Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11 - The P-Block Elements
Uploaded by
Runjhun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageOriginal Title
11_The P-Block Elements
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 page11 - The P-Block Elements
Uploaded by
RunjhunCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
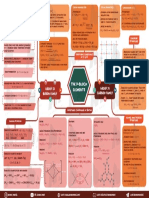
Atomic & Physical Properties Silicates Carbon Monoxide (CO) Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) Carbondioxide (CO2)
. Basic Unit is SiO44– . Preparation: . Preparation
. Covalent, three dimensional
Electronic configuration: [Noble gas] ns2np1 . They exist in different structures like C + 2H2 O → CO + H 2 network solid. CaCO 3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
chain, ring, sheet or 3-D structure. Watergas CH4 + 2O2 CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
. Almost non-reactive due to
. Zeolites are 3-D silicates in which some high Si—O bond enthalpy.
of the Si atoms are replaced by Al+3 ions. 123 K
. 2C + O2 + 4N 2 → 2CO + 4N2
. It is consumed during photosynthesis
Oxidation state: +1 & +3 They are used in water softening. . Acidic in nature. 6CO3 + 12H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Pr oducergas
SiO2 + 2NaOH Na2SiO3 + H2O
. Highly poisnous due to formation of a
Metalliccharacter : B
Al Ge In Tl
complex with haemoglobin.
NonMetal Metals
Silicones . acts as reducing agent Chemical
ZnO(s) + CO(g) Zn(s) + CO2(g) Properties
. Contains repeated R 2Si(OH)2units held
Atomic radii, ionic radii, density & stability
of +1 oxidation state: Generally increase
by Si - O - Si linkage. Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
Cu powder
down the group. 2RQ + Si R2SiCl2 . Reactivity towards air: They form
R2SiCl2 + 2H2O R2Si(OH)2 + 2HCL Important Compounds oxides of the formula EO and EO2
of C & Si on heating with air.
Boiling point & stability of +3 oxidation state: n[R2Si(OH)2 ] Polymerise
Silicone
Decreases down the group. . Acidic strength of their oxides dec. down
. They are water repelling due to non-polar the group.
alkyl group. CO2, SiO2 GeO2 SnO PbO
2, 2
Electronegativity: B > Tl > In > Ga > Al Acidic Less Acidic Amphoteric
. Reactivity towards water: only Sn
reacts with steam.
Al Ga Si Ge
Melting point: Dec. from B to Ga then increases.
B > Al > Ga > In > Tl
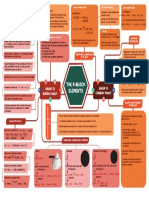
THE P-BLOCK
B GROUP 13 I ELEMENTS C
GROUP 14 Pb
. Reactivity towards halogen: They form
halide of formula EX2 and EX4 most of
BORON FAMILY CARBON FAMILY the EX4 are covalent in nature.
Ionisation Energy: B > Tl > Ga > Al > In
Tl S . Except CCl4 , Other halides are easily
Hydrolysed by water
Lewis Acid: BCl3, AlCl3 etc behaves as Lewis SiCl4 + 4H2O Si(OH)4 + 4HCl
Acid due to incomplete octet. Silicic acid
Important Compounds of Boron
Atomic and Physical
Chemical Properties Borax Diborane
Properties
Orthoboric Acid
Na2B4O7.10H2O B2H6 H3BO3
∆
Reactivity towards Air→ 4E + 3O 2 → 2E2 O3 White Crystalline Solid Preparation . Electronic configuration:
Colourless, highly toxic gas White crystalline solid, Non protic acid [Noble gas] ns2 np2
B
2 O3
Al 2O3 Ga 2O3
In 2O3
Tl 2 O3 4H3 BO3 + Na 2 CO3 → Na 2 B 4O7 + 6H2O + CO2
preparation preparation
Acidi Amphoteri Basic 456 K
. Oxidation state: +2 & +4
Reactions 2BF3 + 6NaH → B 2 H6 + 6NaF Na2 B 4O7 + 2HCl + 5H2 O → 2NaCl + 4H3 BO3
. Atomic radii, metallic
∆ Na 2 B 4O7 + 7H 2O → 2NaOH + 4H3 BO3
2E + N2 → 2En{ Excep Ga, In, Tl } 2NaBH4 + I2 B2H6 + 2NaI + H2 reaction
character & stability of +2
Oxidation state generally increase
Heating 370K
H3 BO3 → HBO2 + H 2 O down the group.
