Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2AB3 CH 8 Notes
2AB3 CH 8 Notes
Uploaded by
aabir ahmedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2AB3 CH 8 Notes
2AB3 CH 8 Notes
Uploaded by
aabir ahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
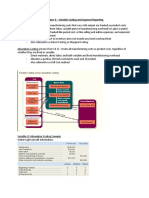
L01: Inventory costing methods:
- Absorption costing:
- Job is assigned the costs of DM, DL, and both VOH, and FOH
- AKA full costing
- Required for external reporting
- All manufacturing costs are charged to or absorbed by the product
- Absorbtion costing is the approach required for external reporting under GAAP
- FMOH are deferred to a future period as part of the cost of ending inventory
- Both variable and fixed selling and administrative expenses are treated as period costs
and are therefore expensed in the year
- Should show higher net income tha variable constant whenever there are more units
produced then sold
- Variable Costing:
- Only DM, DL, VOH are considered product costs
- Companies using variable costing recognie FMOH as the period costs when incurred
- Companies may NOT use Variable costing for external financial reports because GAAP
require the FOH to be accounted for as a product cost
- FMOH of the current period are not deferred to future periods through ending inventory
- When units produced > units sold → income under absorption costing is higher
- When units produced = units sold → net income will be equal under both methods
L02: Net Income Effects:
Example: Units produced = Units sold
- Net income is equal under both approaches
- No increase in ending inventory, no FMOH costs in the year are deferred to future periods
Example: Units produced > Units sold:
- Net income is higher under absorption costing
- Cost of ending invensoty is higher under absorption than variable costing
- Under absorption costing, FMOH is deferred and carried forward as part of inventory
- Under variable costing, the FMOH is expensed in the current period
Example: Units produced < Units sold:
- FMOH costs in beginning inventory are charged under absorption costing
Summary of net income effects:
L03: Decision Making concerns:
GAAP requires companies to use absorption costing for the costing of inventory:
- Net income measured under GAAP (absorbtion costing) is often used internally to evaluate
performance, justify cost reduction, or assess new projects
- Some companies have recognized that net income calculated using GAAP does not highlight the
differences between VC and FC, and may lead to poor business decisions
Performance Evaluation:
- When production exceeds sales, absorption costing reports a higher net income than variable
costing
- The reason is that some fixed manufacturing costs are not expensed in the same period, but are
deferred to future periods
Potential advantages of Variable Costing:
1) The use of variable costing is consistent with CVP and Incremental Analysis
2) Net income calculated under VC is NOT affected by changes in production levels → much easier
to understand the impact of fixed and VC on the calculation of NI when using variable costing
3) Net income calculated under VC is greatly affected by changes in sales levels and therefore
provides a more realistic assessment of the company’s success or failure during a period
4) Because fixed cost and variable cost components are shown in the variable costing income
statement, it is easier to identify these costs and understand their effect on the business
L04: Normal-Absorption Costing:
- Uses actual direct manufacturing costs and actual production units within a prefermined overhead
rate → More practical for assigning fixed manufacturing OH costs to production
L05: Throughput Costing:
Overview:
- Also called super-variable costing
- Based on lean manufacturing principles → reduces buildup of excess inventories
- Treats all costs as period expenses except for DM
- Modified form of a variable costing system that treats DL and VMOH as period expenses
- According to lean manufacturing principles, cost can be reduced and profitability increased by
improvements in the manufacturing workflow
- The process is being increasingly used by many firms to manage their operations more efficiently
and with more control because it eliminates waste and focuses more accurately on the customer’s
needs
Criteria:
1) Only suitable for companies engaged in a manufacturing process in which conversion costs such
as DL and MOH are fixed and do not vary
2) Management must favour cost accounting information that is helpful for short-term incremental
analysis such as whether the company should accept or reject a special offer at a reduced sales
price
- Choice of throughput costing is a logical extension of its choice of variable over
absorption costing
- Product costs are only DM costs
- Inventory is valued using only DM costs and all other manufacturing costs are treated as
expenses in the accounting period they occur
Summary of income effects:
Advantages of Throughput Costing:
- Reduces incentive for management to build up excess inventories in order to spread fixed
manufacturing costs over a larger number of units produced
- Encourages managers to reduce operating costs such as DL and VMOH which are treated as
period costs NOT product costs
