Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Computers
Introduction To Computers
Uploaded by
chessduncan8Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Computers
Introduction To Computers
Uploaded by
chessduncan8Copyright:
Available Formats
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 1 10/17/2023
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
Definition of a computer
- A computer can be define as an electronic
device that process a user’s input usually
referred to as data to a desired output, also
known as information.
- This is made possible by a set of instructions
called computer programs stored in a computer.
- Data can be defined as raw facts that do not have
much meaning to the user and may include:
numbers, letters and symbols.
- Information is the processed data that is
meaningful to the user.
- A computer is said to be electromagnet because
it utilizes electrical signals to process
information.
- The integration of computers and
telecommunication facilities for the purpose of
communication is what is referred to as
Information and Communication Technology
(ICT).
- Computers come in different sizes and designs
but the most common is personal computer (PC).
Used in offices, home, schools and business.
Introduction to computers Page 1 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 2 10/17/2023
Physical part of a computer
- A desktop computer is made up of a collection of
different components that are interconnected in
order to function as a single entity.
- A typical desktop computer is basically made up
of a system unit and other devices connected to
the system unit called peripheral devices.
- Examples of peripheral devices include;
monitor also known as screen,
keyboard and
Mouse.
System Unit
- This is the part that houses the brain of a
computer called the central processing unit
(CPU).
- The system unit also houses other devices called
drives. Drives are used to store, record and read
data.
Peripheral devices
- Peripheral devices are connected to the system
unit using special cables Called interface cables
that transmit data and information to and from
the devices.
- The cables are attached to the system unit
through connectors called ports.
Introduction to computers Page 2 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 3 10/17/2023
Keyboard
- A keyboard is the most common peripheral
device that enables a user to enter data and
instructions to a computer.
Mouse
- A mouse is a pointing device that enables the
user to execute commands.
- It is used to control an arrow displayed on the
screen. To execute a command the user moves
the mouse which consequently moves the pointer
on the screen.
Monitor
- A monitor or simply the screen is a television-
like device used for displaying information. It is
called a monitor because it enables the user to
monitor or see what is going on in the computer.
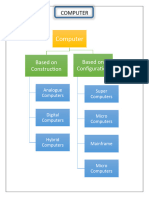
Classification of computers
- Computers can be classified according to
physical size, purpose and functionality.
Classification according to physical size
Introduction to computers Page 3 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 4 10/17/2023
- Based on physical size, computers can be
classified into four main groups namely
supercomputers,
mainframe computers,
minicomputers and
Microcomputers.
Supercomputers
- Supercomputers are the fastest, largest, most
expensive and powerful computers available.
They are to perform many complex operations in
a fraction of a second. Because of its weight; a
supercomputer is kept in a special room. Due to
their huge processing power, super computers
generate a lot of heat. Special cooling system is
therefore required. Sometimes the whole CPU is
immersed in an aquarium like tank containing
liquid fluorocarbon to provide cooling.
- Supercomputers are mainly used for scientific
research, which requires enormous calculations.
Applications that justify use of computers
include aerodynamic design and simulation,
petroleum research, defense and weapon analysis
among others.
Introduction to computers Page 4 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 5 10/17/2023
- Supercomputers are mostly found in main
developed countries such as USA and Japan
where they are used for advanced scientific
research such as nuclear physics.
Mainframe computers
- Mainframe computers are less powerful and less
expensive than supercomputers.
- While supercomputers may be described as giant
computers, mainframes are said to be big in size.
They are used for processing data and
performing complex mathematical calculations.
They have a large storage capacity and support a
verity of peripherals.
- Mainframe computers handle all kinds of
problems whether scientific or commercial.
- They are mostly found in government agencies,
big organization and companies such as banks,
hospitals, and airports etc; which have large
information processing needs.
Minicomputers
- A minicomputer resembles the mainframe but
slightly smaller. Thus it is referred to as small-
scale mainframe computer. Although it supports
fewer peripheral devices and is not as powerful
and fast as the mainframe computer, it was
Introduction to computers Page 5 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 6 10/17/2023
developed as a cheaper alternative to the
mainframes for smaller organizations.
