Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability
Uploaded by
PRIYANKA PRATHAPANCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability
Uploaded by
PRIYANKA PRATHAPANCopyright:
Available Formats
22
1 (a) ABCD is a trapezium.
11 cm
A B
NOT TO
SCALE
4.7 cm
D C
2.6 cm
17 cm
(i) Calculate the length of AD.
Answer(a)(i) AD = .......................................... cm [2]
(ii) Calculate the size of angle BCD.
Answer(a)(ii) Angle BCD = ................................................ [3]
(iii) Calculate the area of the trapezium ABCD.
Answer(a)(iii) ......................................... cm2 [2]
(b) A similar trapezium has perpendicular height 9.4 cm.
Calculate the area of this trapezium.
Answer(b) ......................................... cm2 [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
33
2 There are three different areas, A, B and C, for seating in a theatre.
The numbers of seats in each area are in the ratio A : B : C = 11 : 8 :
7 . There are 920 seats in area B.
(a) (i) Show that there are 805 seats in area C.
Answer(a)(i)
[1]
(ii) Write the number of seats in area B as a percentage of the total number of seats.
Answer(a)(ii) ............................................ % [2]
(b) The cost of a ticket for a seat in each area of the theatre is shown in the table.
Area A $11.50
Area B $15
Area C $22.50
3
For a concert 80% of area B tickets were sold and 5 of area C tickets were sold.
The total amount of money taken from ticket sales was $35 834.
Calculate the number of area A tickets that were sold.
Answer(b) ................................................ [5]
(c) The total ticket sales of $35 834 was 5% less than the ticket sales at the previous concert.
Calculate the ticket sales at the previous concert.
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
44
Answer(c) $ ................................................. [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
55
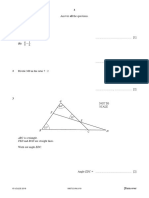
3
A
B
NOT TO
52°
SCALE
D
O
56°
C E
A, B, C and D are points on a circle, centre O.
CE is a tangent to the circle at C.
(a) Find the sizes of the following angles and give a reason for each answer.
(i) Angle DAC = ..................... because ..........................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) Angle DOC = ..................... because .........................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(iii) Angle BCO = ..................... because ..........................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
66
(b) CE = 8.9 cm and CB = 7 cm.
(i) Calculate the length of BE.
Answer(b)(i) BE = .......................................... cm [4]
(ii) Calculate angle BEC.
Answer(b)(ii) Angle BEC = ................................................ [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
77
4 Yeung and Ariven compete in a triathlon race.
The probability that Yeung finishes this race is 35 .
2
The probability that Ariven finishes this race is 3 .
(a) (i) Which of them is more likely to finish this race?
Give a reason for your answer.
Answer(a)(i) ...................................................... because ..........................................................
..................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Find the probability that they both finish this race.
Answer(a)(ii) ................................................ [2]
(iii) Find the probability that only one of them finishes this race.
Answer(a)(iii) ................................................ [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
77
(b) After the first race, Yeung competes in two further triathlon races.
(i) Complete the tree diagram.
First race Second race Third race
7
10 Finishes
6 Finishes
7
Does not
........ finish
Finishes
7
3 10 Finishes
5 ........ Does not
finish
Does not
........ finish
7
10 Finishes
6 Finishes
7
........ Does not
........ finish
Does not
finish 7
10 Finishes
........ Does not
finish
Does not
........ finish
[3]
(ii) Calculate the probability that Yeung finishes all three of his races.
Answer(b)(ii) ................................................ [2]
(iii) Calculate the probability that Yeung finishes at least one of his races.
Answer(b)(iii) ................................................ [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
88
0 -1 1 -2 -3
5 P= f p Q=f p R=e o
1 0 0 1 5
(a) Work out
(i) 4P,
Answer(a)(i) [1]
(ii) P – Q,
Answer(a)(ii) [1]
(iii) P2,
Answer(a)(iii) [2]
(iv) QR.
Answer(a)(iv) [2]
1 0
(b) Find the matrix S, so that QS = f p.
0 1
Answer(b) [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
99
6 (a) Simplify.
(i) x3 ÷ 35
x
Answer(a)(i) ................................................ [1]
(ii) 5xy8 × 3x6y–5
Answer(a)(ii) ................................................ [2]
2
(iii) (64x12) 3
Answer(a)(iii) ................................................ [2]
(b) Solve 3x2 – 7x – 12 = 0.
Show your working and give your answers correct to 2 decimal places.
Answer(b) x = ........................ or x = ........................ [4]
x2 - 25 .
(c) Simplify
x3 - 5x2
Answer(c) ................................................ [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
10
0
7
A P
NOT TO
SCALE
56° 6.5 cm
8 cm 8 cm
O x
C B
Q
The diagram shows a triangle and a sector of a circle.
