Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Format
Uploaded by
Franchie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views16 pagesMrs. P, age 77, is experiencing mild confusion, fatigue, abdominal pain, and weakness. She has been prescribed two medications: Furosemide and Salmeterol. Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat hypertension with potential side effects including increased urination, thirst, headaches, and muscle cramps. The nurse's responsibilities include monitoring for side effects and changes in vital signs, fluid intake/output, weight, and lab results. Salmeterol is an inhaled corticosteroid used for COPD with potential side effects like hoarseness and headaches. It is contraindicated for monotherapy asthma treatment and those with salmeterol allergies. The nurse will assess for contra
Original Description:
Original Title
jhcajh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMrs. P, age 77, is experiencing mild confusion, fatigue, abdominal pain, and weakness. She has been prescribed two medications: Furosemide and Salmeterol. Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat hypertension with potential side effects including increased urination, thirst, headaches, and muscle cramps. The nurse's responsibilities include monitoring for side effects and changes in vital signs, fluid intake/output, weight, and lab results. Salmeterol is an inhaled corticosteroid used for COPD with potential side effects like hoarseness and headaches. It is contraindicated for monotherapy asthma treatment and those with salmeterol allergies. The nurse will assess for contra
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views16 pagesDrug Study Format
Uploaded by
FranchieMrs. P, age 77, is experiencing mild confusion, fatigue, abdominal pain, and weakness. She has been prescribed two medications: Furosemide and Salmeterol. Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat hypertension with potential side effects including increased urination, thirst, headaches, and muscle cramps. The nurse's responsibilities include monitoring for side effects and changes in vital signs, fluid intake/output, weight, and lab results. Salmeterol is an inhaled corticosteroid used for COPD with potential side effects like hoarseness and headaches. It is contraindicated for monotherapy asthma treatment and those with salmeterol allergies. The nurse will assess for contra
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
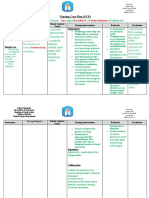
DRUG STUDY FORMAT
Name of Patient : _Mrs. P_ Patient's Health Profile: _patient appears mildly anxious,
Age : _77 yrs. old_ Sex:_F_ _non-dyspneic_
Occupation : _N/A_
Date of Admission :_N/A_
Status : _Married_ Religion : _N/A_ Initial Compliant : _currently experiencing mild confusion, fatigue,
_abdominal pain, and weakness.
Diagnosis : _N/A_
Name of Classification Mechanism of ContraIndicatio Indication Side Effects Nursing
Drug: Action n Route and Dosage Responsibilities
Generic
Name:
Brand
name:
1. Generic Loop diuretic, Furosemide Indication: peeing more than Assess for the
name: antihypertensiv inhibits Furosemide is Hypertension normal mentioned
Furosemide e primarily the contraindicated feeling thirsty with a dry cautions and
absorption of in patients with Route: Oral mouth contraindications
Brand sodium and anuria and in Dosage: 20mg daily headaches to prevent any
name: chloride not patients with a feeling confused or dizzy untoward
Lasix only in the history of muscle cramps or weak complication.
proximal and hypersensitivity muscles Perform a
distal tubules to furosemide. feeling or being sick thorough
but also in the nausea or vomiting physical
loop of Henle. fast or irregular assessment to
The high heartbeat establish
degree of baseline data
efficacy is before drug
largely due to therapy begins,
this unique site to determine
of action. The effectiveness of
action on the therapy, and to
distal tubule is evaluate for
independent of occurrence of
any inhibitory any adverse
effect on effects
carbonic associated with
anhydrase and drug therapy.
aldosterone. Inspect skin to
determine
hydration status
and have a
baseline data for
effectiveness of
drug therapy.
Assess
cardiopulmonary
status to
evaluate fluid
movement and
state of
hydration. It is
also to monitor
the effects on the
heart and lungs.
Obtain an
accurate body
weight to provide
baseline to
monitor fluid
balance.
Monitor intake
and output and
voiding patterns
to evaluate fluid
balance and
renal function.
Evaluate liver
status to
determine
potential
problems in drug
metabolism.
Monitor the
results of
laboratory tests
to determine
drug’s effect.
