Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Words (DC Circuit)
Uploaded by
AC DonozoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Words (DC Circuit)
Uploaded by
AC DonozoCopyright:
Available Formats
Words to ponder (DC Circuit Analysis)
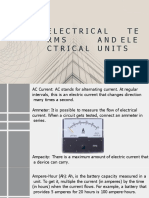
Ammeter
An instrument for measuring the flow of electrical current in amperes. Ammeters are always
connected in series with the circuit to be tested.
Ampacity
The maximum amount of electric current a conductor or device can carry before sustaining
immediate or progressive deterioration.
Ampere-Hour (Ah)
A unit of measure for battery capacity. It is obtained by multiplying the current (in amperes) by the
time (in hours) during which current flows. For example, a battery which provides 5 amperes for
20 hours is said to deliver 100 ampere - hours.
Ampere (A)
A unit of measure for the intensity of an electric current flowing in a circuit. One ampere is equal
to a current flow of one coulomb per second.
Apparent Power
Measured in volt-amperes (VA). Apparent power is the product of the rms voltage and the rms
current.
Capacitance
The ability of a body to store an electrical charge. Measured in farads as the ratio of the electric
charge of the object (Q, measured in coulombs) to the voltage across the object (V, measured in
volts).
Capacitor
A device used to store an electric charge, consisting of one or more pairs of conductors separated
by an insulator. Commonly used for filtering out voltage spikes.
Circuit
A closed path in which electrons from a voltage or current source flow. Circuits can be in series,
parallel, or in any combination of the two.
Circuit Breaker
An automatic device for stopping the flow of current in an electric circuit. To restore service, the
circuit breaker must be reset (closed) after correcting the cause of the overload or failure. Circuit
breakers are used in conjunction with protective relays to protect circuits from faults.
Conductor
Any material where electric current can flow freely. Conductive materials, such as metals, have a
relatively low resistance. Copper and aluminum wire are the most common conductors.
You might also like
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Basic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsDocument6 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsJericho CunananNo ratings yet
- Electrical Terms and UnitsDocument28 pagesElectrical Terms and UnitsMichael PachecoNo ratings yet
- TermsDocument3 pagesTermsivanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Terms ExplainedDocument15 pagesBasic Electrical Terms Explainedilango palaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalJohn Florenz VasquezNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsDocument26 pagesBasic Electronics Terms and Definitionspondu888No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsDocument13 pagesBasic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsHazel NantesNo ratings yet
- List of Power Supply ComponentsDocument29 pagesList of Power Supply ComponentsNazeer AlyasNo ratings yet
- The Basic of ElectricityDocument44 pagesThe Basic of ElectricityBrent Alfred YongcoNo ratings yet
- Essential Electrical MaterialsDocument2 pagesEssential Electrical MaterialsAira Acob MagnoNo ratings yet
- Electricity Nazeer AlyasDocument27 pagesElectricity Nazeer AlyasNazeer AlyasNo ratings yet
- Aru 302Document34 pagesAru 302Michael PachecoNo ratings yet
- Unidades 1,2,3Document10 pagesUnidades 1,2,3JR ALMANZARNo ratings yet
- Some of Their Energy As They Travel Through The AtmosphereDocument3 pagesSome of Their Energy As They Travel Through The AtmosphereLarry CubillasNo ratings yet
- Definition of Electrical Terms and Electrical Units.Document7 pagesDefinition of Electrical Terms and Electrical Units.julianaquino1203No ratings yet
- July 05, 2017 CEIT-05-902E MH 3:30-4:30P EngrDocument34 pagesJuly 05, 2017 CEIT-05-902E MH 3:30-4:30P EngrDiana Ross CustodioNo ratings yet
- Basic EE Module 123Document32 pagesBasic EE Module 123Benmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Electronics & Comp - SkillDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Electronics & Comp - SkillPAnkaj BhamareNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFDocument8 pagesMohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFdragon for pc gamesNo ratings yet
- Subject: 2es103 Basic Electrical Engineering (Bee)Document30 pagesSubject: 2es103 Basic Electrical Engineering (Bee)Jay SathvaraNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Power MeterDocument5 pagesTopic 5 Power MeterAcidDukeNo ratings yet