In triangle ABC, AB = AC = 8 cm and angle BAC = 56°.
Sector OPQ has centre O, sector angle x and radius 6.5 cm.
(a) Show that the area of triangle ABC is 26.5 cm2 correct to 1 decimal place.
Answer(a)
[2]
(b) The area of sector OPQ is equal to the area of triangle ABC.
(i) Calculate the sector angle x.
Answer(b)(i) ................................................ [3]
(ii) Calculate the perimeter of the sector OPQ.
Answer(b)(ii) .......................................... cm [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
11
1
(c) The diagram shows a sector of a circle, radius r cm.
NOT TO
SCALE
r cm
30°
(i) Show that the area of the shaded segment is 14 r 2` 13 π - 1 j cm2.
Answer(c)(i)
[4]
(ii) The area of the segment is 5 cm2.
Find the value of r.
Answer(c)(ii) r = ................................................ [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
12
2
8 (a) A straight line joins the points (–1, –4) and (3, 8).
(i) Find the midpoint of this line.
Answer(a)(i) (...................... , ......................) [2]
(ii) Find the equation of this line.
Give your answer in the form y = mx + c.
Answer(a)(ii) y = ................................................ [3]
(b) (i) Factorise x2 + 3x – 10.
Answer(b)(i) ................................................ [2]
(ii) The graph of y = x2 + 3x – 10 is sketched below.
y
NOT TO
SCALE
x
(a, 0) 0 (b, 0)
(0, c)
Write down the values of a, b and c.
Answer(b)(ii) a = ................................................
b = ................................................
c = ................................................ [3]
(iii) Write down the equation of the line of symmetry of the graph of y = x2 + 3x – 10.
Answer(b)(iii) ................................................ [1]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
13
3
(c) Sketch the graph of y = 18 + 7x – x2 on the axes below.
Indicate clearly the values where the graph crosses the x and y axes.
y
NOT TO
SCALE
x
0
[4]
(d) (i) x2 + 12x – 7 = (x + p)2 – q
Find the value of p and the value of q.
Answer(d)(i) p = ................................................
q = ................................................ [3]
(ii) Write down the minimum value of y for the graph of y = x2 + 12x – 7.
Answer(d)(ii) ................................................ [1]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
14
4
9 (a) Ricardo asks some motorists how many litres of fuel they use in one day.
The numbers of litres, correct to the nearest litre, are shown in the table.
Number of litres 16 17 18 19 20
Number of motorists 11 10 p 4 8
(i) For this table, the mean number of litres is 17.7 .
Calculate the value of p.
Answer(a)(i) p = ................................................ [4]
(ii) Find the median number of litres.
Answer(a)(ii) ....................................... litres [1]
(b) Manuel completed a journey of 320 km in his car.
The fuel for the journey cost $1.28 for every 6.4 km travelled.
(i) Calculate the cost of fuel for this journey.
Answer(b)(i) $ ................................................. [2]
(ii) When Manuel travelled 480 km in his car it used 60 litres of fuel.
Manuel’s car used fuel at the same rate for the journey of 320 km.
Calculate the number of litres of fuel the car used for the journey of 320 km.
Answer(b)(ii) ....................................... litres [2]
(iii) Calculate the cost per litre of fuel used for the journey of 320 km.
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
15
5
Answer(b)(iii) $ ................................................. [2]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
16
6
(c) Ellie drives a car at a constant speed of 30 m/s correct to the nearest 5 m/s.
She maintains this speed for 5 minutes correct to the nearest 10 seconds.
Calculate the upper bound of the distance in kilometres that Ellie could have travelled.
Answer(c) .......................................... km [5]
10 (a)
(3x – 5) cm
NOT TO
(2x – 3) cm SCALE
(15 – 2x) cm
(2x + 7) cm
(i) Write an expression, in terms of x, for the perimeter of the quadrilateral.
Give your answer in its simplest form.
Answer(a)(i) .......................................... cm [2]
(ii) The perimeter of the quadrilateral is 32 cm.
Find the length of the longest side of the quadrilateral.
Answer(a)(ii) .......................................... cm [3]
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
17
7
Question 10(b) is printed on the next page.
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
18
8
(b)
(5a – 2b) m (6b – a) m
14 m
(7a – 6b) m NOT TO
SCALE
am
13.5 m
(3b + a) m
The triangle has a perimeter of 32.5 m.
The quadrilateral has a perimeter of 39.75 m.
Write two equations in terms of a and b and simplify them.
Use an algebraic method to find the values of a and b.
Show all your working.
