Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Chemistry Q A (Autorecovered)
Uploaded by
Yato Qt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesOriginal Title
General Chemistry q a (Autorecovered)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesGeneral Chemistry Q A (Autorecovered)
Uploaded by
Yato QtCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
GENERAL CHEMISTRY C.
Burning of Wood : Combustion (Fuel
1. The study of matter + O2------CO2 +H2O
A. Chemistry D. Distillation of Water
B. Metteriology 8. Correctly balancing a chemical equation
C. Toxicology is a demonstration of which law?
D. Generalism A. Law of Conservation of Mass
2. What is the method used in the B. Law of Definite Proportion
production of dry ice? C. Law of Combining Moles
A. Sublimation D. Law of Combining Volumes
B. Condensation 9. Which of the following is correctly
C. Deposition matched?
D. Evaporation A. Dalton: energy states: solid sphere
3. Simplest forms of substances B. Bohr: Indestructible sphere: Dalton
A. Compound C. Democritus: indivisible particles
B. Elements D. Rutherford: 3D space: Schrodinger
C. Mixture 10. The mass of atom is highly dependent
D. None of the above on
4. Which of the following substance is A. Proton
pure? B. Electron
A. 5% Dextrose: 5mL of dextrose in C. Neutron
100ml of H2O D. A and B
B. Table Sugar: Sucrose (C12H22O11) E. A and C
C. Blood: plasma, hgb, platelets 11. Who was responsible for the
D. Rubbing Alcohol: mixture of 70% development of Periodic Table?
isopropyl alcohol & 30% water A. Avogadro
5. Homogenous mixture : uniform B. Le Chatelier
throughout the mixture C. Lavoisier
A. Solution D. Mendeleev
B. Air 12. Which quantum number determines the
C. Both A and B orientation in space of electrons?
D. None of the Above A. Principal
6. The following are properties of colloids, B. Azimuthal
except: C. Angular
A. Exhibit Brownian motion D. Magnetic
B. Exhibit Tyndall Effect 13. Dumbell-shaped orbital
C. Electrically neutral A. s
D. Include gels, sols, and emulsions B. p
7. Which of the following processes is a C. d
physical change? A(solid)-----A(liquid) D. f
A. Fermentation of Milk: Milk to lactic 14. A d subshell has how many orbitals?
acid (sour) A. 1
B. Neutralization HCl + NaOH – NaCl + B. 3
C. 5
H2O D. 7
E. 9
15. L= 2, which of the following is correct? 22. Compare Gallium and silicon in terms of
A. It can hold a maximum of 6 electronegativity
A. Gallium is more electronegative than Silicon
electrons B. Gallium is less electronegative than Silicon
B. It is an f orbital C. Both have comparable electronegativities
C. It can hold 14 electrons D. They cannot be compared, each is unique
D. It is a d orbital 23. All of the following are characteristics of
16. It is impossible to determine simultaneously the Nonmetals, except:
momentum and position of the electron A. Good conductors of electricity
according to : B. Often combine with each other by forming
A. Hund’s Rule covalent bonds
B. Pauli’s Exclusion Principle C. Tend to form negative ions in chemical
C. Aufbau’s Building Principle reactions with metals
D. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle D. Appear in the Right-hand corner of the
17. Which of the following statements about periodic table
quantum theory is incorrect? 24. Which of the following elements is the most
A. The energy and position of an electron metallic?
cannot be determined simultaneously- A. Br
Heisenberg B. I
B. Lower energy orbitals are filled with C. Cl
electrons before higher orbitals- Aufbau D. F
C. When filling orbitals of equal energy, two 25. Which of the following are metalloids?
electrons will occupy the same orbital A. Sc, Lr, Zn, Uub
before filling a new orbital- deviates hund’s B. B, O, F, Ne
rule C. Ge, As, Te
D. No two electrons can have the same four D. Ne, Ar, Kr
quantum numbers-Paulis exclusion 26. Produced by filling an orbital by an electron
18. Which of the following does not represent any which is not removed from its atom but is held
existing element? mutually by two atoms concerned
A. [Kr] 4d25s2 A. Ionic Bond
B. [Kr] 4d125s25p66s1 B. Covalent Bond
C. [Xe] 4f75d16s2 C. Chemical Bond
D. [Xe] 4f145d106s26p67s1 D. Hydrogen Bond
19. All halogens have the following number of 27. As the number of bonds between two carbons
valence electrons: increases, which of the following decreases?
A. 2 A. Number of Electrons
B. 5 B. Bond Energy
C. 3 C. Bond Length
D. 7 D. All of the above
20. The following increases across period except: 28. A certain bond in Compound J has an
A. Electronegativity electronegativity difference of 1.43, therefore
B. Non-metallic Character the bond is
C. Electron Affinity A. Nonpolar
D. Atomic Radius (along with metallic B. Polar Bond
property) C. Ionic Bond
21. Which pair of elements below have the highest D. None of the Above
and lowest electron affinities, respectively? 29. Substance A is polar while Substance B is non-
A. He and Rn polar, how does the solubility of A compared
B. F and Fr with that of B in hexane?
C. Ac and F A. Solubility A is Lower – since hexane is non-
D. Li and Nb polar, its solubility is greater in substance B.
Like dissolves like
B. Solubility of A is higher
C. Solubilities are equal C. Flask C
D. No conclusion can be made D. All are the same
30. If hydrogen bonds in a molecule increased in 38. Which of the following states the relative
number, the polarity _____ and water-solubility velocities of gases?
