Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light
Uploaded by
Harsh PatelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Light
Uploaded by
Harsh PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter – 10
Light – Reflection & Refraction
Light :-
o Light is an energy due to which human eye is able to see the objects
all around it.
o Light is an electromagnetic radiation.
o Light always travels in a straight line.
o When light strikes any particular surface, following phenomena may
happen :-
1. Reflection
2. Refraction
3. Absorption
Beam of Light :-
o Bunch of infinite light rays which is coming from any source is called
as beam of light.
Reflection :-
o Bouncing back of light when it strikes any polished surface like
mirror.
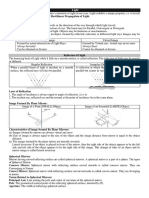
Laws of Reflection :-
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 1
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
o Angle of incidence [Angle between incident ray and normal] and
Angle of reflection [Angle between reflected ray and normal] are
always equal.
o Incident ray, Reflected ray and Normal drawn at the point of
incidence lies in a same plane.
Plane Mirror :-
Object Distance = -u
Image Distance = v
Nature of image = Virtual & Erect
Size of image = Same as object
Spherical Mirror :-
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 2
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
o Center of Curvature(C) :-
o The centre of the spherical glass from where the spherical mirror has
been made up of, is called centre of curvature.
o Pole (P) :-
o Centre of the spherical mirror is called pole.
o Aparture(Q Q’) :-
o The effective length of spherical mirror is called Aparture.
o Principal Axis (PA) :-
o An imaginary line passing through centre of curvature and pole is called
principal axis.
o Radius of Curvature (R) :-
o The distance from the centre of curvature to pole is called radius of
curvature.
o Principal Focus (F) :-
o All the incident rays which are parallel to principal axis, pass through a
fix point after reflection, that fix point is termed as principal focus.
o Focal Length (f) :-
o The distance from principal focus to the pole is called focal length.
NOTE :-
Concave mirror is a converging mirror.
Convex mirror is a diverging mirror.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 3
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
Image Formation by Spherical Mirror
o When the incident rays are parallel to the principal axis after reflection,
they pass through principal found in case of concave mirror and appear
to pass through focus in case of convex mirror.
o When the incident ray passes through the focus, then the reflected
ray will be parallel to the principal axis.
o When the incident ray passes through the centre of curvature, it
reflected back in the same direction.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 4
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
o When the incident ray passes through pole making an angle θ with
the principal axis, then it gets reflected back by making same angle θ
with principal axis.
Image Formation in Concave Mirror :-
When an object is at infinity.
o Object = At Infinity
o Image = At Focus
o Size = Highly Diminished
o Nature = Real & Inverted
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 5
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
When an object is beyond ‘ C ’.
o Object = Beyond ‘ C ‘
o Image = Between C and F
o Size = Diminished
o Nature = Real & Inverted
When an object is at ‘ C ‘.
o Object = At ‘ C ’
o Image = At ‘ C ’
o Size = Same
o Nature = Real & Inverted
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 6
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
When an object is between C and F.
o Object = Between C and F
o Image = Beyond F
o Size = Enlarged
o Nature = Real & Inverted
When an object is at ‘ F ’.
o Object = At ‘ F ’
o Image = At Infinity
o Size = Highly Enlarged
o Nature = Real & Inverted
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 7
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
When an object is between F and P.
o Object = Between F and P
o Image = Behind Mirror
o Size = Enlarged
o Nature = Virtual & Erect
Image Formation in Convex Mirror :-
When an object is at Infinity.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 8
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
o Object = At Infinity
o Image = At Focus
o Size = Diminished
o Nature = Virtual & Erect
When an object is between infinity and pole.
o Object = Between Infinity and Pole
o Image = Between F and P
o Size = Diminished
o Nature = Virtual & Erect
Uses of Concave Mirror :-
o Concave mirror are used by dentist to see large image of teeth of
patient.
o Concave mirror is used as shaving mirror to see a large image of face.
o Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce
heat in solar furnace.
o Concave mirror is used in torches, search lights and headlights of
vehicles to get powerful parallel beam of light.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 9
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
Uses of Convex Mirror :-
o Convex mirrors are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles because they
always give an erect and diminished image, also they have a wider field
of view as they are curved outward.
o Convex mirrors are used at blind turns and on points of merging traffic
to facilate vision of both side of traffic.
o Convex mirror is used as security mirrors.
