Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4
Uploaded by
muqaddasyaqoobCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4
Uploaded by
muqaddasyaqoobCopyright:
Available Formats
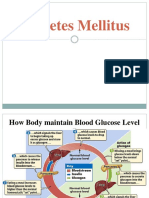
What is glucose intolerance?
Glucose intolerance is an umbrella term for a group of metabolic conditions that results in higher
than normal blood glucose level hyperglycemia.
The major categories of the disorders of glycemia or glucose tolerance are as follows:
1. Type 1 diabetes mellitus(DM) (due to autoimmune B B-cell
cell destruction usually leading to
absolute insulin deficiency)
2. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (due to progressive loss of BB-cell
cell insulin secretion frequently on
the background of insulin resistance)
3. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) (diabetes diagnosed in the second or third trimester
of pregnancy thatt was not clearly overt diabetes prior to gestation)
4. Specific types of diabetes due to other causes (such as neonatal
neonatal-relating
relating to or affecting
the new born, diabetes and maturity onset diabetes of the young, diseases of the exocrine
pancreas and drug-or chemical
emical-induced diabetes)
5. Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT: prediabetes/intermediate hyperglycemia)
6. Impaired fasting glucose (IFG: prediabetes /intermediate hyperglycemia)
According to WHO’ss definitions of IFG and IGT, glucose intolerance is defined as;
A fasting
asting blood glucose lev
level of above 6.0mmol/L
A blood glucose level of over 7.8mmol/L 2 hours after consuming 75g of glucose. glucose
GLUCOSE INTOLERANCE
Symptoms of glucose intolerance
intolerance:
The symptoms of glucose intolerance match those of type 2 diabetes
Feeling very thirsty
Dry mouth
Extreme blindness
Blurred vision
Drowsiness
Frequent need to urinate
Loss of muscle mass
Abdominal pain
Headaches
Depression
Diarrhea, constipation
Bloating
Feeling tired
Skin problems
Unexplained weight loss
The NHS states that not everyone will get these symptoms and symptoms may not be
severe.
Causes of Glucose Intolerance:
An immune-mediated cause of impaired glucose intolerance includes stiff person
syndrome and anti-insulin receptor abnormalities. Other causes of glucose intolerance
are liver diseases (as in cirrhosis-widespread disruption of normal liver structure by
fibrosis and formation of regenerative nodules that is caused by any of various
chronic progressive conditions affecting the liver) and renal failure.
Treatment of Glucose Intolerance:
Treatments for glucose intolerance will either require lifestyle changes or a
combination of lifestyle changes and anti-diabetic medication.
Lifestyle changes involve taking part in regular physical activities, aiming to lose
weight, if appropriate, and cutting down on smoking and alcohol as necessary.
If medication is advised most people will start on a drug, taken in tablet form, called
metformin.
Some people may need to take additional or alternative medication.
Effects on Women:
Women with IGT(impaired glucose tolerance) were at increased risk of;
Rupture of membranes
Preterm birth
Developing type 2 diabetes
High blood glucose in the fetus and low levels after birth
Difficulties during labor and the need of cesarean delivery
A high risk of vaginal tearing during birth and bleeding after birth
Hypoglycemia (high rates of blood glucose) during pregnancy exposes the baby to
following risks;
High birth weight (over 4kg or 8 pounds and 13 ounces)
Hypoglycemia at birth
Jaundice at birth
A dislocated shoulder or other complications at birth
Premature birth due to high volumes of amniotic fluid
A heart and/or lung effect
Glucose Intolerance Diet
The diet recommended by the NHS follows the general healthy eating advice. The
NHS recommends eating a balanced diet based on whole grain foods, rich in fruits
and vegetables and lower in sugar, salt and saturated fat.
Avoiding or significantly limiting the following foods can help moderate blood sugar
level:
Sweetened beverages, including fruit juices, soda, and fountain drinks.
