. Rosa needs that sofa. She (sell) _________________ it.
4. My tooth is aching a lot. I (visit) ____________ my dentist.
1-is going to wash 2- am going to fry 3- isn't going to sell 4- am going to visit
1-se va a lavar 2- voy a freír 3- no va a vender 4-voy de visita
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
Si conocieras a una persona de habla inglesa a través de una red social ¿cómo intercambias información con ella sobre
tu proyecto de vida?
Expresarías de manera autónoma tus ideas utilizando las nociones gramaticales y vocabulario propias para su
formulación.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
What's the right short answer for this?
¿Cuál es la respuesta corta justo para esto?
“Would you like to go to the movies next weekend?”
"¿Quieres ir al cine próximo fin de semana?"
No, I wouldn't.
No, yo no lo haría.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Order the following words to make a coherent sentence.
Ordene las siguientes palabras para formar una frase coherente.
1. he
2. be
3. would
4. the
5. organizing
6. not
7.?
8. evidence
3 1 6 2 5 4 8 7
Would he not be organizing the evidence?
¿No le organizará las pruebas?
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
__
Is the underlined part correct? Why?
¿Es correcta la parte subrayada? ¿Por qué?
“Ignacio wanted to leave early, but his boss wouldn't let him.”
"Ignacio quería salir temprano, pero su jefe no se lo permitió."
It's correct to use “wouldn't” for a refusal in negative in past.
Es correcto usar "no" para una negativa en negativo en el pasado.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
Choose a verb for the sentence:
Cambia el verbo en cada frase:
“The Gomez family members ____ dinner together every night.”
“Los miembros de la familia Gómez _______ comen juntos todas las noches”
Eat
Comer
____________________________________________________________________________________
27
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
The following sentences are in present progressive or simple present tense.
Las siguientes frases están en presente progresivo o tiempo presente simple.
1.Simple present I otfen write poems to my wife.
Escribo poemas a mi esposa.
The sun barely shines with this weather.
El sol apenas brilla con este tiempo.
2. Present continuous My brother is playing the guitar at the moment.
Mi hermano está tocando la guitarra en este momento.
Your parents are talking now.
Sus familiares están hablando ahora.
Jose is taking his grandparents to his house in this moment.
José está hablando a la casa de de sus abuelos en este momento.
Decide which sentences are true.
Decide cuales frases son verdaderas.
1. We use the present continuous to talk about what's happening now. True
Usamos el presente progresivo cuando hablamos de lo que está pasando ahora.
2. "Now", "at the moment" are simple present time expressions. False
“Ahora” “en este momento” son expresiones del tiempo presente simple.
3. In the simple present tense we add "ing" to all the verbs. False
En el tiempo presente simple agregamos “ing” a todos los verbos.
4. We use the auxiliary verb "to be" with the present progressive tense. True
Usamos el verbo auxiliar “to be” con el tiempo presente progresivo.
Choose the correct verb conjugation for the sentence in past continuous.
Cambia la conjugación correcta del verbo para las frases en pasado progresivo.
“My parents ________ for me.”
“Mis familiares _________ por mi”
were waiting
están esperando
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct verb conjugation for the sentence in past continuous.
Cambia la conjugación correcta del verbo para las frases en pasado progresivo.
“ We ____ the four o'clock bus.”
“Nosotros ________ el autobús a las cuatro en punto”.
were taking
tomamos
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
Past progressive indicates:
El pasado progresivo indica:
An action in progress in the past at a specific time.
Una acción en progreso en un tiempo pasado especifico.
____________________________________________________________________________________
Complete the conversation using the correct form of the verbs for past progressive. Use the verbs in
parenthesis.
Completa la conversación usando la forma correcta de los verbos en pasado progresivo. Usa los verbos en paréntesis.
Lupe: I’m afraid I’ve broken the pot for the mole.
Me temo que he roto la olla para el mole.
1
Pedro: Oh no! What _____________ (do)?
¡Oh, no! qué estabas haciendo (hacer)?
2
Lupe: I __________ (take) it into the dinning room.
yo estaba tomando (tomo) en el comedor.
3
I bumped into Chayo. She ____________ (come) out just as
Me topé con Chayo. Ella estaba saliendo (vamos) justo cuando
4
I _________ (go) in.
Yo estaba entrando (ir).
