Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1820-12 Phy P11 Electrostatics e 30Q (1) - 1
Uploaded by
JeevanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1820-12 Phy P11 Electrostatics e 30Q (1) - 1
Uploaded by
JeevanCopyright:
Available Formats
WORK SHEET XII PHYSICS
XII P11 ELECTROSTATICS
WORKSHEET E
1. The intensity of the electric field required to 5. Two equal charges q are placed at a distance
keep a water drop of radius 10 −5 cm just of 2 a and a third charge −2 q is placed at the
suspended in air when charged with one midpoint. The potential energy of the system
electron is approximately is
(A) q2 (B) 6 q 2
(g = 10 newton / kg, e = 1.6 10 −19 coulomb)
8 0 a 8 0 a
(A) 260 volt / cm (B) 260 newton / coulomb
(C) 130 volt / cm (D) 130 newton / coulomb
(C) 7q 2 (D) 9 q 2
−
8 0 a 8 0 a
2. The charges on two sphere are +7C and –
5C respectively. They experience a force F. If 6.
each of them is given and additional charge of A conductor with a positive charge
(A) Is always at + ve (B) Is always at zero
– 2C, the new force of attraction will be
(A) F (B) F / 2 potential potential
(C) Is always at (D) May be at + ve ,
(C) F / 3 (D) 2F
negative potential zero or −ve
potential
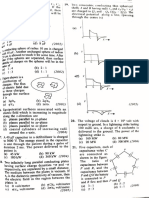
3. Four capacitors are connected in a circuit as 7. A condenser having a capacity of 6F is
shown in the figure. The effective capacitance charged to 100 V and is then joined to an
in F between points A and B will be uncharged condenser of 14 F and then
2F 12F
removed. The ratio of the charges on 6F and
14F and the potential of 6F will be
(A) 6 (B) 14
A 2F B and 50 volt and 30 volt
14 6
(C) 6 (D) 14
(A) 28 (B) 4 and 30 volt and 0 volt
14 6
9
(C) 5 (D) 18
8. Two particle of equal mass m and charge q
4.
As per this diagram a point charge +q is are placed at a distance of 16 cm. They do not
placed at the origin O . Work done in taking experience any force. The value of q is
m
another point charge −Q from the point A (A) l (B) 0
[co-ordinates (0, a) ] to another point B [co- G
ordinates (a, 0)] along the straight path AB is (C) G (D)
4 0 G
Y 4 0
A 9. While a capacitor remains connected to a
battery and dielectric slab is applied between
the plates, then
(A) Potential difference (B) Charge flows from
O B X between the plates the battery to the
(A) Zero (B)
− qQ 1
is changed capacitor
(C) Electric field (D) Energy store in the
4 a 2 2 a
0 between the plates capacitor decreases
increases
(C) (D) qQ 1
qQ 1 a 2a
2
2
4 0 a 2 4 0 a
GEMJEE - 9385412472 / 7338896332
Page 1 of 4
WORK SHEET XII PHYSICS
XII P11 ELECTROSTATICS
WORKSHEET E
10. What is the magnitude of a point charge which 14. The two metallic plates of radius r are placed
produces an electric field of 2 N/coulomb at a at a distance d apart and its capacity is C . If a
distance of 60 cm ( 1 / 4 0 = 9 10 9 N − m 2 / C 2 ) plate of radius r / 2 and thickness d of
(A) 8 10 −11 C (B) dielectric constant 6 is placed between the
2 10 −12 C
plates of the condenser, then its capacity will
be
(C) 3 10 −11 C (D)
6 10 −10 C (A) 7C / 2 (B) 3C / 7
(C) 7C / 3 (D) 9C / 4
11. A metallic sphere has a charge of 10 C . A unit 15. Equal charges q are placed at the vertices A
negative charge is brought from A to B both and B of an equilateral triangle ABC of side a .