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Managerial Acct2 2nd Edition by SawyersDocument20 pagesSolution Manual For Managerial Acct2 2nd Edition by SawyersMariahAndersonjerfn100% (51)
- CA01 VariableCostingFDocument114 pagesCA01 VariableCostingFVenise Balia33% (3)
- ACCA F5 - Part A - Specialist Cost and Management Accounting TechniquesDocument5 pagesACCA F5 - Part A - Specialist Cost and Management Accounting TechniquesMuneera Al Hassan100% (2)
- Tugas 1Document2 pagesTugas 1sella50% (2)
- rsm222 - Chapter 11 Notes (Typed)Document17 pagesrsm222 - Chapter 11 Notes (Typed)ellie smithNo ratings yet
- CH 8Document19 pagesCH 8Isra' I. SweilehNo ratings yet
- Income Effects of Alternative Cost Accumulation SystemsDocument4 pagesIncome Effects of Alternative Cost Accumulation SystemssserwaddaNo ratings yet
- rsm222 - Chapter 12 Notes (Typed)Document21 pagesrsm222 - Chapter 12 Notes (Typed)ellie smithNo ratings yet
- MAS Variable and Absorption CostingDocument11 pagesMAS Variable and Absorption CostingGwyneth TorrefloresNo ratings yet
- Assignment On The Application of Full Costing and Variable Costing in The Manufacturing Industry of BangladeshDocument8 pagesAssignment On The Application of Full Costing and Variable Costing in The Manufacturing Industry of BangladeshManuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document5 pagesChapter 10Ailene QuintoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Variable CostingDocument3 pagesChapter 13 Variable CostingJJ JaumNo ratings yet
- Vendmart - TheDocument6 pagesVendmart - TheSagarrajaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Cost Accumulation TechniquesDocument21 pagesUnit 7 Cost Accumulation Techniquesestihdaf استهدافNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable Costing: Strategic Cost ManagementDocument3 pagesAbsorption and Variable Costing: Strategic Cost ManagementMarites AmorsoloNo ratings yet
- HR Accounting Unit 2Document12 pagesHR Accounting Unit 2Cassidy DonahueNo ratings yet
- Variable Costing Absorption CostingDocument5 pagesVariable Costing Absorption CostingSockYii ChuaNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Questions and Their AnswersDocument5 pagesCost Accounting Questions and Their Answerszulqarnainhaider450_No ratings yet
- MAS-05 Variable and Absorption CostingDocument8 pagesMAS-05 Variable and Absorption CostingKrizza MaeNo ratings yet
- Acct 2321 Essay Q&A Exam - 2Document3 pagesAcct 2321 Essay Q&A Exam - 2Sayyaf NayefNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Absorption and Variable Costing and Inventory ManagementDocument49 pagesChapter 8 Absorption and Variable Costing and Inventory ManagementNatanael PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Acca - F5 Performance ManagementDocument21 pagesAcca - F5 Performance ManagementKelly ChongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document4 pagesChapter 10nobodybutuloveNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1.2.3 Cost Accounting. OHADA ApproachDocument17 pagesMODULE 1.2.3 Cost Accounting. OHADA ApproachegoptiemmaNo ratings yet
- MAS Absorption Costing/Variable Costing Study ObjectivesDocument6 pagesMAS Absorption Costing/Variable Costing Study ObjectivesMarjorie ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cma Unit IiDocument73 pagesCma Unit IiAnonymous kwi5IqtWJNo ratings yet
- CH 20 SMDocument31 pagesCH 20 SMNafisah MambuayNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Relevant CostDocument10 pagesChap 5 Relevant CostChristopher VicenteNo ratings yet
- Intro To Cost AccountingDocument7 pagesIntro To Cost AccountingMadonna KristinaNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absoption Costing PDFDocument69 pagesVariable and Absoption Costing PDFKaren AlonsagayNo ratings yet
- Cma Unit IiDocument95 pagesCma Unit IiAnubhuti AgarwalNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 5 AccountingDocument4 pagesTOPIC 5 Accountingllorcaire100% (1)
- New CMA Part 1 Section BDocument135 pagesNew CMA Part 1 Section Bhmtairek85100% (1)
- CA01 VariableCostingFDocument114 pagesCA01 VariableCostingFSadile May KayeNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting and Control: (Acctg 107 M-F 5:00-6:10)Document38 pagesCost Accounting and Control: (Acctg 107 M-F 5:00-6:10)Korean Drama Fever PHNo ratings yet
- ACCT 311 - Chapter 6 NotesDocument4 pagesACCT 311 - Chapter 6 NotesSummerNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument3 pagesVariable and Absorption CostingAreeb Baqai100% (1)
- Income Effects of Alternative Cost Accumulation SystemsDocument29 pagesIncome Effects of Alternative Cost Accumulation Systems潘伟杰No ratings yet
- Mid Term Assignment On: The Superior University LahoreDocument9 pagesMid Term Assignment On: The Superior University LahoreFaizan ChNo ratings yet
- Marginal and Absorption CostingDocument5 pagesMarginal and Absorption CostingHrutik DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- BEC Notes Chapter 5Document6 pagesBEC Notes Chapter 5cpacfa100% (10)
- Chapter 1 - StudentsDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - StudentsLynn NguyenNo ratings yet
- Absorption CostingDocument3 pagesAbsorption CostingThirayuth BeeNo ratings yet
- Part1 SEC BDocument135 pagesPart1 SEC BKhel MatiasNo ratings yet