1- were you doing 2- was taking 3- was coming 4- was going
haciendo estaba tomando estaba saliendo estaba entrando
28
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
Analyze if the highlighted forms of present or past progressive are adequately used in this context by
choosing correct (C), or incorrect (I) if simple present or simple past should be used. Mark the sequence of
the words in the text when you answer in the chart:
“Now I’m reading about how to be a lot more careful about the environment. I’m living in Mexico City and
Correcto Incorrecto
there´s a lot of pollution. There were trees and birds everywhere in the past, the sun was shining and people
Incorrecto
enjoyed the city a lot more. Moreover, currently violence and crime are affecting us very hard, although
Correcto
everybody is fighting against them. Time’s running fast and we’re requiring some kind of solution.
Correcto Correcto Correcto
_______________________________________________________________________________
Complete the conversation with the correct past forms of verb.
Complete la conversación con las formas correctas del verbo en pasado.
"to be"
“ser o estar”
Lore: I ________ in Istanbul last summer.
Lore: Yo estuve en Estambul el verano pasado.
Roberto: Really? How long ________ you there?
Roberto: En serio? Cuánto estuviste aquí?
Lore: For three weeks
Lore: Por tres semanas.
Roberto: ________you there on business or on vacation?
Roberto: Estuviste aquí de negocios o de vacaciones?
Lore: I _______there for fun.
Lore: Yo estuve aquí por diversión.
was were were was
estuve estuviste estuviste estuve
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct answer according to the picture below.
Cambia la respuesta correcta de acuerdo a la imagen.
Which is the nearest mainland neighbor?
South Korea
________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct form of the adjective in parenthesis for each of the following sentences.
Cambia la forma correcta de los adjetivos de los parentesis para cada una de las siguientes frases.
1. "This is (cheap, cheaper, cheapest) than that one", said the seller.
"Este es (barato, más barato, más barato) que el otro", dijo el vendedor.
2. Today there are (nice, nicer, nicest) people than yesterday.
Hoy hay (bonito, bonitos, agradables) personas que ayer.
29
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
3. Sorry, teacher, could you tell me who the (smarter, smartest, most smart) pupil in your class is?
Lo sentimos, maestro, ¿podría decirme quién es el (inteligente más inteligente más inteligente,,) de los
alumnos en su clase es?
4. There is no doubt about it. She is the (better, best, more good).
No hay duda de ello. Ella es la (mejor, mejor, más bien).
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct plural noun for the following sentence.
Elija el sustantivo plural correcto para la siguiente frase.
“As we get older, so do our _______ !”
"A medida que envejecemos, también lo hacen nuestros ________!"
teeth
dientes
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Decide which answer matches each question.
Decide cual respuesta corresponde a cada pregunta.
Questions Answers
pregunta Respuesta
1.How many servings of fruit do you eat each day? Two or more.
¿Cuántas porciones de frutas come cada día?
2. How much junk food do you eat? Very little.
¿Cuánta comida chatarra come? A lot of it.
3. How often do you exercise or play a sport per day? Never.
¿Con qué frecuencia hace ejercicio o de practicar deporte al día?
Why is the following sentence incorrect?:
¿Por qué es la siguiente frase incorrecta ?:
“Too much mouses threatens public health”
"Demasiado mouses amenaza la salud pública"
Because the plural of "mouse" is "mice". The verb is not used in the correct form.
Debido a que el plural de "mouse" es "ratones". El verbo no se utiliza en la forma correcta.
We don´t use "much" with countable nouns.
No usamos "mucho" con sustantivos contables.
__________________________________________________________________
What is the difference between countable and uncountable nouns?
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre los sustantivos contables e incontables?
Countable nouns have a plural form and the uncountable nouns can't be used in
plural form.
Sustantivos contables tienen una forma plural y los sustantivos incontables no se pueden utilizar en forma plural.
____________________________________________________________________
Indicate which of the following words in the sentence is an uncountable noun:
Indique cuál de las siguientes palabras en la oración es un sustantivo incontable:
The school has 5 backyards, 3 slides and 2 bookstores.
La escuela cuenta con 5 patios, 3 toboganes y 2 librerías.
None
ninguno
__________________________________________________________________
Check if the prepositions "in" , "at", are correct in the following the sentences.
Compruebe si las preposiciones "en", "a", son correctas en las siguientes frases.