Sign Convention by Spherical Mirror :-
For Concave Mirror :-
o Object Distance = -u
o Image Distance = -v [Except when object is between F & P]
o Focal Length = -f
o Object height = +h
o Image height =-h` [Except when object is between F & P]
For Convex Mirror :-
o Object Distance = -u
o Image Distance = +v
o Focal Length = +f
o Object height = +h
o Image Distance = +h`
Mirror Formula :-
o Mirror Formula is an equation which gives the relation between object
distance (u), image distance (v) and focal length (f) which can be given
as :-
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 10
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
Magnification
o Magnification is a ratio of image height to the object height.
o It is represented by m.
o Also, it can be defined as ratio of image distance to the object
distance.
For Plane Mirror :-
o The magnification of plane mirror is always +1, where + denote that
image is virtual and 1 denote that image and object height is same.
For Convex Mirror :-
o The magnification of convex mirror is always + but always less than 1,
where + denotes that image is virtual and less than 1 denotes that
image height is smaller than object height.
For Concave Mirror :-
o The magnification of convex mirror can be + / - , where - value of
magnification can take any value but + value of magnification will
always more than 1.
Refraction :-
o When the light rays travel from one medium to another medium, it
bends due to change of speed and the phenomenon of bending of light
is called refraction of light.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 11
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
o When the light ray travels from rarer to denser medium, it will bend to
the normal.
o When the light ray travels from denser to rarer medium, it will bend
away from normal.
Laws of Refraction :-
o Incident ray, Refracted ray and Normal drawn to the point of incidence
lies in a same plane.
o The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to sine of angle of refraction is
constant and this ratio is called Refractive Index.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 12
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
Refraction Through a Rectangular Glass Slab :-
o As shown in the figure, a rectangular glass slab PQRS is drawn.
o At surface PQ, incident ray AB is drawn making an angle of incidence(i).
o Now, this ray travels from air to glass i.e., from rarer to denser
medium, the refracted ray BC bends towards the normal.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 13
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
o The ray BC will be acting as an incident ray for surface SR and this ray
travels from glass to air, it will bend away from normal and emerge out
as ray CD and CD is called Emergent ray.
o Here, from the diagram, it is clear that the incident ray and emergent
ray, both travel in same direction but emergent ray is shift about a
distance CS as compared to incident ray and distance CS is called
Lateral Shift.
Refraction by Spherical Lenses :-
Spherical Lenses
o Spherical lens is formed by cutting spherical glass.
o Spherical lenses are transparent medium bound by two surfaces of
which one or both surfaces are curved.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 14
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
Rules for image formation for both lens :-
o For a convex lens, if a light ray is parallel to principal axis, it will refract
from the focus and appear to pass through I case of concave lens.
o When the light ray passes through focus, it will refract and passes
parallel through the principal axis.
o When the light ray passes from the optical centre, it will refract and
pass without any deviation.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 15
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
Image Formation in a Convex Lens :-
When Object is at Infinity.
o Object = At Infinity
o Image = At F2
o Size = Highly Diminished
o Nature = Real & Inverted
When Object is beyond 2F1.
o Object = Beyond 2F1
o Image = Between F2 & 2F2
o Size = Diminished
o Nature = Real & Inverted
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 16
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
When Object is at 2F1.
o Object = At 2F1
o Image = At 2F2
o Size = Same
o Nature = Real & Inverted
When object is between 2F1 & F1.
o Object = Between 2F1 & F1
o Image = Beyond 2F2
o Size = Enlarged
o Nature = Real & Inverted
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 17
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
When Object is at F1.
