Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Morphology Glossary
Morphology Glossary
Uploaded by
cheshirecat960 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document defines key terms used in morphology, the study of word formation and structure. It describes different types of morphemes like affixes, allomorphs, and free and bound morphemes. It also defines word formation processes like derivation, compounding, clipping, blending and conversion. Specific compound types are outlined as well as the main constituents of compounds like the head and affixes.
Original Description:
Original Title
MORPHOLOGY GLOSSARY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key terms used in morphology, the study of word formation and structure. It describes different types of morphemes like affixes, allomorphs, and free and bound morphemes. It also defines word formation processes like derivation, compounding, clipping, blending and conversion. Specific compound types are outlined as well as the main constituents of compounds like the head and affixes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesMorphology Glossary
Morphology Glossary
Uploaded by
cheshirecat96This document defines key terms used in morphology, the study of word formation and structure. It describes different types of morphemes like affixes, allomorphs, and free and bound morphemes. It also defines word formation processes like derivation, compounding, clipping, blending and conversion. Specific compound types are outlined as well as the main constituents of compounds like the head and affixes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
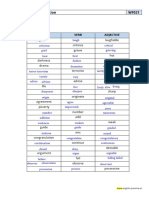
MORPHOLOGY GLOSSARY
affix: an inflectional or derivational morpheme; to attach an inflectional or derivational
morpheme to an expression.
allomorph: a variant phonetic form of a morpheme, or, a unit of meaning that varies in sound
and spelling without changing the meaning.
base: part of word to which an affix may be attached; may but need not be a root morpheme.
bound morpheme: a morpheme that must be attached to another morpheme.
constituent: a unified part of a construction (e.g., of a word, phrase, or sentence).
conversion: derivational relationship between two words of different parts of speech but without
any formal marking of the difference.
coordinative (copulative) compound: a compound word that denotes an entity or property to
which both constituents contribute equally; e.g., bittersweet refers to a quality which is both
bitter and sweet.
derivation: process of changing a word from one part of speech to another or from one subclass
to another, typically by making some change in form. ()
clipping: also called truncation or shortening, is word formation by removing some segments of
an existing word to create a synonym. (front clipping: motorbike-bike, back clipping:
gymnasium-gym, middle clipping: refrigerator-fridge)
blending: a process of taking two or more words, removing parts of each, and joining the
residues together to create a new word whose form and meaning are taken from the source
words. (motor hotel-motel, smoke + fog = smog)
compounding: a process that forms new words from two or more independent words containing
more than one root. ()
endocentric compound: a compound word that denotes a subtype of whatever is denoted by the
head. Armchair represents a type of chair; breath-test represents a kind of test.
exocentric compound: a compound word that denotes a subtype of a category that is not
mentioned within the compound; e.g., pickpocket represents a kind of person, not a kind of
pocket nor a kind of pick.
free morpheme: a morpheme that need not be attached to another morpheme, but can constitute
a word on its own.
head: the main constituent of a compound, which may be modified by the compound’s other
constituents.
inflectional morpheme: a bound morpheme that signals a grammatical function and meaning in
a specific sentence, e.g., plural {-s}, past tense {-ed}, comparative {-er}, superlative {-est}
morph: a minimal meaningful form, regardless of whether it is a morpheme or allomorph.
morpheme: the smallest part of a word that has meaning or grammatical function.
prefix: a bound morpheme attached before a root. (return, preview)
root: the basic constituent of a word, to which other morphemes are attached.
