Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is The Historical Development of World Literature
What Is The Historical Development of World Literature
Uploaded by
ZAKARIA EL YAAGOUBIOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is The Historical Development of World Literature
What Is The Historical Development of World Literature
Uploaded by
ZAKARIA EL YAAGOUBICopyright:
Available Formats
What is the historical development of world
literature
The development of world literature is a complex and multifaceted process that spans
thousands of years. It encompasses the literary achievements of various cultures and
civilizations around the globe. Here is a brief overview of the historical development
of world literature:
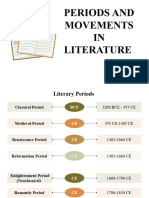
1. Ancient Literature (Before 5th Century CE):
Sumerian and Akkadian Literature (circa 3000 BCE - 2000 BCE): Some of
the earliest known works of literature come from ancient Mesopotamia,
including the Epic of Gilgamesh.
Ancient Egyptian Literature (circa 3000 BCE - 100 CE): Egypt produced a
rich body of literature, including religious texts, poetry, and wisdom literature.
Ancient Greek Literature (8th Century BCE - 6th Century CE): The Greeks
made significant contributions to literature with works like Homer's epics, the
Iliad and the Odyssey, as well as the tragedies of playwrights like Sophocles
and Euripides.
2. Classical Literature (5th Century CE - 15th Century CE):
Latin Literature (c. 75 BCE - 5th Century CE): The Romans produced a
substantial body of literature, including works by authors like Virgil, Cicero,
and Ovid.
Chinese Literature (c. 1000 BCE - 14th Century CE): China has a long literary
tradition, with classics like Confucius' Analects and Daoist texts like the Tao Te
Ching.
Indian Literature (c. 1500 BCE - 15th Century CE): India produced an
extensive body of literature, including Sanskrit epics like the Mahabharata and
the Ramayana, as well as religious texts like the Vedas and Upanishads.
3. Medieval and Renaissance Literature (5th Century CE - 17th Century CE):
Arabic Literature (7th Century CE - 14th Century CE): Arabic literature
flourished during the Islamic Golden Age, producing works in various genres
like poetry, philosophy, and science.
Japanese Literature (7th Century CE - 17th Century CE): The Heian period
produced classics like "The Tale of Genji" by Murasaki Shikibu.
European Literature (8th Century CE - 17th Century CE): The Middle Ages
saw the development of various national literatures in Europe, including Old
English, Middle High German, and Old French.
4. Modern Literature (18th Century CE - Present):
Enlightenment and Romanticism (18th - 19th Centuries CE): This period
saw the emergence of literary movements like the Enlightenment, which
emphasized reason and empiricism, and Romanticism, which focused on
emotion and individualism.
Global Expansion (19th Century CE - Present): The 19th and 20th centuries
saw a surge in literature from non-Western regions, with authors from Africa,
Asia, and Latin America gaining international recognition.
Contemporary Literature (20th Century CE - Present): The 20th century
brought about significant shifts in literary styles and movements, including
modernism, postmodernism, and various experimental forms of writing.
Throughout this entire timeline, the development of world literature has been
influenced by factors such as cultural exchange, technological advancements (like the
printing press), political events, and social movements. Today, world literature
continues to evolve, with authors from diverse backgrounds contributing to the
global literary landscape.
You might also like
- Ancient LiteratureDocument9 pagesAncient LiteratureFat AjummaNo ratings yet
- 2012 A Level SyllabusDocument57 pages2012 A Level SyllabusbaltosNo ratings yet
- Perfect Storm FCE WorksheetDocument10 pagesPerfect Storm FCE Worksheetpaula740003No ratings yet
- Greek LiteratureDocument2 pagesGreek LiteratureTiffany Paño MateoNo ratings yet
- Background of LiteratureDocument25 pagesBackground of LiteratureMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 130.123.99.4 On Wed, 07 Oct 2020 07:28:59 UTCDocument42 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 130.123.99.4 On Wed, 07 Oct 2020 07:28:59 UTCDick WhyteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To World LiteratureDocument17 pagesIntroduction To World LiteratureRain VargasNo ratings yet