Answer(b) a = ................................................
b = ................................................ [6]
Source: Extremepapers/CIE/UCLES
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
1
19
9
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/O/N/14 [Turn over
You might also like
- Cambridge International General Certiþ Cate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certiþ Cate of Secondary EducationtaliassalimNo ratings yet
- Trigo#1 PDFDocument10 pagesTrigo#1 PDFAmmar AdnanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Worksheet - 010333Document5 pagesTrigonometry Worksheet - 010333Mohammad Asjad JillaniNo ratings yet
- 4024 w11 QP 22Document24 pages4024 w11 QP 22Hamza NawazNo ratings yet
- 0580 w14 QP 43Document16 pages0580 w14 QP 43Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Maths Rcis Sem 2 Full PortionDocument13 pagesMaths Rcis Sem 2 Full PortionKavyaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry_1_-_testDocument29 pagesTrigonometry_1_-_testsate BrigaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ProblemsDocument15 pagesTrigonometry ProblemsDhruv KakkarNo ratings yet
- Test # 3Document24 pagesTest # 3Waheed ahmadNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 0580Document600 pagesQuestion Bank 0580saisudhaNo ratings yet
- 0580 Trigonometry P4Document52 pages0580 Trigonometry P4AditiNo ratings yet
- Calculations Involving Compound Shapes P4Document5 pagesCalculations Involving Compound Shapes P4Ucok PandapotanNo ratings yet
- 4024 w11 QP 21Document20 pages4024 w11 QP 21mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Questions.. MensurationDocument31 pagesQuestions.. Mensurationimtiazakhtar012No ratings yet
- 0001Document10 pages0001auricayunneNo ratings yet
- Perimeter and Area of Shapes P4Document7 pagesPerimeter and Area of Shapes P4Ucok PandapotanNo ratings yet
- Trignometry Revison 2020Document30 pagesTrignometry Revison 2020pyanshy soniiNo ratings yet
- 0580 s15 QP 43Document16 pages0580 s15 QP 43yottanodeNo ratings yet
- cs3 - Topical Reinforcement 4.Document4 pagescs3 - Topical Reinforcement 4.MCHNo ratings yet
- Test ShapesDocument8 pagesTest ShapesgdwqfmtzcpNo ratings yet
- Algebra Word ProblemsDocument13 pagesAlgebra Word ProblemsTalha AhmedNo ratings yet
- 0580 w02 QP 1 UnlockedDocument6 pages0580 w02 QP 1 UnlockedGiuseppeGuerreraNo ratings yet
- Mensuration New 23 CombineDocument24 pagesMensuration New 23 CombineAshbeela rashdiNo ratings yet
- Trignonometry Non Right Angled TriangleDocument24 pagesTrignonometry Non Right Angled TriangleMuhammad DanishNo ratings yet
- Mytest 1Document5 pagesMytest 1enock chilufyajrNo ratings yet
- Maths P2 WorksheetDocument6 pagesMaths P2 WorksheetSatyven SoobraydooNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Sin, Cos RuleDocument15 pagesTrigonometry Sin, Cos RuleDevil InsideNo ratings yet
- Math D O Level Style Question Paper 1Document20 pagesMath D O Level Style Question Paper 17a4374 hisNo ratings yet
- 4024 s12 QP 21Document24 pages4024 s12 QP 21Beatrice RossNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level Maths Paper 2 Section A QuestionsDocument20 pagesCambridge O Level Maths Paper 2 Section A QuestionsSheikh Mohammad ForhadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Mathematics 0580/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Mathematics 0580/42Haron HarveyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Math Exam ReviewDocument19 pagesGrade 10 Math Exam ReviewMuhammad Tanvirul IslamNo ratings yet
- 2020 ST Hilda SA2Document28 pages2020 ST Hilda SA2AlexisNo ratings yet
- 0607_s19_qp_21 (1)Document4 pages0607_s19_qp_21 (1)Yakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Trig PracticeDocument9 pagesYear 10 Trig Practice이규민No ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - Date: Time: Instructions To CandidatesDocument10 pagesName: - Class: - Date: Time: Instructions To CandidatesHeba AbidiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations: General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- O Level Mathematics Past QuestionsDocument24 pagesO Level Mathematics Past QuestionsnurlNo ratings yet
- grade 9 maths paper_220915_064011Document24 pagesgrade 9 maths paper_220915_064011yoon tim lamNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Mathematics 0580/31Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Mathematics 0580/31Rehab NagaNo ratings yet
- 4024_w17_qp_21 (1)Document10 pages4024_w17_qp_21 (1)Shahzeb AftabNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2015Document18 pagesMaths Paper 2015aminathNo ratings yet
- 0580 m15 QP 42 PDFDocument16 pages0580 m15 QP 42 PDFNamanNo ratings yet
- 4024 s11 QP 21Document24 pages4024 s11 QP 21AkibNawazNo ratings yet