- Definition of Electrical TermDocument2 pagesDefinition of Electrical TermLuis Carlos100% (1)
- Building Services Book 2Document237 pagesBuilding Services Book 2Africana RoyalNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument53 pagesBasic Principles of ElectricityRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thDocument40 pagesCurrent Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Defi NationsDocument2 pagesDefi Nationsrtjjkhjorv08No ratings yet
- BASIC Elec. TermsDocument5 pagesBASIC Elec. TermsRamces SolimanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits & QuantitiesDocument29 pagesElectrical Circuits & QuantitiesDejaunae Lawson50% (2)
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To ElectricityDocument13 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To ElectricityErika HonorioNo ratings yet
- Power ElexDocument38 pagesPower ElexTin PelingonNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Electrical TermsDocument8 pagesGlossary of Electrical TermsRafael jei GabisanNo ratings yet
- Voltage Load Resistance Dual Current Source: Added/subtracted in Series Must Be Same in ParallelDocument8 pagesVoltage Load Resistance Dual Current Source: Added/subtracted in Series Must Be Same in ParallelDuck520No ratings yet
- What Is An Electric Circuit?Document8 pagesWhat Is An Electric Circuit?Josiah ZeusNo ratings yet
- Building UtilitiesDocument89 pagesBuilding Utilitiesalezandro del rossiNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice IIDocument8 pagesWorkshop Practice IISurendra GhalanNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 6:: Practical To Verify The Ohm's LawDocument4 pagesPractical No. 6:: Practical To Verify The Ohm's Lawعبدالمقیت مرزاNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Symbols GuideDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Symbols Guideanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Electricity PPT Presentation ModifiedDocument22 pagesElectricity PPT Presentation ModifiedMark SyNo ratings yet
- RarDocument3 pagesRarOKEMA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics Theory: English For EEITDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Electronics Theory: English For EEITYou Can Shine AtomNo ratings yet
- Current, voltage and resistance explainedDocument2 pagesCurrent, voltage and resistance explainedJR ALMANZARNo ratings yet
- 107785Document16 pages107785Balu ChanderNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsDocument40 pagesBasic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsIrish Balaba67% (3)
- Experiment 1 ElectricalDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 ElectricalUsamaNo ratings yet
- Gutor UPS System GlossaryDocument33 pagesGutor UPS System Glossarybookbum100% (4)
- Measure Electrical Power with Clamp Meters and Power MetersDocument5 pagesMeasure Electrical Power with Clamp Meters and Power Metersche syakirNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument115 pagesAmmetermhnmndrkNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thDocument11 pagesCurrent Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Jose RizalDocument11 pagesJose RizalBaet RayanNo ratings yet
- EEE Lab ReportDocument4 pagesEEE Lab ReportpikisewNo ratings yet
- 4 Basic Electronic TermsDocument21 pages4 Basic Electronic Termshomer simpsonNo ratings yet
- Module in EE 211 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument39 pagesModule in EE 211 Basic Electrical EngineeringEbacuado, Regine Mae F.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity 1.1Document23 pagesIntroduction To Electricity 1.1August DuqueNo ratings yet
- OSHA 10 Slides 06 - Electrical SafetyDocument64 pagesOSHA 10 Slides 06 - Electrical Safetyasteinb1No ratings yet
- Wire A Wire Is A Flexible Metallic Conductor, Especially One Made of Copper, Usually Insulated, and Used To Carry Electric Current in A CircuitDocument13 pagesWire A Wire Is A Flexible Metallic Conductor, Especially One Made of Copper, Usually Insulated, and Used To Carry Electric Current in A Circuitusman bagoNo ratings yet
- Intro to Electric Circuits: Understanding Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm's LawDocument20 pagesIntro to Electric Circuits: Understanding Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm's LawRee-anne SabanalNo ratings yet
- 3 - Electrics & ElectronicsDocument27 pages3 - Electrics & ElectronicsJoe ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Intro To Electric Circuits: GLAS WiringDocument20 pagesIntro To Electric Circuits: GLAS WiringKrishna BoreddyNo ratings yet
- Building Disign Electrical SymbolsDocument6 pagesBuilding Disign Electrical SymbolsGerry Jimenez Sao-anNo ratings yet