Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ELECTRICITY
Uploaded by
Eugene ColotOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRICITY
Uploaded by
Eugene ColotCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1 MODULE 4 ELECTRICITY
Electricity- is a form of energy that is carried through wires and is used to operate machines, light, etc.
Circuit-is any arrangement of a source of energy (battery), connecting wires, and a load (e.g. bulbs).
Conventional current or simply Current - is the movement of charges from the positive side of the
battery to the negative side.
Electron current - The direction of the flow of electrons is from the negative terminal to the positive
terminal.
Electric current - is a measure of the number of electrical charges passing through a cross-section of a
conductor in a given time.
The symbol for current is capital letter I.
The unit, ampere (A), is named after Andre-Marie Ampere, a French physicist who made important
contributions to the theory of electricity and magnetism.
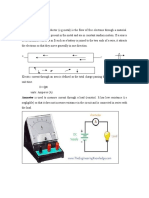
An ammeter measures electric current.
Voltage - is the force of electrical
Unit 1 MODULE 4
ELECTRICITY
Electricity is a part of our daily lives. Many of the activities we do everyday depend on
electricity.
The discovery of electricity changed people’s lives.
There are three quantities that you should be familiar with in the study of electricity. These are
electric current, voltage, and resistance.
Electric Current
Circuit is any arrangement of a source of energy(battery), connecting wires, and a load (e.g.
bulbs).
Complete or a Closed circuit provides a path for electrical charges to flow.
Electric current is a measure of the number of electrical charges passing through a cross-section
of a conductor in a given time.
The symbol for current is capital letter I. The unit, ampere (A), is named after Andre-Marie
Ampere, a French physicist who made important contributions to the theory of electricity and
magnetism.
An ammeter measures electric current. Figure 1 shows how the ammeter is connected in a
circuit.
You might also like
- Chapter 1 Electricity Theory PDFDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Electricity Theory PDFRosalie Vertudes0% (1)
- Voltage: Figure 2. Voltmeter Connected Across The LoadDocument1 pageVoltage: Figure 2. Voltmeter Connected Across The LoadMary RoseNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuit Analysis (EE-101) : Electric QuantitiesDocument15 pagesLinear Circuit Analysis (EE-101) : Electric QuantitiesTehseen HussainNo ratings yet
- Historical Aspects: Alessandro Antonio Volta (1745-1827) - Italian PhysicistDocument16 pagesHistorical Aspects: Alessandro Antonio Volta (1745-1827) - Italian PhysicistppNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument2 pagesElectrical Measuring InstrumentsFranz Joseph Endaya TenorioNo ratings yet
- Basic 20electricity 2060Document24 pagesBasic 20electricity 2060JohntreeNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument7 pagesElectric CircuitsEzio AuditoreNo ratings yet
- Actividad 5 InglesDocument10 pagesActividad 5 InglesVictoria FlorezNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument3 pagesNotesmikko decenaNo ratings yet
- Student Lab Manual: Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument9 pagesStudent Lab Manual: Fundamentals of ElectricityAbdisalam A. MohamedNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument4 pagesBasic ElectricityMae PanlilioNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument22 pagesDC Circuitsandre yudiNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES1 Lecture1Document14 pagesUTILITIES1 Lecture1Potter XxNo ratings yet
- Foundation of ElectricityDocument26 pagesFoundation of ElectricityRaven TarroquinNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document15 pagesModule 7Laiza GranaNo ratings yet
- Elementary Electrical EngineeringDocument28 pagesElementary Electrical EngineeringLopez, Paolo AdonisNo ratings yet
- LAST REVIEWER g12 (Part 2) PDFDocument16 pagesLAST REVIEWER g12 (Part 2) PDFAmylyn CaliguiaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Introduction To Electricity Copy For StudentsDocument31 pagesLESSON 3 Introduction To Electricity Copy For Studentsixearth84No ratings yet
- General Physics 2 ReviewerDocument22 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Reviewercharydel.oretaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics1Document3 pagesIntroduction To Electronics1Jon Teodulo NiervaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document51 pagesPresentation 1Workineh AsefaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit: Ohm's Law CircuitDocument2 pagesElectronic Circuit: Ohm's Law CircuithasnaNo ratings yet
- Torres, Tricia Mae L.-Physics Electric Current Mini-ResearchDocument5 pagesTorres, Tricia Mae L.-Physics Electric Current Mini-ResearchTricia Mae TorresNo ratings yet
- Electricity Power PointDocument13 pagesElectricity Power PointIrish Pales CosidonNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Electrical Circuits: On Completion of This Module, You Will Be Able ToDocument11 pagesModule 3: Electrical Circuits: On Completion of This Module, You Will Be Able ToMustapha IsaadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits - Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesElectrical Circuits - Learning OutcomesonaaaaangNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 EazDocument4 pagesTOPIC 1 Eaz44361brianmainaitl6j024No ratings yet
