Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Diarrhea
NCP Diarrhea
Uploaded by
Glaiza Kate PlazaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Diarrhea
NCP Diarrhea
Uploaded by
Glaiza Kate PlazaCopyright:
Available Formats
NRLE FORM - 10
La Salle University
College of Nursing
Ozamiz City
NURSING CARE PLAN
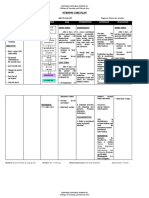
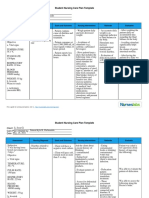
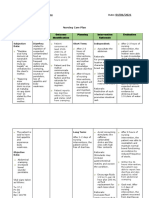
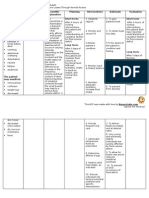
ASSESSMENT NURSING DESIRED OUTCOME INTERVENTION with RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Subjective Data: Diarrhea related to Within 8 hours of nursing Assessment: Assessment: Within 8 hours of nursing
gastrointestinal disorders as interventions, the patient will be interventions, the patient
“Ika 4 nako nalibang karung evidenced by frequency of stools able to: Independent: Independent: was able to:
adlawa ug akong tae kay basa (4x a day) and loose or liquid verbalizes understanding of 1. Assess for abdominal 1. These assessment findings are Verbalized
kaayonga nay dugo gamay” as stools. diarrhea’s causes and the discomfort, pain, cramping, usually linked with diarrhea. understanding of
verbalized by the patient. rationale for treatment. frequency, urgency, lose or Patients differ in their diarrhea’s causes and
consume enough of clear liquid stools, and hyperactive definition of diarrhea, noting
the rationale for
liquids to maintain good skin bowel sensations. loose stool consistency,
increased frequency, the treatment.
turgor and normal weight.
Objective Data: reestablishes and maintains a urgency of bowel movements, consumed enough of
BP: 170/100 normal pattern of bowel or incontinence as key clear liquids to maintain
HR: 58 functioning. symptoms. good skin turgor and
RR: 22 2. Everyone’s bowels are unique normal weight.
Temp.: 36.5 to them. What’s normal for
reestablished and
02 Sat: 100% 2. Evaluate the pattern of one person may not be normal
defecation. for another. A person can maintained a normal
Black tarry stool (+)
have a bowel movement pattern of bowel
anywhere from one to three functioning.
times a day at the most, or
three times a week at the
least, and still be considered
regular, as long as it’s their
usual pattern. Assessment of
defecation pattern will help
direct treatment.
3. Diarrhea can be caused by
certain medications such as
3. Review the medications the thyroid hormone replacement,
patient is or has been taking. stool softeners, laxatives,
prokinetic agents, antibiotics,
chemotherapy,
antiarrhythmics,
antihypertensives,
magnesium-based antacids.
Nursing Care Plan 2019
LA SALLE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING
4. Diarrhea can lead to profound
dehydration. A prolonged
4. Determine hydration status episode of diarrhea or
by assessing input and vomiting can push the body to
output. lose more fluid than it can
take in. The result is
dehydration, which happens
when the body doesn’t have
the fluid it requires to
function correctly.
5. Watery stools are
characteristic of disorders of
the small bowel, while loose,
5. Assess history for semisolid stools are linked
gastrointestinal diseases. more frequently with
disorders of the large bowel.
Voluminous, greasy stools
indicate intestinal
malabsorption, and the
presence of blood, mucus, and
pus in the stools indicates
inflammatory enteritis or
colitis.
6. A decrease in skin turgor is
exhibited when the skin (on
the back of the hand for an
6. Assess skin turgor. adult or the abdomen for a
child) is pinched and released
but does not flatten back to
normal right away. Decreased
skin turgor and tenting of the
skin occur in dehydration.
7. Signs of dehydration include
thirst, urinating less
frequently than normal, dark-
colored urine, dry mouth and
7. Assess for other signs of tongue, feeling tired, sunken
dehydration. eyes or cheeks,
lightheadedness or fainting,
and a decreased skin turgor.
Collaborative: Collaborative:
1. Culture stool. 1. Testing or stool examinations
will distinguish infectious or
parasitic organisms, bacterial
Nursing Care Plan 2019
LA SALLE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING
toxins, blood, fat, electrolytes,
white blood cells, and
potential etiological
organisms for diarrhea.