Reactivity towards halogens: Na2B4O7 → 2NaBO2 + B2O3 reaction Monoboric acid C < Si < Ge < Sn < Pb
2E + 3X 2 → 2EX 3 (Except TlI3) B 2H6 + 3O2 → B2 O 3 + 3H2 O HBO2 B2O3 H
O . Catenation: Decreases down
3B2H6 + 6NH3 3[BH2 (NH3)2]+[BH4]- the group.
( X = F, Cl, Br, I ) Sp2 hybridized
HO
Sp3 hybridized H
B
B
∆ O O Pb does not show catenation.
Boron Atom Boron Atom 2B3N3H6 + 12H2
O
O H H C >> Si > Ge ≈ Sn
Reactivity towards Acids and alkalies HO B O OH 2Na+ . 8H2O
B
H H O O . Ionization enthalpy
H H H
2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq.) 2Al3+ + 6Cl-(aq.) + 3H2(q) H B
O
(aq.)
O
O O
C > Si > Ge > Pb > Sn
B B O
H O B O H B
B
H O
O . Elutronegativity
2Na+[Al(OH)4]-(aq) + 3H2(q)
HO
2Al(s) + 2NaOH(aq.) + 6H2O H
H H H H C > Pb > Si ≈ Ge ≈ Sn
You might also like
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis–1982: Annual Reports in Organic SynthesisFrom EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis–1982: Annual Reports in Organic SynthesisL. G. WadeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryNo ratings yet
- 11 - The P-Block ElementsDocument1 page11 - The P-Block ElementsPuppika DogNo ratings yet
- The P-Block ElementsDocument1 pageThe P-Block ElementsKrish KumarNo ratings yet
- The P-Block ElementsDocument6 pagesThe P-Block ElementsSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PresentationDocument43 pagesChemistry PresentationgabyyyyyyNo ratings yet
- Summary of Period 3 and Group 2 2017 PDFDocument9 pagesSummary of Period 3 and Group 2 2017 PDFdfefeNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document5 pagesCH 12gaminginsane372No ratings yet
- D & F Block - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2024Document2 pagesD & F Block - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2024jagartidubey5842No ratings yet
- 3 Dec - Science - Imp Concept - 1511844465Document20 pages3 Dec - Science - Imp Concept - 1511844465Syed nameerNo ratings yet
- S Block Lecture 1 PDFDocument29 pagesS Block Lecture 1 PDFRobiul AlomNo ratings yet
- 16 Jan Heating EffectDocument18 pages16 Jan Heating Effectsachin anuseNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Group 16 in P Block ElementsDocument4 pagesChemistry of Group 16 in P Block Elementsakino.mitsunaNo ratings yet
- P-Block ElementsDocument14 pagesP-Block ElementsAviNo ratings yet
- D&F Block ElementsDocument1 pageD&F Block ElementsBindu SajithNo ratings yet
- NMDCAT S & P BLOCK ELEMENTS, TRANSITION ELEMENTS - 5aDocument5 pagesNMDCAT S & P BLOCK ELEMENTS, TRANSITION ELEMENTS - 5abaseer ahmedNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument1 pageCHAPTER 1 Chemical Reactions & EquationsSushant KumarNo ratings yet
- 02.laws of Chemical Combination (22-36)Document15 pages02.laws of Chemical Combination (22-36)Vaibhav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound Day 06Document31 pagesCoordination Compound Day 06S MishraNo ratings yet
- HYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE MindmapDocument15 pagesHYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE Mindmapadsaditya24No ratings yet
- Chem 4Document107 pagesChem 4JinyoungNo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument28 pagesHydrogensanjusenthil8No ratings yet
- D & F-Block Elements - Short Notes - VIJETA SERIES CLASS-12THDocument2 pagesD & F-Block Elements - Short Notes - VIJETA SERIES CLASS-12THanshurao112233No ratings yet
- HYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE Mind MapDocument18 pagesHYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE Mind MapTanay1 MitraNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Elements, Carbon, Silicon, Germanium, Tin and Lead: Physical PropertiesDocument18 pagesGroup 4 Elements, Carbon, Silicon, Germanium, Tin and Lead: Physical PropertiesPAUL KOLERE100% (1)
- 70 Trends in PTable2 Chem Revised PDFDocument4 pages70 Trends in PTable2 Chem Revised PDFsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- 11.1, 11.2, 11.3 and 11.4 Group 17Document13 pages11.1, 11.2, 11.3 and 11.4 Group 17safiya_91No ratings yet