- Timeline of LiteratureDocument22 pagesTimeline of Literaturevj rodriguez100% (2)
- Periods in World Literature: Dr. Fatima DarDocument36 pagesPeriods in World Literature: Dr. Fatima DarHajra MirNo ratings yet
- Greek LiteratureDocument3 pagesGreek Literature爽子黒沼No ratings yet
- History of World LiteratureDocument19 pagesHistory of World LiteratureAliza ShaikhNo ratings yet
- European LiteratureDocument47 pagesEuropean LiteratureSantosh Chougule100% (3)
- German LanguageDocument25 pagesGerman LanguageGirish NarayananNo ratings yet
- Bhakti: Then and Now: Bhakti As A Bhāva or A Rasa: Abhinavagupta Brings Bhakti Under Śānta Rasa (RaghavanDocument5 pagesBhakti: Then and Now: Bhakti As A Bhāva or A Rasa: Abhinavagupta Brings Bhakti Under Śānta Rasa (RaghavanDwaritha ViswanathaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Literature Lecture 01 First Year All Groups S2Document28 pagesIntroduction To Literature Lecture 01 First Year All Groups S2abdelkarim BenhalimaNo ratings yet
- Mawazna e Anees o Dabeer MuqadmaDocument43 pagesMawazna e Anees o Dabeer MuqadmaAlbert Williamson50% (2)
- (Midterm) Survey of English American Literature 2Document8 pages(Midterm) Survey of English American Literature 2Ferliza Cudiamat PacionNo ratings yet
- Scher - Paul - Essays On Literature and Music, 1967-2004. Ed. Bernhart&Wolf-Rodopi (2004)Document549 pagesScher - Paul - Essays On Literature and Music, 1967-2004. Ed. Bernhart&Wolf-Rodopi (2004)mcfreittasNo ratings yet
- European Litera-WPS OfficeDocument45 pagesEuropean Litera-WPS OfficeLovely Jane BenihaganNo ratings yet
- European LiteratureDocument38 pagesEuropean LiteratureClaudia SalduaNo ratings yet
- 21st ReportDocument34 pages21st ReportRhea Mae Villaflor ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Greek LiteratureDocument7 pagesGreek LiteraturePepe CuestaNo ratings yet
- Written Report of Group 1Document4 pagesWritten Report of Group 1Snuggel PugNo ratings yet
- Brief History in World LiteratureDocument2 pagesBrief History in World LiteraturekilluhmaylucianoNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document7 pagesGroup 3Ian Dante ArcangelesNo ratings yet
- Lit. 11-Module 2 Class Notes-MidtermDocument17 pagesLit. 11-Module 2 Class Notes-MidtermCyril Grace Alburo BoocNo ratings yet
- European LiteratureDocument32 pagesEuropean LiteratureMr. ZeusNo ratings yet
- Urgel Literary CriticismDocument19 pagesUrgel Literary Criticismmatunoglaica194No ratings yet
- Greek and Roman LiteratureDocument17 pagesGreek and Roman LiteraturejeanmaedalinaNo ratings yet
- Early Written LiteratureDocument3 pagesEarly Written LiteratureDarry BlanciaNo ratings yet
- Ancient EgyptDocument4 pagesAncient EgyptYVONNE BIGTASNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 World Lit 8 GradeDocument4 pagesLesson 1 World Lit 8 GradeBaran FallahiNo ratings yet
- EL REVIEWER FINALdocxDocument23 pagesEL REVIEWER FINALdocxreign acostaNo ratings yet
- Periods and Movements in EnglishDocument16 pagesPeriods and Movements in EnglishCristy Mae BesaNo ratings yet
- Greek LiteratureDocument8 pagesGreek LiteratureFernando da SilvaNo ratings yet
- European LiteratureDocument5 pagesEuropean LiteratureDhiane BuanNo ratings yet
- World Lit - IntroDocument15 pagesWorld Lit - IntroTess UmaliNo ratings yet
- Europian LiteratureDocument13 pagesEuropian LiteratureKeneth CandidoNo ratings yet
- Literature First Year Technical EnglishDocument6 pagesLiterature First Year Technical Englishamrahas13No ratings yet
- Early Period: Hi I'm Philisopher TJ Dapiton! Hi I'm Philisopher Riggs Orbeta!Document32 pagesEarly Period: Hi I'm Philisopher TJ Dapiton! Hi I'm Philisopher Riggs Orbeta!Brenny dotcomNo ratings yet
- Early Period: Hi I'm Philisopher TJ Dapiton! Hi I'm Philisopher Riggs Orbeta!Document32 pagesEarly Period: Hi I'm Philisopher TJ Dapiton! Hi I'm Philisopher Riggs Orbeta!Brenny dotcomNo ratings yet
- Clase Meet Lit I-L-V 1Document12 pagesClase Meet Lit I-L-V 1DANNY ARELY CARRASCO PINEDANo ratings yet
- Espina G00008Document20 pagesEspina G00008matunoglaica194No ratings yet
- History of LiteratureDocument2 pagesHistory of LiteratureClaire Arribe100% (1)
- European LiteratureDocument17 pagesEuropean LiteratureRN AnoganteNo ratings yet
- Literary Arts and PoetryDocument5 pagesLiterary Arts and PoetryCharlene SuliganNo ratings yet
- Literary CriticismDocument10 pagesLiterary Criticismjheiiyanng2002No ratings yet
