Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class: Electrical Circuits and Ohm's Law Date: September 24, 2023 Introduction To Electrical Circuits
Uploaded by
runOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class: Electrical Circuits and Ohm's Law Date: September 24, 2023 Introduction To Electrical Circuits
Uploaded by
runCopyright:
Available Formats
Class: Electrical Circuits and Ohm's Law Date: September 24, 2023
Introduction to Electrical Circuits
An electrical circuit is a closed loop through which electric current flows.
Circuits consist of components like resistors, capacitors, inductors, and voltage sources.
Circuits can be classified as series or parallel depending on the arrangement of components.
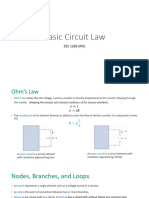
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law relates voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in a circuit.
Ohm's Law equation: V = I * R.
V is measured in volts (V), I in amperes (A), and R in ohms (Ω).
Resistors
Resistors are passive components that oppose the flow of electric current.
Resistors dissipate electrical energy in the form of heat.
Resistance is a measure of how much a resistor resists the flow of current.
Series Circuits
In a series circuit, components are connected in a single path.
Current is the same through all components in a series circuit.
The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of individual resistances.
Parallel Circuits
In a parallel circuit, components are connected in multiple paths.
Voltage is the same across all components in a parallel circuit.
The total resistance in a parallel circuit is calculated differently from series circuits.
Kirchhoff's Laws
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL): The sum of currents entering a node equals the sum of currents
leaving the node.
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL): The sum of voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero.
Calculations in Circuits
Using Ohm's Law to find voltage, current, or resistance in a circuit.
Applying Kirchhoff's Laws to solve complex circuit problems.
Using equivalent resistance for simplifying complex circuits.
Applications of Electrical Circuits
Electrical circuits are fundamental in various engineering fields, including electronics, power
systems, and telecommunications.
They are crucial for designing and analyzing electrical systems.
Lab Exercise
Lab: Measurement of Resistance using Ohm's Law.
Equipment: Multimeter, resistors, breadboard.
Procedure: Measure resistance using Ohm's Law and compare with actual resistor values.
Homework Assignment
Solve practice problems on series and parallel circuits, Ohm's Law, and Kirchhoff's Laws.
Prepare for the upcoming quiz on electrical circuits.
You might also like
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Unit IDocument27 pagesUnit IPratap VeerNo ratings yet
- Jazan University College of CS & IS Chapter 1 Electrical Circuit AnalysisDocument28 pagesJazan University College of CS & IS Chapter 1 Electrical Circuit AnalysisazoozdhamriNo ratings yet
- U 19 MaterialDocument179 pagesU 19 Materialvbhooahmad ibraNo ratings yet
- Phy Assinment 2Document5 pagesPhy Assinment 2umarirfan208No ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDF (16-19)Document18 pagesCurrent Electricity PDF (16-19)Abhay MauryaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Principles Form The Foundation of Modern Electrical Engineering and Are Crucial For Understanding The Behavior of Electrical SystemsDocument1 pageElectrical Circuit Principles Form The Foundation of Modern Electrical Engineering and Are Crucial For Understanding The Behavior of Electrical Systemssuliman bobNo ratings yet
- Electricity PPT Presentation ModifiedDocument22 pagesElectricity PPT Presentation ModifiedMark SyNo ratings yet
- Circuit NotesDocument1 pageCircuit Notestemp manNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits, Ohm's Law, Series and ParallelDocument50 pagesDC Circuits, Ohm's Law, Series and ParallelTamaki DellosaNo ratings yet
- Name: Renzo Jan H. Amorado Date: August 30, 2022 Course-Year-Section: BSME-2-EDocument6 pagesName: Renzo Jan H. Amorado Date: August 30, 2022 Course-Year-Section: BSME-2-ELev ShouyoNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument98 pagesOhms LawIshma BendiolaNo ratings yet
- EE 123 Elementary Electrical Engineering IntroductionDocument17 pagesEE 123 Elementary Electrical Engineering IntroductionRovick TarifeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical EngineeringDocument20 pagesBasics of Electrical EngineeringVenkat TakkellaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab Reportfikadubiruk87No ratings yet
- EE 001 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument71 pagesEE 001 Basic Electrical EngineeringAlbert GambaNo ratings yet