- They are used mainly in scientific laboratories,
research institutions, engineering plants and
places where processing automation is required.
- They well adapted for functions such as
accounting, word processing, data base
management and specific industry applications.
Microcomputers
- A microcomputer is the smallest, cheapest and
relatively least powerful type of computer. It is
called a microcomputer because; its CPU is
called a microprocessor, which is very small
compared to that of microcomputers, mainframe
and supercomputers.
- Microcomputers are commonly used in training
and learning institutions, small business
enterprises, and communication centers, among
others.
- Today, the power of microcomputers has grown
tremendously, closing the gap that formerly
existed and reserved for the minicomputers and
the mainframes.
- Technology advancement has seen the
development of smaller minicomputers.
- Types of minicomputers in operation today;
Introduction to computers Page 6 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 7 10/17/2023
1. Desktop computers: is designed to be placed
on top of an office desk.
2. Notebook or laptop computers: portable
convenient for mobile users.
3. Personal Digital Assistant (PDA): is small
enough to fit in the pocket.
Classification according to purpose.
- Computers can be classified according to
the tasks they perform either as general or special
purpose computers.
General purpose computers.
- General purpose computers have been designed to
be able to perform a variety of tasks when loaded
with appropriate programmes. They are the most
common types of computers in use today.
- Their flexibility enables them to be applied in a
wide range of applications like; document
processing, performing calculations, accounting,
and data and information management among
others.
Special purpose computers.
- Special purpose computers are designed to serve a
specific purpose or to accomplish one particular
task. Such computers can perform no other task
except the one they were meant to do.
Introduction to computers Page 7 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 8 10/17/2023
- This means that the set of instructions, which
drive a special purpose computer, are limited in
number at the time of manufacture. Examples of
such computers include; robots used in the
manufacturing industry, mobile phones for
communication only and electronic calculators
that carry out calculations only.
- Since special purpose computers are dedicated to
a single task, they can perform the task quickly
and very efficiently.
Classification according to functionality.
- Computers can be classified into three types
according to the type of data they process. Data
can either be in discrete or in continuous form.
Digital computers.
- Digital computers process data that is discrete in
nature. Discrete data also known as digital data is
usually represented using a two-state square
wave form.
- Apart from PC’s, most modern home appliances
such as digital TV’s, microwaves, wall clocks
and other electronic home appliances are digital
in nature.
Introduction to computers Page 8 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 9 10/17/2023
Analog computers.
- This refers to computers that process data that is
continuous in nature. Continuous data also
known as analog data is usually represented
using a continuous waveform.
- Analog computers are used in manufacturing
process control like monitoring and regulating
furnace temperatures, pressures etc. They are
also used in other applications like in weather
stations to record and process physical quantities
e.g. wind, cloud speed, temperatures etc.
Hybrid computers.
- Hybrid computers are designed to process both
analog and digital data.
Development of computers.
- Historical development of computers can be
traced back to the time human beings were
struggling to invent non-electronic tools that
would simplify arithmetic such as Abacus and
Napier’s bones.
Abacus.
- An abacus was a Chinese counting instrument
which dates back to 3000 BC. The abacus has
bead-like parts that move along rods. Each bead
Introduction to computers Page 9 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 10 10/17/2023
above the middle bar stands for five units. Each
bead below stands for one unit.
Napier’s bones.
- Napier’s bones was developed by John Napier, a
Scottish mathematician in the 17th century. It
helps in multiplication and division.
The analytical engine.
- The analytical engine was designed by an
English mathematician, Charles Babbage in
1832. The engine is recognized as the first real
computer and Babbage as the father of
computing.
Electronic computers.
- It took several years after Babbage designed the
analytical engine to come up with an electronic
computer. The age of modern electronic
computer can be traced back to 1951. These are
classified into five generations depending on the
technology used to develop them.
1. First generation computer. (1940s to 1958)
- First generation computer were large
physically and used thousands of electronic
gadgets called vacuum tubes or thermionic
valves.
