Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Civil Engineering - 14
Uploaded by
visanuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Civil Engineering - 14
Uploaded by
visanuCopyright:
Available Formats
TRADITIONAL MATERIALS 27
A Roof
Roof
Timber Members
300 cm
Spacers
Platform
B 150 cm
30 cm Pillars
Elevation Section on AB
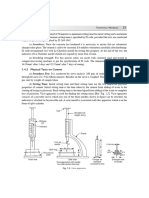
Fig. 1.8. Air seasoning
(ii) Artificial Seasoning: In this method timber is seasoned in a chamber with regulated heat,
controlled humidity and proper air circulation. Seasoning can be completed in 4 to 5 days only. The
different methods of seasoning are:
(a) Boiling
(b) Kiln seasoning
(c) Chemical seasoning
(d) Electrical seasoning.
(a) Boiling: In this method timber is immersed in water and then water is boiled for 3 to 4 hours.
Then it is dried slowly. Instead of boiling water hot steam may be circulated on timber. The process of
seasoning is fast, but costly.
(b) Kiln Seasoning: Kiln is an airtight chamber. Timber to be seasoned is placed inside it. Then
fully saturated air with a temperature 35°C to 38°C is forced in the kiln. The heat gradually reaches
inside timber. Then relative humidity is gradually reduced and temperature is increased, and maintained
till desired degree of moisture content is achieved.
The kiln used may be stationary or progressive. In progressive kiln the carriages carrying timber
travel from one end of kiln to other end gradually. The hot air is supplied from the discharging end so
that temperature increase is gradual from charging end to discharging end. This method is used for
seasoning on a larger scale.
(c) Chemical Seasoning: In this method, the timber is immersed in a solution of suitable salt.
Then the timber is dried in a kiln. The preliminary treatment by chemical seasoning ensures uniform
seasoning of outer and inner parts of timber.
(d) Electrical Seasoning: In this method high frequency alternate electric current is passed through
timber. Resistance to electric current is low when moisture content in timber is high. As moisture content
reduces the resistance reduces. Measure of resistance can be used to stop seasoning at appropriate level.
You might also like
- IMP Workshop ManualDocument336 pagesIMP Workshop Manualsyllavethyjim67% (3)
- PSD SiemensDocument45 pagesPSD Siemensbrijendra2185% (13)
- Two-Stage Gasification Lowers Tar Content With Preheated AirDocument5 pagesTwo-Stage Gasification Lowers Tar Content With Preheated AirgvisanNo ratings yet
- SeasoningDocument2 pagesSeasoningsushilNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 TimberDocument9 pagesUnit 7 TimberhimalbaduhimalbaduNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Timber Info-FinalDocument11 pagesUnit 2-Timber Info-FinalShara DinduNo ratings yet
- Types of SeasoningDocument4 pagesTypes of SeasoningAliNo ratings yet
- Development of A Heat ExchangerDocument7 pagesDevelopment of A Heat ExchangerManicks VelanNo ratings yet
- Wood & Lumber TEST ITEMDocument5 pagesWood & Lumber TEST ITEMREGINE CAPORALNo ratings yet
- Mughal 12378ghokDocument7 pagesMughal 12378ghokSuvarchala SuvviNo ratings yet
- Seasoning Of: t1m ErDocument22 pagesSeasoning Of: t1m ErDISHANo ratings yet
- High Pressure BoilersDocument27 pagesHigh Pressure BoilersAaryaveerNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument14 pagesBoileryudhistharNo ratings yet
- Test Method BitDocument24 pagesTest Method Bitdstv2005No ratings yet
- Joseph Et Al Biochar Cookstoves North VietnamDocument42 pagesJoseph Et Al Biochar Cookstoves North VietnamgladysNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument13 pagesHeatSrirama SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 278 520 1 SM PDFDocument6 pages278 520 1 SM PDFNatalya KarenninaNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 4: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument4 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 4: Back of Chapter QuestionsPugalmeena PugalmeenaNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument47 pagesBoilersAshish RawatNo ratings yet
- A) Why Artificial Draught? Explain With Sketch Forced, Induced and Balanced Draught SystemDocument3 pagesA) Why Artificial Draught? Explain With Sketch Forced, Induced and Balanced Draught Systemking1qNo ratings yet
- Soal Kuis Perpindahan Panas Konduksi Tunak Kelas ADocument3 pagesSoal Kuis Perpindahan Panas Konduksi Tunak Kelas AShafina IstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Sliit PaperDocument6 pagesSliit Papersulaxshan321No ratings yet
- BoilersDocument76 pagesBoilers58-Sanket TupkarNo ratings yet