- CA01 VariableCostingFDocument114 pagesCA01 VariableCostingFAries Gonzales CaraganNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Absorption Variable CostingDocument19 pagesUNIT 3 Absorption Variable Costingannabelle albaoNo ratings yet
- CA Final Project....Document15 pagesCA Final Project....Obaida ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Costing MBA Sem 1Document34 pagesIntroduction of Costing MBA Sem 1prashantmis452No ratings yet
- Contents of The ManualDocument51 pagesContents of The ManualMinaw BelayNo ratings yet
- Absorption CostingDocument23 pagesAbsorption Costingarman_277276271No ratings yet
- Finals Controllership 1Document7 pagesFinals Controllership 1echonntz0515No ratings yet
- CostingDocument32 pagesCostingnidhiNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis - de LeonDocument25 pagesCVP Analysis - de Leonhazel balbuenaNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing Vs Variable CostingDocument2 pagesAbsorption Costing Vs Variable Costingneway gobachew100% (1)
- 1: Traditional/Advanced Costing Methods: Why Need To Know Cost/unit?Document52 pages1: Traditional/Advanced Costing Methods: Why Need To Know Cost/unit?dwalcotNo ratings yet
- MADMDocument5 pagesMADMjuhi.dang8131No ratings yet
- New CMA Part 1 Section CDocument124 pagesNew CMA Part 1 Section CSt Dalfour Cebu100% (1)
- Coppergate Educare Costing Theory NotesDocument106 pagesCoppergate Educare Costing Theory Notespratikjai100% (1)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Materi Just in Time - Bagian 1Document16 pagesMateri Just in Time - Bagian 1Ardho Binuri AdnanNo ratings yet
- Economics of Strategy 6th Edition Besanko Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesEconomics of Strategy 6th Edition Besanko Solutions ManualHannahDeanjrmo100% (58)
- Toppers Institute Kanpur Theory of Production and CostDocument42 pagesToppers Institute Kanpur Theory of Production and Costblack horseNo ratings yet
- In This Chapter, Look For The Answers To These QuestionsDocument8 pagesIn This Chapter, Look For The Answers To These QuestionsFranco ImperialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-2Document67 pagesChapter 2-2Nehal SalemNo ratings yet
- Mixed PDFDocument8 pagesMixed PDFChris Tian FlorendoNo ratings yet
- IA ActivityDocument2 pagesIA ActivityCASTRO, JHONLY ROEL C.No ratings yet
- 2016 Vol 1 CH 4 AnswersDocument15 pages2016 Vol 1 CH 4 Answersbebe_cute06XDNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting MidtermsDocument5 pagesCost Accounting MidtermsJerico Mamaradlo0% (3)
- L4 Notes Micro 2022 23 FinalDocument52 pagesL4 Notes Micro 2022 23 FinalSudeep SubrahmanyaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 10 AnsDocument3 pagesQuiz 10 AnsParth VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Explain How Isoquant Curves and Isocost Lines Determine The Producer's Equilibrium Using GraphsDocument6 pagesExplain How Isoquant Curves and Isocost Lines Determine The Producer's Equilibrium Using GraphsCarlos Lois SebastianNo ratings yet
- Paket January MPDocument4 pagesPaket January MPIT MPSAFINNo ratings yet
- Product Costing: Quizzer (Do-It-Yourself Drill)Document7 pagesProduct Costing: Quizzer (Do-It-Yourself Drill)loraine payuyoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Project Appraisal (Palendeng, Sellya Gabriela)Document7 pagesFinal Exam - Project Appraisal (Palendeng, Sellya Gabriela)tiphanie lumintangNo ratings yet
- Theory of Production CostDocument17 pagesTheory of Production CostDherya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Inventory Models: Multiple ChoiceDocument9 pagesInventory Models: Multiple ChoiceMarwa HassanNo ratings yet
- Micro Chapter 21 Practice Problems #2 Key: $ MC AVC ATCDocument6 pagesMicro Chapter 21 Practice Problems #2 Key: $ MC AVC ATCAhmadnur JulNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Planeación Agregada CAJ DesarrolloDocument1 pageEjercicio Planeación Agregada CAJ DesarrolloDayanna CristanchoNo ratings yet
- Business Math Week 8Document10 pagesBusiness Math Week 8johnNo ratings yet
- Production and Costs Practice Problems - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesProduction and Costs Practice Problems - Answer KeyBeri Z HunterNo ratings yet
- Marginal Productivity Theory of DistributionDocument2 pagesMarginal Productivity Theory of DistributionPriya MannaNo ratings yet
- Units To Account For: 635,000: L2-Practice Problem: EUP-WADocument2 pagesUnits To Account For: 635,000: L2-Practice Problem: EUP-WAlalalalaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics 7Th Edition Gottheil Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesPrinciples of Economics 7Th Edition Gottheil Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFJenniferWashingtonfbiqe100% (11)
- Deterministic InventoryDocument27 pagesDeterministic InventorySrijan ShettyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling in EconomoicsDocument11 pagesMathematical Modeling in EconomoicsRaihan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CVP AnalysisDocument36 pagesChapter 2 CVP AnalysisCabdiraxmaan GeeldoonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Problems & With SolutionsDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Problems & With SolutionsAhmed MohamudNo ratings yet