Oral Communication in Context
MODELS OF COMMUNICATION
Model- a description or analogy used to help visualize something (such as an atom) that
cannot be directly observed.
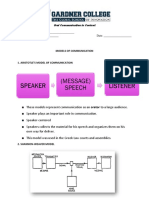
1. Aristotle’s Speaker-Centered Model
It is a speaker centered model as the speaker has the most important role in it and is
the only one active. It is the speaker’s role to deliver a speech to the audience. The role
of the audience is passive, influenced by the speech. This makes the communication
process one way, from speaker to receiver.
This is considered the first model of communication and was proposed before 300 B.C .
It is also the most widely accepted among all communication models.
1
�Oral Communication in Context
2. Schramm’s Communication Model
In 1954, Wilbur Schramm, an American scholar, proposed that encoding or the act of
transforming a message into a verbal or nonverbal medium, and decoding the act of
interpreting the message, are simultaneously done by both the speaker and the listener.
Adler & Rodman (2011) proposed linear model, interactive model, and transactional
model that presents simpler structure and provides meaningful understanding to
communication.
3. Linear Model
The linear communication model illustrates communication as a one-way activity
where message or information flows from the speaker to the listener. This means that
the transmission of message starts from an active sender and ends with the passive
receiver.
2
�Oral Communication in Context
4. The Interactive Communication Model
The interactive communication model shows a two-way exchange which features the
element of feedback. The sender composes and delivers a message to a receiver, who
in return composes and delivers a response. Interactions which require both parties to
respond, such as a job interview or telephone conversation, exemplify this
communication model.
5. Transactional Communication Model
The transactional communication model uses the term participants to refer to the sender
and receiver. It also includes additional elements of noise and environment. Noise
indicates the possibility of unsuccessful communication.
3
�Oral Communication in Context
Environment refers not only to the physical, social, psychological, cultural, and historical
contexts, but also the personal history and schema which every participants brings to
the interaction. The Schema is the participant’s knowledge of the world or his/her
accumulated experiences. It affects the way a participant interprets information.
6. Source-Message-Channel-Receiver (SMCR) Model
This model is proposed by David Berlo (1960). It suggests five elements in the
communication process, namely, the sender or the source of the message; the channel
which is the medium through which the idea is sent; the receiver, who gets the
message; and the feedback, or the response of the receiver. The figure shows how the
elements interact with each other. If one of these is not properly functioning, it can affect
the whole process and can eventually lead to a failure of communication.
Other rhetoricians and communication specialists such as Bitzer, Westley, and Bateson
also came up with their own communication models, however, their work are quite
complicated and difficult to comprehend.