Alcohol particularly beer and grain alcohol
Starchy vegetables, such as potatoes and yams
Processed snacks and boxed foods
Sugary sweet such as cup cake, ice cream etc
Foods high in saturated fats, including chocolate, butter, and salt pork.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plans For Diabetes MellitusDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plans For Diabetes MellitusPuteri AzmanNo ratings yet
- Definition and Diagnostic Criteria For Diabetes Mellitus and Other Categories of Glucose IntoleranceDocument4 pagesDefinition and Diagnostic Criteria For Diabetes Mellitus and Other Categories of Glucose Intolerancevai2No ratings yet
- Seminar DMDocument42 pagesSeminar DMRubina MasihNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument32 pagesDiabetes MellitusGloria KikiNo ratings yet
- 06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument47 pages06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismRizka NizarNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument34 pagesDiabetes MellitusKobby AmoahNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument13 pagesIntroductionSaadNo ratings yet
- DM ReportDocument16 pagesDM ReportWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Bka Case FinalDocument26 pagesBka Case FinalJayson SorianoNo ratings yet
- Hand Out DM Medical Surgical Nursing 2Document11 pagesHand Out DM Medical Surgical Nursing 2Zarlou OtamiasNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument34 pagesDiabetesqurat-ul-ain.sonNo ratings yet
- DM Report1Document16 pagesDM Report1Wendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus, Often Simply Diabetes, Is A Syndrome Characterized by DisorderedDocument8 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus, Often Simply Diabetes, Is A Syndrome Characterized by DisorderedRachel Ann BatayolaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Diabetes MellitusDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plans For Diabetes MellitusRaveen mayi85% (59)
- Case Study - Diabetes Mellitus (Nutrition&Dietetics)Document10 pagesCase Study - Diabetes Mellitus (Nutrition&Dietetics)Summer Suarez100% (1)
- Diabeties NewDocument54 pagesDiabeties NewDipti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument52 pagesDiabetes MellitusMervis masatunyaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus - 2022-2023 - First Semester - DownloadDocument97 pagesDiabetes Mellitus - 2022-2023 - First Semester - DownloadLeoNo ratings yet
- Bio Project On DiabetesDocument17 pagesBio Project On DiabetesNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders-1Document52 pagesEndocrine Disorders-1Nathaniel Mbiu TimNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument99 pagesDiabetes489226fahimNo ratings yet
- Type 1 DiabetesDocument11 pagesType 1 DiabetesLyne Paggic PabloNo ratings yet
- 9 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes MellitusDocument60 pages9 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes Mellitussohaib salamehNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Causes of DiabatesDocument7 pagesPhysiology and Causes of DiabatesasaadsarfrazNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Diabetes Mellitus in Pharmacology LabDocument35 pagesPresentation On Diabetes Mellitus in Pharmacology Labpurwo yuhantoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument21 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitusfpacis_1No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesDiabetes MellitusChristian YuNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus 1Document16 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 1Ajet AsaniNo ratings yet
- DIABETESDocument39 pagesDIABETESSaboorMalikNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Type II Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of Type II Diabetes Mellituschinthaka18389021No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesDiabetes MellitussujithasNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Millitus PDFDocument41 pagesDiabetes Millitus PDFAbdullah BhattiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus DMC 6th SemesterDocument23 pagesDiabetes Mellitus DMC 6th SemesterHuzaifa CHNo ratings yet
- DM1-DM2 OdtDocument5 pagesDM1-DM2 OdtCarlaLuisaVillalunaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument31 pagesDiabetes MellitusElenaCondratscribdNo ratings yet
- DIABETES MELLITUS FinalDocument83 pagesDIABETES MELLITUS FinalYuvi Yuvaraj100% (1)
- 11 DiabetesDocument116 pages11 DiabetesRahman Md.MoshiurNo ratings yet
- Dibetes FinalDocument50 pagesDibetes FinalPiyusha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Smoothies for Diabetics: Reverse Diabetes and Lower Blood Sugar with 36 Quick & Easy Delicious Diabetic Smoothie RecipesFrom EverandSmoothies for Diabetics: Reverse Diabetes and Lower Blood Sugar with 36 Quick & Easy Delicious Diabetic Smoothie RecipesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Glucose, Part1Document33 pagesGlucose, Part1SarahNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Nael HernandezDocument15 pagesType 1 Diabetes Mellitus Nael HernandezShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- 222 Diabetes 2Document61 pages222 Diabetes 2Rahman Md.MoshiurNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Urata Abazi 11.8Document32 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Urata Abazi 11.8Urata AbaziNo ratings yet
- ENDO DiabetesDocument9 pagesENDO DiabetesHajime NakaegawaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and ExerciseDocument23 pagesDiabetes and ExerciseApurba MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: Group 3ADocument8 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Group 3AAradhanaRamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Breaking the Chains of Diabetes. A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandBreaking the Chains of Diabetes. A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Diabetes NaturallyNo ratings yet
