Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat and Temperature2
Heat and Temperature2
Uploaded by
Eugene ColotOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat and Temperature2
Heat and Temperature2
Uploaded by
Eugene ColotCopyright:
Available Formats
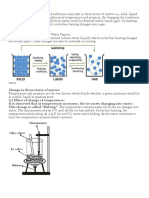
Thermal Expansion, the Working Principle of the Mercury Thermometer
When the bulb is placed in cold water, the liquid contracts and so it goes down the tube. In physics, this is called thermal
expansion, another effect of heat transfer.
Another change that may occur when heat is added to or taken out from an object is phase change. For example, water
can change from solid (ice) to liquid (water) or from liquid to gas (steam).
Figure 5. The graph shows that the ice absorbs heat as evidenced by the temperature rise; the temperature remains the
same when ice starts to melt and until all the ice has melted; then the temperature rises again until water boils.
The amount of heat needed by a material to increase its temperature by a degree is called heat capacity (C). To be more
specific, the term specific heat capacity (c) is used, and this refers to the amount of heat required to increase the
temperature of one unit mass of a given material by one Celsius degree.
You might also like
- Effect of Temperature in The Change of State of Matters PDFDocument4 pagesEffect of Temperature in The Change of State of Matters PDFSourya AichNo ratings yet
- Basic Refrigeration System - MATTERDocument10 pagesBasic Refrigeration System - MATTERCisco StarkNo ratings yet
- Concept of Latent Heat. BaseDocument18 pagesConcept of Latent Heat. BaseHarsh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Temperature Scales: ExerciseDocument6 pagesConversion of Temperature Scales: Exercisekidanemariam HabtemariamNo ratings yet
- FKCH 8 HHM BYSJxe F8 ZG 74Document45 pagesFKCH 8 HHM BYSJxe F8 ZG 74MahaNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument32 pagesLatent HeatAbhijit Kar Gupta100% (11)
- Latent Heat, Phase Change Phase Change: Basic Concept, Definitions and FactsDocument2 pagesLatent Heat, Phase Change Phase Change: Basic Concept, Definitions and FactssanjuranjNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration: Learning Objective: Describe The Stages of Heat Theory and The Principles InvolvedDocument98 pagesRefrigeration: Learning Objective: Describe The Stages of Heat Theory and The Principles Involvedgopinathan_karuthedaNo ratings yet
- Heating and Cooling Curve of A SubstanceDocument62 pagesHeating and Cooling Curve of A SubstanceIan Alfred Brimbuela100% (1)
- Grade 10 States of Matter Handout 2Document6 pagesGrade 10 States of Matter Handout 2Dexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- FT Physics NotesDocument13 pagesFT Physics Notes410230675No ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 9 AssignmentDocument12 pagesChemistry Grade 9 Assignmentmonka assNo ratings yet
- Heat of FusionDocument3 pagesHeat of FusionDaryl Gomez TimatimNo ratings yet
- PHASE CHANGE Hand OutDocument8 pagesPHASE CHANGE Hand Outjoel rosalNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Changes of StateDocument6 pagesUNIT 5 Changes of StatePham Van Tin B1909842No ratings yet
- Heat of Phase ChangeDocument15 pagesHeat of Phase ChangeLyza JavierNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument4 pagesLatent HeatRhenne-Ann OrayanNo ratings yet
- 2 States of Matter NotesDocument14 pages2 States of Matter Notesafnan.6556No ratings yet
- 0a - RDG - Heat and Calorimetry - ReviewDocument8 pages0a - RDG - Heat and Calorimetry - ReviewIgnacio OreiroNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM6Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM6Jonnel RoqueNo ratings yet
- Extensive Parameter Thermodynamic StateDocument2 pagesExtensive Parameter Thermodynamic StateRich Samuel AlmazarNo ratings yet
- Course: ThermodynamicsDocument18 pagesCourse: ThermodynamicsSahar Batool QaziNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument1 pageLatent HeatAndreaNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument3 pagesThermalNisa NiichiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Heat On MatterDocument9 pagesEffect of Heat On MatterIzly Izlya100% (1)
- HeatDocument7 pagesHeatkrushnakadam0029No ratings yet
- Heating and Cooling Curve of A Substance 1Document5 pagesHeating and Cooling Curve of A Substance 1bennaorbino272006No ratings yet
- Transformations of WaterDocument12 pagesTransformations of WatergcpasambaNo ratings yet
- Phase Change DiagramDocument2 pagesPhase Change DiagramHabiba KhababNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 (Done)Document6 pagesWorksheet 1 (Done)samyak jainNo ratings yet
- What Is SteamDocument12 pagesWhat Is SteamZeljko CisarNo ratings yet
- Chem - Week - 2Document44 pagesChem - Week - 2cadaxeshpatelNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry 2023Document10 pagesCalorimetry 2023Yatharth TiwariNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Phys LabDocument3 pagesWeek 9 Phys LabJacob JohnsonNo ratings yet
- The Heating Curve of WaterDocument3 pagesThe Heating Curve of WaterDimpho MasetediNo ratings yet
- Surrounding Air Cools: Latent Heat of Fusion and VaporizationDocument2 pagesSurrounding Air Cools: Latent Heat of Fusion and VaporizationPutriInggitIstiqomahNo ratings yet
