Professional Documents
Culture Documents
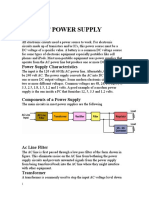
Block Diagram of DC Power Supply
Uploaded by
bess.sangabriel170 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesOriginal Title
block diagram of dc power supply
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesBlock Diagram of DC Power Supply
Uploaded by
bess.sangabriel17Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
San Gabriel, Bess S.
BSME-2B
BASIC DC POWER SUPPLY
1. Block diagram of a DC power supply
2. Functions of each block/ parts
Transformer- used to adjust the supply voltage in accordance with the demands
of the solid-state electronic devices and circuits that will be powered by dc
power supplies.
Rectifier- Using a rectifier, you can change sinusoidal ac voltage into either
positive or negative pulsating dc. For rectification, or the conversion of ac into
dc, a P-N junction diode can be employed, which conducts when forward biased
and typically does not conduct when reverse biased.
Filter- is a device which passes dc component to the load and blocks I ac
components of the rectifier output.
Voltage regulator- The voltage regulator can be made of a Zener diode, discrete
transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), or any combination of these. Its major job is
to keep the dc output voltage steady. Any ac ripple voltage that isn't reduced by
the filter is also rejected. Protective components like short-circuit protection,
current limiting, thermal shutdown, or over-voltage protection may also be part
of the regulator.
Output voltage- has a pulsing quality, meaning that in addition to its desired dc
component, it also contains undesirable ac components. Constant direct voltage
is required for the majority of supply uses rather than the rectifier's output. A
filter circuit is needed to lower the voltage's ac components coming from the
rectifier output.
3. Discuss the difference between half wave and full wave rectification.
In a half-wave, only one diode is used, and only the positive half of each cycle is
rectified, whereas on a full-wave, two diodes are used, and both the positive and
negative half cycles are rectified, and the current is continuously flowing.
4. Describe how a center-tapped full-wave rectifier works.
The input AC voltage of the center tapped full wave rectifier is changed into the
output DC voltage using a center tapped transformer. The center-tapped
transformer's secondary winding separates the input AC voltage into positive
and negative components when input AC voltage is supplied.
5. Describe how a bridge full-wave rectifier works.
Using both half cycles of the applied ac voltage, it transforms an ac voltage into a
pulsing dc voltage. It uses two diodes, one of which conducts during one half
cycle of the applied ac voltage and the other during the other half cycle.
6. Describe the operation of a capacitor filter.
This capacitor's operation primarily relies on the capacitive reactance concept. It
merely describes how a capacitor's impedance changes as a signal with a
particular frequency passes through it. Apart from the frequency of the signal, a
resistor, a nonreactive component, provides a similar resistance to a signal. In
other words, equal resistance allows impulses at 1Hz and 100KHz to pass
through a resistor.
7. Discuss voltage regulators
A voltage regulator is a circuit that establishes and maintains a constant output
voltage, regardless of alterations in the input voltage or load conditions.
You might also like
- DC Power Supply CircuitDocument7 pagesDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument4 pagesDC Power SupplySohaib Ahmed100% (1)
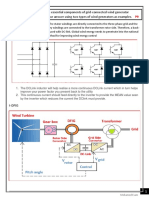
- Ass 2 Wind0.02Document25 pagesAss 2 Wind0.02Šämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- LEARNING GUIDE 02 AC DC RectifierDocument27 pagesLEARNING GUIDE 02 AC DC Rectifiermeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- SIMULINKDocument5 pagesSIMULINKshresth.gupta.ug22No ratings yet
- TWO Power Conversion Systems 2.1 Power Electronic ConvertersDocument17 pagesTWO Power Conversion Systems 2.1 Power Electronic ConvertersAlhussain EmbarkNo ratings yet
- Adjustable DC Power Supply 0-30V: Laboratory Project Report Semiconductors Devices LabDocument5 pagesAdjustable DC Power Supply 0-30V: Laboratory Project Report Semiconductors Devices LabMISHAL FATIMANo ratings yet
- Automatic Hand Washing SystemDocument10 pagesAutomatic Hand Washing SystemmathuraNo ratings yet
- 10 DC RegulatedDocument3 pages10 DC Regulatedamandeepsingh_adsNo ratings yet
- Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing NC Ii: Gilbert B. TamayoDocument40 pagesElectronic Products Assembly and Servicing NC Ii: Gilbert B. Tamayogilbert tamayoNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Power SupplyDocument81 pagesLecture On Power SupplyMATE0100% (2)
- Experiment 3 Eng NaderDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 - Creativity LabDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 1 - Creativity LabhloNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Lab Report 03Document8 pagesLab Report 03fkhan201160No ratings yet
- Reduction of AC MainsDocument3 pagesReduction of AC MainsFaizan NaeemNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument21 pagesUnit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringAJAY SNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyDocument56 pagesTopic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyKu AliyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document18 pagesUnit 4H. ShekharNo ratings yet
- AC DC Power SupplyDocument26 pagesAC DC Power SupplyNathaniel RogeroNo ratings yet
- Power Supply 1Document79 pagesPower Supply 1samuelNo ratings yet
- ECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Build a regulated power supply in 40 stepsDocument7 pagesBuild a regulated power supply in 40 stepsAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic of ElectricalDocument10 pagesBasic of ElectricalAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Inverters and Applications Requirements of The Final ReportDocument5 pagesInverters and Applications Requirements of The Final ReportHuỳnh BảoNo ratings yet
- Battery Charging UnitDocument19 pagesBattery Charging UnitAbinMiranda100% (1)
- Emergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractDocument20 pagesEmergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractAakash SheelvantNo ratings yet
- Study of AC and DC Converter: Efficient Power ConversionDocument6 pagesStudy of AC and DC Converter: Efficient Power ConversionBeena PalNo ratings yet
- Assignment MEDocument3 pagesAssignment MESaad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier PDFDocument23 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier PDFArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power Supply ExplainedDocument14 pagesDC Regulated Power Supply ExplainedMegha Projects100% (2)
- DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDC Power Supplyweaam raedNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDC Power Supplyweaam raedNo ratings yet
- Essential Components of DC Power SuppliesDocument4 pagesEssential Components of DC Power SuppliesSyed Hassan Abbas RizviNo ratings yet
- A Buad Power SectionDocument7 pagesA Buad Power SectionSamNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument13 pagesRectifiersInfidragon GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Practical 12thDocument7 pagesPractical 12thkumarnareshNo ratings yet
- Unit-12Document36 pagesUnit-12ahmed bashaNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument4 pagesRectifierAngellicaNo ratings yet
- REEEFFFSESDocument6 pagesREEEFFFSESezradural99No ratings yet
- Security Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1Document30 pagesSecurity Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1DebashishParida100% (1)
- Project Report Regulated Power SupplyDocument36 pagesProject Report Regulated Power SupplyPeerzada Wahid73% (11)
- Lab Report 2 Phy547: Experiment 2: Zener Diode and Power SupplyDocument8 pagesLab Report 2 Phy547: Experiment 2: Zener Diode and Power SupplyAtikah IzzatiNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument2 pagesDC Regulated Power Supplysean ballocanagNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier Circuit GuideDocument21 pagesBridge Rectifier Circuit GuideTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Effect of Source InductanceDocument25 pagesEffect of Source InductanceSriram Anil Kumar Gandham100% (1)
- Industrial Electronics 1st ExamDocument34 pagesIndustrial Electronics 1st ExamJomar Bonje100% (1)
- Power Electronics Lab # 1 Lab 1-Introduction To Power Electronics BoardDocument2 pagesPower Electronics Lab # 1 Lab 1-Introduction To Power Electronics BoardShyk ShakirNo ratings yet
- IE Mod 01 PowerSupplyDocument25 pagesIE Mod 01 PowerSupplyRy AnNo ratings yet
- (Industrial Electronics) : ECE 312aDocument7 pages(Industrial Electronics) : ECE 312aRon DomanaisNo ratings yet
- Emergency LightDocument12 pagesEmergency LightEysha qureshiNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase RectificationDocument30 pages3 Phase RectificationKobby Brine100% (1)