Introduction to computers Page 10 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 11 10/17/2023
- Examples of first generation computers
include Electronic Numeric Integrator and
calculator (ENIAC) and the Electronic
Discrete Variable Automatic Computer.
2. Second generation computers. (1958-19640
- Computers in this generation operated using
tiny solid-state electronic devices called
transistors that were much smaller than the
vacuum tubes. These computers produced
less heat, were much faster, smaller in size
and more reliable than those made of
vacuum tubes. Examples of second
generation computers include IBM1401
AND 7070, UNIVAC 1107, ATLAS LEO
Mark III and Honeywell 200.
3. Third generation computers. (1964-1970)
- The third generation computers used
electronic devices called integrated circuits
(ICs). An integrated circuit consists of
thousands of small transistor circuits etched
on a semiconductor called a silicon chip.
- Third generation computers emitted less
heat, were smaller in size and were easier to
program, use and maintain compared to their
predecessors. Examples of third generation
computers include smaller and less
expensive minicomputer such as IBM 360
and ICL 19000 series.
Introduction to computers Page 11 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 12 10/17/2023
4.Fourth generation computers.
- From 1970, further technological
improvement was done on the silicon chip
design by compressing more tiny circuits
and transistors into even smaller space. This
design produced what is called large scale
integrated (LSI) and very large scale
integrated (VLSI) circuits which were used
in the innovation and technological
development of the brain of the computer
called the microprocessor.
- Fourth generation computers are
characterized by very low emissions of heat,
are small in size and easier to use and
maintain.
- Examples of fourth generation computers
include IBM 370 and 4300, Honeywell
DPS-88 and Burroughs 7700.
5.Fifth generation computers.
- In this generation falls today’s computer that
has very high processing power and speed
than their predecessors, whose size is
increasingly becoming smaller. These
computers have special instructions sets that
allow them to support complex programs
Introduction to computers Page 12 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 13 10/17/2023
that mimic human intelligence often referred
to as artificial intelligence.
- Fifth generation computers are characterized
by artificial intelligence, connectivity to
internet, superior hardware and software and
are very small in size.
- A lot of research is being done to try and
come up with machines that can work
without human intervention. One of the
most successful developments in this field is
the advent of computers that can help
managers to make decisions and those that
can offer critical expert services to users
instead of relying on human intervention.
Areas where computers are used.
Supermarkets
- Most retail stores use computers to help in the
management of daily activities like stock
control. The stock control system keeps
account of what is sold and what is out of
stock. The management is automatically
alerted whenever a particular item or items are
running out of stock that needed reordering.
Offices
Introduction to computers Page 13 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 14 10/17/2023
- Computers have increased efficiency in offices
by reducing the time and effort needed to
access and receive information. Most modern
office functions have been automated for faster
information distribution and document
processing.
Banks
- Special cash dispensing machines called
automated teller machines (ATMs) have
enabled automation of cash deposit and
withdrawal services. Efficiency has also been
increased due to better record keeping and
document processing brought about by use of
computers.
Industries
- Computers are being used to monitor and
control industrial processes.
- The computers age has seen wide use of
remote controlled devices called robots. A
robot is a machine that works like human
being but performs tasks that are too
unpleasant, dangerous, or complex and tedious
to assign to human beings.
Introduction to computers Page 14 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 15 10/17/2023
Hospitals
- Computers are used to keep patient’s records
in order to provide easy access to a patient’s
treatment and diagnosis history.
- Computerized medical devices are now being
used to get across sectional view of the
patient’s body that enables physicians to get
proper diagnosis of affected body parts with
high levels of accuracy.
- Computers also control life support machines
in Intensive Care Units (ICU).
Transport
- Computers are used to monitor vehicles traffic
in busy towns, in aircrafts navigation and in
making reservations.
Communication
- Integration of computers and
telecommunication facilities has made
message transmission and reception to be very
fast and efficient. Because of the speed with
which information can be transmitted around
the world using computers, the world is said to
have become a global village.
