Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mysql Cheat Sheet Ledger
Uploaded by
David ZhangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mysql Cheat Sheet Ledger
Uploaded by
David ZhangCopyright:
Available Formats
MySQL Cheat Sheet
MySQL is a popular open-source relational database
management system known for its ease of use and scalability. CREATING TABLES QUERYING DATA INSERTING DATA
Sometimes, you will need a little help while working on a To create a table: To select data from a table, use the SELECT command. To insert data into a table, use the INSERT command:
project. That's why we created this MySQL Cheat Sheet. CREATE TABLE habitat ( An example of a single-table query: INSERT INTO habitat VALUES
id INT, SELECT species, AVG(age) AS average_age (1, 'River'),
name VARCHAR(64) FROM animal (2, 'Forest');
Instructions for installing MySQL are available at:
); WHERE id != 3
https://dev.mysql.com
GROUP BY species
HAVING AVG(age) > 3
Use AUTO_INCREMENT to increment the ID automatically You may specify the columns in which the data is added. The
CONNECTING TO A MYSQL with each new record. An AUTO_INCREMENT column must
ORDER BY AVG(age) DESC;
remaining columns are filled with default values or NULLs.
be defined as a primary or unique key: INSERT INTO habitat (name) VALUES
SERVER CREATE TABLE habitat ( An example of a multiple-table query: ('Savanna');
Connect to a MySQL server with a username and a password id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, SELECT city.name, country.name
using the mysql command-line client. name VARCHAR(64) FROM city
MySQL will prompt for the password: ); [INNER | LEFT | RIGHT] JOIN country
mysql -u [username] -p ON city.country_id = country.id;
UPDATING DATA
To update the data in a table, use the UPDATE command:
To connect to a specific database on a MySQL server using a To create a table with a foreign key: Use +, -, *, / to do some basic math. UPDATE animal
username and a password: CREATE TABLE animal ( To get the number of seconds in a week: SET
mysql -u [username] -p [database] id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, SELECT 60 * 60 * 24 * 7; -- result: 604800 species = 'Duck',
name VARCHAR(64), name = 'Quack'
species VARCHAR(64), WHERE id = 2;
To export data using the mysqldump tool:
mysqldump -u [username] -p \
age INT, AGGREGATION AND GROUPING
habitat_id INT, AVG(expr) − average value of expr for the group.
[database] > data_backup.sql
FOREIGN KEY (habitat_id) COUNT(expr) − count of expr values within the group.
To exit the client: );
REFERENCES habitat(id) MAX(expr) − maximum value of expr values within the DELETING DATA
group.
quit or exit To delete data from a table, use the DELETE command:
MIN(expr) − minimum value of expr values within the
DELETE FROM animal
group.
For a full list of commands: MODIFYING TABLES SUM(expr) − sum of expr values within the group.
WHERE id = 1;
help Use the ALTER TABLE statement to modify the table
structure.
To count the rows in the table:
This deletes all rows satisfying the WHERE condition.
CREATING AND DISPLAYING To change a table name:
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM animal;
To delete all data from a table, use the TRUNCATE TABLE
statement:
DATABASES ALTER TABLE animal RENAME pet;
TRUNCATE TABLE animal;
To create a database: To count the non-NULL values in a column:
CREATE DATABASE zoo; To add a column to the table: SELECT COUNT(name)
ALTER TABLE animal FROM animal;
To list all the databases on the server: ADD COLUMN name VARCHAR(64); CASTING
SHOW DATABASES; To count unique values in a column: From time to time, you need to change the type of a value.
To change a column name: SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT name) Use the CAST() function to do this.
