Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 2-09
Uploaded by
Felix HabarugiraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 2-09
Uploaded by
Felix HabarugiraCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
3rd YEAR CE
SOIL MECHANICS I
ASSIGNMENT 2
Date due: 7/05/2009
1. The mass of an oven-dried sample of clay is 11.26 gm and its volume is 5.83 cm3. If the
specific gravity of the soil particles is 2.67 determine the shrinkage limit of the soil. The
shrinkage limit is the moisture content the soil would have had if fully saturated at its
minimum volume.
2. In a compaction test a bulk unit weight of 16 kN/m 3 was measured at a moisture content
of 8%. What would the moisture content have been if the soil had been fully saturated.
Assume Gs = 2.70.
3. In a deep deposit of clay the water table lies 3 m below the soil surface. Calculate the
total and effective stresses at depths of 1 m, 3 m and 5 m below the surface. Assume that
the soil remains fully saturated above the water table, and that sat = 16.5 kN/m3.
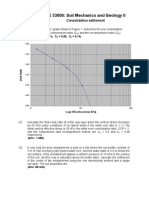
4. A clay has properties Cc = 0.4, Cr = 0.05. Determine the final void ratio for the following
situations:
a) Initially = 50 kPa, e = 1.2, pc = 100 kPa, Finally = 90 kPa
b) Initially = 50 kPa, e = 1.2, pc = 100 kPa, Finally = 190 kPa
c) Initially = 50 kPa, e = 1.2, pc = 50 kPa, Finally = 90 kPa
d) Initially = 50 kPa, e = 1.2, pc = 100 kPa, Finally = 30 kPa
e) Initially = 50 kPa, e = 1.2, pc = 50 kPa, Finally = 30 kPa
5. A soil deposit consists of 2 m of gravel overlaying an 8 m thick deposit of an over-
consolidated clay overlaying rigid permeable sandstone. The gravel has a unit weight of 22
kN/m3 when saturated and a unit weight of 18 kN/m3 when dry. The properties of the clay
are uniform throughout the layer and indicated below:
Void Ratio e 1.2
Specific Gravity Gs 2.7
Pre-consolidation pressure pc 70 kPa
Compression Index Cc 0.1
Recompression Index Cr 0.02
Consolidation coefficient cv 0.5 m2/year
Calculate the settlement under the centre of a square tank of side 5 m exerting an average
pressure of 175 kPa constructed on the ground surface after a long period of time and
estimate the time for 75% of this settlement to occur. Assume that initially the water table is
at the surface of the gravel but that after construction it is lowered to the surface of the clay.
The clay should be divided into two equal sub-layers.
6. Calculate the vertical effective stress at the centre of a 5m thick clay layer, free to drain
from its upper and lower boundaries, 2 years after the application of a sudden uniform
increase in total stress of 100 kPa. At the centre of the layer the initial (total) vertical stress =
100 kPa, the initial pore pressure = 30 kPa, and cv = 1 m2/year.
7. A square rigid footing of side 3 m is to be used to support a column carrying a load of
1.5 MN. The ground conditions at the site comprise a 15 m deep firm clay layer,
overlying competent impermeable rock. The clay has properties E´ = 10 Mpa, ´ = 0.2,
and the rock may be assumed to be rigid. Calculate:
(i) the immediate settlement
(ii) the final, long term settlement
(iii) the settlement after 2 years if cv = 3 m2/yr
You might also like
- On The Art of Building in Ten BooksDocument5 pagesOn The Art of Building in Ten BooksJosef Bolz0% (1)
- Consolidation Settlement Examples 1 - Solutions (2) - 2Document14 pagesConsolidation Settlement Examples 1 - Solutions (2) - 2Sujani MaarasingheNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam 2017 18Document2 pagesMidterm Exam 2017 18Ellarence RafaelNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument6 pagesProblemsNoor Mohd0% (1)
- Assignments and Tutorials - Soil Mechanics - Spring NewDocument42 pagesAssignments and Tutorials - Soil Mechanics - Spring NewmanthanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Compressibility of SoilDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Compressibility of SoilJommarVocalTagalog25% (4)
- Quiz 2Document1 pageQuiz 2senior highNo ratings yet
- Consolidation TutorialDocument6 pagesConsolidation TutorialJavidaNo ratings yet
- Consolidation of SoilDocument8 pagesConsolidation of SoilRay JillNo ratings yet
- 620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Document4 pages620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Mona fabrigarNo ratings yet
- Consolidation Settlement Examples 3 - Solutions (2) - 2Document6 pagesConsolidation Settlement Examples 3 - Solutions (2) - 2Sujani MaarasingheNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentsajjadsiyal144No ratings yet
- Homework - Plate No. 4aDocument1 pageHomework - Plate No. 4atest userNo ratings yet
- Compressibility of SoilDocument5 pagesCompressibility of SoilDupio German IINo ratings yet