o Object = At F1
o Image = At Infinity
o Size = Highly Enlarged
o Nature = Real & Inverted
When Object is between F1 & O.
o Object = Between F1 & O
o Image = Beyond 2F1
o Size = Enlarged
o Nature = Virtual & Erect
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 18
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
Image Formation for a Concave Lens :-
When Object is at Infinity.
o Object = At Infinity
o Image = At F1
o Size = Highly Diminished
o Nature = Virtual & Erect
When Object is between Infinity and O.
o Object = Between infinity & O
o Image = Between F1 & O
o Size = Diminished
o Nature = Virtual & Erect
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 19
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
Sign Convention By Lens :-
For Concave Lens :-
o Object Distance = -u
o Image Distance = +v
o Object height = +h
o Image height =+h`
For Convex Lens :-
o Object Distance = -u
o Image Distance = -v[Except when object is between F1 & O]
o Object height = +h
o Image Distance = -h` [Except when object is between F1 & O]
Lens Formula :-
o It is a mathematical formula which gives the relationship between
Object Distance(u), Image Distance(v) and Focal Length(f) for a lens.
Power of Lens :-
o It is defined as the reciprocal of focal length.
o It is presented by P.
o The SI unit of power is Dioptre (D) / m-1.
o To find power, we need to convert the focal length in m (metre).
o Power of Lens can be Positive or Negative.
o If the Power of Lens is Positive, that means focal length is positive,
that happen only in case of convex lens.
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 20
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
o If the Power of Lens is Negative, that means focal length is negative,
that happen only in case of concave lens.
-By MD
master_1701
LIGHT – REFLECTION AND REFRACTION NOTES Page 21
BY INFINITY TUTORIAL POINT
You might also like
- Generator System Fault Calculation Design GuideDocument22 pagesGenerator System Fault Calculation Design Guidedheerajdorlikar100% (2)
- Lecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsDocument33 pagesLecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument28 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesJohn Malig100% (1)
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument37 pagesPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionved bhaskerNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionANJALI RANANo ratings yet
- S7SDocument336 pagesS7S217469492100% (1)
- Air Ticket Booking - Book Flight Tickets - Cheap Air Fare - LTC Fare - IRCTC AIRDocument2 pagesAir Ticket Booking - Book Flight Tickets - Cheap Air Fare - LTC Fare - IRCTC AIRMohitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Reflection RefractionDocument10 pagesPhysics Light Reflection RefractionsudhaNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument89 pagesOpticsKarunya nidhi100% (1)
- Training ReportDocument56 pagesTraining ReportRavimini100% (2)
- GPSForex Robot V2 User GuideDocument40 pagesGPSForex Robot V2 User GuideMiguel Angel PerezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 The Rise of Instrumental Music - 141-152Document8 pagesCHAPTER 8 The Rise of Instrumental Music - 141-152Aleksandre Roderick-LorenzNo ratings yet
- Light, Reflection, Refraction - CBSE Class 10 PhysicsDocument7 pagesLight, Reflection, Refraction - CBSE Class 10 PhysicsGurukul24x794% (17)
- 10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1Document18 pages10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1Anonymous loKgur100% (1)
- Opticks: Or, A Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections, and Colours of LightFrom EverandOpticks: Or, A Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections, and Colours of LightNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument22 pagesLight Reflection and Refractionapi-246793885100% (1)
- CHAPTER 10 Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 10 Light-Reflection and RefractionMohammedNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Revision Notes Light Reflection & RefractionDocument19 pagesClass 10 Science Revision Notes Light Reflection & RefractionMadhanNo ratings yet
- LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTIONDocument34 pagesLIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTIONmuhammad umair100% (1)