Interventions: Interventions:
Independent: Independent:
1. Weigh daily and note 1. Diarrhea causes severe water
decreased weight. loss from the body. As a
result, the body loses weight.
An accurate daily weight is an
important indicator of fluid
balance in the body.
2. Have the patient keep a diary 2. Stool consistency needs to be
of their bowel movements. evaluated, which may be
accomplished by the patient
keeping a self-care log or
diary. Evaluation of
defecation pattern will help
direct treatment, especially
for cancer-related diarrhea.
Diary log should include the
time of day defecation occurs;
a usual stimulus for
defecation; consistency,
amount, and frequency of
stool; type of, amount of, and
time food consumed; fluid
intake; history of bowel habits
and laxative use; diet;
exercise patterns;
obstetrical/gynecological,
medical, and surgical
histories; medications;
alterations in perianal
sensations; and present bowel
regimen.
3. Explain the need to avoid 3. Caffeine may stimulate the
stimulants (e.g., caffeine, intestines and increase
carbonated beverages, motility. Aside from caffeine,
artificial sweeteners) some sugary sodas also
contain high-fructose corn
syrup, a combination of
fructose and dextrose that
may lead to fructose
Nursing Care Plan 2019
LA SALLE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING
malabsorption. Symptoms
include bloating and stomach
pain, heartburn, diarrhea, and
gas. Artificial sweeteners can
have a laxative effect. They
pull water into the colon and
aid to mobilize the stool,
which can cause the runs.
4. Record the number and 4. Documentation of output
consistency of stools per day provides a baseline and helps
direct replacement fluid
therapy. The Fecal Collection
System can also be used. It is
a closed catheter system used
in managing incontinence
patients with liquid or semi-
liquid stool.
5. Encourage intake of fluids 5. It’s necessary to increase fluid
1.5 to 2 L/24 hr plus 200 mL intake, especially when
for each loose stool in adults experiencing diarrhea.
unless contraindicated; Increased fluid intake and
consider nutritional support. liquid meal replacements can
replenish fluid loss.
6. Encourage to take oral 6. Drinking more water may not
rehydration solution. be enough for a patient with
diarrhea. Aside from fluids,
the patient is also losing
important minerals and
electrolytes that water can’t
supply.
7. Educate patient or caregiver 7. These measures include
about dietary measures to avoiding spicy, fatty foods,
control diarrhea. alcohol, and caffeine;
broiling, baking, or boiling
foods instead of frying in oil;
and avoiding disagreeable
foods. Specific foods and
diets are often incriminated as
causes of diarrhea, some with
good evidence and others less
so. These dietary changes can
slow the passage of stool
8. Remind the patient of the through the colon and reduce
importance of diet or eliminate diarrhea.
Nursing Care Plan 2019
LA SALLE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING
modification. 8. Diet modification is an
important part of self-
management for patients with
diarrhea. Advise patient to
look for foods with potassium
(such as potatoes, bananas,
and fruit juices), salt (such as
Dependent: pretzels and soup), and yogurt
1. Give antidiarrheal drugs as with active bacterial cultures.
ordered. Dependent:
1. Most antidiarrheal drugs
suppress gastrointestinal
motility, thus allowing for
more fluid absorption.
Supplements of beneficial
bacteria (“probiotics”) or
yogurt may reduce symptoms
2. Educate patient or caregiver by reestablishing normal flora
on the proper use of in the intestine.
antidiarrheal medications as 2. Antidiarrheal medications are
found in most drug stores or
ordered.
pharmacies, or a physician
can prescribe them. In taking
antidiarrheal medications,
discuss with the patient the
proper use of each
antidiarrheal medication to
prevent worsening of the
condition and prevent further
dehydration. Appropriate use
of antidiarrheal medications
can promote effective bowel
elimination.
