Professional Documents
Culture Documents
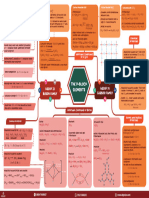
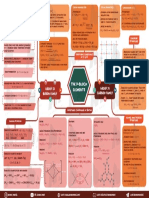
The P-Block Elements
Uploaded by
Krish KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The P-Block Elements
Uploaded by
Krish KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
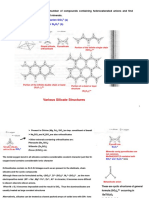
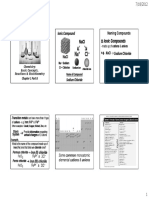
Atomic & Physical Properties Silicates Carbon Monoxide (CO) Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) Carbondioxide (CO2)
. Basic Unit is SiO4– . Preparation
4
. Preparation: . Covalent, three dimensional
Electronic configuration: [Noble gas] ns2np3 . They exist in different structures like network solid. CaCO 3 + 2HCl → CaCl 2 + CO2 + H2O
chain, ring, sheet or 3-D structure. C + 2H 2 O → CO + H 2
. Almost non-reactive due to
. Zeolites are 3-D silicates in which some Watergas . It is consumed during photosynthesis
high Si—O bond enthalpy.
Oxidation state: +1 & +3 of the Si atoms are replaced by Al+3 ions. 6CO 2 + 12H 2O
hv
→ C6H 12O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2O
They are used in water softening. 123 K
. 2C + O 2 + 4N 2 → 2CO + 4N 2
Silicons
Metalliccharacter :
B
Al Ge I Tl Pr oducergas
. Contains repeated R2 SiO
Metalloid Metals
Anomalous Behaviour of Boron units held by Si - O - Si linkage.
Chemical
Atomic radii, ionic radii, density & stability . Highly poisnous due to formation of a Properties
. Difference in behaviour of B is due to complex with haemoglobin. . They are water repelling
of +1 oxidation state: Generally increase due to non-polar alkyl groups.
small size high ionisation energy & absence
down the group.
of d-orbital.
. B has high M.P. & B.P. . Reactivity towards air: They form
Boiling point & stability of +3 oxidation state: . B exhibits allotrpy. Important Compounds oxides of the formula EO and EO 2
Decreases down the group. . B forms only covalent compounds. of C & Si on heating with air.
. Acidic strength of their oxides dec. down
Electronegativity: First decreases from B to the group.
A1 & increases from A1 to Ga & then dec. CO 2 , SiO 2 GeO 2 SnO 2 , PbO 2
marginally down the group.
Acidic LessAcidic Amphoteric
Melting point: Dec. from B to Ga then increases. . Reactivity towards water: only S
can decompose.
Al Ga Si Ge ∆
Ionisation Energy: B > Tl > Ga > Al > I
THE P-BLOCK water → Sn + 2H 2 O → SnO 2 + 2H 2
GROUP 13 GROUP 14
B
BORON FAMILY
I
ELEMENTS C
CARBON FAMILY
Pb . Reactivity towards halogen: Except C,
all reacts directly with halogens.
Lewis Acid: BCl3, AlCl3 etc behaves as Lewis
Acid due to incomplete octet. Tl S
Atomic and Physical
Complex formation: Due to small size, high Properties
Anomalous Behaviour
charge density & availability of vacant
d-orbitals.
. Due to small size, high ionisation energy & absence of d-orbitals. . Electronic configuration: [Noble
gas] ns 2 np 2
of C
Chemical Properties . C is hardest having m pt & b pt amont the elements of 9-14.
. Oxidation state: +2 & +4
. Shows maximum covalency of 4 while rest show maximum of 6.
Reactivity towards Air → 4E + 3O 2 → ∆
2E2 O3 . Atomic radii, metallic
. C has maximum tendency for catenation & multiple bonding (pπ-pπ) & show allotropy. character & stability of +2
B
2 O3 Al2 O3 Ga 2O3 I
2 O
3 Ti2 O3
O.S: Generally increase down
Acidi Amphoteri Basic the group.
Important Compounds of Boron
∆ . Catenation: Decreases down
2E + N 2 → 2En {Except + Ga, In, Tl} the group.