100 cm away from the sphere but A being east The magnitude of electric field at the point C
of it while B being on west. The net work done is
is (A) q (B) 2q
(A) Zero (B) 2 / 10 joule 4 0 a 2
4 0 a 2
(C) 3q (D) q
(C) −2 / 10 joule (D) −1 / 10 joule
4 0 a 2
2 0 a 2
12. Three charges 2q, − q, − q are located at the 16. The equivalent capacitance in the circuit
vertices of an equilateral triangle. At the
between A and B will be
centre of the triangle
(A) The field is zero (B) The field is non-
1F 1F 1F
but potential is non- zero but potential is
A B
zero zero
(C) Both field and (D) Both field and (A) 1 F (B) 2 F
potential are zero potential are non-
zero (C) 3 F (D) 1
F
13. To charges q 1 and q 2 are placed 30 cm apart, 3
shown in the figure. A third charge q 3 is moved
17. In the adjoining figure, four capacitors are
along the arc of a circle of radius 40 cm from
shown with their respective capacities and the
C to D. The change in the potential energy of
q3 P.D. applied. The charge and the P.D. across
the system is k , where k is the 4 F capacitor will be
4 0
q3
C 20F
300 Volt
40 cm 4F 4F
12F
q2
q1 D
30 cm (A) 600 C; 150 volts (B) 300 C; 75 volts
A B
(A) 8 q 2 (B) 8 q 1
(C) 800 C; 200 volts (D) 580 C; 145 volts
(C) 6q 2 (D) 6q 1
GEMJEE - 9385412472 / 7338896332
Page 2 of 4
WORK SHEET XII PHYSICS
XII P11 ELECTROSTATICS
WORKSHEET E
18. Three identical point charges, as shown are 22. Two charges +5 C and +10 C are placed 20
placed at the vertices of an isosceles right cm apart. The net electric field at the mid-
Point between the two charges is
angled triangle. Which of the numbered vectors
(A) 4 .5 10 6 N/C (B) 4 .5 10 6 N/C
coincides in direction with the electric field at
directed towards directed towards
the mid-point M of the hypotenuse +5 C +10 C
3 (C) 13 .5 10 6
N/C (D) 13 .5 10 6N/C
2
directed towards directed towards
4
+5 C +10 C
M 23. Twenty seven drops of water of the same size
1
are equally and similarly charged. They are
(A) 1 (B) 2 then united to form a bigger drop. By what
(C) 3 (D) 4 factor will the electrical potential changes
(A) 9 times (B) 27 times
19. The points resembling equal potentials are
(C) 6 times (D) 3 times
S
P Q 24. Two small spheres each carrying a charge q
are placed r metre apart. If one of the spheres
R
is taken around the other one in a circular path
of radius r , the work done will be equal to
(A) P and Q (B) S and Q (A) Force between them (B) Force between them
r 2r
(C) S and R (D) P and R
(C) Force between (D) Zero
20. A conducting sphere of radius 10cm is them / 2r
charged 10 C . Another uncharged sphere of 25. Two charges of 4 C each are placed at the
radius 20 cm is allowed to touch it for some corners A and B of an equilateral triangle of
time. After that if the sphere are separated, side length 0.2 m in air. The electric potential
then surface density of charges, on the spheres 1 N - m2
at C is = 9 10 9
will be in the ratio of 4 0 C 2
(A) 1 : 4 (B) 1 : 3 (A) 9 10 4 V (B) 18 10 4 V
(C) 2 :1 (D) 1 :1 (C) 36 10 4 V (D) 36 10 −4 V
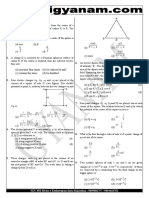
21. Ten electrons are equally spaced and fixed 26. −6
around a circle of radius R. Relative to V = 0 A pendulum bob of mass 30 .7 10 kg and
−8
at infinity, the electrostatic potential V and the carrying a charge 2 10 C is at rest in a
electric field E at the centre C are horizontal uniform electric field of 20000 V/m.