- DM IntroductionDocument3 pagesDM IntroductionKrishelle Kate PannigNo ratings yet
- Classification: Blood Sugar Insulin Hormone Pancreas HyperglycemiaDocument20 pagesClassification: Blood Sugar Insulin Hormone Pancreas Hyperglycemiabammu21No ratings yet
- Dad ADocument107 pagesDad Abammu21No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument13 pagesDiabetes Mellitusdreneavalentinstefan100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus: WAHYUDI, S.Farm., AptDocument31 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: WAHYUDI, S.Farm., AptMayesti FransiskaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PPT FinalDocument39 pagesDiabetes PPT Finalimee cNo ratings yet
- Food, Nutrition and Dietetics.: TopicDocument8 pagesFood, Nutrition and Dietetics.: TopicT-7502 SAMITA BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Bhs InggrisDocument13 pagesBhs Inggrisciko sisca bintang pamungkhasNo ratings yet
- Aims and ObjectivesDocument13 pagesAims and Objectivesmamun183No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument19 pagesDiabetes MellitusHaleelu Abdul JaleelNo ratings yet
- Sweet Noon To AllDocument55 pagesSweet Noon To AllJheann Del Rio100% (1)
- DM ThyroidDocument184 pagesDM ThyroidtentenNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Coma in Type 2 Diabetes ExplanationDocument8 pagesDiabetic Coma in Type 2 Diabetes ExplanationCrystal Ann Monsale TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Milk ProteinsDocument5 pagesMilk ProteinsFadil NurhidayatNo ratings yet
- SITHCCC018 Research Report TemplateDocument9 pagesSITHCCC018 Research Report TemplateMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Dthe Sunshine Vitamin 2012Document10 pagesVitamin Dthe Sunshine Vitamin 2012Arturo RNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants NotesDocument7 pagesNutrition in Plants NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Eating Disorders - CausesDocument2 pagesEating Disorders - Causes19PSY05 ATULYA VENKATESHNo ratings yet
- The Use of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers and Its Effect On The Quality of Corn Products in The Philippines: A ReviewDocument19 pagesThe Use of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers and Its Effect On The Quality of Corn Products in The Philippines: A ReviewAziz KudaratNo ratings yet
- Ingles Ensayo Causa Efecto DesnutricxionDocument2 pagesIngles Ensayo Causa Efecto DesnutricxionBrayan Murphy Crespo EspinozaNo ratings yet
- PREVIEW Activate 2 Student BookDocument6 pagesPREVIEW Activate 2 Student BookPaulNo ratings yet
- 00 Harinas Italianas - Caputo Pizza MetroDocument1 page00 Harinas Italianas - Caputo Pizza MetroRuper NoSoyNo ratings yet
- A Look at Your Child's NutritionDocument2 pagesA Look at Your Child's NutritionAslul KhitanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Fermentation As A Method For Food Preservation (Balisalisa)Document13 pagesChapter 9 - Fermentation As A Method For Food Preservation (Balisalisa)Phil MarcoNo ratings yet
- Radiation: The Transmission of Electromagnetic Waves Through The Microwave OvenDocument8 pagesRadiation: The Transmission of Electromagnetic Waves Through The Microwave OvenzarahNo ratings yet
- Fish Oil and Heart HealthDocument11 pagesFish Oil and Heart Healthapi-302974665100% (1)
- Nutrition Therapy and Pathophysiology 3rd Edition Nelms Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesNutrition Therapy and Pathophysiology 3rd Edition Nelms Solutions Manualwonders.stufferlx27100% (18)
- Medic NesDocument29 pagesMedic Nespink_key711No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Preventing Foodborne Illness in SchoolDocument27 pagesGuidelines For Preventing Foodborne Illness in Schoolnaveed_akbar_2No ratings yet
- JBDocument37 pagesJBJebie SanchezNo ratings yet
- Fish Oil Infographic FINALDocument2 pagesFish Oil Infographic FINALpierna casa casaNo ratings yet
- pr2 IntroductionDocument1 pagepr2 IntroductionMarco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Liquid Seaweed Fertilizer On Yield and Quality of Okra - JSIR 67 (12) 1115-1117Document3 pagesEffect of Liquid Seaweed Fertilizer On Yield and Quality of Okra - JSIR 67 (12) 1115-1117mackampalaNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Capacity of The Mediterranean Diet SAURA CALIXTO PDFDocument6 pagesAntioxidant Capacity of The Mediterranean Diet SAURA CALIXTO PDFjoelNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Nursing Training ManualDocument77 pagesVeterinary Nursing Training ManualKeyshaNo ratings yet
- PT Profile (Editable) AFMARVELSDocument8 pagesPT Profile (Editable) AFMARVELSEarl LarroderNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Science of Nutrition 4th Edition by Thompson PDFDocument10 pagesTest Bank For The Science of Nutrition 4th Edition by Thompson PDFa808910087100% (2)
- Strategic Marketing Project Report On NESTLE MILKPAKDocument15 pagesStrategic Marketing Project Report On NESTLE MILKPAKSalman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Tikole Rushikesh V Et Al / Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 4 (4), Jul - Aug 2013Document3 pagesReview Article: Tikole Rushikesh V Et Al / Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 4 (4), Jul - Aug 2013cantuscantusNo ratings yet
- Tiếng Anh 6 Friends Plus - Unit 5 Test 2 (Key)Document6 pagesTiếng Anh 6 Friends Plus - Unit 5 Test 2 (Key)Thao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cilento DietDocument2 pagesCilento Dietsil.laplataNo ratings yet
- Carbs - 2 Ways You Can Earn Them - Strength SenseiDocument7 pagesCarbs - 2 Ways You Can Earn Them - Strength SenseigomitadelimonNo ratings yet
- Growing Mushrooms On Coffee Waste: 5 Benefits ofDocument8 pagesGrowing Mushrooms On Coffee Waste: 5 Benefits ofdavigno7302100% (1)