Monitor liver and
renal function
tests to identify
need for possible
dose adjustment
and toxic effects.
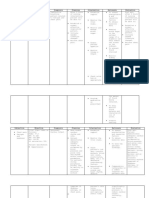
2. Generic Corticosteroids Beta-2 Indication: Hoarseness Assess for
name: adrenoceptor Salmeterol is used to treat throat irritation possible
Salmeterol stimulation COPD headache contraindications
causes contraindicated rapid heartbeat or cautions: any
Brand relaxation of for Route: Oral Inhalation nervousness known allergies
name: bronchial monotherapy cough to prevent
Serevent smooth muscle, treatment of Dosage: 2 inhalations dry mouth/throat hypersensitivity
bronchodilation asthma. It b.i.d. upset stomach reactions.
, and increased should not be Perform a
airflow. used without physical
Salmeterol is an asthma examination to
hypothesized controller establish
to bind to 2 medication. baseline data for
sites on the Salmeterol assessing the
beta-2 should not be effectiveness of
adrenoceptor. used in patients the drug and the
The saligenin who have occurrence of
moiety binds to demonstrated a any adverse
the active site hypersensitivity effects
of the beta-2 reaction to associated with
adrenoceptor. salmeterol or to drug therapy.
any of the Perform a skin
components in examination,
the commercial including color
product. and the presence
of lesions, to
provide a
baseline as a
reference for
drug
effectiveness.
Monitor blood
pressure, pulse,
cardiac
auscultation,
peripheral
perfusion, and
baseline
electrocardiogra
m to provide a
baseline for
effects on the
cardiovascular
system.
Assess bowel
sounds and do a
liver evaluation
and monitor liver
and renal
function tests to
provide a
baseline for renal
and hepatic
function tests.
Evaluate urinary
output and
prostate
palpation as
appropriate to
monitor
anticholinergic
effects.
Evaluate
orientation,
affect, and
reflexes to
evaluate CNS
effects.
3. Generic Anticholinergic Ipratropium is Indication: Dizziness Protect solution
Name: an Ipratropium Used to treat nausea for inhalation
Ipratropium acetylcholine bromide is air flow stomach upset from light. Store
bromide antagonist via contraindicated blockage and dry mouth unused vials in
blockade of to patients with prevent the constipation foil pouch.
Brand muscarinic closed angle worsening of Use nebulizer
name: cholinergic glaucoma, chronic mouthpiece
Atrovent receptors. blockage of the obstructive instead of face
Blocking urinary bladder, pulmonary mask to avoid
cholinergic enlarged disease (COPD). blurred vision or
receptors prostate, and aggravation of
decreases the an inability to Route: Oral narrow-angle
production of completely Inhalations glaucoma.
cyclic empty the Can mix albuterol
guanosine bladder. Dosage: 2 inhalations in nebulizer for
monophosphat b.i.d. up to 1 hr.
e (cGMP). This Ensure adequate
decrease in the hydration,
lung airways control
will lead to environmental
decreased temperature to
contraction of prevent
the smooth hyperpyrexia.
muscles. Have patient void
before taking
medication to
avoid urinary
retention.
Teach patient
proper use of
inhaler.
4. Generic Bronchodilators Albuterol acts Indication: nervousness or Monitor
Name: on beta-2 Albuterol is Prevent and treat shakiness ECG, serum
Albuterol adrenergic contraindicated difficulty breathing, headache electrolytes
(Salbutamol receptors to to patients with wheezing, shortness throat or nasal irritation and thyroid
) relax the overactive of breath, coughing, muscle aches function test
bronchial thyroid gland, and chest tightness tachycardia results.
Brand smooth muscle. diabetes, caused by COPD. palpitations Administer
Name: It also inhibits ketoacidosis, the
Proventil, the release of excess body Route: Oral Inhalation medication
Ventolin immediate acid, low accurately
hypersensitivity amount of Dosage: 2 puffs prn. because
mediators from potassium in q.4h adverse
cells, especially the blood, high reactions
mast cells. blood pressure, and
diminished tolerance
blood flow might occur.
through Raise side
arteries of the rails up
heart, low because
supply of
client might
oxygen rich be restless
blood to the and drowsy
heart, because of
prolonged QT this drug.
interval on EKG, Keep room
abnormal heart well-lit and
rhythm, see to it that
abnormal EKG client has a
with QT person with
changes from him closely
birth, and in case of
seizures. vertigo.
