Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Three Phase Relationships
Uploaded by
hussein darwishCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter Three Phase Relationships
Uploaded by
hussein darwishCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil Mechanics and Foundations and
Testing properties of materials
Chapter Two
Phase relationships
Dr. Lina Jaber
Chapter Three
Phase Relationships
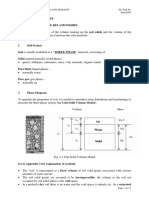
In natural occurrence, soils are three-phase systems consisting of soil solids, water, and air.
To develop the weight–volume relationships, we must separate the three phases
(that is, solid, water, and air) .Thus, the total volume of a given soil sample can be
expressed as:
V = Vs + Vv = Vs + Vw + Va
where Vs = volume of soil solids
Vv = volume of voids
Vw = volume of water in the voids
Va= volume of air in the voids
Dr. Lina Jaber
Soil behavior is effected by the varying amounts of solid, water, and air present in a soil
mass.
Density and Unit weight
The unit weight in kN/m3 can be obtained from densities in kg/m3 as
where g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/sec2.
Dr. Lina Jaber
Note that: unit weight of water (gw) is equal to 9.81 kN/m3 or 62.4 lb/ft3 or 1000 kgf/m3.
the submerged unit weight is: γ’ = γ – γ w
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
• The Specific gravity of soil is defined as the ratio of the unit weight of solids to the unit
weight of water. For most soils, it ranges between 2.6 to 2.8. It is unit‐less.
Assuming that the weight of the air is negligible, we can give the total weight of the
sample as :
W = Ws + Ww
where Ws = weight of soil solids
Ww = weight of water
• Void ratio (e) is defined as the ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of solids.
Thus,
Dr. Lina Jaber
• Porosity (n) is defined as the ratio of the volume of voids to the total volume, or
Thus,
The degree of saturation (S) is defined as the ratio of the volume of water to the
volume of voids, for dry Soil S= 0 %, for totally saturated soil S=100%
• Moisture content (w) is also referred to as water content and is defined as the ratio
of the weight of water to the weight of solids in a given volume of soil:
Dr. Lina Jaber
• Unit weight (g) is the weight of soil per unit volume. Thus,
• the weight per unit volume of soil, excluding water. This weight is referred to as the
dry unit weight, γd Thus,
To obtain a relationship among unit weight
(or density), void ratio, and moisture content,
let us consider a volume of soil in which
the volume of the soil solids is one,
Dr. Lina Jaber
where Gs = specific gravity of soil solids
w = moisture content
γw = unit weight of water
Thus , with S = 1,
If the soil sample is saturated—that is, the void spaces are completely filled with water,
the relationship for saturated unit weight (γ sat) can be derived :
Dr. Lina Jaber
Relative Density
The term relative density is commonly used to indicate the in situ denseness or
looseness of granular soil. It is defined as
where Dr = relative density, usually given as a percentage
e = in situ void ratio of the soil
e max = void ratio of the soil in the loosest state
e min = void ratio of the soil in the densest state
The values of Dr may vary from a minimum of 0% for very loose soil to a maximum
of 100% for very dense soils.
Dr. Lina Jaber
Problem 1
A moist silty clay soil has a unit weight of 19.2 KN/m³ and a water content of
9.8 %. If the specific gravity of the soil is 2.69, compute the:
a. void ratio
b. unit weight
c. degree of saturation
Problem 2
A wet soil sample weighs 2350 kg and occupies a volume of 1.2 m³.
The water content in the soil is equal to 8.6 % and Gs = 2.71. Estimate
the wet density, dry density, void ratio, and porosity.