To use a specified database: ALTER TABLE animal FROM animal; In MySQL, you can cast to these data types:
USE zoo; RENAME COLUMN id TO identifier; CHAR NCHAR BINARY DATE DATETIME
DECIMAL DOUBLE FLOAT REAL SIGNED
GROUP BY UNSIGNED TIME YEAR JSON spatial_type
To delete a specified database: To change a column data type:
To count the animals by species:
DROP DATABASE zoo; ALTER TABLE animal
SELECT species, COUNT(id)
MODIFY COLUMN name VARCHAR(128);
FROM animal
To list all tables in the database: GROUP BY species; To get a number as a signed integer:
SHOW TABLES; To delete a column: SELECT CAST(1234.567 AS signed);
ALTER TABLE animal -- result: 1235
To get the average, minimum, and maximum ages by habitat:
DROP COLUMN name;
To get information about a specified table: SELECT habitat_id, AVG(age),
DESCRIBE animal; MIN(age), MAX(age)
It outputs column names, data types, default values, and To delete a table: FROM animal To change a column type to double:
more about the table. DROP TABLE animal; GROUP BY habitat_id; SELECT CAST(column AS double);
TEXT FUNCTIONS NUMERIC FUNCTIONS DATE AND TIME EXTRACTING PARTS OF DATES
To extract a part of a date, use the functions YEAR, MONTH,
FILTERING THE OUTPUT To get the remainder of a division: There are 5 main time-related types in MySQL:
WEEK, DAY, HOUR, and so on.
SELECT MOD(13, 2); -- result: 1 DATE TIME DATETIME TIMESTAMP YEAR
To fetch the city names that are not Berlin: SELECT YEAR(CAST('2021-12-31' AS date));
SELECT name -- result: 2021
FROM city To round a number to its nearest integer: DATE – stores the year, month, and day in the YYYY-MM-DD SELECT MONTH(CAST('2021-12-31' AS date));
WHERE name != 'Berlin'; SELECT ROUND(1234.56789); -- result: 1235 format. -- result: 12
SELECT DAY(CAST('2021-12-31' AS date));
To round a number to three decimal places: TIME – stores the hours, minutes, and seconds in the -- result: 31
TEXT OPERATORS
SELECT ROUND(1234.56789, 3); HH:MM:SS format.
To fetch the city names that start with a 'P' or end with an
-- result: 1234.568
's':
SELECT name DATETIME – stores the date and time in the YYYY-MM-DD
FROM city To round a number up: HH:MM:SS format. The supported range is '1000-01-01
DATE ARITHMETICS
SELECT CEIL(13.1); -- result: 14 00:00:00' to '9999-12-31 23:59:59'. To add or subtract an interval from a DATE, use the
WHERE name LIKE 'P%' OR name LIKE '%s';
SELECT CEIL(-13.9); -- result: -13 ADDDATE() function:
ADDDATE('2021-10-31', INTERVAL 2 MONTH);
To fetch the city names that start with any letter followed by TIMESTAMP – stores the date and time. The range is
-- result: '2021-12-31'
'ublin' (like Dublin in Ireland or Lublin in Poland): The CEIL(x) function returns the smallest integer not less '1970-01-01 00:00:01' UTC to '2038-01-19
ADDDATE('2014-04-05', INTERVAL -3 DAY);
SELECT name than x. To round the number down: 03:14:07' UTC. MySQL converts TIMESTAMP values from
-- result: '2014-04-02'
FROM city SELECT FLOOR(13.8); -- result: 13 the current time zone to UTC for storage, and back from UTC
WHERE name LIKE '_ublin'; SELECT FLOOR(-13.2); -- result: -14 to the current time zone for retrieval.
The FLOOR(x) function returns the greatest integer not To add or subtract an interval from a TIMESTAMP or
CONCATENATION YEAR – stores the year in the YYYY format.
DATETIME, use the TIMESTAMPADD() function:
greater than x. To round towards 0 irrespective of the sign of
Use the CONCAT() function to concatenate two strings: TIMESTAMPADD(MONTH, 2,
a number:
SELECT CONCAT('Hi ', 'there!'); INTERVALS '2014-06-10 07:55:00');
SELECT TRUNCATE(13.56, 0); -- result: 13
-- result: Hi there! -- result: '2014-08-10 07:55:00'
SELECT TRUNCATE(-13.56, 1); -- result: An interval is the duration between two points in time.