Assess lung
sounds, PR
and BP
before drug
administrati
on and
during peak
of
medication.
Assess pulse
for rhythm.
Provide oral
care or let
patient
gurgle after
inhalation to
get rid of the
unpleasant
aftertaste of
the
inhalation.
Auscultate
lungs for
presence of
adventitious
breath
sounds that
may signal
pulmonary
edema,
airway
resistance or
bronchospas
m.
Inspect
client’s nail
bed and oral
mucosa for
pallor.
Place client
in position of
comfort to
facilitate
optimum
rest and
sleep.
5. Generic Statins Atorvastatin is Indication: diarrhea Obtain liver
Name: a selective, Atorvastatin is Used to lower Cold symptoms function test as a
Atorvastatin competitive contraindicated cholesterol. It Joint pain baseline and
inhibitor of to patients with also prevents Insomnia periodically
Brand HMG-CoA untreated heart disease, UTI during therapy.
Name: reductase, the decreased level including heart Nausea Discontinue drug
Lipitor rate- limiting of thyroid attacks. Loss of appetite if AST or ALT
enzyme that hormones, Indigestion symptoms levels increase to
converts 3- alcoholism, Route: Oral 3 times normal
Increased transaminases
hydroxy-3- hemorrhage in levels.
Muscle spasms
methylglutaryl- the brain, liver Dosage: 40mg daily Withhold
Musculoskeletal pain
coenzyme A to failure, liver atorvastatin in
Muscle pain
mevalonate, a problems, any acute,
Limb pain
precursor of decreased serious condition
Mouth and throat pain
sterols, kidney function, that may suggest
rhabdomyolysis Chest pain (angina)
including myopathy or
, recent Lightheadedness and
cholesterol. serve as risk
operation, fainting
factor for
memory loss, Shortness of breath or
development of
high blood other breathing
renal failure.
sugar, problems
Ensure that
abnormal liver Muscle weakness or loss
patient has tried
function tests, of muscle strength
cholesterol-
major Anaphylaxis
lowering diet
traumatic Stevens-Johnson
regimen for 3–6
injury, syndrome
months before
pregnancy, Muscle inflammation
beginning
lactating therapy.
mother, muscle Administer drug
pain or without regard to
food, but at same
tenderness time each day.
with increase Atorvastatin may
creatine kinase, be combined
and immune- with a bile acid–
mediated binding agent. Do
necrotizing not combine with
myopathy. other HMG-CoA
reductase
inhibitors or
fibrates.
6. Generic Anticoagulants Heparin Indication: Bruising more easily. Adjust dose
Name: catalyzes the Heparin is Used to treat Bleeding that takes according to
Heparin inactivation of contraindicated and prevent longer to stop. coagulation test
thrombin by to patients with blood clots in Irritation, pain, redness, results
Brand ATIII by acting uncontrolled the veins, or sores at the injection performed just
Name: as a template bleeding or a arteries, or site. before injection.
Hemochron to which both severe lack of lungs. Allergic reactions, such Always check
Hep-Lock the enzyme platelets in the as hives, chills, and fever. compatibilities
and inhibitor blood, or have Route: Subcutaneous Increased liver enzymes with other IV
bind to form a low platelets on liver function test solutions.
ternary caused by using Dosage: 5000 units results. Use heparin lock
complex. heparin or b.i.d. needle to avoid
pentosan repeated
polysulfate. injections.
Give deep
subcutaneous
injections. Do not
give heparin by
IM injection.
Apply pressure to
all injection sites
after needle is
withdrawn.
Inspect injection
sites for signs of
hematoma. Do
not massage
injection sites.
Mix well when
adding heparin to
IV infusion.
Do not add
heparin to
infusion lines of
other drugs, and
do not piggyback
other drugs into
heparin line. If
this must be
done, ensure
drug
compatibility.
Provide for safety
measures to
prevent injury
from bleeding.
Check for signs of
bleeding;
monitor blood
tests.
Alert all health
care providers of
heparin use.
