Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tamil Grammer Basics v1.0
Uploaded by
kamarajk22Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tamil Grammer Basics v1.0
Uploaded by
kamarajk22Copyright:
Available Formats
Tamil is a Dravidian language spoken primarily in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu
and in Sri Lanka, Singapore, Malaysia, and various other diaspora communities. It
has a rich literary tradition and a unique grammar system. Here are some basics of
Tamil grammar:
Alphabet: Tamil has its own script, which consists of 12 vowels and 18 consonants.
It is an abugida script, meaning each character represents a consonant with an
inherent vowel sound, which can be modified with diacritic marks.
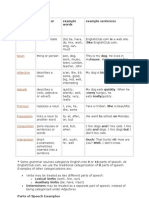
Nouns:
Gender: Tamil nouns don't have grammatical gender (masculine or feminine).
Number: Nouns can be singular or plural. Plurals are often formed by adding
suffixes to the singular form.
Case: Tamil nouns can take different case endings to indicate their grammatical
function in a sentence. Some common cases include nominative, accusative, and
dative.
Verbs:
Tense: Tamil verbs are conjugated based on tense. There are three tenses: past,
present, and future.
Aspect: Tamil verbs also have aspectual distinctions, such as simple, continuous,
and perfect.
Mood: Verbs can be conjugated in different moods, including indicative, imperative,
and conditional.
Subject-Object-Verb Order: Tamil typically follows a subject-object-verb (SOV) word
order in sentences. The subject often comes first, followed by the object and then
the verb.
Pronouns:
Tamil has separate pronouns for different levels of formality and politeness.
Pronouns also indicate gender, number, and case.
Adjectives and Adverbs: Adjectives in Tamil usually come after the noun they
modify, and adverbs often follow the verb.
Prepositions: Tamil uses postpositions, which are similar to English prepositions
but come after the noun or pronoun they govern.
Questions: Questions are formed by using question words like "yaar" (who), "enna"
(what), and "eppadi" (how) at the beginning of a sentence.
Negation: To make a negative sentence, the word "illai" is often used, which means
"not."
Conjunctions: Tamil has a variety of conjunctions to connect words and sentences,
such as "intha vayathil" (meanwhile), "athu pole" (like that), and "athukku munbu"
(before that).
Particles: Particles like "aanaal" (but), "athuvaraikum" (until then), and
"evalavu" (how much) are used to add nuance to sentences.
Verb Endings: Tamil verbs have different endings for different persons and numbers,
making it important to conjugate verbs correctly based on the subject.
Remember that Tamil grammar can be quite complex, and this is just a basic
overview. As with any language, practice and exposure to native speakers will help
you become more proficient in Tamil grammar.
You might also like
- Thai Picture Dictionary: Learn 1,500 Thai Words and Phrases - The Perfect Visual Resource for Language Learners of All Ages (Includes Online Audio)From EverandThai Picture Dictionary: Learn 1,500 Thai Words and Phrases - The Perfect Visual Resource for Language Learners of All Ages (Includes Online Audio)No ratings yet
- DNS CheatSheet V1.02Document1 pageDNS CheatSheet V1.02kamarajk22No ratings yet
- Grammar HandbookDocument111 pagesGrammar HandbookMieder van Loggerenberg100% (4)
- VXLANDocument2 pagesVXLANkamarajk22No ratings yet
- Cisco Firepower Presentation 123Document58 pagesCisco Firepower Presentation 123kamarajk22No ratings yet
- Fortigate Cli Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFortigate Cli Cheat Sheetmyreza123100% (3)
- Fortigate Cli Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFortigate Cli Cheat Sheetmyreza123100% (3)
- FEX CheatSheet V1.00Document1 pageFEX CheatSheet V1.00kamarajk22No ratings yet
- Malayalam Grammar Basics v1.0Document1 pageMalayalam Grammar Basics v1.0kamarajk22No ratings yet