suffix: a bound morpheme attached after a root. (spiteful, slowly)
You might also like
- SyntaxDocument25 pagesSyntaxRhaenyra Targaryen100% (1)
- Morphology RevisionDocument9 pagesMorphology RevisionTuyết Hường TrầnNo ratings yet
- MORPHOLOGYDocument51 pagesMORPHOLOGYMahnoor IrfanNo ratings yet
- Morpheme AllomorphDocument6 pagesMorpheme AllomorphRizwan SharifNo ratings yet
- De Ning The WordDocument8 pagesDe Ning The Wordジョシュア ジョシュア100% (1)
- Madd As Silah - HandoutDocument2 pagesMadd As Silah - HandoutBishara SaitNo ratings yet
- General Linguistics: Morphology Word StructureDocument45 pagesGeneral Linguistics: Morphology Word StructureReemNo ratings yet
- Inflectional and DerivationalDocument41 pagesInflectional and Derivationalummi zulaikha bt mohd nor100% (2)
- 10 - Léxico. Características de La Formación de Palabras en Inglés - UpdatedDocument13 pages10 - Léxico. Características de La Formación de Palabras en Inglés - UpdatedMariette Quesnel100% (1)
- Japanese Verb Tenses & Forms: The Guide ToDocument1 pageJapanese Verb Tenses & Forms: The Guide Toer4a3100% (1)
- Subject - Verb Agreement - QuizDocument3 pagesSubject - Verb Agreement - QuizRose Mariel GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Technically, A Word Is A Unit of Language That Carries Meaning and Consists of One orDocument7 pagesTechnically, A Word Is A Unit of Language That Carries Meaning and Consists of One orDoni Setiawan sinagaNo ratings yet
- Morphology Test (Lexicology), With Answers, 2021Document16 pagesMorphology Test (Lexicology), With Answers, 2021Amer Mehovic100% (2)
- Lexical Contrastive AnalysisDocument42 pagesLexical Contrastive AnalysisEssam Kassab100% (1)
- Ques - Wild Horses of Sable IslandDocument4 pagesQues - Wild Horses of Sable IslandRafan HasanNo ratings yet
- ADocument2 pagesASHAFQAT MEHMOODNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Word FormationDocument21 pagesMorphology and Word FormationAstri Situmorang100% (1)
- Grammatical Aspects of LanguageDocument4 pagesGrammatical Aspects of LanguageAlNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document11 pagesGroup 4Ahmad HairulNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document2 pagesWeek 8PutriRahimaSariNo ratings yet
- ESSAY. Zhumakhanova M. Â Derivational vs. Inflectional MorphemesÂDocument1 pageESSAY. Zhumakhanova M. Â Derivational vs. Inflectional MorphemesÂMadina ZhumakhanovaNo ratings yet
- Wuolah-Free-Conceptos-Completos (1) - Gulag-FreeDocument6 pagesWuolah-Free-Conceptos-Completos (1) - Gulag-FreeMariangeles Laguna BenítezNo ratings yet
- Definition of DerivationDocument2 pagesDefinition of DerivationHan D-RyNo ratings yet
- Heroine Derived From Hero Is An Example of Diminutive Derivational SuffixesDocument2 pagesHeroine Derived From Hero Is An Example of Diminutive Derivational SuffixesHồng NhungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Humamx TimeZfoldNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument8 pagesMorphologyWissam KhudairNo ratings yet
- Morphemes Types of Morpheme: Group 1 - Alfini Khoirunnisa - Nihmatun Halifah - Siska AndiniDocument8 pagesMorphemes Types of Morpheme: Group 1 - Alfini Khoirunnisa - Nihmatun Halifah - Siska AndiniJuwita SariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MorphologyDocument50 pagesChapter 3 Morphologymochen439No ratings yet
- Uas MorpologhyDocument3 pagesUas Morpologhyzulkarnaen hudaNo ratings yet
- MORPHOLOGYgroup 3Document15 pagesMORPHOLOGYgroup 3palprocalla15No ratings yet
- Ver. English Introduction To Linguistic MorphologyDocument6 pagesVer. English Introduction To Linguistic Morphologywinda lestaryNo ratings yet
