Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 01-Nov-2023
Uploaded by
Shanjai VadivelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 01-Nov-2023
Uploaded by
Shanjai VadivelCopyright:
Available Formats
her e is
h l o r m i n e is
formcu
hlorin
is
r disi nlectant
beter han chloriye Ihus,
respons
I
NL, CINII chlorinc HOC). HØCI
wive
L.4 DH
Thc
HOCIIIypochlorous acid) Watcr
Ca0CL (Bleachingpowder)
Bactcriast e killed the 4
B atMin J. Fre
poveliul geicle + lICL 2. Br:
Bactcrias
UOC
3. Se
Brenk point Chloriuntlon i1puriiCs Sea
lillOriny
contuins he The
Hater
)Bactcrias. 1) E
(ii) Organic inpuritics. H).S, ctc,).
substances( e " bleaching powder 2) R
form of
úm)
Rcducing
in he grapbicallv in the
When 3) 1
fol owintheg
Imonia. 2as Or depictcd
(iv) Free directly as a
can be chlorine adderi 10 water and 4) }
to watcrresulIs obtained annount of
be ndded the the 1.4.
Chlorinc may valer, bctwecn
4pplicd to relationship W
chlorine is shows the
graph
Figure. The chlorine Sol
residual chlorine. l'ormalion of free
of chkor-organic pr
& presence
compounds not destroyed
residual
Chiorine
residal
(ppm) Destructionofchloramifes Frec
residual
and chloro organic comp
combined
Formation ofchloro-organic and
0.3 compounds and chloramines I Free
Destruction Combined
of residuai
Chlorine by
01reducing D'Break
compound Combinedresidial
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9
Chlorine Added (p.p.m.)
It is observed from the graph that initially the applied chlorine is used to kill the
Oxidises all the reducing substances present in the water and there is no free residual chlorin bacterias and
As the amount of applied chlorine increases, the amount of combined
increases. This is due to the formation of chloramine and other residual chlorine also
chloro compounds.
15
You might also like
- 9 The Ultimate Igcse Guide To Chemistry by CgpwnedDocument272 pages9 The Ultimate Igcse Guide To Chemistry by CgpwnedRewanNo ratings yet
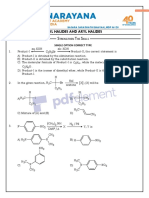
- Alkyl Halides and Aryl Halides - QBDocument23 pagesAlkyl Halides and Aryl Halides - QBNETHAKANI SUJATHA100% (1)
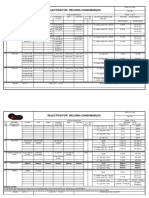
- Selection For Welding Consumables: A 479 Gr.316LDocument2 pagesSelection For Welding Consumables: A 479 Gr.316LanandmlNo ratings yet
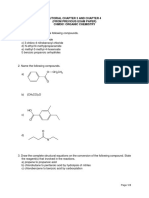
- Module 7 KISS Notes (HSC Chemistry)Document15 pagesModule 7 KISS Notes (HSC Chemistry)rsorani8No ratings yet
- Empirical Metallogeny: Depositional Environments, Lithologic Associations and Metallic OresFrom EverandEmpirical Metallogeny: Depositional Environments, Lithologic Associations and Metallic OresNo ratings yet
- Electrodes EquivalentDocument15 pagesElectrodes Equivalentgrameshkreddy2013100% (1)
- NMR Problems Dec 2012Document8 pagesNMR Problems Dec 2012Biswajit Gopal RoyNo ratings yet
- Material Selection For Refinery ApplicationDocument86 pagesMaterial Selection For Refinery ApplicationAvinaw100% (4)
- Uncoupler PDFDocument7 pagesUncoupler PDFTuan HoangNo ratings yet
- 314 Stereochem ProbsDocument14 pages314 Stereochem ProbsAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding FULL NOTES PDFDocument77 pagesChemical Bonding FULL NOTES PDFArsh KumarNo ratings yet
- PTM-1 ChemsitryDocument6 pagesPTM-1 ChemsitrymohakjainNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Diastereoselective Bromination of Trans-Cinnamic AcidDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Diastereoselective Bromination of Trans-Cinnamic AcidAliNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Characterization of Lignin PDFDocument7 pagesExtraction and Characterization of Lignin PDFDebrah DebbieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper PatternDocument1 pageChemistry Paper PatternAfzaal JanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9th ObjectiveDocument1 pageChemistry 9th ObjectiveFarhatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Session - 1 AIMDocument100 pagesChemical Bonding: Session - 1 AIMMOHAMMED RASHIDNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesChemistry - Aromatic Hydrocarbonswakeetha cNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Part 5: Stereochemistry: Topic: Identifications and ComparisonsDocument14 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Part 5: Stereochemistry: Topic: Identifications and ComparisonsMoùümîtà KhäñráNo ratings yet
