0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views5 pagesBCG Matrix
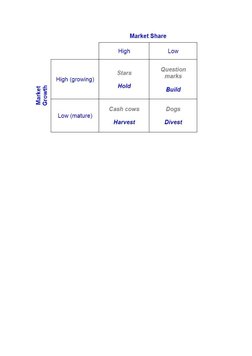
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix is a marketing management tool used to analyze a firm's product portfolio. It classifies products based on their market share and market growth into four categories: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs. Stars have high market share in fast growing markets while cash cows have high market share in slow growing markets. Question marks have low market share but are in fast growing markets, while dogs have low market share in slow growing markets.
Uploaded by
Sawar Raj AroraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views5 pagesBCG Matrix
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix is a marketing management tool used to analyze a firm's product portfolio. It classifies products based on their market share and market growth into four categories: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs. Stars have high market share in fast growing markets while cash cows have high market share in slow growing markets. Question marks have low market share but are in fast growing markets, while dogs have low market share in slow growing markets.
Uploaded by
Sawar Raj AroraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- BCG Matrix Overview
- BCG Matrix Elements
- Product Portfolio Strategy