I heard a terrible noise in the middle of the night. I was awake because I usually
work at night.”
Oí un ruido horrible en el medio de la noche. Yo estaba despierto porque yo suelo trabajar en la noche ".
Both are correct because they are standard expressions.
Ambas son correctas porque son expresiones normales.
__________________________________________________________________
30
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
In which of these sentences are the prepositions used correctly?
¿En cuál de estas frases las preposiciones se utilizan correctamente?
1.My daughter is coming home next Monday. Si
Mi hija viene a casa el próximo lunes.
2. I am used to watching TV in the morning. Si
Estoy acostumbrado a ver la televisión por la mañana.
3. In Mexico everybody usually goes home at every No
Christmas.
En México todo el mundo por lo general va a casa en cada Navidad.
4.My children always get up late on Sunday mornings. Si
Mis hijos siempre se levantan a última hora del domingo por la mañana.
Match the correct grammar preposition of time. Prepositions may repeat.
Relaciona con la preposición gramática correcta del tiempo. Las preposiciones pueden repetirse.
Example Preposition of time
1._on_ February 14th, is Valentine's day. on
El 14 de febrero, es el Día de San Valentín.
2. _at_ half past three, i'm going to the at
cinema.
Las tres y media, voy al cine.
3. _in_ June, I will do it. in
en junio, lo haré.
____________________________________________________________________
Complete the next paragraph with the correct time expressions given in
parenthesis.
Complete el siguiente párrafo con las expresiones temporales correctas dadas en paréntesis.
Write the answer following the sequence of the numbers.
Escribe la respuesta siguiendo la secuencia de los números.
“We traveled1 _on_ (on-it-at) Friday.
"viajamos el Viernes.
We got to the airport2 on (on-in-at) time to have a coffee before checking in, 3 _at_
(on-in-at)
the airline's counter.
Llegamos a la Airport a tiempo para tomar un café antes de registrarse, antes del registro del contador de la aerolínea.
Fortunately, the plane took off 4 _on_ (on-in-at) time.
Afortunadamente, el avión despegó a tiempo.
__________________________________________________________________
Choose the correct words to complete the next text in English.
Elige las palabras correctas para completar el siguiente texto en Inglés.
If it´s necessary you can use a word more than once.
Si fuera necesario, puedes usar una palabra más de una vez.
“Tell me, please. Why _did_you invite him when Mary did know he was the thief?
"Dime, por favor. ¿Por qué María le saben que él era el ladrón?
__________________________________________________________________
What's the contraction of "will not"?
¿Cuál es la contracción de "no"?
won't
no lo hará
____________________________________________________________________
Order 6 of the following numbers to make a coherent sentence.
Ordena los 6 números siguientes para hacer una frase coherente.
31
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
1. potato chips
2. the saltiest
3. why
4. are
5. snack
6. ?
3 4 1 2 5 6
Why are potato chips the saltiest snack?
¿Por qué son las papas fritas saladas?
_____________________________________________________________________
Is this question correct or not? Why?
¿Esta pregunta es correcta o no? ¿Por qué?
“Did she tell you what time did the last train leave?”
"¿Le dijo a qué hora dejó el último tren?"
It's incorrect because in an embedded question after the Wh word we can't use
another auxiliary before the subject, the second sentence has to be affirmative or
negative.
Es incorrecta porque en una pregunta incrustada después de la palabra Wh no podemos utilizar otro auxiliar
antes el tema, la segunda frase tiene que ser afirmativa o negativa.
____________________________________________________________________
Order the next words to make a meaningful sentence.
Ordene las siguientes palabras para hacer una frase con sentido.
1. you
2. last
3. ?
4. go
5. week
6. did
7. where
7 614253
Where did you go last week?
¿A dónde fuiste la semana pasada?
____________________________________________________________________
Rewrite the sentence using the simple future tense
Vuelva a escribir la frase con el futuro simple
"I am a teacher".
"Yo soy un profesor".
I will be a teacher.
Voy a ser un maestro.
____________________________________________________________________
32
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
What does this sentence express?
¿Qué expresa esta frase?
“I'll take a seat. Look over there, there's an empty chair.”
"Voy a tomar un asiento. Mira hacia allá, hay una silla vacía ".
A decision made at the moment of speaking.
Una decisión tomada en el momento de hablar.
____________________________________________________________________
Order the following words to make a coherent sentence.