-13.5 To define an interval: INTERVAL 1 DAY TIMESTAMPADD(MONTH, -2,
If any of the string is NULL, the result is NULL: This syntax consists of the INTERVAL keyword, a value, and '2014-06-10 07:55:00');
SELECT CONCAT(Great ', 'day', NULL); a time part keyword (YEAR, QUARTER, MONTH, WEEK, DAY, -- result: '2014-04-10 07:55:00'
To get the absolute value of a number:
-- result: NULL HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND, MICROSECOND).
SELECT ABS(-12); -- result: 12
MySQL allows specifying a separating character (separator)
To get the square root of a number: You may combine different INTERVALs using the + or - To add or subtract TIME from a DATETIME, use the
using the CONCAT_WS() function. The separator is placed
SELECT SQRT(9); -- result: 3 operator: ADDTIME() function:
between the concatenated values:
INTERVAL 1 YEAR + INTERVAL 3 MONTH ADDTIME('2018-02-12 10:20:24',
SELECT CONCAT_WS(' ', 1, 'Olivier',
You may also use the standard SQL syntax: '12:43:02');
'Norris'); -- result: 1 Olivier Norris
USEFUL NULL FUNCTIONS INTERVAL '1-3' YEAR_MONTH -- result: '2018-02-12 23:03:26'
To fetch the names of the cities whose rating values are not -- 1 year and 3 months ADDTIME('2018-02-12 10:20:24',
OTHER USEFUL TEXT FUNCTIONS missing: INTERVAL '3-12' HOUR_MINUTE '-12:43:02');
To get the count of characters in a string: SELECT name -- 3 hours 12 minutes -- result: '2018-02-11 21:37:22'
SELECT LENGTH('LearnSQL.com'); FROM city
-- result: 12 WHERE rating IS NOT NULL; WHAT TIME IS IT?
To answer this question, use: To find the difference between two dates, use the
To convert all letters to lowercase:
SELECT LOWER('LEARNSQL.COM'); COALESCE(x, y, ...) CURRENT_TIME or CURTIME – to get the current time. DATEDIFF() function:
To replace NULL in a query with something meaningful: CURRENT_DATE or CURDATE – to get the current date. DATEDIFF('2015-01-01', '2014-01-02');
-- result: learnsql.com
SELECT domain, NOW() or CURRENT_TIMESTAMP – to get the current -- result: 364
COALESCE(domain, 'domain missing') timestamp with both of the above.
To convert all letters to uppercase:
FROM contacts;
SELECT UPPER('LearnSQL.com');
The COALESCE() function takes any number of arguments CREATING VALUES To find the difference between two times, use the
-- result: LEARNSQL.COM
and returns the value of the first argument that is not NULL. TIMEDIFF() function:
To create a date, time, or datetime, write the value as a string
To get just a part of a string: and cast it to the proper type. SELECT TIMEDIFF('09:30:00', '07:55:00');
-- result: '01:35:00'
SELECT SUBSTRING('LearnSQL.com', 9); NULLIF(x, y) SELECT CAST('2021-12-31' AS date),
-- result: .com To save yourself from division by 0 errors: CAST('15:31' AS time),
SELECT SUBSTRING('LearnSQL.com', 1, 5); SELECT last_month, this_month, CAST('2021-12-31 23:59:29' AS datetime);
-- result: Learn this_month * 100.0 To find the difference between two datetimes (in a given unit
/ NULLIF(last_month, 0) You may skip casting in simple conditions; the database of time), use the TIMESTAMPDIFF() function. Here's an
To replace a part of a string: AS better_by_percent knows what you mean. example with the difference given in weeks:
SELECT REPLACE('LearnSQL.com', 'SQL', FROM video_views; SELECT airline, flight_no, departure_time SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(