Have protamine
sulfate (heparin
antidote) readily
available in case
of overdose;
each mg
neutralizes 100
units of heparin.
Give very slowly
IV over 10 min,
not to exceed 50
mg.
7. Generic Opioid Morphine has Indication: Constipation Instruct patient
Name: analgesics an affinity for Morphine is Pain relief Nausea &vomiting how and when to
Morphine delta, kappa, contraindicated ( post and peri- Sedation ask for pain
and mu opioid to patients with operative) Pruritus medication. Do
Brand receptors. This hypersensitivity Respiratory depression & not stop taking
Name: drug produces to morphine, Route: IV apnea without
Avinza the majority of head injuries, Circulatory depression & discussing with
its analgesic impaired Dosage: 1mg every 6 shock health care
effects by pulmonary mins., lockout professional. It
binding to the function, and 10mg/h may cause
mu-opioid pregnancy. withdrawal
receptor within symptoms if
the central discontinued
nervous system abruptly after
(CNS) and the prolonged use.
peripheral Discuss safe use,
nervous system risks, and proper
(PNS). The net storage and
effect of disposal of opioid
morphine is the analgesics.
activation of Caution patient
descending to call for
inhibitory assistance when
pathways of ambulating or
the CNS as well smoking and to
as inhibition of avoid driving or
the nociceptive other activities
afferent requiring
neurons of the alertness until
PNS, which response to
leads to an medication is
overall known.
reduction of Advise patient
the nociceptive that morphine is
transmission. a drug with
known abuse
potential. Protect
it from theft, and
never give to
anyone other
than the
individual for
whom it was
prescribed.
Advise patient to
change positions
slowly to
minimize
orthostatic
hypotension.
Caution patient
to avoid
concurrent use of
alcohol or other
CNS depressants
with this
medication.
Encourage
patients who are
immobilized or
on prolonged
bed rest to turn,
cough, and
breathe deeply
every 2 hr to
prevent
atelectasis.
Explain to patient
how and when to
administer
morphine and
how to care for
infusion
equipment
properly.
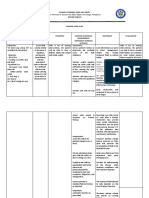
8. Generic Histamine-2 Famotidine is a Indication: fatigue Monitor for
Name: blockers competitive Famotidine is To decrease vomiting improvement in
Famotidine inhibitor of contraindicated the amount of nausea GI distress.
histamine H2- in patients with acid made in abdominal Monitor for signs
Brand receptors. The a history of the stomach discomfort of GI bleeding.
Name: primary serious anorexia
Pepcid clinically hypersensitivity Route: Oral dry mouth
important reactions to rash
pharmacologic famotidine or Dosage: 20mg b.i.d. muscle cramps
activity is other H2
inhibition of receptor
gastric juice antagonists.
secretion.
Famotidine
reduces the
acid and pepsin
content, as well
as the volume,
of basal,
nocturnal, and
stimulated
gastric
secretion.