Ordene las siguientes palabras para formar una frase coherente.
1. be
2. will
3. Christmas
4. where
5. Eve
6. you
7. on
8. ?
4 2 6 1 7 3 5 8
Where will you be on Christmas eve ?
¿Dónde vas a estar en la víspera de Navidad?
____________________________________________________________________
Complete the conversation using the modal auxiliary would.
Complete la conversación utilizando el auxiliar modal haría.
You are on a bus. You have a seat but an elderly man is standing. You offer him
your seat.
Usted está en un autobús. Usted tiene un asiento pero un anciano está de pie. Tú le ofreces tu asiento.
You: _________________________________
Usted: ________________________________________
Man: Oh, that's very kind of you. Thank you very much.
Hombre: Oh, eso es muy amable de su parte. Muchas gracias.
Would you like to sit down?
¿Quieres sentarte?
__________________________________________________________________
If we are planning to buy a new book in preparation for an exam, it is best to use:
Si estamos pensando en comprar un nuevo libro en preparación para un examen, lo mejor es:
going to buy
ir a comprarlo
33
Descargado por Charly Nieto (carlos27nc@gmail.com)
Encuentra más documentos en www.udocz.com
You might also like
- 12 Guia Mdulo 12 Mi 444812 Downloadable 4685341Document34 pages12 Guia Mdulo 12 Mi 444812 Downloadable 4685341Janai ReyesNo ratings yet
- 12-Guia Mã"dulo 12 Mi Vida en Otra LenguaDocument33 pages12-Guia Mã"dulo 12 Mi Vida en Otra Lenguaaventuras en familiaNo ratings yet
- Módulo 12 - Preguntas EvaluativasDocument31 pagesMódulo 12 - Preguntas EvaluativasMargely HerreraNo ratings yet
- Need FreeDocument31 pagesNeed Freedmahin34No ratings yet
- Ingles Practica 1-3Document19 pagesIngles Practica 1-3juan pintoNo ratings yet
- Colegio Santa Barbara - Actividades de adjetivos terminados en '-ed' e '-ingDocument14 pagesColegio Santa Barbara - Actividades de adjetivos terminados en '-ed' e '-ingyuli pachecoNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument6 pagesPronounsRizky ExterminateurNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review 1Document64 pagesGrammar Review 1Jafeth Candia MoralesNo ratings yet
- Clases Lunes y Martes RepasoDocument9 pagesClases Lunes y Martes RepasoYessica GalindezNo ratings yet
- Guía Primer Parcial Inglés 5Document18 pagesGuía Primer Parcial Inglés 5Mayte LópezNo ratings yet
- John's Basic English Reviewer (Notes)Document40 pagesJohn's Basic English Reviewer (Notes)Mary Bianca ZipaganNo ratings yet
- The 8 Parts of Speech in 40 CharactersDocument12 pagesThe 8 Parts of Speech in 40 CharactersMamaMo PanotNo ratings yet
- Learn!: Let' SDocument36 pagesLearn!: Let' Ssim williamNo ratings yet
- Observations from the Wounded Yak: A Relationship's Journey Through Space and TimeFrom EverandObservations from the Wounded Yak: A Relationship's Journey Through Space and TimeNo ratings yet
- PRESENT PROGRESSIVE TENSEDocument6 pagesPRESENT PROGRESSIVE TENSEFriskaLubisAzahra SNo ratings yet
- Some Points About English Language: M.N.SamavatiDocument20 pagesSome Points About English Language: M.N.SamavatiMaryamNo ratings yet
- Pedro Ruiz Gallo National UniversityDocument7 pagesPedro Ruiz Gallo National UniversityWalter FabianNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris 1: Prodi D3 Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Ilmu Terapan Universitas TelkomDocument31 pagesBahasa Inggris 1: Prodi D3 Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Ilmu Terapan Universitas TelkomAnik DarwatiNo ratings yet
- Airforce Group X 4 November 2020 Memory Based Paper 84e6dcb8Document51 pagesAirforce Group X 4 November 2020 Memory Based Paper 84e6dcb8Spy HanNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument51 pages8 Parts of Speech in EnglisharmanoticNo ratings yet
- Chuyên Đề 1: Be/ Pronouns/ Possessive Adjectives/ Countable NounsDocument8 pagesChuyên Đề 1: Be/ Pronouns/ Possessive Adjectives/ Countable NounsHienNo ratings yet