'Python'); The NULLIF(x, y) function returns NULL if x equals y, FROM airport_schedule WEEK, '2018-02-26', '2018-03-21'
-- result: LearnPython.com else it returns the value of x value. WHERE departure_time < '12:00'; ); -- result: 3
LearnSQL.com is owned by Vertabelo SA
Try out the interactive SQL from A to Z in MySQL course at LearnSQL.com, and check out our other SQL courses. vertabelo.com | CC BY-NC-ND Vertabelo SA
You might also like
- SQL Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSQL Cheat SheetArul Mani Subramaniam100% (1)
- Intro To Kafka PDFDocument58 pagesIntro To Kafka PDFBarathNo ratings yet
- SQL Server Cheat Sheet A4Document2 pagesSQL Server Cheat Sheet A4Mashref HoqueNo ratings yet
- Fashion StoresDocument26 pagesFashion StoresAryan Raheja80% (5)
- Hands - On Exercise: Using The Spark Shell..................................Document13 pagesHands - On Exercise: Using The Spark Shell..................................miyumi100% (2)
- PowerBI Developer - Business Analyst Resume - Hire IT People - We Get IT DoneDocument5 pagesPowerBI Developer - Business Analyst Resume - Hire IT People - We Get IT Donesparjinder8No ratings yet
- MySQL NotesDocument58 pagesMySQL NotesPrecious WaseniNo ratings yet
- MysqlDocument81 pagesMysqlAayush Sahu100% (1)
- Cloud Data Lakes For Dummies Snowflake Special Edition V1 4Document10 pagesCloud Data Lakes For Dummies Snowflake Special Edition V1 4CarlosVillamilNo ratings yet
- (SSIS) Expressions (PDFDrive)Document166 pages(SSIS) Expressions (PDFDrive)SsNo ratings yet
- SAP.C - HANATEC - 17.v2021-04-28.q84: Leave A ReplyDocument22 pagesSAP.C - HANATEC - 17.v2021-04-28.q84: Leave A ReplyAmrita NandaNo ratings yet
- Mysql Cheat Sheet A4Document2 pagesMysql Cheat Sheet A4Như Thủy Phạm ThịNo ratings yet
- Mysql Cheat Sheet LetterDocument2 pagesMysql Cheat Sheet Letterdaniela.turcin89No ratings yet
- SQL CommandsDocument10 pagesSQL CommandsRucha GavaskarNo ratings yet
- Nimakarimian Sql-Cheatsheet - BWDocument7 pagesNimakarimian Sql-Cheatsheet - BWRushikesh Salunke PatilNo ratings yet
- Cassandradatamodeling 150520131838 Lva1 App6891Document50 pagesCassandradatamodeling 150520131838 Lva1 App6891Pauline TykochinskyNo ratings yet
- Life Without Tools: Monitoring Database Activity With The Power of SQLDocument27 pagesLife Without Tools: Monitoring Database Activity With The Power of SQLSANJAY BALANo ratings yet
- CS Practical .Term 2Document16 pagesCS Practical .Term 2Aryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hdip Software Project: DR Martina NaughtonDocument48 pagesHdip Software Project: DR Martina NaughtonMalcolm BellNo ratings yet
- APP8Document46 pagesAPP8the prankstersNo ratings yet
- Requested Solutions For Ch. 3Document8 pagesRequested Solutions For Ch. 3Enjoy LifeNo ratings yet
- PHP Database ConnectivityDocument5 pagesPHP Database ConnectivitySumitha NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Writeup 2Document10 pagesWriteup 2183-52 -TY Arshad ShirgaveNo ratings yet
- MySQL SQL Injection Cheat Sheet - PentestmonkeyDocument4 pagesMySQL SQL Injection Cheat Sheet - PentestmonkeyAllison SnipesNo ratings yet
- Pentestmonkey: Mysql SQL Injection Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPentestmonkey: Mysql SQL Injection Cheat Sheetguess meNo ratings yet
- L24 - Mysql 2Document30 pagesL24 - Mysql 2C-dawgNo ratings yet