Borax Diborane Orthoboric Acid (H3BO3) . Allotropy: Except Pb, all other show
Reactivity towards alkalies: allotropy.
773 K
2B + 6KOH → 2K 3 BO 3 + 3H 2 Na2B4O7.10H2O B2H6 H3BO3 . Complex compounds formed by
all except C due to presence of
Reactivity towards halogens: White crystalline solid with soapy touch vacant d-orbital.
Whtie Crystalline Solid Colourless, highly toxic gas
2E + 3X 2 → 2EX 3 (Except7lI 3 ) preparation preparation preparation
456 K
2BF3 + 6NaH → B 2 H 6 + 6NaF Na 2 B 4 O 7 + 2HCl + 5H2 O → 2NaCl + 4H3 BO3
4H 3 BO 3 + Na 2 CO 3 → Na 2 B 4 O 7 + 6H 2 O + CO 2
Reactivity towards Acids reaction reaction
reaction
Con.H 2 SO 4 370 K
B + 3HNO 3 → H 3 BO 3 + 3NO 2 B 2 H 6 + 3O 2 → B 2 O 3 + 3H 2 O H 3 BO 3 → HBO 2 + H 2 O
∆ Na 2 B 4 O 7 + 7H 2 O → 2NaOH + 4H 3 BO 3 Monoboric acid
You might also like
- Sodium Borohydride DigestDocument212 pagesSodium Borohydride DigestDmitry67% (3)
- Oxidation Behaviour of Silicon Carbide - A Review PDFDocument11 pagesOxidation Behaviour of Silicon Carbide - A Review PDFcleitononline4599No ratings yet
- M-I 19 - CorrosionDocument25 pagesM-I 19 - CorrosionShaykh AlthamasNo ratings yet
- Helpful For CAPE U1 Chemistry - Transition ElementsDocument30 pagesHelpful For CAPE U1 Chemistry - Transition ElementsDenison Dwarkah100% (1)
- 11 - The P-Block ElementsDocument1 page11 - The P-Block ElementsRunjhunNo ratings yet
- 11 - The P-Block ElementsDocument1 page11 - The P-Block ElementsPuppika DogNo ratings yet
- Carbon Family - BrahmastraDocument35 pagesCarbon Family - BrahmastraStevensonNo ratings yet
- Group IVA - SiliconDocument34 pagesGroup IVA - SiliconAwatifNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PresentationDocument43 pagesChemistry PresentationgabyyyyyyNo ratings yet
- D&F Block ElementsDocument1 pageD&F Block ElementsBindu SajithNo ratings yet
- Summary of Period 3 and Group 2 2017 PDFDocument9 pagesSummary of Period 3 and Group 2 2017 PDFdfefeNo ratings yet
- Group 14 Short Notes DWxerQJ9pEiQa9a7Document22 pagesGroup 14 Short Notes DWxerQJ9pEiQa9a7Gully GamingNo ratings yet
- S&P Block PDFDocument1 pageS&P Block PDFvrtbhgmngfNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Microbial InteractionsDocument52 pagesAquatic Microbial InteractionsMusicPlayerNo ratings yet
- Oup 14 Elements - IV A - 187-200Document12 pagesOup 14 Elements - IV A - 187-200Anonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- S-Block Elements - BrahmastraDocument60 pagesS-Block Elements - BrahmastraStevensonNo ratings yet
- D and F BlockDocument1 pageD and F Blockharshit13082006.palNo ratings yet
- Ishan InorganicDocument47 pagesIshan InorganicAshik jhaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - Part II (P Block Elements - Group 14)Document30 pagesCHAPTER 5 - Part II (P Block Elements - Group 14)NURUL ZAKIRAH BINTI BORHANUDINNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Post-CMP Cleaning of Dielectric Surface Contaminated With CeriaDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Post-CMP Cleaning of Dielectric Surface Contaminated With CeriaAverage JoeNo ratings yet
- Metal and Nonmetal ElementsDocument64 pagesMetal and Nonmetal ElementsSherly Christina OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Metallurgy: P. NagarajaDocument70 pagesPrinciples of Metallurgy: P. NagarajaPs Strange 13No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument9 pagesChemistryudbhav789123No ratings yet
- D & F-Block ElementsDocument18 pagesD & F-Block ElementsIshita SoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 02-2 BondingDocument42 pagesChapter - 02-2 BondingAbdulNo ratings yet
- Tecnologías Aplicadas A Nanomateriales: Zeolites Tecnologías Aplicadas A Nanomateriales: ZeolitesDocument8 pagesTecnologías Aplicadas A Nanomateriales: Zeolites Tecnologías Aplicadas A Nanomateriales: ZeolitesMAURICIO NICARAGUA MENDEZNo ratings yet