- Morphological F-1Document6 pagesMorphological F-1PRECIOUSNo ratings yet
- Affixation Is A Word FormationDocument1 pageAffixation Is A Word FormationIoana LauraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. Word Building For StudentsDocument10 pagesLecture 4. Word Building For StudentsШвидка Вікторія ТарасівнаNo ratings yet
- The Islamia University of Bahawalpur PakistanDocument13 pagesThe Islamia University of Bahawalpur PakistanAdnan BalochNo ratings yet
- 2015morphologydraftversion PDFDocument37 pages2015morphologydraftversion PDFYuki JudaiNo ratings yet
- Lexicology GlossaryDocument3 pagesLexicology GlossaryAiganymNo ratings yet
- 21-087 Maryam Ulfa Linguistik 3Document3 pages21-087 Maryam Ulfa Linguistik 321-087 Maryam UlfaNo ratings yet
- The MorphemesDocument2 pagesThe MorphemesOrsy FloresNo ratings yet
- Lexicology Seminar 4-5Document11 pagesLexicology Seminar 4-5Олександр СмутнякNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Ke7Document5 pagesPresentasi Ke7vanxiaojienuwaNo ratings yet
- Advance Grammar NotesDocument3 pagesAdvance Grammar NotesCrisnelynNo ratings yet
- Open-Class Words:: An Allomorph IsDocument3 pagesOpen-Class Words:: An Allomorph IsГуменюк ВеронікаNo ratings yet
- Word RootsDocument18 pagesWord Rootshpeter195798No ratings yet
- Word, Word-Form, Lexeme: 21 October 2011Document22 pagesWord, Word-Form, Lexeme: 21 October 2011MikkemaheswaraNo ratings yet
- Reporte - MorphologyDocument6 pagesReporte - MorphologyMontse EncisoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Word Formation - deDocument16 pagesChapter 3 - Word Formation - deMai Vy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentCHEW YE-HAUR IAN MoeNo ratings yet
- The MorphemeDocument3 pagesThe MorphemeСоня ГалійNo ratings yet
- Inflectional and Derivational MorphemesDocument3 pagesInflectional and Derivational MorphemesoserobritonNo ratings yet
- Word FormationDocument3 pagesWord FormationCindy Palen BocaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. The Word. Definition and Characteristics. Changes of MeaningDocument12 pagesLecture 3. The Word. Definition and Characteristics. Changes of MeaningАннаNo ratings yet
- Morphology Exam NotesDocument18 pagesMorphology Exam NotesAlba25DG DomingoNo ratings yet
- Morfologia: Parts of SpeechDocument5 pagesMorfologia: Parts of SpeechAnita TrendakNo ratings yet
- Lexico Grammar PDFDocument25 pagesLexico Grammar PDFDidik Tri WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Morphological Structure of A Word. Word-Formation in Modern English 1. Give The Definition of The MorphemeDocument22 pagesMorphological Structure of A Word. Word-Formation in Modern English 1. Give The Definition of The MorphemeIvan BodnariukNo ratings yet
- Morphology: Mukambetova A Abdullaeva MDocument9 pagesMorphology: Mukambetova A Abdullaeva MAijamal MukambetovaNo ratings yet
- Lexico Grammar 1: Prof - Dr.Sumsrsih, M.PDDocument11 pagesLexico Grammar 1: Prof - Dr.Sumsrsih, M.PDRivaldo SiregarNo ratings yet
- Employer Means A Person or Company That Pays People To Work For Them. The DerivedDocument2 pagesEmployer Means A Person or Company That Pays People To Work For Them. The DerivedLING JIE SEE MoeNo ratings yet
- L 1 Introduction To MorphologyDocument31 pagesL 1 Introduction To MorphologyIftkhar GorsiNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument3 pagesMorphologyomayma KAZIZOUNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Flashcards Tool For The Study of Language, 5 Edition'Document23 pagesWelcome To The Flashcards Tool For The Study of Language, 5 Edition'Hayder Mohamad SadiqNo ratings yet