_____ A. Henry’s Law
A. Increases; decreases B. Boyle’s Law
B. Increases; increases C. Dalton’s Law
C. Decreases; increases D. Graham’s Law
D. Decreases; decreases 39. Given the equation: C2H2 + O2 if 8g of O2 was
31. What intermolecular force/s exist between Cl2 present. What amount of Ethyne could have
and CBr4 reacted with all that O2 and how much CO2
A. Dipole-Dipole could have been produced? Use AW in whole
B. Ion-induced dipole number
C. London A. 13g Ethyne and 11g CO2
D. Both A and B B. 2.3g Ethyne and 7.3g CO2
32. The following substances can form H bond with C. 3.2g Ethyne and 6.4g CO2
water, except: D. 2.6g Ethyne and 8.8g CO2
A. NH3 40. When Barium Chloride reacts with Sodium
B. HCOOH Sulfate, the products are table salt and BaO4.
C. CH4 What type of reaction is this?
D. HF A. Combustion
33. A compound with the general formula AX2E2 has B. Neutralization
which geometry? C. Combination
A. Tetrahedral D. Metathesis
B. Bent BaCl2 + Na2SO4 ----NaCl + BaSO4
C. Square planar 41. Mg (s) + ZnCl2
D. See-saw A. ZnCl2 + MgCl2
34. Which of the following is correct? B. Zn + MgCl2
A. 1 atm = 760mmHg C. Zn + Mg + Cl2 (g)
B. 1 atm=760 torr D. No reaction occurs
C. 1 atm = 1.101x105 Pa 42. Absolute Zero Temperature
D. All of the above A. 0o C
35. Which of the following is not a value of the B. 0 K
universal gas constant R? C. 0o F
A. 0.0820 L.atm/K.mol D. 0oK
B. 0.0845 L.bar/K.mol 43. States that the entropy of a pure, crystalline
C. 8.314 J/K.mol solid at absolute zero temperature is zero
D. 8.3145 L.kPa/K.mol A. Third law of thermodynamics
36. The body temperature is about 308K. On a cold B. Second law of thermodynamics
day, what volume of air at 273K must a person C. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
with a lung capacity of 2.00L breathe in order to D. First law of thermodynamics
fill the lungs? This situation is governed by which 44. Gibbs Free Energy
law? A. G= H+T S
A. Avogadro’s Law B. G = H -T S
B. Boyle’s Law C. G= S–T H
C. Charle’s Law D. G= S + T H
D. Dalton’s Law 45. Which of the following has the highest entropy?
37. Consider three 1-L flasks at STP. Flask A contains A. Butter
NH3 gas, Flask B contains NO2 gas, and Flask C B. Coffee
contains N2 gas. Which contains the largest C. Mind
number of Molecules? D. Freon -GAS
A. Flask A 46. Positive H denotes a/an:
B. Flask B A. Exothermic Reaction
B. Endothermic Reaction
C. Spontaneous Reaction
D. Non-spontaneous Reaction
47. Which of the following facts illustrates the effect
of the nature of reactants on the reaction rates?
A. In 0.1M HCl solution, powdered CaCO3
dissolves faster than a chunk of CaCO3
B. Mg dissolves faster in 6M HCl than in 1M
HCl --Concentration
C. In 3M HCl solution, Mg ribbon reacts faster
than Fe filling
D. Formation of cloudy mixture from
decomposition of sodium thiosulfate in
water takes shorter time at 50oC than at
25oC—Temperature
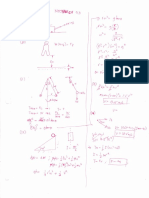
48. What statements apply for the energy diagram
presented?
A. Exothermic
B. A positive enthalpy
C. Spontaneous
D. Two of the above
49. A catalyst performs the following except:
A. Raises activation energy
B. Lowers activation energy
C. Favors formation of product
D. Two of the above
50. A system in which two opposing reactions are
proceeding at the same rate:
A. Chemical Equilibrium
B. Chemical Reaction
C. Chemical Kinetics
D. Chemical Thermodynamics
You might also like
- Fluid Mechanics 2 - Project Andres GalvanDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics 2 - Project Andres GalvanYato QtNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics-III Project Satur GuzmanDocument5 pagesThermodynamics-III Project Satur GuzmanYato QtNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus 01 67-99Document2 pagesIntegral Calculus 01 67-99Yato QtNo ratings yet
- DC 02 Problems With SolutionsDocument7 pagesDC 02 Problems With SolutionsYato QtNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech 2Document13 pagesFluid Mech 2Yato QtNo ratings yet
- CamscannerDocument8 pagesCamscannerYato QtNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 03 9-19Document1 pageMechanics 03 9-19Yato QtNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument258 pagesUntitledYato QtNo ratings yet
- Algebra 02Document10 pagesAlgebra 02Yato QtNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 50 AssignmentDocument3 pagesProblem Set 1 50 AssignmentYato QtNo ratings yet
- Probability: Prepared byDocument40 pagesProbability: Prepared byYato QtNo ratings yet
- PPE Coaching ProblemsDocument37 pagesPPE Coaching ProblemsYato QtNo ratings yet
- Fluids Mechanics 02Document17 pagesFluids Mechanics 02Yato QtNo ratings yet
- Ibong Tiririt Math 3Document9 pagesIbong Tiririt Math 3Yato QtNo ratings yet
- Instructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaDocument13 pagesInstructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaYato QtNo ratings yet
- IM11. Geothermal Power PlantDocument8 pagesIM11. Geothermal Power PlantYato Qt100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)