- Project Report Chapter 3Document7 pagesProject Report Chapter 3ibrar82No ratings yet
- Report For A Power Supply With A Rated Output of 9.9V /1aDocument8 pagesReport For A Power Supply With A Rated Output of 9.9V /1aSend noobsNo ratings yet
- physicsprojectDocument7 pagesphysicsprojectgamerdk6577No ratings yet
- Components Required - : Block DiagramDocument8 pagesComponents Required - : Block DiagramJethro MolenoNo ratings yet
- Present 2Document35 pagesPresent 2Jayesh JainNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Simulation of Controlled and Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument32 pagesMATLAB Simulation of Controlled and Uncontrolled RectifiersAnime X100% (1)
- CW-5000 - 5200 Industrial ChillerDocument13 pagesCW-5000 - 5200 Industrial ChillerJoseph MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Control Unit ECUDocument14 pagesElectronic Control Unit ECUnico Nico100% (1)
- CablesDocument94 pagesCablesMrudulaNo ratings yet
- Moto Guzzi Breva 1100 Manuale RiparazioneDocument106 pagesMoto Guzzi Breva 1100 Manuale RiparazioneAndrea NeriNo ratings yet
- Berghof: Ethernet ControllerDocument3 pagesBerghof: Ethernet ControllerДима ЧеснейшийNo ratings yet
- Gs01e24a01-01en AxwDocument57 pagesGs01e24a01-01en AxwRobby AmrioNo ratings yet
- Power Amplifier For Driving A Deflection Circuit of A Color TelevisionDocument5 pagesPower Amplifier For Driving A Deflection Circuit of A Color TelevisionShamol KormokerNo ratings yet
- RT differential pressure switch specificationsDocument3 pagesRT differential pressure switch specificationsSebastiánCastrillónNo ratings yet
- Windows Uefi Firmware Update PlatformDocument46 pagesWindows Uefi Firmware Update PlatformPantea Constantin AlinNo ratings yet
- GSE ElectricDocument46 pagesGSE ElectricoespanaNo ratings yet
- SM10LZ47: Ac Power Control ApplicationsDocument3 pagesSM10LZ47: Ac Power Control Applicationsmanuel riascosNo ratings yet
- TG589vac User GuideDocument71 pagesTG589vac User GuidePaul GreenwoodNo ratings yet
- Pool EU StarFlo Datasheet enDocument2 pagesPool EU StarFlo Datasheet enagus rahmadanyNo ratings yet
- Technical Quiz Questions & Answers: Q. What Is PAN, ISM Band?Document5 pagesTechnical Quiz Questions & Answers: Q. What Is PAN, ISM Band?Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 12-SDMS-02 REV. 02: Saudi Electricity CompanyDocument20 pages12-SDMS-02 REV. 02: Saudi Electricity CompanyMichael Camit EsoNo ratings yet
- ECU de 4 ConectoresDocument1 pageECU de 4 ConectoresHarold Rodriguez CastilloNo ratings yet
- A Combined Antijamming and Antispoofing Algorithm For GPS ArraysDocument10 pagesA Combined Antijamming and Antispoofing Algorithm For GPS ArraysMojtaba KhakiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Subject: Digital Logic Circuits Subject Code: EE 2255 Part - B Unit - IDocument12 pagesQuestion Bank Subject: Digital Logic Circuits Subject Code: EE 2255 Part - B Unit - IsunvenkatNo ratings yet
- FireFinder PLUS Fire Brigade Response GuideDocument128 pagesFireFinder PLUS Fire Brigade Response GuidePeter van der BurgNo ratings yet
- Svms User Manual: Answer Drives S.R.L. - Partially Owned by Ansaldo Sistemi Industriali - S.p.ADocument41 pagesSvms User Manual: Answer Drives S.R.L. - Partially Owned by Ansaldo Sistemi Industriali - S.p.AMohamed Alkharashy100% (1)
- Technical Requirements for Power TransformersDocument24 pagesTechnical Requirements for Power Transformersni60No ratings yet
- Water Watch Information BookletDocument20 pagesWater Watch Information BookletWater WatchNo ratings yet
- Wolf Safety Lamp Company - Rechargeable TorchDocument3 pagesWolf Safety Lamp Company - Rechargeable TorchPandu BirumakovelaNo ratings yet
- Complete Panel Report - NFS2-3030V27.0 - Notifier VeriFire Tools 10.55 Build 19 - 07192023 - 175833Document68 pagesComplete Panel Report - NFS2-3030V27.0 - Notifier VeriFire Tools 10.55 Build 19 - 07192023 - 175833brycuellarNo ratings yet
- Basic Control Device Function Numbers: GE Power SystemsDocument1 pageBasic Control Device Function Numbers: GE Power SystemsPercyRiveraNo ratings yet
- Pcits600 - 2 & Pcits2000 - 2Document37 pagesPcits600 - 2 & Pcits2000 - 2elie awadNo ratings yet
- Comp Woofer: Technical SpecificationDocument1 pageComp Woofer: Technical SpecificationIvan PetrovNo ratings yet
- ZTE ZXSDR B8200 Product DescriptionDocument31 pagesZTE ZXSDR B8200 Product Descriptionrdmiguel_1983685% (13)
- Analog Telephony OverviewDocument11 pagesAnalog Telephony OverviewEamon FaceacheNo ratings yet