- P2S Chemistry The D & F Block Elements, Coordination CompoundsDocument108 pagesP2S Chemistry The D & F Block Elements, Coordination Compoundsavith777No ratings yet
- Handwritten: MetalsDocument6 pagesHandwritten: MetalsarjunNo ratings yet
- Group 14Document44 pagesGroup 14sholahus shomadanyNo ratings yet
- Tick The Correct Answers From The Following: 8: Inter Part-IiDocument2 pagesTick The Correct Answers From The Following: 8: Inter Part-IiAdeel RazaNo ratings yet
- 7 Revealing Secrets of SilicatesDocument6 pages7 Revealing Secrets of SilicatesGajiniNo ratings yet
- Watermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFDocument15 pagesWatermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFMeerab ShahNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction - Part 2Document30 pagesOxidation and Reduction - Part 2Mila GiarainiNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry (EM) 2022-2023 SampleDocument25 pages12th Chemistry (EM) 2022-2023 Sample11B CHARAN ANANDNo ratings yet
- What Are Solids?: Chapter: Solid StatesDocument25 pagesWhat Are Solids?: Chapter: Solid StatesAryabhatta BorahNo ratings yet
- Silicate StructuresDocument14 pagesSilicate Structureschandramohan1999No ratings yet
- Gpiv PDFDocument4 pagesGpiv PDFSamson AmosNo ratings yet
- 01 S and P Block Elements Theory Final E 1Document17 pages01 S and P Block Elements Theory Final E 1gnkstarNo ratings yet
- Simple Silicate Anion Sio (A) Pyrisilicate or Disilicate Anion Si O (B)Document8 pagesSimple Silicate Anion Sio (A) Pyrisilicate or Disilicate Anion Si O (B)Puneet KaurNo ratings yet
- PCM Chapter 01 Part BDocument7 pagesPCM Chapter 01 Part BAlif AzmirNo ratings yet
- D & F Block - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2024Document2 pagesD & F Block - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2024jagartidubey5842No ratings yet
- D and F Block 20 MinsDocument43 pagesD and F Block 20 MinsStsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and Balancing Chemical EquationDocument36 pagesChemical Reaction and Balancing Chemical EquationChelsia Venice MorilloNo ratings yet
- Ullmans EncylopaediaDocument14 pagesUllmans EncylopaediaKnowchemNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument31 pagesS Block ElementsMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- The P-Block ElementsDocument6 pagesThe P-Block ElementsSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- S&P Block PDFDocument1 pageS&P Block PDFvrtbhgmngfNo ratings yet
- E-Learning - PHARM 121 - Chapter 5Document4 pagesE-Learning - PHARM 121 - Chapter 5Trixie Anne FelicitasNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen - Mind MapDocument1 pageHydrogen - Mind Mapsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- S BlockDocument18 pagesS BlockHENo ratings yet
- 2 Struktur KeramikDocument93 pages2 Struktur KeramikMichael Robert Tua NababanNo ratings yet
- H.D.A. 2021Document54 pagesH.D.A. 2021Every Time Chemistry [ ETC]No ratings yet
- Group 14Document44 pagesGroup 14Ramazan AshirkhanNo ratings yet
- DHS H1 CHEM P1 QP With Answer KeyDocument15 pagesDHS H1 CHEM P1 QP With Answer KeyLim EnningNo ratings yet
- Alkaline MetalsDocument29 pagesAlkaline MetalsAigerim TurlanovaNo ratings yet
- Carbide Precipitation in Inconel 718. M. SundararamanDocument18 pagesCarbide Precipitation in Inconel 718. M. SundararamanJulio Cesar Garcia GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Redox: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions of CourseDocument2 pagesRedox: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions of Coursejoshua kabweNo ratings yet