- LIGHT FinalDocument32 pagesLIGHT Finalehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- 10 TH Class NotesDocument27 pages10 TH Class NotesPavana Kumar KallakuriNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument41 pagesRay Opticssangitat082No ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1Document19 pages10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1GAURAV K SHARMANo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics Physics BHU NotesDocument50 pagesGeometrical Optics Physics BHU NotesCentral DogmaNo ratings yet
- Class - X Mr. Subhasish MohantaDocument36 pagesClass - X Mr. Subhasish MohantasubhaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesScienceInkspireNo ratings yet
- LIGHT FinalDocument31 pagesLIGHT FinalyourmoNo ratings yet
- Notes On RefractionDocument10 pagesNotes On RefractionramkrishnapasalaNo ratings yet
- Light Class XDocument109 pagesLight Class XLekshmipriya PNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics 1 (22-23)Document49 pagesRay Optics 1 (22-23)Maitrayee TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument48 pagesChapter 9 - Light - Reflection and Refractionsekhsayan0102No ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument19 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light at Curved SurfacesDocument10 pagesReflection of Light at Curved SurfacesSAI PRANEETH REDDY DHADINo ratings yet
- LightDocument15 pagesLightAfrina Asmi MINo ratings yet
- Light Chapter'sDocument24 pagesLight Chapter'sPratik ChavanNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument56 pagesOpticsahsan shahNo ratings yet
- Light - ReflectionDocument28 pagesLight - ReflectionDavy jonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 pagesChapter Notes Light - Reflection & Refractionroseanneblossom.kimNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics NotesDocument35 pagesRay Optics NotesNarenNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionAnant WatsNo ratings yet
- Light Refraction and Image FormationDocument5 pagesLight Refraction and Image FormationAninda RoyNo ratings yet
- 2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S EoDocument6 pages2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S Eony9197171No ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A Plane MirrorJazelle PaciaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsX PDFDocument124 pagesPhysicsX PDFcitsNo ratings yet
- LightDocument30 pagesLightElvin Joseph Pualengco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors PDFDocument9 pagesSpherical Mirrors PDFAditya SudhakarNo ratings yet
- ch-10 Light and Reflection-1Document5 pagesch-10 Light and Reflection-1MISHKA KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- WP4 Light WavesDocument16 pagesWP4 Light Waveswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Reflection and Refraction of Light Study Notes 2015-16Document15 pagesClass 10 Reflection and Refraction of Light Study Notes 2015-16dvrao_chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Properties of Light Waves ReflectionDocument4 pagesProperties of Light Waves ReflectionHoneyNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction ExplainedDocument18 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction ExplainedAyush BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Reflection of LightDocument48 pagesReflection & Reflection of LightChanderKishoreJoshiNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Reflection of LightDocument29 pagesRay Optics: Reflection of LightAbishek ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Geometric Optics ExplainedDocument23 pagesGeometric Optics ExplainedanubhavmaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument43 pages10 Light Reflection and Refractiong8one2020No ratings yet
- Physics Formula Class10Document38 pagesPhysics Formula Class10srizwan.1979No ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Forliveteaching 3 220616045804 9ea2c7ebDocument32 pagesForliveteaching 3 220616045804 9ea2c7ebPrincess Rehanne PadiosNo ratings yet