(A) V 0 and E 0 (B) V 0
and E = 0 The tension in the thread of the pendulum is
(g = 9.8 m / s 2 )
(C) V = 0 (D) V = 0
and E=0 and E0 (A)
3 10 −4 N (B)
4 10 −4 N
(C)
5 10 −4 N (D)
6 10 −4 N
GEMJEE - 9385412472 / 7338896332
Page 3 of 4
WORK SHEET XII PHYSICS
XII P11 ELECTROSTATICS
WORKSHEET E
27. There is 10 units of charge at the centre of a
circle of radius 10m. The work done in
moving 1 unit of charge around the circle once
is
(A) Zero (B) 10 units
(C) 100 units (D) 1 unit
28. Two point charges +3 C and +8 C repel each
other with a force of 40 N . If a charge of −5 C
is added to each of them, then the force
between them will become
(A) −10 N (B)
+10 N
(C) +20 N (D)
−20 N
29. Two charges + 3.2 10 −19 C and − 3.2 10 −9 C kept
2.4 Å apart forms a dipole. If it is kept in
uniform electric field of intensity 4 10 volt/m
5
then what will be its electrical energy in
equilibrium
(A) + 3 10 −23 J (B)
− 3 10 −23 J
(C) − 6 10 −23 J (D)
− 2 10 −23 J
30. If a charged spherical conductor of radius 10 cm
has potential V at a point distant 5 cm from its
centre, then the potential at a point distant 15 cm
from the centre will be
(A) 1
V (B) 2
V
3 3
(C) 3
V (D) 3 V
2
GEMJEE - 9385412472 / 7338896332
Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- DC Pandey Objective - 16 PDFDocument40 pagesDC Pandey Objective - 16 PDFAnchitNo ratings yet
- #NEET DPYQ Test Paper - 4 - Electricity & MagnetismDocument8 pages#NEET DPYQ Test Paper - 4 - Electricity & MagnetismZombie GamerNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesElectrostaticsnagavali200006No ratings yet
- Physics (Main) Question Paper-47Document13 pagesPhysics (Main) Question Paper-47Rishit GoelNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Test 2Document7 pagesElectrostatics Test 2HarshNo ratings yet
- Physics: Rapid Crash CourseDocument16 pagesPhysics: Rapid Crash CourseHudsun HornetNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Exercise PDFDocument21 pagesCapacitance Exercise PDFwhybangadNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument11 pagesElectrostaticsphysicist sharmaNo ratings yet
- Item 0 20180627014138320Document40 pagesItem 0 20180627014138320DEBJIT SHARMANo ratings yet
- 12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Document33 pages12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ds Ds DS: Physics For XIIDocument4 pagesDs Ds DS: Physics For XIIC.p. RawatNo ratings yet
- Capacitor One PDFDocument3 pagesCapacitor One PDFcolorado wildernessNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - DPP 01 - (Shaurya Fastrack)Document3 pagesElectrostatics - DPP 01 - (Shaurya Fastrack)ccjakharNo ratings yet
- 2 - Capacitance - Exercise - 1 & 2 Module-4Document16 pages2 - Capacitance - Exercise - 1 & 2 Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Student Copy. DPP No. 24 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesStudent Copy. DPP No. 24 ElectrostaticsDushyanth S JNo ratings yet
- L1 - Assignment On Electric FluxDocument3 pagesL1 - Assignment On Electric FluxdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Electro Statics - 26-08-2020 PDFDocument10 pagesElectro Statics - 26-08-2020 PDFPonharish kumar.JNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Electrostatics (Charge, Electric Field)Document2 pagesAssignment 1 Electrostatics (Charge, Electric Field)Vijay Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics (JEE MAIN Online) PDFDocument15 pagesElectrostatics (JEE MAIN Online) PDFAnanya DwivediNo ratings yet
- Sankalp Phaseiv El 12 Lecture-11Document5 pagesSankalp Phaseiv El 12 Lecture-11SuyashNo ratings yet
- CAPACITORPOTENDocument5 pagesCAPACITORPOTENAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- 2nd PUC Physics Important MCQsDocument51 pages2nd PUC Physics Important MCQsUrav SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Forces)Document7 pagesChapter 1 (Forces)Chandrika AnchanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Practice Problems Capacitor - 1: Level - I 1Document4 pagesLecture Practice Problems Capacitor - 1: Level - I 1AryanNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type) : IIT - JEE: 2022 Xii - TW Test DATE: 19/07/20 TIME: 1 Hr. Physics MARKS: 100Document8 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type) : IIT - JEE: 2022 Xii - TW Test DATE: 19/07/20 TIME: 1 Hr. Physics MARKS: 100pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Arora: Target 2021 DPP - 3Document4 pagesGaurav Arora: Target 2021 DPP - 3Devansh SangwanNo ratings yet