- Aizhamal Is Super Twice PDFDocument9 pagesAizhamal Is Super Twice PDFAijamal MukambetovaNo ratings yet
- On the Evolution of Language: First Annual Report of the Bureau of Ethnology to the Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution, 1879-80, Government Printing Office, Washington, 1881, pages 1-16From EverandOn the Evolution of Language: First Annual Report of the Bureau of Ethnology to the Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution, 1879-80, Government Printing Office, Washington, 1881, pages 1-16No ratings yet
- Morphological ProductivityDocument6 pagesMorphological ProductivityMuhammad KhayamNo ratings yet
- Superlative AdjectivesDocument1 pageSuperlative Adjectivesliz_santiago_4No ratings yet
- Chapters 1 and 2Document6 pagesChapters 1 and 2TuaTelaVideaulasNo ratings yet
- Poem WinterDocument1 pagePoem Winteryoungdor8No ratings yet
- Grinch Grammar )Document2 pagesGrinch Grammar )Osman AhmadovNo ratings yet
- The Adverb 1Document4 pagesThe Adverb 1Laura ChetrariNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 2 Video 13 - Present Perfect Continuous TenseDocument2 pagesIELTS Writing Task 2 Video 13 - Present Perfect Continuous TenseBaljeetNo ratings yet
- Causative PassiveDocument2 pagesCausative PassiveKateryna TaylorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document7 pagesUnit 1بروف فى اللغة الإنجليزيةNo ratings yet
- CEBRAC English - Book 1 - Review 5Document2 pagesCEBRAC English - Book 1 - Review 5musich.vsong16No ratings yet
- Morphs and AllomorphsDocument3 pagesMorphs and AllomorphsVicky Galih DewanggaNo ratings yet
- While: Work Work Go Go Work Work Go Go Work Work Go GoDocument2 pagesWhile: Work Work Go Go Work Work Go Go Work Work Go GoshaNo ratings yet
- English Homework For Summer VacationDocument1 pageEnglish Homework For Summer VacationMuhammad Jawwad67% (3)
- Paper Pattern ENGLISH (Objective) : Primary Standard Annual/ Scholarship Examination 2021-22Document3 pagesPaper Pattern ENGLISH (Objective) : Primary Standard Annual/ Scholarship Examination 2021-22Tahir SaeedNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of English Language & Applied Linguistics) WarningDocument3 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of English Language & Applied Linguistics) WarningMoazama BatoolNo ratings yet
- Active Voice & Passive Voice in 16 TensesDocument4 pagesActive Voice & Passive Voice in 16 TensesAchmad Iqbal RahmaddanNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar in UseDocument319 pagesBasic Grammar in Useheng91645No ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs WheelDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs WheelMicka Ella PortoNo ratings yet
- B2 Word Formation WF021: Complete The TableDocument2 pagesB2 Word Formation WF021: Complete The TableGülsüm Sude Altınışık100% (1)
- Line Graph - IELTS Writing Task 1 - Overall CommentsDocument2 pagesLine Graph - IELTS Writing Task 1 - Overall CommentsDistance From LoveNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense - Grade 8 KAMISDocument3 pagesSimple Present Tense - Grade 8 KAMISdinalwayscheerfulNo ratings yet
- CEBRAC English - Book 1 - Review 1Document2 pagesCEBRAC English - Book 1 - Review 1Matheus Cebrac100% (1)
- 5.1 16. (Textbook) Present Continuous PDFDocument4 pages5.1 16. (Textbook) Present Continuous PDFUDAYAN SHAHNo ratings yet
- Korean Basic CourseDocument4 pagesKorean Basic CourseDiana Amaya JáureguiNo ratings yet
- Basic Phrasal Verbs: Watch and WriteDocument2 pagesBasic Phrasal Verbs: Watch and WriteCat JonesNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument2 pagesEnglishNAYLA SALSA RAGITA PUTRINo ratings yet