Submitted by: Submitted to:
Name of Student: _Glacyl Joy D. Barola___________________________ _Miss Liezl B. Pagas___________________________
Year Level: _BSN-4________ Name of Clinical Instructor
Date: _January 20, 2023______ Date: _ January 20, 2023_______
Nursing Care Plan 2019
LA SALLE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING
You might also like
- Doctor On Call Preview-1Document58 pagesDoctor On Call Preview-1Fourth YearNo ratings yet
- Cmucat Reviewer 1Document16 pagesCmucat Reviewer 1Cylit Jhames SalomonNo ratings yet
- Cosmic Nutrition: The Taoist Approach to Health and LongevityFrom EverandCosmic Nutrition: The Taoist Approach to Health and LongevityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Guidelines Rotator Cuff InjuryDocument5 pagesGuidelines Rotator Cuff InjuryAlberto GrpNo ratings yet
- Primates and CetaceansDocument445 pagesPrimates and CetaceansZander PangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Uterine MyomaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Uterine Myomashiramu86% (50)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetPrincess Mildred AbdonNo ratings yet
- CHA NCPDocument6 pagesCHA NCPMonty_Legaspi_5664No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Objective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Objective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetCess YNo ratings yet
- Client: Care Plan Initiated By: DateDocument3 pagesClient: Care Plan Initiated By: DateSIMON KYLE BAKIL DICHUASIDONo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Assessment Diagnosis Analysis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Assessment Diagnosis Analysis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationjoanneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationJoanna Jaira SalcedoNo ratings yet
- BSN2 C Ihps NCP FinalDocument7 pagesBSN2 C Ihps NCP FinalAdrian DecolongonNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Assessment Diagnosis Analysis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Assessment Diagnosis Analysis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationjoanneNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCP Constipation NauseatedDocument3 pagesNCP Constipation NauseatedEzekiel Seth UmangayNo ratings yet
- Maraming Tubig at Kakain NG Prutas para Makadumi Ako."Document2 pagesMaraming Tubig at Kakain NG Prutas para Makadumi Ako."Cayla Mae CarlosNo ratings yet
- Pedia NCPDocument6 pagesPedia NCPZel MartinezNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- KUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE ConstipationDocument2 pagesKUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE Constipationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Rle Nursing Care Plan: To Have Baseline Data. Normal Values Indicate Adequate Tissue PerfusionDocument7 pagesNCM 112 - Rle Nursing Care Plan: To Have Baseline Data. Normal Values Indicate Adequate Tissue Perfusiontherese BNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2deadgrave16No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyLouel VicitacionNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer NCP and FDAR FinalDocument8 pagesColorectal Cancer NCP and FDAR Finalnot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- Quinto, Gemma (NCP & DRUG STUDY)Document13 pagesQuinto, Gemma (NCP & DRUG STUDY)Mariam Yiani Aspiras RacelesNo ratings yet
- His Mother Stated That He Experienced Diarrhea and Abdominal Pain For Last 3 DaysDocument3 pagesHis Mother Stated That He Experienced Diarrhea and Abdominal Pain For Last 3 DaysKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan - AgeDocument7 pagesNursing-Care-Plan - AgePanda JocyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- NCP (Diarrhea)Document2 pagesNCP (Diarrhea)Rodj Bilang Jr.83% (30)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationpamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationLight EstelleNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- NCP - Mod9Document3 pagesNCP - Mod9designericlelynsoronioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentEva Marielle CezaldoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument31 pagesNursing Care PlansCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNo ratings yet
- Garcia NCPDocument3 pagesGarcia NCPpamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Relos, Kristel Joyce D. Bsn2e - NCPDocument3 pagesRelos, Kristel Joyce D. Bsn2e - NCPKristel Joyce RelosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan of IonDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan of IonvhentesixNo ratings yet
- Constipation NCPDocument3 pagesConstipation NCPSeth Amiel MotaNo ratings yet
- Constipation NCPDocument2 pagesConstipation NCPAbby GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Document1 pageNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- Ninda Komplementer Mual MuntahDocument12 pagesNinda Komplementer Mual MuntahanisaNo ratings yet
- Name: Babu Kaji Maharjan: Patient's IdentificationDocument6 pagesName: Babu Kaji Maharjan: Patient's IdentificationAlisha MaharjanNo ratings yet
- NCP AxelDocument10 pagesNCP AxelTan TanNo ratings yet