- Geotech - 2Document2 pagesGeotech - 2Sanket AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 2 - SettlementDocument64 pages2 - SettlementNICKAJO DIVINONo ratings yet
- Geotech Practice QuestionDocument2 pagesGeotech Practice QuestionLucifer ShiversNo ratings yet
- GEO 2 LectureDocument37 pagesGEO 2 LecturePin YNo ratings yet
- CECA 2 - Problem Set No. 06Document3 pagesCECA 2 - Problem Set No. 06carldomingoNo ratings yet
- CE - 321: Foundation Engineering 6 Semester (Spring-2021) : Final Term Paper ExamDocument2 pagesCE - 321: Foundation Engineering 6 Semester (Spring-2021) : Final Term Paper ExamBilal SaifNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 2 - Geotechnical EngineeringDocument4 pagesModel Question Paper 2 - Geotechnical EngineeringMuhd FaridNo ratings yet
- Assessment Exam 04Document10 pagesAssessment Exam 04TachooNo ratings yet
- 100 Problems in GeotechDocument5 pages100 Problems in GeotechALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- GT Assignment - IIDocument1 pageGT Assignment - IIanpyaaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Foundation EngineeringDocument5 pagesProblem Set Foundation EngineeringJohn Mathew BrionesNo ratings yet
- M5 2241 Cepc19 2Document2 pagesM5 2241 Cepc19 2Honey MishraNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentBogale SenayNo ratings yet
- GEO 2 Prob Set Take 2 Chap 9Document3 pagesGEO 2 Prob Set Take 2 Chap 9John Pierce GumapacNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 1 - Geotechnical EngineeringDocument4 pagesModel Question Paper 1 - Geotechnical EngineeringShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Consolidation 2 - CorrectedDocument13 pagesSolutions For Consolidation 2 - CorrectedLin RongrongNo ratings yet
- F eDocument3 pagesF eXDXDXDNo ratings yet
- 1-D Settlement Examples Week 6-2Document2 pages1-D Settlement Examples Week 6-2jihe0020No ratings yet
- ES 621-Course Plan - 2018-19Document2 pagesES 621-Course Plan - 2018-19Khan Mohd SaalimNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #2 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem Set #2 PDFIM AM THE ONENo ratings yet
- 3) Bearing CapacityDocument19 pages3) Bearing CapacityhaftamuTekle100% (1)
- Plate 1 (Soil Composition) PDFDocument18 pagesPlate 1 (Soil Composition) PDFCaleb JalmascoNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics PracticalDocument19 pagesSoil Mechanics PracticalRanjan Kumar DahalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - CE631ADocument2 pagesAssignment 3 - CE631AAbhishek Mishra100% (1)
- ConsolidationDocument13 pagesConsolidationthuaiyaalhinaiNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment-01 - FinalDocument2 pagesHome Assignment-01 - Finaljsyadav.nithNo ratings yet
- Tutorial of SoilsDocument25 pagesTutorial of SoilsPrashant Chhetri100% (1)
- FrictionDocument19 pagesFrictionFirman KhaerulNo ratings yet
- Capitulo - Dinamica de Una ParticulaDocument6 pagesCapitulo - Dinamica de Una ParticulaHairoMatNo ratings yet
- Semester Earth Retaining Structures Subject code-CE 616Document2 pagesSemester Earth Retaining Structures Subject code-CE 616ATISH KUMAR DASNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Tariku BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Assignmnet 4Document2 pagesAssignmnet 4AshutoshKumarNo ratings yet
- Consolidation (Lecture-4) : Assignment Problems On Consolidation ChapterDocument2 pagesConsolidation (Lecture-4) : Assignment Problems On Consolidation ChapterDipankar NathNo ratings yet
- CE2112 Problem Sheet - Consolidation 2 - 23082015Document4 pagesCE2112 Problem Sheet - Consolidation 2 - 23082015Chen JianxiongNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Tushar GautamNo ratings yet
- AssignmentsDocument10 pagesAssignmentsAlsits LvtNo ratings yet
- Geo TechnicalDocument105 pagesGeo TechnicalSigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- Hge Mid PreboardDocument7 pagesHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Consolidation ExamplesDocument4 pagesConsolidation ExamplesAmpumuza MmukundaNo ratings yet
- Consolidation of ClayDocument17 pagesConsolidation of ClayMD Anan MorshedNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1finalsDocument1 pageQuiz 1finalsJhyne AezellNo ratings yet
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationFrom EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationGuilhem BourrieNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- Mid (Term Examination, 2 Semester Spring 2006: CE-104 Mechanics of Solids-1Document2 pagesMid (Term Examination, 2 Semester Spring 2006: CE-104 Mechanics of Solids-1Maniko ManikoNo ratings yet
- C++ NotesDocument54 pagesC++ NotesFelix HabarugiraNo ratings yet