- CONTENTDocument44 pagesCONTENTkamawisNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns and Verb "To BeDocument13 pagesPersonal Pronouns and Verb "To BeMaryurys SalasNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous TenseDocument5 pagesPast Continuous TenseDost JanNo ratings yet
- English Word Order RulesDocument4 pagesEnglish Word Order RulesSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- Handout - Nominative, Accusative, and Dative - When To Use ThemDocument2 pagesHandout - Nominative, Accusative, and Dative - When To Use ThemZulqarnain ShahNo ratings yet
- Power Point PronounDocument14 pagesPower Point PronounRIANTO OTNIELNo ratings yet
- Tense and TimeDocument6 pagesTense and TimeSatarupa SenNo ratings yet
- English WarmDocument3 pagesEnglish WarmNataly BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Les PronomsDocument4 pagesLes Pronomsapi-299513272No ratings yet
- What is a PronounDocument4 pagesWhat is a PronounWhy ShortNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesPast Continuous TenseDr. Amr AboelmagdNo ratings yet
- Learn English: Student's Guide to Grammar RulesDocument80 pagesLearn English: Student's Guide to Grammar RulesEduardo Casanova100% (1)
- Verb BE BritishCouncilDocument4 pagesVerb BE BritishCouncilFAVargasANo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns and Verb "To Be"Document13 pagesPersonal Pronouns and Verb "To Be"Maryurys SalasNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous: Affirmative Form + + +Document4 pagesPresent Continuous: Affirmative Form + + +Sara HagemannNo ratings yet
- The Verb + A Policeman. Happy. A Teacher. and Sad. Small. A Student. Tired. 1. Select The Correct For The FollowingDocument4 pagesThe Verb + A Policeman. Happy. A Teacher. and Sad. Small. A Student. Tired. 1. Select The Correct For The FollowingNicoleta FloreaNo ratings yet
- Basic English Grammar: By: Ashwini H Asst - Prof of English Department of Humanities Canara Engineering CollegeDocument20 pagesBasic English Grammar: By: Ashwini H Asst - Prof of English Department of Humanities Canara Engineering CollegeDhanush ShastryNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar UkinDocument44 pagesBahan Ajar Ukinagustina kurnianingsihNo ratings yet
- Noun Pronoun Verb Adjective Adverb Preposition Conjunction InterjectionDocument19 pagesNoun Pronoun Verb Adjective Adverb Preposition Conjunction InterjectionFerizalGunawanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Symbols For Nouns and AdjectivesDocument4 pagesGrammar Symbols For Nouns and Adjectiveshelena23jNo ratings yet
- Noun and Pronoun GuideDocument17 pagesNoun and Pronoun GuideFariz KareemNo ratings yet
- Project Paper GrammarDocument20 pagesProject Paper GrammarAisyah Nurhuda Ahmad FirdausNo ratings yet
- BASIC GRAMMAR FOR TOEFLDocument9 pagesBASIC GRAMMAR FOR TOEFLHimatul AuliaNo ratings yet
- Momo's WorkDocument77 pagesMomo's WorkEne AideyanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech - English: They Went To The StoreDocument1 pageParts of Speech - English: They Went To The Storeg8legendaryNo ratings yet
- Hybrid English 4 Q2 M3 W3Document10 pagesHybrid English 4 Q2 M3 W3Jedasai PasambaNo ratings yet
- English Language: Semester 2Document63 pagesEnglish Language: Semester 2lelanieNo ratings yet
- Elementary - Eng 210712 201735Document471 pagesElementary - Eng 210712 201735Marco Antonio WilmotNo ratings yet
- Lectura Unidad 1Document15 pagesLectura Unidad 1brandon jonesNo ratings yet
- There Is/there AreDocument23 pagesThere Is/there ArePris FeversaniNo ratings yet
- Tips On How To Answer Paper 1: English Language 014/1Document56 pagesTips On How To Answer Paper 1: English Language 014/1gracie beadloverNo ratings yet
- THE MATERIAL FOR 3rd MEETINGDocument9 pagesTHE MATERIAL FOR 3rd MEETINGRahmiati IsnainiNo ratings yet
- English 101Document15 pagesEnglish 101MothNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument1 pageInglesJim_mexNo ratings yet
- Les PronomsDocument9 pagesLes PronomsTanvi NaikNo ratings yet