- 1770-12 Phy-Electrostatics 40Q Level3 (4) - 1Document3 pages1770-12 Phy-Electrostatics 40Q Level3 (4) - 1JeevanNo ratings yet
- 25 GhanaINSET Sourcebook M5Document6 pages25 GhanaINSET Sourcebook M5Preeti dasNo ratings yet
- (@bohring - Bot) Pks ElectrostatsDocument10 pages(@bohring - Bot) Pks ElectrostatsxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- CPP-3 Electrostatics: Electric PotentialDocument4 pagesCPP-3 Electrostatics: Electric Potentialkartikagarwal7986No ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance PYQsDocument4 pagesElectrostatic Potential and Capacitance PYQspatiminati2020No ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- 12 - JM - P1 - M1 Q 1305CJM202021230001-Allen 070523Document16 pages12 - JM - P1 - M1 Q 1305CJM202021230001-Allen 070523PRITAM KumarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (02) - Electrostatic Potential (KP)Document10 pagesWorksheet (02) - Electrostatic Potential (KP)Harish ChinthalNo ratings yet
- Potential and CapacitanceDocument7 pagesPotential and CapacitanceAngsuman PatraNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01-Pages-27-72Document46 pagesSheet - 01-Pages-27-72Hemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Class XII Level 1 AssignmentDocument72 pagesClass XII Level 1 AssignmentK VIKASNo ratings yet
- Apacitance: Section (A) : Definition of CapacitanceDocument7 pagesApacitance: Section (A) : Definition of CapacitanceSwayam JindalNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-Extra Questions 1 REVIEW TEST-6Document30 pagesPHYSICS-Extra Questions 1 REVIEW TEST-6Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- MCQ-Ch-1-Electric Fields and ChargesDocument4 pagesMCQ-Ch-1-Electric Fields and ChargesPragati RathoreNo ratings yet
- Electrostastics ExDocument28 pagesElectrostastics ExTejus VishwanathNo ratings yet
- Kvpy ElectrostaticDocument9 pagesKvpy ElectrostaticUdbhav DikshitNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Field - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Document5 pagesElectric Charges and Field - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Divya KumariNo ratings yet
- Cbse PMT 2012Document33 pagesCbse PMT 2012Vishal RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- PHY Class - 12 WPP No. 2 - CapacitanceDocument3 pagesPHY Class - 12 WPP No. 2 - CapacitanceArya jasmin MaharanaNo ratings yet
- Potential DPPDocument11 pagesPotential DPPMoksh amberkarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Problems SetDocument10 pagesElectrostatics Problems SetRatan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics DPPDocument10 pagesElectrostatics DPPhimesh2006hNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsDocument7 pagesChapter - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsAkash SureshNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: (Physics)Document5 pagesElectrostatics: (Physics)Tom HollandNo ratings yet
- Charged 2 12) Potential: Conducting Spherical Having Along (PassingDocument1 pageCharged 2 12) Potential: Conducting Spherical Having Along (PassingShyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- 1 CapacitanceEx-I1Document6 pages1 CapacitanceEx-I1Ashwani KumarNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsExercise 2Document3 pagesElectrostaticsExercise 2Rushwin VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Electro Statics - 27-08-2020 PDFDocument12 pagesElectro Statics - 27-08-2020 PDFPonharish kumar.JNo ratings yet
- The Electric Field at A DistanceDocument8 pagesThe Electric Field at A DistanceprashantNo ratings yet
- 29.12.23 Electrostatics - JEEDocument3 pages29.12.23 Electrostatics - JEERittamNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Exercise PDFDocument20 pagesElectrostatics Exercise PDFAshish Ranjan0% (1)