- Lamp Server: Lecturer: Dr. Bui Ha Duc Dept. of Mechatronics Email: Ducbh@hcmute - Edu.vnDocument31 pagesLamp Server: Lecturer: Dr. Bui Ha Duc Dept. of Mechatronics Email: Ducbh@hcmute - Edu.vnTrạngNo ratings yet
- TriggersDocument9 pagesTriggersnellutlaramyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SQLDocument41 pagesChapter 5 SQLminichelagumas143No ratings yet
- Mysql Lecture2Document71 pagesMysql Lecture2Lumbani Marshall KumwendaNo ratings yet
- SQL 10Document26 pagesSQL 10D.V. ClassesNo ratings yet
- MySQL Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMySQL Cheat SheetPetros PapapostolouNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document22 pagesCH 3Bereket AlemuNo ratings yet
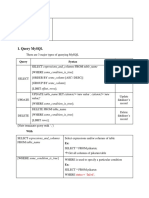
- Query MysqlDocument4 pagesQuery MysqllucasNo ratings yet
- SQL IntrermediateDocument13 pagesSQL IntrermediateMr. QuitNo ratings yet
- Module 7 PHP MysqlDocument3 pagesModule 7 PHP MysqlWaren L ParingitNo ratings yet
- DBMS Experimentdbms-5Document4 pagesDBMS Experimentdbms-5Deepak SwamiNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document6 pagesModule 4Mohd KaifNo ratings yet
- PHP MysqlDocument18 pagesPHP MysqlByambasuren GanboldNo ratings yet
- Mysql QueriesDocument9 pagesMysql QueriesGopalsamy PonnurajNo ratings yet
- Computer 3Document18 pagesComputer 3MarifelNo ratings yet
- Ommand MysqlDocument3 pagesOmmand Mysqlricos123No ratings yet
- MySQL Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesMySQL Cheat SheetGen. HavocNo ratings yet
- R7 SQL - Injection - Cheat - Sheet.v1 PDFDocument1 pageR7 SQL - Injection - Cheat - Sheet.v1 PDFAlhadiNo ratings yet
- Injection SQL Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesInjection SQL Cheat Sheet: by ViaTursunjon HamidovNo ratings yet
- WK 17 DSA Content 4.7 JoinsDocument18 pagesWK 17 DSA Content 4.7 JoinsDanna ValdezNo ratings yet
- MySQL SQL Injection Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMySQL SQL Injection Cheat SheetAbhijit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Arrays, Structures and ValDocument10 pagesArrays, Structures and ValARVIND HNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Activity Suggested SolutionsDocument2 pagesTeaching and Learning Activity Suggested SolutionsBonginkosiNo ratings yet
- Data Dictionary / Directory Tables Views of DD/D TablesDocument13 pagesData Dictionary / Directory Tables Views of DD/D Tablesapi-26309301No ratings yet
- MysqlDocument4 pagesMysqlNihal JadhavNo ratings yet
- 5 Arrays For eDocument23 pages5 Arrays For esrishreyan10bNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - SQLDocument19 pagesChapter 13 - SQLKrishna JyotishNo ratings yet
- L 26 MYSQL TriggersDocument28 pagesL 26 MYSQL Triggerssarthaksainia12No ratings yet
- Lab Manual 3Document5 pagesLab Manual 3surafielmekonen16No ratings yet
- Ip Sample Paper 6 Answer KeyDocument6 pagesIp Sample Paper 6 Answer KeyNEEMA GANDHINo ratings yet
- Web Design2 - ch7Document38 pagesWeb Design2 - ch7د. محمد الجودةNo ratings yet
- SQL Injection Fundamentals Module Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSQL Injection Fundamentals Module Cheat SheetLucas LuqueNo ratings yet
- Asterisk MySQL Cluster PresentationDocument37 pagesAsterisk MySQL Cluster PresentationsandmanpayneNo ratings yet
- MysqlDocument7 pagesMysqlHarshitNo ratings yet