- Lilavatibai Podar High School (Isc) Atomic Structure Grade: 7 Subject: ChemistryDocument2 pagesLilavatibai Podar High School (Isc) Atomic Structure Grade: 7 Subject: ChemistryMahesh hamneNo ratings yet
- Group 1: The Alkali MetalsDocument10 pagesGroup 1: The Alkali MetalsGershonNo ratings yet
- D - Block Compounds: Inorganic ChemistryDocument11 pagesD - Block Compounds: Inorganic ChemistryApoorv RastogiNo ratings yet
- The P - Block Elements: Unit 11Document19 pagesThe P - Block Elements: Unit 11laddu100% (1)
- E14015 Bro en A4 v4 Cga Diss Cylinder ConnectionsDocument4 pagesE14015 Bro en A4 v4 Cga Diss Cylinder ConnectionsGUDANG KARAOKE KITANo ratings yet
- Mixed FormulasDocument3 pagesMixed FormulasasierNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Volume 1 Study Material em 215251Document21 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Volume 1 Study Material em 215251Aakaash C.K.75% (4)
- P-Block Elements and Their Compounds - I: Module - 6Document33 pagesP-Block Elements and Their Compounds - I: Module - 6TeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNo ratings yet
- CHE-501Carboranes and Boranes Metal ClusterDocument40 pagesCHE-501Carboranes and Boranes Metal Clusteranuthakur100% (1)
- Pipeline Colour CodeDocument25 pagesPipeline Colour CodeRahul KadamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Qbank PDFDocument106 pagesChemistry Qbank PDFgowrimanohar1975No ratings yet
- Hydrides and Oxides of Boron FamilyDocument5 pagesHydrides and Oxides of Boron FamilybhartiyaanujNo ratings yet
- The P-Block Elements (Group 13 - 14)Document136 pagesThe P-Block Elements (Group 13 - 14)May HarukaNo ratings yet
- P-Block ElementsDocument38 pagesP-Block Elementskaushik247No ratings yet
- Exercise-01 Check Your GraspDocument31 pagesExercise-01 Check Your GraspHet PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- STYX Rules and Structure of Higher BoranesDocument11 pagesSTYX Rules and Structure of Higher Boranesneharamkrishna75% (4)
- Metal ClusterDocument30 pagesMetal ClusterGokul KannanNo ratings yet
- CHEM 103-Problem Set 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesCHEM 103-Problem Set 2 SolutionsAracsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Kota Level Study Materialfor Emerge BatchDocument49 pagesChemical Bonding Kota Level Study Materialfor Emerge Batchkrutika goharkarNo ratings yet
- 2016 Australian Science Olympiad Exam: Chemistry - Sections A & BDocument28 pages2016 Australian Science Olympiad Exam: Chemistry - Sections A & BAZZAHRA SHINTA BILQIS NURFATANo ratings yet
- Fiitjee All India Test Series: JEE (Main) - 2019Document18 pagesFiitjee All India Test Series: JEE (Main) - 2019Dhruv BajajNo ratings yet
- The P-Block ElementsDocument14 pagesThe P-Block ElementsAbhay100% (2)
- Boron FamilyDocument12 pagesBoron FamilyGaurav DubeyNo ratings yet
- BoranesDocument2 pagesBoranesmilukrNo ratings yet
- Assignement 2Document3 pagesAssignement 2Al FianNo ratings yet
- Grand Test 8 Organic Chemistry Level 2Document12 pagesGrand Test 8 Organic Chemistry Level 2Dhruv SarkarNo ratings yet
- Daftar Bahan Berbahaya Dan BeracunDocument8 pagesDaftar Bahan Berbahaya Dan BeracunSylvia Yemita100% (1)
- Appendix B: Supplemental Practice ProblemsDocument7 pagesAppendix B: Supplemental Practice ProblemsMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Borides - Boron Nitrides (Eng)Document16 pagesBorides - Boron Nitrides (Eng)Reisty PutraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Home Assignment 01Document11 pagesChemistry Home Assignment 01Nishali Sam100% (1)
- BoranesDocument32 pagesBoranessaumya satyarthyNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) : SP SP SP D DSPDocument10 pagesI. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) : SP SP SP D DSPAamerNo ratings yet