- Topic 3.2 - Trends in The Properties of Metal and Non-Metal Oxides and Group Reactivity (GP 1 & 17)Document22 pagesTopic 3.2 - Trends in The Properties of Metal and Non-Metal Oxides and Group Reactivity (GP 1 & 17)Perpetua SaeedNo ratings yet
- DPP - 05 (Video Solution) - MetallurgyDocument2 pagesDPP - 05 (Video Solution) - MetallurgybrrrrrrrrrrrrruNo ratings yet
- Redox (Multiple Choice) QPDocument8 pagesRedox (Multiple Choice) QPBăng Băng LêNo ratings yet
- Period 3 Elements and Their CompoundsDocument5 pagesPeriod 3 Elements and Their Compoundsshamsul aminNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 redox-22-23-IGDocument16 pagesCh. 7 redox-22-23-IGvfdfdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision Notes PDFDocument22 pagesChemistry Revision Notes PDFtanish gehlotNo ratings yet
- 19 Jan S Block 2Document17 pages19 Jan S Block 2sachin anuseNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Science Chapter 1Document10 pagesClass-10 Science Chapter 1Alok YadavNo ratings yet
- Section (A), (B) (C) : General Facts About Elements, Based On Periodic Trends Based On Chemical BondingDocument28 pagesSection (A), (B) (C) : General Facts About Elements, Based On Periodic Trends Based On Chemical BondingAnuragPandeyNo ratings yet
- Section (A), (B) (C) : General Facts About Elements, Based On Periodic Trends Based On Chemical BondingDocument28 pagesSection (A), (B) (C) : General Facts About Elements, Based On Periodic Trends Based On Chemical BondingRadhika PuralaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class - VIII Topic-MetallurgyDocument46 pagesChemistry Class - VIII Topic-Metallurgyrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- S-Block CompleteDocument16 pagesS-Block CompleteANSHEEKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen in 1 Shot - Class Notes - JEEDocument22 pagesHydrogen in 1 Shot - Class Notes - JEESaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- P Block2012 457Document143 pagesP Block2012 457Abhishek Bansal100% (1)
- D and F BlockDocument1 pageD and F Blockharshit13082006.palNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument17 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and Equationcashewnut_mish100% (1)
- Group 7 The Halogens KLASSDocument12 pagesGroup 7 The Halogens KLASSKimberly LinderholmNo ratings yet
- P Block Group IV OnlyDocument10 pagesP Block Group IV OnlyRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- InorganicDocument67 pagesInorganicAyanavo Das100% (1)
- HydrogenDocument22 pagesHydrogenKeerthana MNo ratings yet
- Form 5 RedoxDocument3 pagesForm 5 RedoxSulaiman Mohamad100% (1)
- Alkane and Alkyl Halides PP5Document9 pagesAlkane and Alkyl Halides PP5odubade opeyemiNo ratings yet
- CHM 202 To StudentsDocument12 pagesCHM 202 To Studentsprudylove03No ratings yet
- UNIT # 04: S-Block Exercise # 1Document3 pagesUNIT # 04: S-Block Exercise # 110A31 Irfan HashmiNo ratings yet
- P Block2012 457Document145 pagesP Block2012 457AaravNo ratings yet
- Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedDocument13 pagesTest4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedEga SukmaNo ratings yet
- D and F Block 20 MinsDocument43 pagesD and F Block 20 MinsStsNo ratings yet
- 10 FEB HydrogenDocument27 pages10 FEB Hydrogensachin anuseNo ratings yet
- S&P Block PDFDocument1 pageS&P Block PDFvrtbhgmngfNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Metals and NonmetalsDocument7 pagesSynopsis Metals and NonmetalsSaumya DhokariyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 10 PDFDocument11 pagesLecture9 10 PDFMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4 PRDocument14 pagesToaz - Info SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4 PRAlyssa Shao Wen XinNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1985From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1985Martin J. O'DonnellNo ratings yet