- mme306secondmidexamDocument1 pagemme306secondmidexamزينب فرجNo ratings yet
- Seasoning of TimberDocument2 pagesSeasoning of TimberKrishnaSahNo ratings yet
- Preservation of Boiler During Idle PeriodDocument4 pagesPreservation of Boiler During Idle PeriodSachin PatelNo ratings yet
- حسين عباس22Document14 pagesحسين عباس22احمد كريم خلفNo ratings yet
- 07 Heat TransferDocument39 pages07 Heat TransfergodiewamuchuNo ratings yet
- A Method For Direct Harvest of Bacterial Cellulose Filaments During Continuous Cultivation of Acetobacter Xylinum PDFDocument5 pagesA Method For Direct Harvest of Bacterial Cellulose Filaments During Continuous Cultivation of Acetobacter Xylinum PDFFiqa SuccessNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Pressure SensorDocument14 pagesFabrication of Pressure SensorTuan Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Specs 2 Prelim 303Document4 pagesSpecs 2 Prelim 303Jen AgabinNo ratings yet
- Serth ProblemsDocument7 pagesSerth ProblemsRuel CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Torrefaction of Wood Part 2. Analysis of ProductsDocument6 pagesTorrefaction of Wood Part 2. Analysis of Products김형진No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Practice ExerciseDocument1 pageHeat Transfer Practice ExerciseRugi Vicente RubiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 Evaporation MeasurementDocument4 pagesAssignment 7 Evaporation MeasurementKhushalchand BhandariNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Evaporator TypesDocument3 pagesComparison of Evaporator TypesLon カンイェテNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument2 pagesThermalAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument38 pagesBoilersAshlin Augusty92% (24)
- CarpentryDocument21 pagesCarpentryAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- 117 Sample Chapter PDFDocument17 pages117 Sample Chapter PDFAlen ShajiNo ratings yet
- Pulp & PaperNew-1Document24 pagesPulp & PaperNew-1shamsul amin100% (1)
- Biomorphic Cellular Ceramics ResearchDocument5 pagesBiomorphic Cellular Ceramics ResearchRafael GomesNo ratings yet
- Boilers Explained: Types, Components, and Efficiency (less than 40 charsDocument39 pagesBoilers Explained: Types, Components, and Efficiency (less than 40 charsFahad Aziz100% (1)
- Chandrabhusan ProposalDocument5 pagesChandrabhusan Proposalyadavchandrab000999No ratings yet
- Shell BoilerDocument12 pagesShell BoilerMochamad Fajar RamdaniNo ratings yet
- Boilers and Their FunctionsDocument13 pagesBoilers and Their FunctionsRamNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Heat Pipe Fabrication, Performance Testing and ModelingDocument6 pagesStainless Steel Heat Pipe Fabrication, Performance Testing and ModelingAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- 500mwboilermahagenco 140115124304 Phpapp02Document38 pages500mwboilermahagenco 140115124304 Phpapp02Lakshmi NarayanNo ratings yet
- Trial p2 Section C No-11Document4 pagesTrial p2 Section C No-11malaomar0% (1)
- Methods and Processes of Seasoning TimberDocument2 pagesMethods and Processes of Seasoning Timberemmanuelkipngetich68No ratings yet
- presentation on building materialsDocument19 pagespresentation on building materialssafianuharunNo ratings yet
- Metales PesadosDocument8 pagesMetales PesadosXochiitl' DiiegooNo ratings yet
- Seasoning of ti-WPS Office by EmpDocument4 pagesSeasoning of ti-WPS Office by Empjacobodogbo5No ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Fired HeatersDocument9 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Fired HeatersLakshman TumpatiNo ratings yet
- Kiln SeasoningDocument45 pagesKiln SeasoningarancyppNo ratings yet
- zanziV2A 17Document4 pageszanziV2A 17luaweb123No ratings yet
- Lecture No. 3 ProblemsDocument4 pagesLecture No. 3 Problemspriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Boilers and ThermicFluidHeatersDocument42 pagesBoilers and ThermicFluidHeatersHolayilNo ratings yet
- Design Construction Manual2002 - 6Document1 pageDesign Construction Manual2002 - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 6Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 8Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 8visanuNo ratings yet
- Design Construction Manual2002 - 10Document1 pageDesign Construction Manual2002 - 10visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 1Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 12Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 12visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 4Document1 pageBentonite 4visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 10Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 10visanuNo ratings yet