Law enforcement agencies
Introduction to computers Page 15 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 16 10/17/2023
- Information stored in computers such as
fingerprint, images and other identification
details help law enforcers carry out criminal
investigations.
Education
- Computers are widely used in learning
processes. Learning and teaching using
computers is referred to as Computer Aided
Learning (CAL) and Computers Aided
Institution (CAI). For example, experiments in
subjects like chemistry or physics may be
demonstrated using a special computer
program that can depict them on the screen
through a process called simulation.
Domestic and entertainment
- Computers can be used at home for
recreational activities such as watching
movies, playing music and computer games.
They can also be used in storing personal
information, calculating, keeping home
budgets and research.
Library services
- In a computerized library, a computer enables
library personnel to easily access and keep
Introduction to computers Page 16 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 17 10/17/2023
updated records of books and other library
materials.
- Library users can also use computers to search
for titles instead of using the manual card
catalogue.
THE COMPUTER LABORATORY
-A computer laboratory or simply a computer lab is a
room set aside and prepared specifically for safe
installation and use of computers
-in schools a computer provides a safe conducive
environment for learning and teaching computer
studies.
- Factors to be considered when preparing a
computer laboratory;
Security of the computer software and
hardware
Reliability of the source of power
Number of computer to be setup
Maximum number of users
Introduction to computers Page 17 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 18 10/17/2023
SAFETY PRECAUTION AND PRACTISES
-The computer lab there is rules that protect both user
and the computer
MEASURES TO PROTECT THE COMPUTERS
Burglar proofing –This includes fitting grills on
doors, windows and roof, to deter forceful entry
into the computer lab. Installation of security
guards and intrusion of detection of alarm system
thus increasing the level of security alertness
against theft of computers
Installation of fire prevention and control
equipments –equipments such as smoke
detectors, non liquid based and non-powder based
fire extinguishers are gaseous type. This is
because liquid may cause rusting and corrosion of
computer components. On the other hand, powder
particles may increase friction and wear and wear
of movable parts. Their particles may also cause
disks to crash.
The room should be well laid out- with enough
space for movement. Computers should be placed
on tables, wide desks to avoid accidentally
knocking them down. Cables should be laid out in
trunks away from user paths to avoid people
stumbling on them.
Introduction to computers Page 18 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 19 10/17/2023
PROVIDING STABLE POWER SUPPLY.
- Computers are delicate devices that require a
stable source of power. Power from mains
supply is not always stable and may
sometimes experience power surges or under
voltage sometimes referred to as brownout. To
protect the computer from being damaged due
tom power instabilities, avoid connecting it
directly to the main electricity. Instead,
connect it to a special device called
uninterruptible power supply (UPS) then
connect the UPS to the mains.
Dust and dump control- Dust can be controlled
by fitting good window curtains and an air
conditioning system that filters dust particles
from the air entering the room. Also computers
should be covered with dust covers when not in
use.
Dampness or humidity in the lab can be
controlled by using dehumidifiers. High
humidity leads to rusting of the computer
metallic parts.
Cables and power sockets should be well
insulated- and of the correct power rating to
Introduction to computers Page 19 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 20 10/17/2023
avoid short circuits that can cause damage to the
computer components.
The users should not eat or drink- in the
computer laboratory. Food particles may fall in
moving computer parts like the keyboard and
clog them while liquids may pour into electrical
circuits and cause short circuits.
MEASURES THAT PROTECT THE USER.
All cables should be insulated-to avoid the
danger of electric shock to users.
Cables should be laid away- from users’ paths
to avoid tripping on them.
Providing standard furniture- to avoid poor
posture which may lead to strain injury and limb
fatigue. The table should be of the right height
relative to the sea to provide comfortable hand
positioning. The seat should have an upright
backrest and should be high enough to allow the
eyes of the user to be level with the top of the
screen.
Providing antiglare screens- (light filters) and
adjustable screens top avoid eye strain and
fatigue caused by over bright cathode ray tube
(CRT) monitors. However, modern flat Panel
displays such as crystal liquid display (LCD) do
not strain the eye.