- NSTC Sample TestDocument23 pagesNSTC Sample Testumer farooqNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Pesticide Use QuestionnaireDocument13 pagesVietnam Pesticide Use QuestionnaireSharmadevan SundrasegaranNo ratings yet
- Ashima JMLDocument11 pagesAshima JMLPrachi PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Lecithins, Acetylated Product Safety SummaryDocument3 pagesLecithins, Acetylated Product Safety SummaryHabtamu Asmare100% (1)
- MSDS Lem Tikus Papan 2018Document4 pagesMSDS Lem Tikus Papan 2018abdul ropiNo ratings yet
- Practical No 2Document6 pagesPractical No 2shubhamtapryaly9No ratings yet
- Lyphase 11760I-Reagent A 510 Reagent B 300 Sample 9 Standard 113Document1 pageLyphase 11760I-Reagent A 510 Reagent B 300 Sample 9 Standard 113mahinNo ratings yet
- HIG.F.151-FISPQ - MONOMERO DE ESTIRENO - ACN Filial - Ingês - Ver.5Document13 pagesHIG.F.151-FISPQ - MONOMERO DE ESTIRENO - ACN Filial - Ingês - Ver.5Renato PimentaNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec Viii D2 Ma App 5 PDFDocument15 pagesAsme Sec Viii D2 Ma App 5 PDFMarín HernándezNo ratings yet
- CE215 GeoLab Manual - Determination of Specific GravityDocument2 pagesCE215 GeoLab Manual - Determination of Specific GravityJoy MondalNo ratings yet
- ISO 17556: 2012 (Second Edition)Document34 pagesISO 17556: 2012 (Second Edition)Vidya Laminators Pvt Ltd100% (1)
- Thermal Effects of Large Bodies of Intrusive Serpentinite On Overlying Monterey Shale, Southern Diablo Range, Cholame Area, CaliforniaDocument13 pagesThermal Effects of Large Bodies of Intrusive Serpentinite On Overlying Monterey Shale, Southern Diablo Range, Cholame Area, CaliforniaNursonia MesirNo ratings yet
- Metode Antioksidan AEACDocument7 pagesMetode Antioksidan AEACFira KuswandariNo ratings yet
- Vanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 14th Edition Widmaier Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesVanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 14th Edition Widmaier Solutions Manualconsignedurylic75hi100% (24)
- Electrophoresis Ge - Introduction: Lecture Notes - Handouts 10/3/2013Document5 pagesElectrophoresis Ge - Introduction: Lecture Notes - Handouts 10/3/2013iftikharNo ratings yet
- MSDS D.Col - Xlinker - Zr50Document6 pagesMSDS D.Col - Xlinker - Zr50Deepak CharanNo ratings yet
- Bundwall InspectionDocument89 pagesBundwall InspectionmorizoneNo ratings yet
- Data Bank Reid SherwoodDocument88 pagesData Bank Reid SherwoodAlejandro Sandoval GuillénNo ratings yet
- Kiln RefractoryDocument73 pagesKiln RefractoryMehmet C100% (1)
- Crystal Growth Mechanism and Prevention of Crystal GrowthDocument19 pagesCrystal Growth Mechanism and Prevention of Crystal Growthmadhuvarnakula100% (1)
- 0178 910 enDocument189 pages0178 910 enmahmoud mohamedNo ratings yet
- Revised Pharmaceutical Chemistry Course Outline 2023-2024Document11 pagesRevised Pharmaceutical Chemistry Course Outline 2023-2024motlhankanalaronaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocument10 pagesDifference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleKuresh RabidNo ratings yet
- Design and Applications of Photobioreactors - A ReviewDocument12 pagesDesign and Applications of Photobioreactors - A ReviewJoan BNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper For Grade 6Document4 pagesSample Paper For Grade 6Navvye AnandNo ratings yet
- Electrical Actuator 21 31 42 Datasheet English PDFDocument4 pagesElectrical Actuator 21 31 42 Datasheet English PDFHeru Purwanto HeruNo ratings yet
- Superior Ink MSDS PDFDocument2 pagesSuperior Ink MSDS PDFPrepress SNo ratings yet
- Evs MCQDocument21 pagesEvs MCQArunodhaya N100% (3)
- Lapindo Mud Flood EffectDocument2 pagesLapindo Mud Flood EffectAlexander MichaelNo ratings yet
- Industrial Seals CatalogDocument40 pagesIndustrial Seals CatalogAnonymous C05BLcNo ratings yet