- DTRA Russian Grammar Course ReviewDocument240 pagesDTRA Russian Grammar Course ReviewNor Nor CHNo ratings yet
- Ingles IIDocument14 pagesIngles IINatalia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Becs I Week 5 ModuleDocument11 pagesBecs I Week 5 ModuleJayson GarciaNo ratings yet
- Disjunctive Questions - Short AnswersDocument12 pagesDisjunctive Questions - Short AnswersIrina SavchikNo ratings yet
- Wo F CL PDFDocument376 pagesWo F CL PDFdumezil3729No ratings yet
- Present Simple V.2Document20 pagesPresent Simple V.2manuelNo ratings yet
- Guia - Lic. Ariana MendozaDocument55 pagesGuia - Lic. Ariana MendozaEsteban Molina RamosNo ratings yet
- You Are What You Eat: VocabularyDocument12 pagesYou Are What You Eat: VocabularyRoux McNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech Explanation Video What Is Direct and Indirect Speech Definition?Document21 pagesDirect Indirect Speech Explanation Video What Is Direct and Indirect Speech Definition?Estelle Nica Marie DunlaoNo ratings yet
- (15 Quyển) Test Pack - ElementaryDocument47 pages(15 Quyển) Test Pack - Elementaryvip01No ratings yet
- That's A Cool CarDocument7 pagesThat's A Cool CarBetsy TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: He Wants, She Needs, He Gives, She ThinksDocument10 pagesSimple Present: He Wants, She Needs, He Gives, She ThinksAisyah RasdiNo ratings yet
- Pragmatic Strategies and Linguistic Structures in Making Suggestions'Document12 pagesPragmatic Strategies and Linguistic Structures in Making Suggestions'Andreea TabarnacNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument13 pagesReported Speechhellrider244No ratings yet
- Evision: Present Simple - Present ContinuousDocument28 pagesEvision: Present Simple - Present ContinuousMaha Al AmadNo ratings yet
- Ingles 4 Unit 1 Past Simple Tense in Affirmative, Negative and Interrogative FormDocument4 pagesIngles 4 Unit 1 Past Simple Tense in Affirmative, Negative and Interrogative FormMANUEL ARMANDO NEVAREZ NIETONo ratings yet
- Past Simple Continuous 7 Tasks BW With Key Tests 72223Document3 pagesPast Simple Continuous 7 Tasks BW With Key Tests 72223milenerato2240No ratings yet
- Judgment and PropositionDocument7 pagesJudgment and PropositionJeanette FormenteraNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Grammar And: MairovergaraDocument23 pagesVocabulary Grammar And: MairovergaraGabriel R. FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 啊Document83 pages啊Julian LeeNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs-2Document23 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs-2Atasha GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Ingles Sec1 PDFDocument26 pagesIngles Sec1 PDFJoselin RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Unit-01 SentenceDocument18 pagesUnit-01 SentencekhaniicuevasNo ratings yet
- 1 EPS-ToPIK English Book - 1 BolanDocument324 pages1 EPS-ToPIK English Book - 1 BolanBrightNo ratings yet
- Greetings and introductions unit for ESL learnersDocument11 pagesGreetings and introductions unit for ESL learnersAri SusiloNo ratings yet
- iPLAN 1Document2 pagesiPLAN 1Marlyn CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Technical Communication MCQDocument53 pagesTechnical Communication MCQATUL SHARMA64% (14)
- Present Simple Interrogative: We Use Do or Does To Make Questions The Verb Doesn'T Change in 3Rd Person Singular!Document2 pagesPresent Simple Interrogative: We Use Do or Does To Make Questions The Verb Doesn'T Change in 3Rd Person Singular!luis figueroaNo ratings yet
- Inglês SIMPLE PAST - ExercisesDocument4 pagesInglês SIMPLE PAST - Exercisesclaudiamsmonteiro-1No ratings yet
- Manual InglesDocument46 pagesManual InglesveracampinaNo ratings yet
- P - 7 English Lesson Notes PDFDocument48 pagesP - 7 English Lesson Notes PDFsimbi yusuf50% (2)
- Redundancy3 PDFDocument17 pagesRedundancy3 PDFMaisa KraizemNo ratings yet
- Rules For Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesRules For Reported SpeechPannaNo ratings yet