- Classify Bricks by Quality for Construction ProjectsDocument1 pageClassify Bricks by Quality for Construction ProjectsvisanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 5Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 5visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 9Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 9visanu100% (1)
- Basic Civil Engineering - 13Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 13visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 6Document1 pageBentonite 6visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 2Document1 pageBentonite 2visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 1Document1 pageBentonite 1visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 3Document1 pageBentonite 3visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 7Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 7visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 6Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 5Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 5visanuNo ratings yet
- Types of Cement ExplainedDocument1 pageTypes of Cement ExplainedvisanuNo ratings yet
- Humour and IdentityDocument12 pagesHumour and IdentityLyann MartinezNo ratings yet
- Theosophical Quarterly v23 1925-1926Document424 pagesTheosophical Quarterly v23 1925-1926Joma SipeNo ratings yet
- Notified Autonomous Bodies of The Federal Government PDFDocument7 pagesNotified Autonomous Bodies of The Federal Government PDFGull SabeerNo ratings yet
- Data Types and Data AnalysisDocument52 pagesData Types and Data AnalysisParag Shah100% (2)
- Technical Datasheet 0027141131 003Document4 pagesTechnical Datasheet 0027141131 003Faizal SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Forest Mensuration: Manisha Kumari Faculty Associate Usha Martin UniversityDocument15 pagesForest Mensuration: Manisha Kumari Faculty Associate Usha Martin UniversityManisha KumariNo ratings yet
- NoNuke Spec SheetDocument1 pageNoNuke Spec SheetEster TerneroNo ratings yet
- MCE 244 Course OutlineDocument1 pageMCE 244 Course OutlineKaren DavisNo ratings yet
- Limits of Program VerificationDocument24 pagesLimits of Program VerificationBrian Cantwell SmithNo ratings yet
- IL6 AdvtDocument9 pagesIL6 AdvtManoj Kumar100% (1)
- Vector Network AnalyzersDocument33 pagesVector Network AnalyzersRea Gusti HermawanNo ratings yet
- Course Assignment: Language Analysis and Language Learning 681 Assignment 1Document11 pagesCourse Assignment: Language Analysis and Language Learning 681 Assignment 1Đinh Lan KhánhNo ratings yet
- STS Assignment1Document3 pagesSTS Assignment1Cagabcab Canibel Melany0% (1)
- First Principle Applications in RoRo-Ship Design PDFDocument7 pagesFirst Principle Applications in RoRo-Ship Design PDFFerdy Fer DNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Crops - D.Tay-2Document27 pagesEvolution of Crops - D.Tay-2liam peinNo ratings yet
- M.E. MPCDocument103 pagesM.E. MPCShobana SNo ratings yet
- Delhi Skill and Entrepreneurship University: Application Form Session 2021-2022Document3 pagesDelhi Skill and Entrepreneurship University: Application Form Session 2021-2022Shyam DubeyNo ratings yet
- Development of High Temperature Superconducting Transformers PDFDocument6 pagesDevelopment of High Temperature Superconducting Transformers PDFBen McConnellNo ratings yet
- Daily Stoic Amor Fati Excerpt From The Obstacle Is The WayDocument7 pagesDaily Stoic Amor Fati Excerpt From The Obstacle Is The WaySirLouen100% (9)
- Saptamsa and Navamsa Charts PDFDocument37 pagesSaptamsa and Navamsa Charts PDFjyothiNo ratings yet
- User Manual Servo Driver SZGH-302: (One Driver To Control Two Motors Simultaneously)Document23 pagesUser Manual Servo Driver SZGH-302: (One Driver To Control Two Motors Simultaneously)Zdeněk HromadaNo ratings yet
- Nakshatra Revati: According To Prash TrivediDocument8 pagesNakshatra Revati: According To Prash TrivediazzxdNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT CONTROL SYSTEMS IN NON-PROFITSDocument26 pagesMANAGEMENT CONTROL SYSTEMS IN NON-PROFITSPranita NarainNo ratings yet
- GS Ep Saf 321 enDocument27 pagesGS Ep Saf 321 enHi PersonneNo ratings yet
- Copper Pipe Leak Test and VacuumDocument2 pagesCopper Pipe Leak Test and Vacuumalone160162l100% (1)
- qf001 - Welocalize Supplier Mutual Nda - 2018-Signed PDFDocument9 pagesqf001 - Welocalize Supplier Mutual Nda - 2018-Signed PDFapaci femoNo ratings yet
- Resume 2024-FinalDocument1 pageResume 2024-Finalapi-716723342No ratings yet