- Kannada Grammar Basics v1.0Document2 pagesKannada Grammar Basics v1.0kamarajk220% (1)
- Grammar and PunctuationDocument17 pagesGrammar and PunctuationSarika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- ThaiDocument1 pageThaiAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Tamil MorphologyDocument1 pageTamil MorphologyamrikesaNo ratings yet
- Telugu Grammar Basics v1.0Document1 pageTelugu Grammar Basics v1.0kamarajk22No ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument38 pagesMorphologySorayaHermawanNo ratings yet
- Continue: Tamil Alphabets PDFDocument2 pagesContinue: Tamil Alphabets PDFvel muruganNo ratings yet
- Everyday Thai Language School Bangkok.20140827.105439Document1 pageEveryday Thai Language School Bangkok.20140827.105439supplyweed22No ratings yet
- Special GrammarDocument170 pagesSpecial GrammarSanaullah RahmanzaiNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Difficulty of Learnin PDFDocument100 pagesAn Analysis of The Difficulty of Learnin PDFNinthCircleOfHellNo ratings yet
- CSEET Business Communication May 2022 Revision NotesDocument42 pagesCSEET Business Communication May 2022 Revision NotesSAHAJPREET BHUSARINo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument48 pagesEnglish GrammarEhsanullah RahimiNo ratings yet
- Morphology: DR Arup Kumar NathDocument43 pagesMorphology: DR Arup Kumar NathWhantyNo ratings yet
- Tamil PhonologyDocument2 pagesTamil PhonologyamrikesaNo ratings yet
- Tls Thai Language School Bangkok.20140827.121932Document1 pageTls Thai Language School Bangkok.20140827.121932supplyweed22No ratings yet
- The 8 Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesThe 8 Parts of SpeechGlycel Angela JacintoNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument74 pagesMorphologyFatin Aqilah100% (2)
- Contempory Linguistics Over ViewDocument8 pagesContempory Linguistics Over ViewLets learn languagesNo ratings yet
- Function and Content WordsDocument7 pagesFunction and Content WordsRieZky Ramadhani100% (1)
- Morphology - Group 6Document17 pagesMorphology - Group 6Riska BatubaraNo ratings yet
- Malay: Gayatri Purigilla 20171309Document18 pagesMalay: Gayatri Purigilla 20171309Gayatri PurigillaNo ratings yet
- Thai Language School Bangkok.20140527.225428Document1 pageThai Language School Bangkok.20140527.225428bar7starNo ratings yet
- Stylistics: Ma'am Dr. Mamona KhanDocument26 pagesStylistics: Ma'am Dr. Mamona KhanSyeda Haya BatoolNo ratings yet
- Linguistics and Phonetics Shorts Questions (1) Define Linguistics?Document5 pagesLinguistics and Phonetics Shorts Questions (1) Define Linguistics?Zaeem AhMadNo ratings yet
- Syntax in Sentences: Annisa Meliani P Lara Yuliawati Shaffira Maisarah Yesi AdriyaniDocument12 pagesSyntax in Sentences: Annisa Meliani P Lara Yuliawati Shaffira Maisarah Yesi AdriyaniTia DelvannyNo ratings yet
- Problems: 1. Vietnamese Is Kind of Language Which Has Single Words With No Ending SoundsDocument6 pagesProblems: 1. Vietnamese Is Kind of Language Which Has Single Words With No Ending SoundsTuyen Thanh HoangNo ratings yet
- Analysis of LanguageDocument3 pagesAnalysis of LanguageDarryl LavegaNo ratings yet
- Sentence AnalysisDocument32 pagesSentence AnalysisPantho BaruaNo ratings yet
- Interjections: What Is An Interjection?Document2 pagesInterjections: What Is An Interjection?Ana Karem Kashmir DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Morphology in LinguisticsDocument13 pagesMorphology in LinguisticsEvitaaNo ratings yet
- Word Classes or Parts of Speech For TamilDocument30 pagesWord Classes or Parts of Speech For TamilKumar RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Nine Parts of Speech (Grammar) : Prepositions and Interjections. We Will Add One More Type: ArticlesDocument2 pagesNine Parts of Speech (Grammar) : Prepositions and Interjections. We Will Add One More Type: ArticlesReeta KannusamyNo ratings yet
- Assignment of SyllableDocument9 pagesAssignment of SyllableAcademic ReadingNo ratings yet