- G8 - London 2021Document15 pagesG8 - London 2021MahomedallyBilallNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGrade 10 TrigonometryMuqsit UsmanNo ratings yet
- Mocktest 10Document11 pagesMocktest 10KIEN NGUYENDACCHINo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/31Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/31Raj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Maya Of: Cambridge O LevelDocument16 pagesMaya Of: Cambridge O Levelfatima malhiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationPrince YugNo ratings yet
- 4024 w11 QP 21Document20 pages4024 w11 QP 21SyedMaazAliNo ratings yet
- 4024 s12 QP 22Document20 pages4024 s12 QP 22Beatrice RossNo ratings yet
- EshanDocument9 pagesEshanNerd 101No ratings yet
- 4024 s12 QP 21Document24 pages4024 s12 QP 21mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certifi Cate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certifi Cate of Secondary EducationNamanNo ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument10 pagesSolution of TrianglesMohd HarrisNo ratings yet
- ERC 2018 O Level Math P1 - v4 Final PDFDocument15 pagesERC 2018 O Level Math P1 - v4 Final PDFLim Kew ChongNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 05802 PDFDocument600 pagesQuestion Bank 05802 PDFkdd987100% (2)
- PerspectiveDocument12 pagesPerspectiveamardhiahNo ratings yet
- 03 - Chain Rule With Trig PDFDocument2 pages03 - Chain Rule With Trig PDFLeo Rene Astacaan LeonidaNo ratings yet
- Bending 6.3-6.4: Longitudinal Strain Flexure FormulaDocument33 pagesBending 6.3-6.4: Longitudinal Strain Flexure FormulaPrasad GNNo ratings yet
- Equations and Geometry Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesEquations and Geometry Practice ProblemsJed ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Math-8 Q4 M1Document7 pagesMath-8 Q4 M1LADY ANN GRACE LAGAS100% (1)
- Worksheet Vsepr Theory Using The Knowledge of VSEPR Theory, Complete The Table Given BelowDocument2 pagesWorksheet Vsepr Theory Using The Knowledge of VSEPR Theory, Complete The Table Given Belownidhi1478No ratings yet
- Straight Line QuestionsDocument26 pagesStraight Line QuestionsDaniel NimabwayaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Chapter 16Document32 pagesDynamics - Chapter 16Hamza PagaNo ratings yet
- Examples and Problems On Conics PDFDocument216 pagesExamples and Problems On Conics PDFAnilNo ratings yet
- Quaternions cs520 6upDocument6 pagesQuaternions cs520 6upzhaodong.liangNo ratings yet
- Matusiak - Dynamics of A Rigid ShipDocument153 pagesMatusiak - Dynamics of A Rigid ShipMaciej ReichelNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics: by R.Nathan Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument16 pagesEngineering Graphics: by R.Nathan Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical EngineeringChowkidar KarthikNo ratings yet
- FormasDocument8 pagesFormaspigotoNo ratings yet
- Classnotes Ma1101 PDFDocument139 pagesClassnotes Ma1101 PDFBhupi.SamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Solutions 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1 Solutions 1boyarskyNo ratings yet
- ACT FORMULA SHEET CHEAT SHEETDocument3 pagesACT FORMULA SHEET CHEAT SHEETkimmy730No ratings yet
- Control of Quadrotor: Master ProjectDocument19 pagesControl of Quadrotor: Master ProjectYessica Rosas CuevaNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument67 pagesRay OpticsSURBHI TOMAR100% (1)
- Maths WorkbookDocument106 pagesMaths Workbookdnes9999No ratings yet
- Trigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument8 pagesTrigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsJpricarioNo ratings yet
- 11th Class Physics :kinematics in One Dimension + Calculus at VireshDocument2 pages11th Class Physics :kinematics in One Dimension + Calculus at VireshViresh SinghNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument15 pagesGeometryMajeanxNo ratings yet
- IET Lucknow - Mathematical Paper - SumanDocument6 pagesIET Lucknow - Mathematical Paper - SumanAnchit GautamNo ratings yet
- Unequal Angles PDFDocument2 pagesUnequal Angles PDFmuathNo ratings yet
- Aplicatii Ale Math in Physics PDFDocument127 pagesAplicatii Ale Math in Physics PDFAurelian Solon100% (1)
- Grade 5 Sample Math Challenge Questions and AnswerDocument8 pagesGrade 5 Sample Math Challenge Questions and AnswerChelsea Martinez100% (1)
- Conservation of Angular Momentum from SymmetriesDocument21 pagesConservation of Angular Momentum from Symmetrieszijun yuNo ratings yet
- March Formative Assessment MYP-III RetakeDocument3 pagesMarch Formative Assessment MYP-III RetakeArslan Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Fractals DiffusionDocument11 pagesFractals Diffusionscribd4tavoNo ratings yet
- Adance Maths PDFDocument39 pagesAdance Maths PDFharshdh1No ratings yet