- S42-Class10ScienceNCERTSummaryPart-IIDocument129 pagesS42-Class10ScienceNCERTSummaryPart-IIsandeepkumarreddy2201No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument31 pagesLight - Reflection & RefractionsagarNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light Printed Notes Class 8Document13 pagesReflection of Light Printed Notes Class 8Typist VBCNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesChapter - 10: Light: Reflection and Refractionuma mishraNo ratings yet
- FAQ in EnglishDocument2 pagesFAQ in EnglishHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- FAQ in EnglishDocument2 pagesFAQ in EnglishHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Vimm's LairDocument1 pageVimm's Lairred yoshiNo ratings yet
- Computer Practical Final Exam Schedule V - IX, XI (2022-2023) PDFDocument1 pageComputer Practical Final Exam Schedule V - IX, XI (2022-2023) PDFHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Computer Practical Final Exam Schedule V - IX, XI (2022-2023) PDFDocument1 pageComputer Practical Final Exam Schedule V - IX, XI (2022-2023) PDFHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- "Employee Payroll Management System": Miss - Priyanka Abhaynath YadavDocument31 pages"Employee Payroll Management System": Miss - Priyanka Abhaynath Yadavhabeb TubeNo ratings yet
- Independent ConsultantDocument8 pagesIndependent ConsultantNaveen GowdaNo ratings yet
- Solution:: Ex 3.3 Consider The Following Parallelograms. Find The Values of The Unknowns X, Y, ZDocument9 pagesSolution:: Ex 3.3 Consider The Following Parallelograms. Find The Values of The Unknowns X, Y, ZpadmaNo ratings yet
- Quality Control and Assurance Processes for Coffee ProductionDocument5 pagesQuality Control and Assurance Processes for Coffee ProductionSharifah NuruljannahNo ratings yet
- Lippo Karawaci Review 30 September 2019 FINAL PDFDocument149 pagesLippo Karawaci Review 30 September 2019 FINAL PDFAndy AghastaNo ratings yet
- Remote Access Portal User GuideDocument3 pagesRemote Access Portal User GuidezeljavaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For ETABSDocument2 pagesSyllabus For ETABSSandgrouse RajNo ratings yet
- School Annual Data For Financial YearDocument3 pagesSchool Annual Data For Financial YearRamesh Singh100% (1)
- LS - 0 - 2 - 1 - 02384346aa856-Essay Writing For SSC T-3 (English) PDFDocument47 pagesLS - 0 - 2 - 1 - 02384346aa856-Essay Writing For SSC T-3 (English) PDFBHARATH S RNo ratings yet
- (Eng) Advanced Concept Training - 2d Concrete Members en 1992 - 2017Document69 pages(Eng) Advanced Concept Training - 2d Concrete Members en 1992 - 2017Muscadin MakensonNo ratings yet
- 1 An Overview of Physical and Phase ChangeDocument5 pages1 An Overview of Physical and Phase ChangeGede KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MCMC Methods For Multi-Response Generalized LinearDocument22 pagesMCMC Methods For Multi-Response Generalized LinearkyotopinheiroNo ratings yet
- Q 0092r1 - Mastersizer 3000 MAZ6222 2022 Kimia FarmaDocument4 pagesQ 0092r1 - Mastersizer 3000 MAZ6222 2022 Kimia FarmaCapital ExpenditureNo ratings yet
- S/4HANA Margin Analysis, Predictive Accounting, and Continuous CloseDocument27 pagesS/4HANA Margin Analysis, Predictive Accounting, and Continuous Closessbhagat001No ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument36 pagesChapter Onepretoria agreement21No ratings yet
- How To Write Field Notes Teaching Practice-I 8607 AIOU B.EdDocument2 pagesHow To Write Field Notes Teaching Practice-I 8607 AIOU B.EdMazhar ShahzadNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Effects of Unsteady Parameters On The Aerodynamics of A Low Reynolds Number Pitching AirfoilDocument15 pagesAn Investigation Into The Effects of Unsteady Parameters On The Aerodynamics of A Low Reynolds Number Pitching AirfoilMANNE SAHITHINo ratings yet
- 6.4 Qualitative Quantitative AnalysisDocument6 pages6.4 Qualitative Quantitative AnalysisAndrea PagsuguironNo ratings yet
- Title of Training Presentation: Presented by Your NameDocument14 pagesTitle of Training Presentation: Presented by Your NameJudy UnreinNo ratings yet
- Mercedes 220 AirmaticDocument7 pagesMercedes 220 AirmaticadinxNo ratings yet
- Effecta WoodyDocument21 pagesEffecta WoodyMR XNo ratings yet
- 1025 (1029) Anaerobic ChamberDocument8 pages1025 (1029) Anaerobic ChamberSoma GhoshNo ratings yet
- ECT ModelDocument12 pagesECT Modelhii_bhartiNo ratings yet
- Methanol from Syngas Plant DesignDocument13 pagesMethanol from Syngas Plant DesignKhalidMadaniNo ratings yet