- Tamil To English Dictionary (241KB)Document7 pagesTamil To English Dictionary (241KB)SureshNo ratings yet
- The Structure of English LanguageDocument15 pagesThe Structure of English LanguageMusersame100% (1)
- 8 Indonesian Part of SpeechDocument7 pages8 Indonesian Part of SpeechRestu BisnisNo ratings yet
- Korean Grammar - WikipediaDocument17 pagesKorean Grammar - WikipediaDamn GoodNo ratings yet
- Words ClassesDocument1 pageWords ClassesDR BaoucheNo ratings yet
- Limitations of English Letters in The Aspect of PronunciationDocument2 pagesLimitations of English Letters in The Aspect of PronunciationFaizur RahmanNo ratings yet
- What Is MorphologyDocument9 pagesWhat Is MorphologySulis TiyaniNo ratings yet
- Morphemes 090930154800 Phpapp02Document76 pagesMorphemes 090930154800 Phpapp02Fadhilah Mohd ShaherNo ratings yet
- Alphabet Cards IntroDocument2 pagesAlphabet Cards IntroGgffccNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MorphologyDocument3 pagesUnit 5 MorphologyNuria AragónNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURE OF ENGLISH Reviewer MidtermsDocument19 pagesSTRUCTURE OF ENGLISH Reviewer MidtermsMarissa EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Basic Hindi Grammar CompiledDocument49 pagesBasic Hindi Grammar CompiledRandy Dookheran100% (2)
- Parts of Speech, Words Classified According To Their Functions in Sentences, For Purposes ofDocument3 pagesParts of Speech, Words Classified According To Their Functions in Sentences, For Purposes ofRhitzle AnnNo ratings yet
- Origin: Thai (ภาษาไทย), a Tai-Kadai language spoken by about 25 million people in ThailandDocument3 pagesOrigin: Thai (ภาษาไทย), a Tai-Kadai language spoken by about 25 million people in ThailandṬhạnwa HimaNo ratings yet
- Gramatica Inglesa ApuntesDocument24 pagesGramatica Inglesa Apuntesadiana.s2002No ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah MorphologyDocument9 pagesMateri Kuliah MorphologyMuhammad Hidayatul RifqiNo ratings yet
- Part of LinguisticsDocument37 pagesPart of LinguisticsNorlina CipudanNo ratings yet
- Knowledge of WordsDocument35 pagesKnowledge of Wordserlina nurliaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Grade 3,4 2023Document21 pagesEnglish Grammar Grade 3,4 2023Sumera BokhariNo ratings yet
- AdverbDocument7 pagesAdverbhhheeellldddaaaNo ratings yet
- Grammar MKRDocument20 pagesGrammar MKRПереяслав ПереяславNo ratings yet
- RT of SpeechDocument7 pagesRT of SpeechDavid Vijay ColeNo ratings yet
- Telugu AlphabetsDocument20 pagesTelugu Alphabetsvenka07No ratings yet
- Ospf OuputDocument3 pagesOspf Ouputkamarajk22No ratings yet
- Abfall Englisch Bilder - V2Document1 pageAbfall Englisch Bilder - V2kamarajk22No ratings yet
- 03 CidrDocument20 pages03 CidrrishabhNo ratings yet
- IseDocument8 pagesIsekamarajk22No ratings yet
- Sosuave Guide To WomenDocument1 pageSosuave Guide To WomenJay MNo ratings yet
- Ise PDFDocument3 pagesIse PDFkamarajk22No ratings yet
- Ise PDFDocument3 pagesIse PDFkamarajk22No ratings yet
- FW MonitorDocument1 pageFW Monitorkamarajk22No ratings yet
- FW MonitorDocument2 pagesFW Monitorbbcu2005No ratings yet
- Tufin 01 BrochureDocument4 pagesTufin 01 Brochurekamarajk22No ratings yet
- Fortigate Ha 56Document305 pagesFortigate Ha 56kamarajk22No ratings yet
- Amit Singh Dharmesh2Document8 pagesAmit Singh Dharmesh2kamarajk22No ratings yet
- Cli GSGDocument56 pagesCli GSGkamarajk22No ratings yet
- Ospf Lsa TypesDocument1 pageOspf Lsa TypessuloxxNo ratings yet
- DMVPNDocument43 pagesDMVPNHassan Adeleke SamusideenNo ratings yet
- Unix CommandsDocument4 pagesUnix CommandsAzmat NaseemNo ratings yet
- CMPDocument17 pagesCMPRamesh VishalNo ratings yet
- Tamil Culture Is TheDocument33 pagesTamil Culture Is TheduetheeshNo ratings yet
- Tamil LanguageDocument13 pagesTamil LanguagePravin RamNo ratings yet
- Tamil GrammarDocument1 pageTamil GrammaramrikesaNo ratings yet
- Tamil Grammer Basics v1.0Document1 pageTamil Grammer Basics v1.0kamarajk22No ratings yet