Introduction to computers Page 20 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 21 10/17/2023
The room should be properly ventilated- to
avoid dizziness caused by lack of enough
oxygen and to allow computers to cool.
The walls of the computer room should not
be painted- with over bright reflective oil paints
and the screen should face away from the
window to avoid glare caused by bright
backgrounds.
Overcrowding- in the computer room is not
allowed. This may cause suffocation.
PRACTICAL HAND ON SKILLS.
Cold booting a computer.
- Once you turn on the computer, it
automatically goes through a process of self-
test and preparation for use. This process is
called cold booting or boot up.
- Cold booting: Starting the computer from
mains power supply.
- Warm booting: Starting the computer using
the restart button when it was already on.
- Once you turn on the computer, you may hear
the sound of the cooler fan running. After a
few seconds, lines of text start scrolling up on
the screen. This process is referred to as
Power-on self test (POST). POST checks on
Introduction to computers Page 21 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 22 10/17/2023
the existing drives, basic input and output
devices such as the keyboard, monitor and the
mouse. If a problem is encountered, the
process is halted and an error message is
displayed on the screen.
- POST is accomplished by a special firmware
program called the Basic input/Output system
(BIOS) which is held in a ROM chip mounted
on the motherboard.
- After POST, the computer reads some
instructions such as the current time and date
from a special memory known as the
complimentary metal-oxide semiconductor
(CMOS). CMOS is powered by a dry cell that
mostly resembles that of a digital watch. If the
cell is down, the computer requires the user to
enter the current date and time.
- Lastly, a special type of computer program
used to manage computers called an operating
system is loaded to the computer memory.
Shutting down a computer
- The correct procedure of shutting down a
computer at all times must be followed in order
to curb:
Data loss
Damage of computer programs
Damage of computer components
Introduction to computers Page 22 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 23 10/17/2023
Procedure of shutting down
- Ensure that all the work has been properly
stored this process is called saving.
- Close all programs that may be currently
running
- If your computer is running on Microsoft
windows XP or VISTA
Click the start button
On the start menu click turn off computer
On the message box that appears click TURN
OFF
Earlier versions of windows procedure
On the start menu click shut down
In the shut down message window, select shut
down and then click ‘OK’
Key boarding and mouse skills
Key board lay out
Classification of key board keys
1. Alphanumeric keys
-also called typing keys
They include; alphabetical letters a-z,
Numbers arranged on line 1, 2, 3
-12
Special symbols i.e.?,/,%.
Introduction to computers Page 23 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 24 10/17/2023
Caps lock, enter, tab, spacebar,
and backspace.
Caps lock key-pressing it once helps the user
to write in upper case letters [capital] to switch
back to lower case letters press same key
again.
Enter key [return key]-pressing this key
forces the text cursor to move to the beginning
of the next line
Cursor-a blinking under score [-] or vertical
beam [I]that shows where the text appears
Enter key is also used to instruct the computer
to execute a command that has been selected
on the screen
Tab key-it is used to move the text cursor at
set intervals on the same line.
The space bar-This bar creates a space
between words during typing.
The back space key- This key deletes
characters from right to left on the same line.
2. Function keys
–These are used for tasks that occur frequently
in various programs. This are usually located a
long the top of the keyboard and are labeled
F1 up to F12
3. Cursor movement and editing keys
Introduction to computers Page 24 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 25 10/17/2023
- These are keys used to move cursor on the
screen
- Includes:-
Arrow key-pressing the right or left arrow key
moves the cursor on characters to right or left
respectively. Up or down arrow key moves the
text cursor one line up or down respectively.
Page up and page down keys-page up moves
the cursor up one page incase the document
has many pages. Page down moves the cursor
down one page incase the document has many
page.
Home and end keys
Pressing home key moves the cursor to the
beginning of the current line
Pressing the end keys moves the cursor to the
end of the current line
Editing keys-are used to delete or insert
character in document
They include;
Insert key- this key inserts or replaces a
character at the cursor position
Delete [Del] keys-this deletes character at
the cursor at the position from left to right
Introduction to computers Page 25 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 26 10/17/2023
4. Special purpose keys
- They are used in combination with the other
keys to give certain commands for example
CTL+ESC is used to display the start menu
- They include; shift, ctrl, alt and esc.