- Bascon postoperativeNCP DischargeplanDocument4 pagesBascon postoperativeNCP DischargeplanLacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Care PlanDocument4 pagesCare PlanRapunzel LeanneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Review BulletsDocument53 pagesNursing Review BulletscauldroNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 - Class 1A - NCP of DiarrheaDocument4 pagesGROUP 2 - Class 1A - NCP of DiarrheaOrin Qadriatul NursyiNo ratings yet
- NCP - ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermLorie May GuillangNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 3Document6 pagesNCP 1 3Allyzah Faith BernalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment in NCM 106 LectureDocument6 pagesAssignment in NCM 106 LectureJeanessa Delantar QuilisadioNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP ConstipationKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1Mary Antonette Adriano EnriquezNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument3 pagesDiarrheaBert GasalNo ratings yet
- Activity On Care PlanningDocument14 pagesActivity On Care PlanningClaire Maurice JuaneroNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Long Term Objective: Long Term ObjectiveDocument2 pagesSubjective: Long Term Objective: Long Term ObjectiveRAFNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument16 pagesDrug Study FormatFranchieNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocument2 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
- Polarity Therapy: How Re-Polarizing Your Body Can Heal YouFrom EverandPolarity Therapy: How Re-Polarizing Your Body Can Heal YouRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesFrom EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia-Induced Immune Modulation: ReviewDocument7 pagesAnesthesia-Induced Immune Modulation: ReviewFIA SlotNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics: Assignment Topic: Impact of Coronavirus Lockdown in IndiaDocument6 pagesBusiness Ethics: Assignment Topic: Impact of Coronavirus Lockdown in IndiaRajat KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Spring Mount Public School: Senior Secondary, CBSEDocument17 pagesSpring Mount Public School: Senior Secondary, CBSESaindava Vedhika.B.RNo ratings yet
- Yogsandesh Jan 15Document68 pagesYogsandesh Jan 15rkpdmNo ratings yet
- Street Children A Challenge To Social Workers in ZambiaDocument48 pagesStreet Children A Challenge To Social Workers in ZambiaEvangelist Kabaso Sydney100% (2)
- Common Posture Faults: University of Eastern PhilippinesDocument10 pagesCommon Posture Faults: University of Eastern PhilippinesEdgar ElgortNo ratings yet
- Why Black Women With Ovarian Cancer Require Greater FocusDocument1 pageWhy Black Women With Ovarian Cancer Require Greater FocusMicheleFontanaNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking PaperDocument13 pagesCritical Thinking PaperAdelaideNo ratings yet
- Infantile Hemangioendothelioma: Bafana Elliot Hlatshwayo, Daba Ipfi, Sipho SitholeDocument4 pagesInfantile Hemangioendothelioma: Bafana Elliot Hlatshwayo, Daba Ipfi, Sipho SitholeDrAbdullah HajarNo ratings yet
- Pir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFDocument10 pagesPir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFbentoeNo ratings yet
- Vector 302 To 323Document22 pagesVector 302 To 323Jin SiclonNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Kanker OkDocument79 pagesPatofisiologi Kanker OkleilaNo ratings yet
- Project Roomkey Fact SheetDocument4 pagesProject Roomkey Fact SheetDesiNo ratings yet
- 2-HEAD AND NECK PrintDocument30 pages2-HEAD AND NECK Printsaddam hussain100% (1)
- CDPR F2 EditedDocument82 pagesCDPR F2 EditedCzarina PadlanNo ratings yet
- Brucker, Mary C. - Jevitt, Cecilia - King, Tekoa L. - Osborne, Kathryn - Varney's Midwifery-Jones & Bartlett (2019) - 5-23Document19 pagesBrucker, Mary C. - Jevitt, Cecilia - King, Tekoa L. - Osborne, Kathryn - Varney's Midwifery-Jones & Bartlett (2019) - 5-23narendraNo ratings yet
- Superficial Skin Ulcers: Histopathological Analysis and Review of The LiteratureDocument6 pagesSuperficial Skin Ulcers: Histopathological Analysis and Review of The Literaturepka25No ratings yet
- Prevent Platelet Plugs.: Never IMDocument1 pagePrevent Platelet Plugs.: Never IMdekspeerNo ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Community and Environmental HealthDocument24 pagesHealth: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Community and Environmental Healthma kathrine cecille macapagal100% (1)
- Ventricular Shunting ProceduresDocument22 pagesVentricular Shunting ProceduresAndika GhifariNo ratings yet
- L87 - Walk in Indrapuram Lab 2 (Saya) Plot No.-GH-11, Ahinsa Khand II, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh GhaziabadDocument2 pagesL87 - Walk in Indrapuram Lab 2 (Saya) Plot No.-GH-11, Ahinsa Khand II, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh GhaziabadNimisha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Final Reports of Technical Review of Costing Tools PDFDocument250 pagesFinal Reports of Technical Review of Costing Tools PDFCakama MbimbiNo ratings yet
- Tim 2007acrysof - RestorDocument22 pagesTim 2007acrysof - Restorghitza80No ratings yet
- Gastroenterology: Student NameDocument8 pagesGastroenterology: Student Namemishal zikriaNo ratings yet
- N Comms 14644Document16 pagesN Comms 14644Vivien JusztusNo ratings yet