- CE 206 Surveving 1 MidDocument1 pageCE 206 Surveving 1 MidIbrahim MohmandNo ratings yet
- 2009 Making The Most of Your MentorsDocument1 page2009 Making The Most of Your MentorsFelix HabarugiraNo ratings yet
- Consol SivakuganDocument29 pagesConsol SivakuganFelix HabarugiraNo ratings yet
- Permeability and Seepage: N. SivakuganDocument29 pagesPermeability and Seepage: N. SivakuganHunegnaw AynalemNo ratings yet
- Capter Four-Flow NetDocument51 pagesCapter Four-Flow NetAndualem KidusNo ratings yet
- Shear Strenght of SoilDocument26 pagesShear Strenght of SoilHiritik Kishore SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 MineralogyDocument36 pagesCH 2 MineralogyALIKNFNo ratings yet
- Uniform & Gradually Varied Open-Channel FlowDocument46 pagesUniform & Gradually Varied Open-Channel FlowFelix HabarugiraNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - How Do People Destroy Natural ResourcesDocument2 pagesActivity 6 - How Do People Destroy Natural ResourcesLeomille C Tubac83% (6)
- Earth and Rock Fill DamsDocument119 pagesEarth and Rock Fill Damsseprwgl100% (1)
- Accumulation and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Sugarcane Irrigated With Industrial Effluent in Some Rural Areas of Uttarakhand, IndiaDocument12 pagesAccumulation and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Sugarcane Irrigated With Industrial Effluent in Some Rural Areas of Uttarakhand, IndiaJose CuevasNo ratings yet
- % de Agu en PectinaDocument89 pages% de Agu en PectinaMayra Valdivieso100% (1)
- Environmental Solutions For Walls Slopes Water ApplicationsDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Solutions For Walls Slopes Water ApplicationsfaridNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Investigation and Mapping in The Lower Indus Plain 2020Document85 pagesGroundwater Investigation and Mapping in The Lower Indus Plain 2020fatimaNo ratings yet
- Proj Agreement With StateDocument25 pagesProj Agreement With StatelamaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report Tunnel Farming in PakistanDocument77 pagesInternship Report Tunnel Farming in PakistanMuhammad IrshadNo ratings yet
- Proposed Ligawasan Marsh Protected Ara v1 PDFDocument138 pagesProposed Ligawasan Marsh Protected Ara v1 PDFPochieNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Form 4-5Document93 pagesSocial Studies Form 4-5Tlotlo carvin NthokgoNo ratings yet
- APPSC Group 1 Mains Geography - PYQDocument15 pagesAPPSC Group 1 Mains Geography - PYQDevaraj BillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Municipal Socio Economic ProfileDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Municipal Socio Economic ProfileMichael RiveraNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Bamboo Industry in Kerala-Problems in Production and MarketingDocument11 pagesSynopsis Bamboo Industry in Kerala-Problems in Production and MarketingSasiNo ratings yet
- Example2 LL, PL& HydrometerDocument14 pagesExample2 LL, PL& Hydrometertes100% (1)
- Crop Coc Based QuistionsDocument4 pagesCrop Coc Based QuistionsWeredaw Bizualem BazezewNo ratings yet
- Agriculture-UC3 - Care and Maintain CropsDocument24 pagesAgriculture-UC3 - Care and Maintain CropsSUPER M SCHOOL OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Stem 2c-Music On Plant Growth FinalDocument91 pagesStem 2c-Music On Plant Growth FinalYonaNo ratings yet
- CompactionDocument64 pagesCompactionRamesh Konakalla100% (1)
- Water Content of Soil and Rock in Place by Nuclear Methods (Shallow Depth)Document5 pagesWater Content of Soil and Rock in Place by Nuclear Methods (Shallow Depth)Brenda HVNo ratings yet
- 7th Sem AssignmentDocument1 page7th Sem AssignmentAsnan KhanNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument8 pagesDocumentThoha SyNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S016599361830520X MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S016599361830520X MainBárbara RaniNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 9Document5 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 9Viola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Company Information PT For PVD, PHD Customer 2019Document43 pagesCompany Information PT For PVD, PHD Customer 2019Wences LunarNo ratings yet
- AIS 2310 Vol 1Document144 pagesAIS 2310 Vol 1Lilly ScottNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing Design PDFDocument45 pagesIsolated Footing Design PDFChau Suktana Enling0% (1)
- Textile Exchange - Organic Cotton Market Report - 2020 20200810Document62 pagesTextile Exchange - Organic Cotton Market Report - 2020 20200810sebastian rosalesNo ratings yet
- Pollution: Rachel CarsonDocument5 pagesPollution: Rachel CarsonBen TarcauNo ratings yet