5. Numeric key pad keys
- They are located on the right hand side of
the key board they consist of numbers 0-
9and arithmetical signs [+, _, x, /]
- They help the user to rapidly enter
numeric data
- NB-the number on the numeric key pad
can only be used when the num lock key
[situated on the numeric key pad] is on.
- They can be used as cursor movement and
editing keys when num lock key is turned
off.
Using typing tutor
This is a type of soft ware that helps in increasing
your typing speed and accuracy
Examples of tutor soft ware
Mavis beacon
Teaches typing
Typing poll
Typing master
Touch tutor
Introduction to computers Page 26 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 27 10/17/2023
Mouse skills
- Moving a mouse on a flat surface makes the
pointer on the screen to move in the same
direction as the mouse itself.
- When using the mouse follow the following
guidelines:-
1. Place the mouse on a flat smooth surface
2. Gently hold the mouse with your right hand
using the thumb and the two fingers
3. The index finger should rest on the left
button while the middle finger rests on the
right button
Four mouse operations
- Clicking-this means pressing and
releasing the left mouse button once. a click
often selects on objects
- Double clicking-this means pressing
the left button twice in quick succession.
Double clicking usually opens a file or starts a
program.
Right clicking-pressing the right hand mouse
button once displays lists of commands from
which the user can make a selection. This list of
commands is called a short cut menu or context
sensitive menu
- Drag and drop-this is where the user drags an
item from one location on the screen to another
Introduction to computers Page 27 17/10/2023
©2010 –computers for schools kenya Page 28 10/17/2023
Procedure for drag and drop
Point to the item you want to drag
Press the left hand mouse button and hold it
down
Slide the mouse until the pointer reaches the
desired position on the screen.
Finally release the mouse button and the item
will be dropped in the new location.
Introduction to computers Page 28 17/10/2023
You might also like
- VLSI Design Quick GuideDocument68 pagesVLSI Design Quick GuideMayur Agarwal100% (1)
- Topic 1: Introduction To ComputingDocument123 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To ComputingKartel Gunter100% (1)
- Computer Application in BusinessDocument64 pagesComputer Application in BusinessFatima Ali100% (2)
- Module 1a A Brief History of Computer ArchitectureDocument53 pagesModule 1a A Brief History of Computer ArchitectureMairos Kunze BongaNo ratings yet
- Webinar SigrityDocument54 pagesWebinar Sigrityjagadees21No ratings yet
- Embeded Systems WikibooksDocument126 pagesEmbeded Systems WikibooksRavi SankarNo ratings yet
- Black BoxDocument7 pagesBlack Boxlokesh_045No ratings yet
- Bioelectronics Report PDFDocument42 pagesBioelectronics Report PDFDr Ezema Chukwuedozie NnaemekaNo ratings yet
- TP Advanced IC Packaging Technology OverviewDocument25 pagesTP Advanced IC Packaging Technology Overviewalbertsdeguzman100% (1)
- LED Packaging 2011: Yole DeveloppementDocument13 pagesLED Packaging 2011: Yole DeveloppementFatih HökeNo ratings yet
- Concepts On Oracle SCM PDFDocument31 pagesConcepts On Oracle SCM PDFAravindAllamNo ratings yet
- Microelectronics Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesMicroelectronics Lecture NotesJoanna Fabricante0% (1)
- Computer HardwareDocument18 pagesComputer HardwareArtur100% (144)
- ICT NotesDocument34 pagesICT Notestalhahassanalvi786No ratings yet
- Ict Notes 2022Document66 pagesIct Notes 2022Alex MitemaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing PrelimDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Computing PrelimApril Jane AndresNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes SimplifiedDocument121 pagesComputer Notes SimplifiedSeth MophanNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1Lata SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer (ICRI)Document43 pagesBasics of Computer (ICRI)Harshada VasaneNo ratings yet