- 1.Dr - Ahmed Samy - PhysicsDocument21 pages1.Dr - Ahmed Samy - PhysicsKhaled AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Projectaditya varteNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry SynopsisDocument4 pagesCalorimetry Synopsissreevaishnava01No ratings yet
- What Is Steam?: Triple PointDocument9 pagesWhat Is Steam?: Triple PointAhmed Mohamed KhalilNo ratings yet
- HW Chemistry 3may2024Document3 pagesHW Chemistry 3may2024rabiotadrien068No ratings yet
- Chem2in This experim-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageChem2in This experim-WPS OfficeKathrynn NaipaoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesThermal Properties of MatterPeter KachouhNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Las Week 2c February 20 2024Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Las Week 2c February 20 2024Denisse OrigNo ratings yet
- Bses 29 ReviewerDocument8 pagesBses 29 Reviewerjerico.lapurgaNo ratings yet
- Chem2 G2-1Document29 pagesChem2 G2-1Mariz TanNo ratings yet
- Create By: Basic Physics IIDocument7 pagesCreate By: Basic Physics IIM Umar Said TyhnNo ratings yet
- (AA) - What Is Steam MARINE STEAM SYSTEMDocument65 pages(AA) - What Is Steam MARINE STEAM SYSTEMrajpratik1561No ratings yet
- Temperature and Thermal Energy: Matter Is Made Up of Tiny Particles CalledDocument22 pagesTemperature and Thermal Energy: Matter Is Made Up of Tiny Particles CalledCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagrams and Heating CurveDocument4 pagesPhase Diagrams and Heating Curvexamcarat17No ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument79 pagesThermal Properties of MatterHafiza JaweriaNo ratings yet
- Practice 3Document16 pagesPractice 3Marco YordanNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument3 pagesLatent HeatFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Understanding Specific Latent HeatDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Specific Latent HeatNoraidah Harun100% (1)
- Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument9 pagesProperties of Pure SubstancesMLNDG boysNo ratings yet
- Specialized Training For Oil Tankers CH 2 Basic Properties of Petroleum and Its HazardsDocument36 pagesSpecialized Training For Oil Tankers CH 2 Basic Properties of Petroleum and Its HazardsFairuz TotoqNo ratings yet
- Experiment-No 1Document2 pagesExperiment-No 1Sandra GonzalesNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsLhenny Albos GumbanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Remedial ExamDocument3 pages3rd Remedial ExamEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- P.E Powerpoint Grade 12Document13 pagesP.E Powerpoint Grade 12Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- LAS Week 5 Grade 12Document4 pagesLAS Week 5 Grade 12Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- EUGENECOLOT Sci8 RAT Item-Analysis Sy23-24Document14 pagesEUGENECOLOT Sci8 RAT Item-Analysis Sy23-24Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- DLL PEH 11 Q2 M6 Michelle GDocument5 pagesDLL PEH 11 Q2 M6 Michelle GEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Long QuizDocument6 pagesLong QuizEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Q - Grade 8 - WorkDocument2 pagesQ - Grade 8 - WorkEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Done-EDITED-hope1 q1 Mod6 ProperEtiquetteand-Safetyinthe-UseofFacilitiesEquip v1Document34 pagesDone-EDITED-hope1 q1 Mod6 ProperEtiquetteand-Safetyinthe-UseofFacilitiesEquip v1Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument4 pagesAnswer KeyEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Activity. Grade 8Document2 pagesActivity. Grade 8Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- DLL 2022 PE and HealthDocument12 pagesDLL 2022 PE and HealthEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Quiz G-8 MotionDocument1 pageQuiz G-8 MotionEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument2 pagesELECTRICITYEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Calculating WorkDocument1 pageCalculating WorkEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Electricity LectureDocument1 pageElectricity LectureEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Work 2Document1 pageWork 2Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- WorkDocument2 pagesWorkEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- LDM2 Module1Document5 pagesLDM2 Module1Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Nature of The Different Dances M1Document3 pagesNature of The Different Dances M1Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Unit TestDocument2 pagesUnit TestEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Pe11 q2 Mod3 My-Fitness-GoalsDocument29 pagesPe11 q2 Mod3 My-Fitness-GoalsEugene Colot100% (2)
- Pe11 - q2 - Mod7 - Organize For Fitness and HealthDocument24 pagesPe11 - q2 - Mod7 - Organize For Fitness and HealthEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Pe11 q2 Mod2 Fitness-Enhancement-Through-SportsDocument32 pagesPe11 q2 Mod2 Fitness-Enhancement-Through-SportsEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Pe11 - q2 - Mod1 - Physical Education Managing Stress Through SportsDocument35 pagesPe11 - q2 - Mod1 - Physical Education Managing Stress Through SportsEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Annotations RPMS 2021 2022 New123 2Document25 pagesAnnotations RPMS 2021 2022 New123 2Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- DLP Template 2023 - JHDocument2 pagesDLP Template 2023 - JHEugene ColotNo ratings yet