- Basics of Photochemistry and Norrish Type I Reaction: Presented By: Dr. Nidhi VashisthaDocument12 pagesBasics of Photochemistry and Norrish Type I Reaction: Presented By: Dr. Nidhi Vashisthanidhi vashisthaNo ratings yet
- Madeleine Ceri - Final Exam CHE-A-02Document6 pagesMadeleine Ceri - Final Exam CHE-A-02Madeleine CeriNo ratings yet
- CarbonDocument19 pagesCarbonYen Cotejo-SanchezNo ratings yet
- Section 3 - StereochemistryDocument21 pagesSection 3 - Stereochemistrysf9 fanfareNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes CompleteDocument42 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Completekarmanyaraina4No ratings yet
- 3 CopiesDocument8 pages3 CopiesKarthikeya PuttaguntaNo ratings yet
- Chlorophyll Extraction From Microalgae A PDFDocument12 pagesChlorophyll Extraction From Microalgae A PDFМиска КопэчянуNo ratings yet
- Set 11 HaloalkanesDocument2 pagesSet 11 HaloalkanesNurul FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Bonding and Isomerism Practice2Document4 pagesChapter1 Bonding and Isomerism Practice2sugNo ratings yet
- Chem261, B2 Practice Questions For The Midterm Exam, AnswersDocument8 pagesChem261, B2 Practice Questions For The Midterm Exam, Answerschemistry tutorialNo ratings yet
- 5b Stereochemistry PostDocument41 pages5b Stereochemistry Postapi-3767370100% (1)
- Organic Halogenoalkanes 2 QPDocument11 pagesOrganic Halogenoalkanes 2 QPHalal BoiNo ratings yet
- cbcc9 Guided Reading ch03Document13 pagescbcc9 Guided Reading ch03Andrew MoszutiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set II CompilationDocument4 pagesProblem Set II CompilationKeith Erwin PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Alkenes Part 1 - QuestionsDocument4 pagesAlkanes and Alkenes Part 1 - QuestionsZac D2006No ratings yet
- OrganicChemistryChapter5 PDFDocument19 pagesOrganicChemistryChapter5 PDFJuliet Tatiana CumbeNo ratings yet
- 3.15 Revision Guide NMRDocument5 pages3.15 Revision Guide NMRyimiyeh441No ratings yet
- 2008Document7 pages2008prakhar vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Fischer and Schrock CarbenesDocument8 pagesFischer and Schrock Carbenesharmanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction: Addition Substitution Elimination RearrangementDocument39 pagesOrganic Reaction: Addition Substitution Elimination RearrangementJulJayaNo ratings yet
- Part B (Chemistry) : HyperconjugationDocument6 pagesPart B (Chemistry) : HyperconjugationPrecisive OneNo ratings yet
- Ruang Lingkup Kimia AnorganikDocument6 pagesRuang Lingkup Kimia AnorganikAr RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chm301 Chapter 3 & 4Document2 pagesTutorial Chm301 Chapter 3 & 4fatinNo ratings yet
- MET180 - Chapter 8Document38 pagesMET180 - Chapter 8saeed khanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Revision DPP 2 SolutionDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY Revision DPP 2 SolutionPraphul Pulkit GiriNo ratings yet
- 08wear 3Document1 page08wear 3AadelNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Problems 5th Edition PDFDocument6 pagesCH 4 Problems 5th Edition PDFnisannn100% (1)
- Pericyclic Reactions: PresenterDocument12 pagesPericyclic Reactions: PresenterHarman Preet KaurNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument18 pagesChemistryMurtaza AbbasNo ratings yet
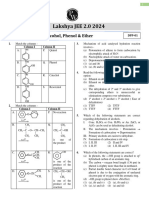
- Alcohol, Phenol, & Ether - DPP 01 - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesAlcohol, Phenol, & Ether - DPP 01 - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024chitranshpriyanshu80No ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 18 Asal ChemistryDocument4 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter 18 Asal ChemistryMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Ment 2023Document3 pagesMent 2023Rayhan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CamphorDocument16 pagesCamphorSunitha Katta0% (1)
- NMR Practice 2 Answers Question One (Four Marks) : 3 Diastereotopic Diastereotopic DiastereotopicDocument10 pagesNMR Practice 2 Answers Question One (Four Marks) : 3 Diastereotopic Diastereotopic DiastereotopicGhazwan GhazwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Chemistry of Coordination CompoundsDocument15 pagesChapter 24 - Chemistry of Coordination CompoundsBarnishikha BoruahNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Chemistry Tutorial #8 2018-2019 AnswersDocument6 pagesCarbonyl Chemistry Tutorial #8 2018-2019 AnswersZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 2CDocument10 pagesPractice Exam 2CĐình Thư LêNo ratings yet