- Digital ComputerDocument4 pagesDigital Computerakintweh231No ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument77 pagesComputer NotesvoeacyberNo ratings yet
- CS NotezDocument207 pagesCS Notezcollins chinsungweNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument17 pagesClassification of Computerscossykin19No ratings yet
- Git Unit 3Document2 pagesGit Unit 3Vivien LancinNo ratings yet
- Computers: What Is A Computer?Document24 pagesComputers: What Is A Computer?Mohit ChhabriaNo ratings yet
- Ict NotesDocument102 pagesIct NotesEsther WambuiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IctDocument8 pagesIntroduction To IctAringo ArumNo ratings yet
- Understanding ComputerDocument4 pagesUnderstanding ComputerRoselyn BelgaNo ratings yet
- Ste4208: Ict in Science Education Overview of Information and Communication Technology (ICT)Document18 pagesSte4208: Ict in Science Education Overview of Information and Communication Technology (ICT)Yusha'u SaniNo ratings yet
- LAS WEEK 1 - Grade 10 ICTDocument4 pagesLAS WEEK 1 - Grade 10 ICTNaj CumlaNo ratings yet
- Ict Notes-3Document124 pagesIct Notes-3WAFULA STEPHENNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computers - Quick Guide - TutorialspointDocument50 pagesBasics of Computers - Quick Guide - TutorialspointJames MukhwanaNo ratings yet
- Comuter: 1. What Is Computer ?Document4 pagesComuter: 1. What Is Computer ?PenjNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Chapter 1 (Part-3) (21-22)Document14 pagesClass 9 Chapter 1 (Part-3) (21-22)anjumjamal8174No ratings yet
- 1 - IT - Systems-Intro RevisedDocument9 pages1 - IT - Systems-Intro RevisedJosh TorcedoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Types of ComputerDocument8 pagesClassification of Types of Computershawai8009No ratings yet
- Computer Notes Form 1 4 Topical BookletDocument196 pagesComputer Notes Form 1 4 Topical BookletFànèlè Fèrìđý GwebuNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction To Computer: of ComputersDocument8 pagesChapter One Introduction To Computer: of ComputershaileNo ratings yet
- 1.basics of Computers - Quick Guide - TutorialspointDocument47 pages1.basics of Computers - Quick Guide - TutorialspointChinmoyee BiswasNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument22 pagesChapter Onejohn mwangiNo ratings yet
- ComputersDocument4 pagesComputersZujajah Gull100% (1)
- Basic Programing Slide Intro Tade DayDocument60 pagesBasic Programing Slide Intro Tade DayYoomif TubeNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument4 pagesClassification of Computersisimarkaur21No ratings yet
- A Term PaperDocument9 pagesA Term PaperitaobedNo ratings yet
- Basics of ComputersDocument52 pagesBasics of ComputersAlfred SalazarNo ratings yet
- HRCU 102: Introduction To Communication and Computer Application SkillsDocument50 pagesHRCU 102: Introduction To Communication and Computer Application SkillsDickson MusoniNo ratings yet
- Csitnepal: Unit 1: Introduction To Computer System Information TechnologyDocument15 pagesCsitnepal: Unit 1: Introduction To Computer System Information TechnologyEpi TechNo ratings yet
- Computer ClassificationDocument13 pagesComputer ClassificationOloka George OkwirNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computers BBADocument14 pagesBasics of Computers BBAsaraNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputerDocument6 pagesTypes of ComputerRajalNo ratings yet
- Different Types of ComputerDocument11 pagesDifferent Types of ComputerMehtab KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Data Operations or Calculations ResultDocument7 pagesUnit-I: Data Operations or Calculations ResultSiva SankariNo ratings yet
- Categories of Computer and Computer LanguageDocument3 pagesCategories of Computer and Computer LanguageSameerNo ratings yet
- Computer Science 2Document15 pagesComputer Science 2selsabilhaddab2004No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Computer ApplicationDocument26 pagesLecture 1 Computer ApplicationAisha LawalNo ratings yet