You might also like
- ZSMU, Ukraine Pharmacology MCQs by Gankidi Raghavender Reddy,,,Used For Preparation of FMGE (Mci Screening Test) TooDocument117 pagesZSMU, Ukraine Pharmacology MCQs by Gankidi Raghavender Reddy,,,Used For Preparation of FMGE (Mci Screening Test) Toogrreddy836100% (2)
- Lecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument57 pagesLecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDBalakrishnan Thangaraj100% (1)
- Drugs in Medicine by Medad Team FinalDocument5 pagesDrugs in Medicine by Medad Team Finalعبد الرحمن100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav May100% (3)
- ConstipationDocument3 pagesConstipationmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Balance Monitoring PosterDocument1 pageFluid Balance Monitoring PosterSania oktaNo ratings yet
- Asthma & COPD Medication List PDFDocument11 pagesAsthma & COPD Medication List PDFabdullah992011No ratings yet
- Radiant Balance: A Comprehensive 90 Day Program to Improve Balance & Prevent FallsFrom EverandRadiant Balance: A Comprehensive 90 Day Program to Improve Balance & Prevent FallsNo ratings yet
- Mar ChecklistDocument18 pagesMar ChecklistMin MawNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBij Hilario100% (1)
- Med Surg Week 6Document11 pagesMed Surg Week 6Eunice Cortés100% (1)
- AAH v2 Acute AsthmaDocument81 pagesAAH v2 Acute AsthmaEssa SmjNo ratings yet
- Polarity Therapy: How Re-Polarizing Your Body Can Heal YouFrom EverandPolarity Therapy: How Re-Polarizing Your Body Can Heal YouRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Ipratropium Bromide Plus SalbutamolDocument3 pagesIpratropium Bromide Plus SalbutamolA sison100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Excess (CRF)Document4 pagesFluid Volume Excess (CRF)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationCelyn Nicole Fernandez RollanNo ratings yet
- NCP JaundiceDocument9 pagesNCP JaundiceMeena Koushal100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Excess Related To Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium RetentionDocument6 pagesFluid Volume Excess Related To Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium RetentionKristel Abe100% (1)
- HALOPERIDOL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHALOPERIDOL Drug Studyanreilegarde89% (9)
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea Wu100% (1)
- Kuwait Medicine PriceDocument225 pagesKuwait Medicine PriceKimberley White88% (50)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal DiseaseDocument12 pagesChronic Renal DiseaseNohaira SADANGNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument13 pagesHypertensionkennedy1434450% (4)
- Vagus Nerve Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Anxiety, Inflammation, and Depression Through Diet, with Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandVagus Nerve Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Anxiety, Inflammation, and Depression Through Diet, with Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- NCP MS Ward 2ND RotationDocument2 pagesNCP MS Ward 2ND RotationIvan Jules P. PALMARESNo ratings yet
- NCP DiarrheaDocument5 pagesNCP DiarrheaGlaiza Kate PlazaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- NC JaundiceDocument9 pagesNC JaundiceMeena KoushalNo ratings yet
- Cardio Activityinto NCPDocument3 pagesCardio Activityinto NCPIcel Jean QuimboNo ratings yet
- Name: Age/Sex: Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Short Term Goal: Long Term GoalDocument5 pagesName: Age/Sex: Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Short Term Goal: Long Term GoalThoLitz AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- BulimiaDocument2 pagesBulimiakharla suriagaNo ratings yet
- NCP2 (Sultan, J.) - Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesNCP2 (Sultan, J.) - Chronic Kidney DiseaseJohanisa SultanNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- Drug Study or QuintanaDocument2 pagesDrug Study or Quintanatohavefunonly16No ratings yet
- Group 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaAngel Joyce MontezaNo ratings yet
- NCP With DsDocument11 pagesNCP With DsMissDyYournurseNo ratings yet
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- CHA NCPDocument6 pagesCHA NCPMonty_Legaspi_5664No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiss GNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument31 pagesNursing Care PlansCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNo ratings yet
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument12 pagesCourse in The Wardmikhaela sencilNo ratings yet
- 3 NCP FormDocument3 pages3 NCP FormRawan KNo ratings yet
- Subjective Objective Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesSubjective Objective Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAlethen Janine SagunNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Measuring & Managing FluidDocument5 pagesMeasuring & Managing FluidDip Ayan MNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AmebiasisDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan AmebiasisCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Constipation NCPDocument2 pagesConstipation NCPAbby GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2deadgrave16No ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument13 pagesHypertensionAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Ms. Hicks Dehydration NCPDocument9 pagesMs. Hicks Dehydration NCPSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Tromadol + ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Tromadol + Paracetamol6fq2cmfgn4No ratings yet
