Professional Documents
Culture Documents
المستند
Uploaded by
zzaassddffxxccOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
المستند
Uploaded by
zzaassddffxxccCopyright:
Available Formats
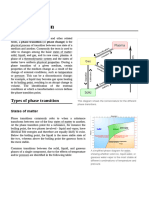
1. What does the flat line on the cooling curve represent?
The flat line on a cooling curve represents the phase transition during which a substance
changes its state (e.g., from liquid to solid) at a constant temperature. During this phase
transition, the substance absorbs or releases heat energy without changing its temperature,
leading to a flat or horizontal line on the cooling curve.
2. What does the phase transformation also involve?
Phase transformation also involves the rearrangement of atoms or molecules within a
substance, leading to a change in its internal structure and properties. This rearrangement
can result in the substance transitioning from one phase (such as liquid) to another phase
(such as solid or gas).
3. What is the effect of cooling rate onto the transformation period?
The cooling rate significantly affects the transformation period. A faster cooling rate generally
results in a shorter transformation period. Rapid cooling can lead to the formation of smaller
crystals or an amorphous structure, while slower cooling allows larger crystals to form. The
cooling rate influences the final properties of the material, including its hardness, strength,
and other mechanical properties
You might also like
- Basic Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument95 pagesBasic Engineering Thermodynamicspapaye371275% (4)
- Fluids and Physical State of SubstanceDocument15 pagesFluids and Physical State of SubstanceLynley Dave Simbajon EstandarteNo ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0201 FDDocument18 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0201 FDKhayh Jhyv Hyasynth A. VillagraciaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument23 pagesAtomic StructureJoya BhatiagharuNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Melting and Freezing Processes PDFDocument34 pagesMathematical Modeling of Melting and Freezing Processes PDFAjit KambleNo ratings yet
- Project On Phase TrasitionDocument7 pagesProject On Phase TrasitionSuhail SarwarNo ratings yet
- PHASE CHANGES OF MATTER DEaRDocument3 pagesPHASE CHANGES OF MATTER DEaRolameonfrixandrei486No ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0201 FDDocument18 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0201 FDJade MayorNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangeDocument59 pagesPhase ChangeAnsel MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Science Activities 11 13 15Document5 pagesScience Activities 11 13 15Marielyz GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - States of MatterDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - States of Matterclaudia gomesNo ratings yet
- 2-Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pages2-Thermal PhysicsSamah Hafez100% (1)
- Phase TransitionDocument13 pagesPhase TransitionMirha NisarNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Phase ChangesDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Phase ChangesJubel Andrea SalungaNo ratings yet
- 2 States of Matter NotesDocument14 pages2 States of Matter Notesafnan.6556No ratings yet
- Chemeistry Form OneDocument72 pagesChemeistry Form OneHamza KahemelaNo ratings yet
- Phase TransitionDocument16 pagesPhase Transitionyehtt0212No ratings yet
- JYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesDocument16 pagesJYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Latent Heat. BaseDocument18 pagesConcept of Latent Heat. BaseHarsh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Science 8 ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience 8 ReviewerMercurio, Katrina EuniceNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangeDocument61 pagesPhase ChangeAnsel MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- Grade 10 States of Matter Handout 2Document6 pagesGrade 10 States of Matter Handout 2Dexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- Heating and Cooling Curve of A Substance 1Document5 pagesHeating and Cooling Curve of A Substance 1bennaorbino272006No ratings yet
- REVIEW - HEAT and THERMODocument6 pagesREVIEW - HEAT and THERMOAna MarieNo ratings yet
- Heating and Cooling Curve of A SubstanceDocument3 pagesHeating and Cooling Curve of A SubstanceGrim ReaperNo ratings yet
- Reviwer 3RD QuarterDocument19 pagesReviwer 3RD QuartermoraledazoesophiaNo ratings yet
- Handout # 2.4 Particle Model For MatterDocument5 pagesHandout # 2.4 Particle Model For MatterMr. KhanNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer-Cheg-2084 Notes Chapter-1Document12 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer-Cheg-2084 Notes Chapter-1Anonymous GUExuPNo ratings yet
- HT Unit 1 - Mechanism of Heat TransferDocument7 pagesHT Unit 1 - Mechanism of Heat TransferSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument60 pagesKinetic Particle Theoryapi-305909325100% (2)
- Phase Change DiagramDocument2 pagesPhase Change DiagramHabiba KhababNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer-Cheg-2084 Notes Chapter-1Document12 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer-Cheg-2084 Notes Chapter-1Anonymous GUExuPNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Thermal Energy: Matter Is Made Up of Tiny Particles CalledDocument22 pagesTemperature and Thermal Energy: Matter Is Made Up of Tiny Particles CalledCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Week 2 Q3Document9 pagesScience 8 Week 2 Q3PeterClomaJr.No ratings yet
- MME-18-14 - Afnan Sadaqat - Physical MetallurgyDocument19 pagesMME-18-14 - Afnan Sadaqat - Physical MetallurgyMuhammed AfnanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument83 pagesChemistryEnzo ValendinoNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument13 pagesHeatDreamNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - WEEK 2Document21 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - WEEK 2RODEL AZARES100% (1)
- Module-2: SolidificationDocument16 pagesModule-2: SolidificationSachin AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Summary of Section of 12.2Document2 pagesSummary of Section of 12.2RafiqNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Day 1Document2 pagesWeek 4 Day 1Jamicah LucindoNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer With Phase ChangeDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer With Phase ChangeImaneNo ratings yet
- ExploreDocument3 pagesExploreLourdes Joy LibradoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Infinitesimal Dissipation Thermodynamic EquilibriumDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Infinitesimal Dissipation Thermodynamic EquilibriumphooolNo ratings yet
- Quimica Universidad PRINCIPIANTES TraducidaDocument5 pagesQuimica Universidad PRINCIPIANTES TraducidaAUSTRANo ratings yet
- Aire AcondicionadoDocument11 pagesAire Acondicionadoalejandroolivo2023No ratings yet
- RevisionDocument26 pagesRevisionAbisan ArulananthamNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument11 pagesHeat TransferArnab HazraNo ratings yet
- Transformations of WaterDocument12 pagesTransformations of WatergcpasambaNo ratings yet
- Changes in MatterDocument2 pagesChanges in MatterKayelNo ratings yet
- 5 CH 2 Sec 2 Changes in State and Energy - UploadDocument74 pages5 CH 2 Sec 2 Changes in State and Energy - Uploadapi-270861823No ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Heat TransferDocument168 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Heat TransferMohit MittalNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument9 pagesStates of Mattervidya pmNo ratings yet
- Chemisty Igcse Updated Till SyllabusDocument97 pagesChemisty Igcse Updated Till Syllabusapi-181176018No ratings yet