- Understanding ComputerDocument27 pagesUnderstanding ComputermarkNo ratings yet
- KMB 108 Unit I: Computer Application & Management Information and SystemDocument15 pagesKMB 108 Unit I: Computer Application & Management Information and SystemDeepankar singhNo ratings yet
- Module 1. Introduction To Information SystemDocument22 pagesModule 1. Introduction To Information SystemMontenegroNo ratings yet
- 1538 - CSC Week One Lecture NoteDocument15 pages1538 - CSC Week One Lecture NoteArun Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 NotesAshley MainaNo ratings yet
- English IV It Lesson NotesDocument45 pagesEnglish IV It Lesson NotesJoaquim CHICONo ratings yet
- IT ReviewerDocument15 pagesIT ReviewerMarjorie Baya BidlanNo ratings yet
- Computer Module 3 Lesson 1Document2 pagesComputer Module 3 Lesson 1yuuna yuunaNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of ComputerDocument96 pagesBasic Parts of ComputerDawin DessertNo ratings yet
- Founder of AppleDocument8 pagesFounder of ApplemeenuNo ratings yet
- C NotesDocument2 pagesC NotesMamta Mohit DhandaNo ratings yet
- Type of CoputerDocument21 pagesType of CoputerMohit SainiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer: Information TechnologyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Computer: Information TechnologyAmolika PatelNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Computers and Internet - A Practical PresentationFrom EverandAn Introduction to Computers and Internet - A Practical PresentationNo ratings yet
- NVRAM ReplacementDocument12 pagesNVRAM ReplacementAfix RohmanNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and ControlDocument4 pagesInstrumentation and ControlTrustWorthy100No ratings yet
- 06062-Integrated Handler Solutions Prod BriefDocument2 pages06062-Integrated Handler Solutions Prod Briefwaikok jeffreyNo ratings yet
- Classifications of ComputersDocument3 pagesClassifications of Computersjaimededios80% (5)
- Quick Charge Device ListDocument23 pagesQuick Charge Device ListPhaneesh BasavaniNo ratings yet
- Microfluidics and Microfluidic Devices - A Review - ElveflowDocument1 pageMicrofluidics and Microfluidic Devices - A Review - ElveflowAjaykumarNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermal Engineering: SciencedirectDocument15 pagesApplied Thermal Engineering: Sciencedirectcitra widyasariNo ratings yet
- Ruehli-Inductance Calculations in A Complex Integrated Circuit EnvironmentDocument12 pagesRuehli-Inductance Calculations in A Complex Integrated Circuit EnvironmentH LNo ratings yet
- Power Aware TestabilityDocument7 pagesPower Aware Testabilityvaneetmahajan10No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document42 pagesLecture 1Tania Khan75% (4)
- CRAY-1 Computer Technology: Fig. 1. CRAY-IS MainframeDocument6 pagesCRAY-1 Computer Technology: Fig. 1. CRAY-IS MainframeSalahNo ratings yet
- The Phase Control Circuit The TC787Document10 pagesThe Phase Control Circuit The TC787nansusanNo ratings yet
- Automated Programming SystemDocument8 pagesAutomated Programming SystemXeltekNo ratings yet
- ME 2017 Reg Exam Time Table 2018-19Document48 pagesME 2017 Reg Exam Time Table 2018-19vishnuNo ratings yet
- Integrated CircuitsDocument68 pagesIntegrated CircuitsZymone Eiron DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Advanced View Pic Microcontroller Projects List PIC MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesAdvanced View Pic Microcontroller Projects List PIC MicrocontrollerGeneration GenerationNo ratings yet
- 1179Document26 pages1179Miko F. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 43UJ67xV - 655V - 701V - UD74PDocument99 pages43UJ67xV - 655V - 701V - UD74PtaviNo ratings yet
- Access and Access 2 USB ManualDocument95 pagesAccess and Access 2 USB Manualmusz730No ratings yet
- Charles L. Brown Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Undergraduate Handbook Ee CurriculumDocument25 pagesCharles L. Brown Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Undergraduate Handbook Ee CurriculumaksimhalNo ratings yet