- NCP AxelDocument10 pagesNCP AxelTan TanNo ratings yet
- Altered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalDocument4 pagesAltered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalAlyNo ratings yet
- BSN2 C Ihps NCP FinalDocument7 pagesBSN2 C Ihps NCP FinalAdrian DecolongonNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPLouise GumilaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentJesse ViolaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetPrincess Mildred AbdonNo ratings yet
- Assessing Abdominal Distensión After GastrectomyDocument1 pageAssessing Abdominal Distensión After GastrectomyEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- NCP Updated Aug312022Document2 pagesNCP Updated Aug312022Mariella BadongenNo ratings yet
- Final - Food PoisoningDocument10 pagesFinal - Food PoisoningCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Kami Kagina, Gulpiyada Lang Siya Nadulaan Kusog Kag Gapukol Iya Hambalanon, Kag Nagakiwi Iya Nga Itsura." As VerbalizedDocument4 pagesKami Kagina, Gulpiyada Lang Siya Nadulaan Kusog Kag Gapukol Iya Hambalanon, Kag Nagakiwi Iya Nga Itsura." As VerbalizedKoleen Lhyte T. UYNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument2 pagesDrug Study ICUErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Care Planjohncarlo ramosNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Long Term Objective: Long Term ObjectiveDocument2 pagesSubjective: Long Term Objective: Long Term ObjectiveRAFNo ratings yet
- Assess The Plan To Provide Advice The Advice TheDocument3 pagesAssess The Plan To Provide Advice The Advice TheDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledCherry CayabyabNo ratings yet
- INtususs Nursing DiagDocument5 pagesINtususs Nursing DiagVictoria EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Activity: /admendoza2020Document2 pagesTracheostomy Activity: /admendoza2020FranchieNo ratings yet
- Franchie M. Hsu Case StudyDocument5 pagesFranchie M. Hsu Case StudyFranchieNo ratings yet
- Name: FRANCHIE M. HSU Score: - I. Interpret The Following: 1Document7 pagesName: FRANCHIE M. HSU Score: - I. Interpret The Following: 1FranchieNo ratings yet
- Nursing and TechnologyDocument4 pagesNursing and TechnologyFranchieNo ratings yet
- Johari Window Model Known To Self Not Known To SelfDocument1 pageJohari Window Model Known To Self Not Known To SelfFranchieNo ratings yet
- Franchie M. HsuDocument2 pagesFranchie M. HsuFranchieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationFranchieNo ratings yet
- Agam Pharm CompressedDocument265 pagesAgam Pharm CompressedthisaiofficialNo ratings yet
- Emrgency Guidelines 3 RD EditionDocument123 pagesEmrgency Guidelines 3 RD EditionMitz MagtotoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Fadhila AsthmaDocument32 pagesJurnal Fadhila AsthmaJannah Miftahul JannahNo ratings yet
- 5 - Drugs For AsthmaDocument75 pages5 - Drugs For Asthmanica velano100% (1)
- Case # 4 Difficulty of BreathingDocument6 pagesCase # 4 Difficulty of BreathingGrace TanajuraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Nebulization MedicationsDocument5 pagesDrug Study On Nebulization MedicationsDonald BidenNo ratings yet
- Drugs For AsthmaDocument7 pagesDrugs For Asthmaapi-3736350No ratings yet
- LIST OF REGISTERED DRUGS As of December 2012: DR No Generic Brand Strength Form CompanyDocument19 pagesLIST OF REGISTERED DRUGS As of December 2012: DR No Generic Brand Strength Form CompanyBenjamin TantiansuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument5 pagesDrug Study Pediajulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument11 pagesCHF Drug StudySeth Michael Daniel BenauroNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument43 pagesDRUG StudyNathalie Faith CotengNo ratings yet
- COPD AsthmaDocument16 pagesCOPD Asthma09172216507No ratings yet
- Most Common MedsDocument13 pagesMost Common MedsMaria Zenaida BonoanNo ratings yet
- Paediatrica Indonesiana: Matahari Harumdini, Bambang Supriyatno, Rini SekartiniDocument9 pagesPaediatrica Indonesiana: Matahari Harumdini, Bambang Supriyatno, Rini SekartiniArlita Mirza Dian PrastiwiNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic System: Parasympatholytics: ClassificationDocument3 pagesCholinergic System: Parasympatholytics: ClassificationAmit KochharNo ratings yet
- Free Drug Bank GUIDE 3 PDFDocument128 pagesFree Drug Bank GUIDE 3 PDFRaouf Ra'fat Soliman88% (8)
- Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument71 pagesDrugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDShabnam Binte AlamNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyShenna RegaspiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Cholinoceptor Blockers & Amp Cholinesterase RegeneratorsDocument8 pagesChapter 8. Cholinoceptor Blockers & Amp Cholinesterase RegeneratorsChrysler Hans GuttenbergNo ratings yet