- Voltage Load Resistance Dual Current Source: Added/subtracted in Series Must Be Same in ParallelDocument8 pagesVoltage Load Resistance Dual Current Source: Added/subtracted in Series Must Be Same in ParallelDuck520No ratings yet
- PHYS101L LabReport9Document13 pagesPHYS101L LabReport9Leidee Charmellie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Measurements of Electrical QuantitiesDocument9 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Measurements of Electrical QuantitiesbbbbgcbgbeNo ratings yet
- 5.1: Electrical DistributionDocument31 pages5.1: Electrical DistributionShuhada SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Basic ElectricityDocument18 pagesModule 3: Basic ElectricityApriljoy DannugNo ratings yet
- Direct Current and PowerDocument5 pagesDirect Current and PowerElizabeth AnyegaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Document51 pagesElectrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Fiorella Amer CarrNo ratings yet
- Intro-Duction To Electricity: Force Field Which Is Neither Gravitational Nor Nuclear. To Understand What ThisDocument9 pagesIntro-Duction To Electricity: Force Field Which Is Neither Gravitational Nor Nuclear. To Understand What ThisAbdisalam A. MohamedNo ratings yet
- Voltage Current Resistance and Ohms LawDocument62 pagesVoltage Current Resistance and Ohms LawAllysa Nicole AldaNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law: Arch'T. Ricky Rance Mojica, UapDocument39 pagesOhm'S Law: Arch'T. Ricky Rance Mojica, UapJohn Lloyd AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics ProjectthaswikaamaraNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument85 pagesElectricityapi-2851792610% (1)
- Module 5 - Energy and Electricity ConservationDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Energy and Electricity ConservationParth KumarNo ratings yet
- 02 Basic Electrical SaftyDocument31 pages02 Basic Electrical SaftySujit PradhanNo ratings yet
- Supw ProjectDocument30 pagesSupw ProjectAbhik BiswasNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS2L/Exp. No. 1/page 2Document10 pagesPHYSICS2L/Exp. No. 1/page 2Aldrin Kenneth AllanigueNo ratings yet
- What Is Electricity?: From?"Document4 pagesWhat Is Electricity?: From?"MichaelNo ratings yet
- Elec 102 Module 3Document35 pagesElec 102 Module 3Kylle Bryan AranceNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES1 Lecture1Document14 pagesUTILITIES1 Lecture1Carjez LoveNo ratings yet
- Soldering IronDocument12 pagesSoldering IronfjsabNo ratings yet
- Electricity Is The Set ofDocument2 pagesElectricity Is The Set ofSam Axel BenedictoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 3Document13 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 3richie cuizonNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2Aaa Rian Andre BolongaitaNo ratings yet
- EIM 11 Q1 Modules Week 5 8 FinalDocument31 pagesEIM 11 Q1 Modules Week 5 8 FinalFranklin BallonNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lec-1Document41 pagesBasic Electronics Lec-1world cup 2019No ratings yet
- Electricity Hand OutsDocument3 pagesElectricity Hand OutsKayser Jeff FernandezNo ratings yet
- Preguntas TecnologíaDocument4 pagesPreguntas TecnologíaMARINA DEL AMO BERNALNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- Apuntes TecnologíaDocument1 pageApuntes TecnologíaZaryanGamerNo ratings yet
- AIRCRAFT Basic ElectricityDocument327 pagesAIRCRAFT Basic ElectricityndrmnlngNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Electric and Magnetic Circuits and FieldsDocument9 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Electric and Magnetic Circuits and Fieldstobechukwuevarestus9No ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument13 pagesOhms LawAnna ParedesNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument4 pagesAnswer KeyEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- DLL PEH 11 Q2 M6 Michelle GDocument5 pagesDLL PEH 11 Q2 M6 Michelle GEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Long QuizDocument6 pagesLong QuizEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Done-EDITED-hope1 q1 Mod6 ProperEtiquetteand-Safetyinthe-UseofFacilitiesEquip v1Document34 pagesDone-EDITED-hope1 q1 Mod6 ProperEtiquetteand-Safetyinthe-UseofFacilitiesEquip v1Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- LAS Week 5 Grade 12Document4 pagesLAS Week 5 Grade 12Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- DLL 2022 PE and HealthDocument12 pagesDLL 2022 PE and HealthEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Pe11 q2 Mod3 My-Fitness-GoalsDocument29 pagesPe11 q2 Mod3 My-Fitness-GoalsEugene Colot100% (2)
- Pe11 - q2 - Mod7 - Organize For Fitness and HealthDocument24 pagesPe11 - q2 - Mod7 - Organize For Fitness and HealthEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Pe11 q2 Mod2 Fitness-Enhancement-Through-SportsDocument32 pagesPe11 q2 Mod2 Fitness-Enhancement-Through-SportsEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Pe11 - q2 - Mod1 - Physical Education Managing Stress Through SportsDocument35 pagesPe11 - q2 - Mod1 - Physical Education Managing Stress Through SportsEugene ColotNo ratings yet
- Annotations RPMS 2021 2022 New123 2Document25 pagesAnnotations RPMS 2021 2022 New123 2Eugene ColotNo ratings yet
- DLP Template 2023 - JHDocument2 pagesDLP Template 2023 - JHEugene ColotNo ratings yet