- 1 AC and DC Circuit No Multiple ChoiceDocument147 pages1 AC and DC Circuit No Multiple ChoiceJimuelle CallejoNo ratings yet
- CurrentDocument10 pagesCurrentShanto NiceschoolNo ratings yet
- KIRCHHOFF'S CURRENT LAWDocument139 pagesKIRCHHOFF'S CURRENT LAWIzzat Syamer Iskandar AliNo ratings yet
- Observation and AnalysisDocument3 pagesObservation and AnalysisNova Jane EdradNo ratings yet
- Electrical Theory ExplainedDocument5 pagesElectrical Theory ExplainedMustapha Isaad100% (1)
- Circuit Elements: Voltage & Current Sources Electrical Resistance (Ohm's Law) Kirchhoff's LawsDocument26 pagesCircuit Elements: Voltage & Current Sources Electrical Resistance (Ohm's Law) Kirchhoff's Lawsgulzar ahmadNo ratings yet
- 1 DC Circuits Review WideDocument109 pages1 DC Circuits Review WideMarc RiveraNo ratings yet
- TEKNOLOGI ELEKTRIK 1 - VoltageDocument10 pagesTEKNOLOGI ELEKTRIK 1 - Voltagehazreen othman100% (1)
- Bee MidtermsDocument103 pagesBee MidtermsROSABELLE CABADINNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering I: (Circuit Analysis-I) Course Instructor: Engr. M. Owais ManzoorDocument23 pagesElectrical Engineering I: (Circuit Analysis-I) Course Instructor: Engr. M. Owais Manzooriqra zafarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Circuits: Ohm's Law, Components, Measurements (40chDocument22 pagesBasic Electrical Circuits: Ohm's Law, Components, Measurements (40chButch ArmonesNo ratings yet
- Voltage Current Resistance and Ohms LawDocument62 pagesVoltage Current Resistance and Ohms LawAllysa Nicole AldaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY FUNDAMENTALSDocument36 pagesELECTRICITY FUNDAMENTALSSa HaNo ratings yet
- UnitNo1DCCircuitspptx 2022 10 08 15 08 30pptx 2022 11 03 21 34 27Document66 pagesUnitNo1DCCircuitspptx 2022 10 08 15 08 30pptx 2022 11 03 21 34 27DUSHIMIMANA ROBIN mefgiNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit 1 Lecture 2Document35 pagesECE131 Unit 1 Lecture 2Vijay ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Fundamentals of D.C. CircuitsDocument80 pagesUNIT-1: Fundamentals of D.C. CircuitsGURMEHAK MIGLANINo ratings yet
- 107785Document16 pages107785Balu ChanderNo ratings yet
- Study MaterialsDocument47 pagesStudy MaterialsGURU DAKKUNo ratings yet
- Made by:-Pushkar.U X - CDocument36 pagesMade by:-Pushkar.U X - Cpushkar umarjiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics1Document3 pagesIntroduction To Electronics1Jon Teodulo NiervaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design PackageDocument6 pagesElectrical Design Packageapi-272622659No ratings yet
- DC CircuitDocument142 pagesDC CircuitBela FirmantoyoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Electrical Quantities and UnitsDocument39 pagesFundamental Electrical Quantities and UnitsJC LoplopNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2surajNo ratings yet
- SSS 1 3RD TermDocument21 pagesSSS 1 3RD TermabiodunokoyaNo ratings yet
- Pee Unit 1 NotesDocument9 pagesPee Unit 1 NotesGopi chand GamerNo ratings yet
- Electives 2 Part 3Document155 pagesElectives 2 Part 3Johnfer AquinoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components and Circuits Not MineDocument21 pagesElectrical Components and Circuits Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering IntroductoryDocument78 pagesElectrical Engineering Introductoryandi lisnaini ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics Components and TheoryDocument3 pagesApplied Electronics Components and TheorySifa RahmaniaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Portfolio 3Document5 pagesElectricity Portfolio 3Ashish KumarNo ratings yet
- Series Connection of Resistances: The Law Which Govern The Resistances That Are Connected in SeriesDocument4 pagesSeries Connection of Resistances: The Law Which Govern The Resistances That Are Connected in SeriesShien CabzNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Module 311Document21 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Module 311Juan De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory FundamentalsDocument61 pagesCircuit Theory FundamentalsNeli Aguilar SenupeNo ratings yet
- Learn Electrical TheoryDocument6 pagesLearn Electrical TheoryonaaaaangNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Study Combination of Resistors in Series.Document11 pagesStudy Combination of Resistors in Series.Tooba Rizwan100% (1)
- ' ElectricityDocument98 pages' Electricitya9758127118No ratings yet
- Basic Circuit LawDocument13 pagesBasic Circuit LawMd.Mahmudur Rahman AkandaNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Analysis LawsDocument50 pagesBasic Circuit Analysis LawsMuhd RzwanNo ratings yet
- Bee Experiments: Pointers To FollowDocument35 pagesBee Experiments: Pointers To FollowPratik Mishra100% (1)
- Electric Currents & DC CircuitsDocument49 pagesElectric Currents & DC CircuitsHergene FanerNo ratings yet
- Bee Viva Prep.Document11 pagesBee Viva Prep.Pratik MishraNo ratings yet