- Testbank 1 1 PDFDocument7 pagesTestbank 1 1 PDFMyk AbayaNo ratings yet
- 9 Alkenes Alkynes PostDocument26 pages9 Alkenes Alkynes Postapi-3767370No ratings yet
- 3 15 Revision Guide NMRDocument5 pages3 15 Revision Guide NMRPraveenaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes 1 QPDocument7 pagesAlkenes 1 QPemanNo ratings yet
- Alkylidene Mechanism For The Fischertropsch SynthesisDocument2 pagesAlkylidene Mechanism For The Fischertropsch SynthesishoseiNo ratings yet
- Sebatian Karbon / Carbon Compound Alkana / Alkane: N 2n N 2n+2 N 2n+1 N 2n+1Document19 pagesSebatian Karbon / Carbon Compound Alkana / Alkane: N 2n N 2n+2 N 2n+1 N 2n+1OMAR SHAHNo ratings yet
- 2906 Chemistry Paper With Solution EveningDocument7 pages2906 Chemistry Paper With Solution EveningPoojan ShahNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryFrom EverandOrganometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryF. G. A. StoneNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Chlorine and ChlorideDocument2 pagesDifference Between Chlorine and ChlorideEvaavivahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document6 pagesChapter 9rickyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions MCQsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions MCQsMifrah KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 2&3Document46 pagesModule 2&3Alias SimounNo ratings yet
- Welding ConsumablesDocument79 pagesWelding Consumablesazam RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Activity Series LabDocument2 pagesActivity Series Labswimmerdude1234No ratings yet
- Https:/seo Manager.s3.amazonaws - Com/prod/content Files Downloadable ModifiDocument12 pagesHttps:/seo Manager.s3.amazonaws - Com/prod/content Files Downloadable ModifilegixopNo ratings yet
- Test 18 - Periodic Table - Bottom of PyramidDocument6 pagesTest 18 - Periodic Table - Bottom of PyramidJay PatelNo ratings yet
- BRTC Test Rates 2019Document6 pagesBRTC Test Rates 2019তন্ময় হোসেন0% (1)
- Quiz 1 Group 2 MCQDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 Group 2 MCQTee Xin RuiNo ratings yet
- WS Starter - Magnetism - WordsearchDocument1 pageWS Starter - Magnetism - Wordsearchsam mirisonNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: ChemistryDocument16 pagesEdexcel GCE: ChemistryzinNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Sulfur and Its CompoundsDocument6 pagesOxidation of Sulfur and Its CompoundsKeishaNo ratings yet
- Redox, Group 2 and Group 7 TestDocument7 pagesRedox, Group 2 and Group 7 Testpaulcampbell37No ratings yet
- Usw Alloy Designation AND Description Issued Data Sheet: Revision No. ADocument1 pageUsw Alloy Designation AND Description Issued Data Sheet: Revision No. AbrunizzaNo ratings yet
- Programming Data For Spectrophotometer and Spectroquant Test Kits Measured With A Reference SpectrophotometerDocument17 pagesProgramming Data For Spectrophotometer and Spectroquant Test Kits Measured With A Reference SpectrophotometerGustavo SánchezNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Oxide Lab ReportDocument5 pagesMagnesium Oxide Lab ReportNarendran Sairam65% (17)
- Report (Sculpture Materials)Document32 pagesReport (Sculpture Materials)triziasisonNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibria ProblemsDocument6 pagesIonic Equilibria Problemsティン ヨロベNo ratings yet
- Alien Periodic TableDocument29 pagesAlien Periodic TableAsif Ali JaferyNo ratings yet
- PVB-Based Star Compositions: Red Orange Green YellowDocument3 pagesPVB-Based Star Compositions: Red Orange Green YellowHenryNo ratings yet
- D Block ElementDocument48 pagesD Block ElementPrabhakar BandaruNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - The Halogens (Multiple Choice) QP PDFDocument7 pagesGroup 7 - The Halogens (Multiple Choice) QP PDFNiaz MorshedNo ratings yet
- Suggest Possible Structures For The Cation in (Fe (NO) ) (PF) - How Would You Distinguish Between These Structures Experimentally?Document10 pagesSuggest Possible Structures For The Cation in (Fe (NO) ) (PF) - How Would You Distinguish Between These Structures Experimentally?Wing Chi Rainbow TamNo ratings yet
- What Is The Systematic Name of The Following Compound (Solved)Document7 pagesWhat Is The Systematic Name of The Following Compound (Solved)Debayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements SR: Strontium 2, 8, 18, 8, 2Document58 pagesPeriodic Table of Elements SR: Strontium 2, 8, 18, 8, 2ChrisNo ratings yet