- MySQL Cheatsheet - CodeWithHarryDocument13 pagesMySQL Cheatsheet - CodeWithHarrybishal sarmaNo ratings yet
- Rimas Silkaitis: From Postgres To CassandraDocument95 pagesRimas Silkaitis: From Postgres To CassandraKoushikKc ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Curso MysqlDocument3 pagesCurso MysqlCarlos HernandezNo ratings yet
- SQ L Codes ExampleDocument8 pagesSQ L Codes ExampleDanilo Jr EscotoNo ratings yet
- Extracting Multiple Values (Programming PHP)Document4 pagesExtracting Multiple Values (Programming PHP)Emma WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document31 pagesChapter 4Shish DattaNo ratings yet
- MS SQL Server: Beginner To Advance TutorialDocument27 pagesMS SQL Server: Beginner To Advance Tutorialfrediizee WinsNo ratings yet
- Database Week 7 15Document6 pagesDatabase Week 7 15Tejas IngleNo ratings yet
- Using Basic Structured Query LanguageDocument55 pagesUsing Basic Structured Query LanguageGalaxy teckNo ratings yet
- AIS CH3 (Relational Database)Document71 pagesAIS CH3 (Relational Database)Cabdixakiim-Tiyari Cabdillaahi AadenNo ratings yet
- ETL Testing Training: Training Topics: Chapter 1: Data WarehousingDocument3 pagesETL Testing Training: Training Topics: Chapter 1: Data Warehousingnagushankar8840No ratings yet
- Department of Cyber Security: Faculty of Computing and Artificial IntelligenceDocument17 pagesDepartment of Cyber Security: Faculty of Computing and Artificial Intelligencefarhan mahmoodNo ratings yet
- HackTheBox Zipping Insane Machine Walkthrough-1Document17 pagesHackTheBox Zipping Insane Machine Walkthrough-1ahor4 RootNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project ProposalDocument13 pagesFinal Year Project ProposalAdrian ZayasNo ratings yet
- MSBTE Solution AppDocument13 pagesMSBTE Solution AppRameshwarNo ratings yet
- PL SQLDocument42 pagesPL SQLRohit PachlorNo ratings yet
- Xii Cs Practical File kv2 2023-24Document35 pagesXii Cs Practical File kv2 2023-24MentalistNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19nkNo ratings yet
- RSA Archer Performance Troubleshooting GuideDocument7 pagesRSA Archer Performance Troubleshooting GuideJuani CardonaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Relational Database Design: by Paul LitwinDocument33 pagesFundamentals of Relational Database Design: by Paul LitwinMalek AhmmadNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of DBMSDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of DBMSAnggi Saputri MaulaniNo ratings yet
- These Beldjoudi SamiaDocument164 pagesThese Beldjoudi SamiaSaida GharbiNo ratings yet
- Database Architecture Final FinalDocument23 pagesDatabase Architecture Final FinalRabin KCNo ratings yet
- Graded Quiz - Advanced SQL For Data EngineersDocument3 pagesGraded Quiz - Advanced SQL For Data Engineersf.alzaqriNo ratings yet
- Name: Rudra Dave Board Roll No.: 11633201 Class: 12 Science BDocument31 pagesName: Rudra Dave Board Roll No.: 11633201 Class: 12 Science BRUDRA DAVENo ratings yet
- M6Document26 pagesM6babynettNo ratings yet
- Distributed Database Systems: Computer NetworksDocument2 pagesDistributed Database Systems: Computer NetworksAbdul Rehman ButtsarkarNo ratings yet
- BI AssignmentDocument7 pagesBI AssignmentTTK CreationNo ratings yet
- MIS 406 Final Practical Assignment 2018-2!10!017Document27 pagesMIS 406 Final Practical Assignment 2018-2!10!017Towhid Ul IslamNo ratings yet