- DPP#25 To 31 Electrostatics 7 Capacitance 15.06.2013 HOMEWORKDocument32 pagesDPP#25 To 31 Electrostatics 7 Capacitance 15.06.2013 HOMEWORKJustin Willis64% (11)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document5 pagesWa0000.JeevanNo ratings yet
- Database Commands - Class 12Document9 pagesDatabase Commands - Class 12JeevanNo ratings yet
- Database Commands - Class 12Document9 pagesDatabase Commands - Class 12JeevanNo ratings yet
- 1822-12 Phy P15 Ray Optics B 30Q (1) - 1Document3 pages1822-12 Phy P15 Ray Optics B 30Q (1) - 1JeevanNo ratings yet
- Dreams - Interpreting Your Dreams and How To Dream Your Desires - Lucid Dreaming, Visions and Dream Interpretation PDFDocument70 pagesDreams - Interpreting Your Dreams and How To Dream Your Desires - Lucid Dreaming, Visions and Dream Interpretation PDFJshsNo ratings yet
- Ground RulesDocument2 pagesGround RulespulithepogiNo ratings yet
- PelicanStores QMDocument26 pagesPelicanStores QMPhuntru PhiNo ratings yet
- F Accountancy MS XI 2023-24Document9 pagesF Accountancy MS XI 2023-24bhaiyarakesh100% (1)
- Francisco Vs NLRCDocument2 pagesFrancisco Vs NLRCCamille GrandeNo ratings yet
- Moneymax X Citibank GCash Exclusive Campaign T&CsDocument3 pagesMoneymax X Citibank GCash Exclusive Campaign T&CsProsserfina MinaoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance SlidesDocument38 pagesCorporate Finance SlidesHaymaan Rashid DarNo ratings yet
- Evasco Vs Montanez Ruling On Substantive Due ProcessDocument2 pagesEvasco Vs Montanez Ruling On Substantive Due ProcessMacTavish PriceNo ratings yet
- Art 7 Beso vs. Dagunan, 323 SCRA 566Document2 pagesArt 7 Beso vs. Dagunan, 323 SCRA 566Tom Louis HerreraNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument5 pagesReportapi-358359361No ratings yet
- 2 Sem SyllabusDocument3 pages2 Sem SyllabusShubham Jain ModiNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Simon Mnyele..appe VS The Repub..respo Crim Appe No4Document26 pagesGabriel Simon Mnyele..appe VS The Repub..respo Crim Appe No4DATIUS DIDACE(Amicus Curiae)⚖️100% (1)
- Sample Formal OfferDocument4 pagesSample Formal OfferMominur Rahman DiptoNo ratings yet
- Rights of The AccusedDocument9 pagesRights of The AccusedVeah CaabayNo ratings yet
- Icc OpinionsDocument19 pagesIcc OpinionsJhoo AngelNo ratings yet
- العراق وامريكا 1958-59Document126 pagesالعراق وامريكا 1958-59Bassam ShabebNo ratings yet
- Goodale and Miller ComplaintDocument2 pagesGoodale and Miller ComplaintLeigh Egan100% (1)
- Rajiv Gandhi National University of Law, PunjabDocument2 pagesRajiv Gandhi National University of Law, PunjabShubham PandeyNo ratings yet
- Decide Which Answer (A, B, C or D) Best Fits Each Space.: Inspector Crumbs InvestigatesDocument2 pagesDecide Which Answer (A, B, C or D) Best Fits Each Space.: Inspector Crumbs InvestigatesХристина КоникNo ratings yet
- Invoice OAD0000137925Document1 pageInvoice OAD0000137925mikhaelyosiaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Government AccountingDocument43 pagesModule 7 Government AccountingElla EspenesinNo ratings yet
- The Modern Prince: A Review of The Prince and On Machiavellianism of TodayDocument7 pagesThe Modern Prince: A Review of The Prince and On Machiavellianism of TodayRafael Kieran MondayNo ratings yet
- AHRI Standard 310 380-2014 CSA C744-14Document28 pagesAHRI Standard 310 380-2014 CSA C744-14Christian DoriaNo ratings yet
- 1 Oblicon RealFamDocument31 pages1 Oblicon RealFamEfrean BianesNo ratings yet
- 10NM60Document17 pages10NM60Jose Barroso GuerraNo ratings yet
- COA Findings On BaseyDocument7 pagesCOA Findings On BaseyGie Bernal CamachoNo ratings yet
- Letter Defending Bless Me, UltimaDocument2 pagesLetter Defending Bless Me, UltimancacensorshipNo ratings yet
- Fly S5Document77 pagesFly S5eliorlopezbNo ratings yet
- NSTP 1 Common ModuleDocument120 pagesNSTP 1 Common ModuleKenneth Dave SaguirreNo ratings yet
- Manipalcigna Prohealth Group Insurance PolicyDocument3 pagesManipalcigna Prohealth Group Insurance PolicykeviletuoNo ratings yet
- Googleapps Notes MigrationDocument82 pagesGoogleapps Notes MigrationnarendraidealNo ratings yet