- Human CivilizationDocument37 pagesHuman Civilizationpramodacharya.073No ratings yet
- Ancient Period (Eunice)Document3 pagesAncient Period (Eunice)Gina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Latin LiteratureDocument18 pagesLatin Literaturemhiccijamaicah09No ratings yet
- European Literature 2Document3 pagesEuropean Literature 2Lemuel Adrian100% (1)
- Ancient LiteratureDocument8 pagesAncient Literaturec1832765No ratings yet
- Early Periods of Literature (Classical and Medieval Periods)Document2 pagesEarly Periods of Literature (Classical and Medieval Periods)Renz Vincent TagalogNo ratings yet
- Development of Literary CriticismDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Literary CriticismAri GunawanNo ratings yet
- European Literature BackgroundDocument2 pagesEuropean Literature BackgroundRichlyNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument18 pagesPDF DocumentHawda BaxtyarNo ratings yet
- Greek Literature Dates Back From The: Iliad OdysseyDocument2 pagesGreek Literature Dates Back From The: Iliad OdysseyJolly Ducoy PuertosNo ratings yet
- Introduction and History of English LiteratureDocument18 pagesIntroduction and History of English LiteratureEman AleemNo ratings yet
- World Literature in Different AgesDocument15 pagesWorld Literature in Different AgesABDUL MAJIDNo ratings yet
- Early Periods of LiteratureDocument3 pagesEarly Periods of LiteratureJennyfer ToledoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Literary Periods and MovementsDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Literary Periods and MovementsClaNo ratings yet
- Literary CriticismDocument4 pagesLiterary Criticismjheacawayan1018No ratings yet
- Egyptian LiteratureDocument41 pagesEgyptian LiteratureEgiel Anne RojoNo ratings yet
- En9 LessonsDocument16 pagesEn9 Lessonsmark lachicaNo ratings yet
- 21stCL Reviewer (World)Document3 pages21stCL Reviewer (World)MA.CECILIA CASUPANANNo ratings yet
- Assigment Hendri Ceza AroziDocument6 pagesAssigment Hendri Ceza Arozihendricezaarozi02No ratings yet
- Davv Cet - LR IiiDocument101 pagesDavv Cet - LR IiiPriyam Jain100% (2)
- Nature The Gentlest MotherDocument4 pagesNature The Gentlest MotherMeeta Sharma100% (4)
- Bi Ya 18 PDFDocument11 pagesBi Ya 18 PDFRohaizan AbuNo ratings yet
- Action Plan TemplateDocument16 pagesAction Plan TemplateRina MajinNo ratings yet
- Least Learned Lessons in English: Socorro National High SchoolDocument8 pagesLeast Learned Lessons in English: Socorro National High SchoolRilyn Limbaro CantaNo ratings yet
- Old English ProseDocument5 pagesOld English ProseSuren Kumar100% (1)
- LLL and Renaissance Vision of LoveDocument17 pagesLLL and Renaissance Vision of LoveElenaNo ratings yet
- Thiruppavai Paasuram 13Document6 pagesThiruppavai Paasuram 13Dr.Srinivasan KannappanNo ratings yet
- Nida FazliDocument20 pagesNida FazliRajesh ShastriNo ratings yet
- Book Review One Night at Call CenterDocument20 pagesBook Review One Night at Call CenterKishori PatelNo ratings yet
- Alarm Clock Stylistics Joyce Kilmerfor WordDocument16 pagesAlarm Clock Stylistics Joyce Kilmerfor Wordvanessa joy cuevas100% (1)
- Adam BedeDocument9 pagesAdam BedeSadaf Mushtaq100% (1)
- Bhaja-Govindam Tamil PDF File4958Document35 pagesBhaja-Govindam Tamil PDF File4958Rajendran SekarNo ratings yet
- The Passionate Shepherd To His Love: Christopher MarloweDocument4 pagesThe Passionate Shepherd To His Love: Christopher Marlowejohn reycel gacaNo ratings yet
- Choi, M. H. (2004) - Recastıng Vladimir Propp's Formalist Method Through Traditional Asian NarrativesDocument104 pagesChoi, M. H. (2004) - Recastıng Vladimir Propp's Formalist Method Through Traditional Asian NarrativesYunus ErdoğanNo ratings yet
- Romanticism and EnlightenmentDocument3 pagesRomanticism and Enlightenmentapi-301037423No ratings yet
- Eng - LLDocument19 pagesEng - LLNumaan Bashir MirNo ratings yet
- Rough DraftDocument4 pagesRough DraftColynn MorenoNo ratings yet
- Text Typology ChartDocument2 pagesText Typology Chartapi-299890247No ratings yet
- 0165 Sputnik SweetheartDocument11 pages0165 Sputnik SweetheartSoham SahaNo ratings yet
- Idealism in Rizal's PoetryDocument6 pagesIdealism in Rizal's PoetryWanderlust WengNo ratings yet
- Frost at Midnight - AnalysisDocument12 pagesFrost at Midnight - AnalysisaliNo ratings yet
- Afro Asian Syllabus Ist Sem 2012 Elsa UpdatedDocument33 pagesAfro Asian Syllabus Ist Sem 2012 Elsa UpdatedHan Ya DaNo ratings yet