Dr. Lina Jaber
Solution
Problem 1
Dr. Lina Jaber
Problem 2
Dr. Lina Jaber
You might also like
- Soil Properties and Phase RelationshipsDocument8 pagesSoil Properties and Phase RelationshipsjulspdNo ratings yet
- Fingertip Injuries Diagnosis, Management and ReconstructionDocument197 pagesFingertip Injuries Diagnosis, Management and Reconstructionokida192No ratings yet
- Geotechnical Module 1Document52 pagesGeotechnical Module 1athira100% (2)
- Psychedelic Drugs-A New Era in Psychiatry?Document9 pagesPsychedelic Drugs-A New Era in Psychiatry?PeterNo ratings yet
- Early Years and Childcare Safeguarding AuditDocument4 pagesEarly Years and Childcare Safeguarding AuditEarly Years Careers100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Weight Volume RelationshipDocument30 pagesChapter 2 - Weight Volume RelationshipShahrull Rule50% (2)
- Module 2. Physical Properties of SoilDocument24 pagesModule 2. Physical Properties of SoilMark Andykenn Liaga MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Soil Engineering Chapter -2-2Document15 pagesSoil Engineering Chapter -2-2Bhavya zaveriNo ratings yet
- 2chapter-2 PPT - (Final)Document61 pages2chapter-2 PPT - (Final)Muhe JsNo ratings yet
- GeotechDocument27 pagesGeotechGina ClamorNo ratings yet
- Phase Relations and Soil PropertiesDocument12 pagesPhase Relations and Soil Propertiesjavier100% (1)
- Handout Minggu 02b Mektan - Soil Index and Gravimetry-1Document19 pagesHandout Minggu 02b Mektan - Soil Index and Gravimetry-1IkeNo ratings yet
- Phase Relations Key Terms and ConceptsDocument16 pagesPhase Relations Key Terms and ConceptsCasao JonroeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3anon_749279665No ratings yet
- 5 - Weight Volume RelationshipsDocument32 pages5 - Weight Volume Relationshipsmaame25No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Index PropertiesDocument26 pagesLecture 3 Index PropertiesMd. Ariful IslamNo ratings yet
- Weight Volume RelationshipsDocument32 pagesWeight Volume Relationshipssyedumairali100% (1)
- Chapter Two Physical Characteristics of SoilsDocument32 pagesChapter Two Physical Characteristics of SoilsHiwot DemisseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1Document36 pagesChapter 2-1Chalachew MesfinNo ratings yet
- Soil Profiles, Types and Classification MethodsDocument65 pagesSoil Profiles, Types and Classification MethodsBazimya DixonNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagram of Soil ExplainedDocument6 pagesPhase Diagram of Soil ExplainedLaxamana, MarcNo ratings yet
- 003 - Weight-Volume RelationshipDocument29 pages003 - Weight-Volume RelationshipCristina Marie Pegarro AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Permeability and Seepage: Course Code: Course Title: Credit HoursDocument15 pagesPermeability and Seepage: Course Code: Course Title: Credit HoursSHAHRIER NAZIM SHUVRONo ratings yet
- Department of Geology University of Liberia Semester II-2019-2020Document37 pagesDepartment of Geology University of Liberia Semester II-2019-2020Edwin BallahNo ratings yet
- GTEL01E: Physical Properties of Soil: Modules inDocument14 pagesGTEL01E: Physical Properties of Soil: Modules inHatsuieeNo ratings yet
- Geotecheng Module 01 Chapter 02Document32 pagesGeotecheng Module 01 Chapter 02Ace De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 6 Composition of SoilDocument15 pages6 Composition of SoilLovely Mae Cruza GawinganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Physical Properties of SoilDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Physical Properties of SoilChristian BonoanNo ratings yet
- Soil MechanicsDocument30 pagesSoil MechanicsShivang VivekNo ratings yet
- Composition of SoilDocument38 pagesComposition of SoilRegina MerasNo ratings yet
- Basic Soil MechanicsDocument30 pagesBasic Soil MechanicsAfham AhmadNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document7 pagesModule 1Shanu AhmadNo ratings yet
- Problem 11Document6 pagesProblem 11Anonymous GtcMxTNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering 1 T2Document16 pagesGeotechnical Engineering 1 T2ERJEAN SILVERIONo ratings yet
- chapter2-weightvolumerelationship (1)Document35 pageschapter2-weightvolumerelationship (1)AbuNo ratings yet
- MKCP-3313-WEEK-2-SYNCHRONOUSDocument21 pagesMKCP-3313-WEEK-2-SYNCHRONOUSXen GamesNo ratings yet
- Ce 122 Chapter 2 PDFDocument11 pagesCe 122 Chapter 2 PDFJeisther Timothy GalanoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Soil: Types of Soil (On The Basis of Moisture Content) :-1. Dry: - 2. SaturatedDocument14 pagesClassification of Soil: Types of Soil (On The Basis of Moisture Content) :-1. Dry: - 2. Saturatedshalini negiNo ratings yet
- TDP 2 - Soils Eng. Soil Properties 1Document14 pagesTDP 2 - Soils Eng. Soil Properties 1Laura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document32 pagesLec 2ahmed alhajNo ratings yet
- CON4341 - E - Note - 02 Phase RelationshipDocument12 pagesCON4341 - E - Note - 02 Phase Relationship123No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 and 4Document28 pagesChapter 3 and 4Alyssa Jane FloresNo ratings yet
- Problem 11Document6 pagesProblem 11Elbrent Paul M ObedencioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03Document23 pagesLecture 03Zakawat SadiNo ratings yet
- GEOTECH 1: SOIL MECHANICS FUNDAMENTALSDocument167 pagesGEOTECH 1: SOIL MECHANICS FUNDAMENTALSClariselle MarisgaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of SoilsDocument96 pagesThe Nature of SoilsMohammed OumerNo ratings yet
- 02 Phase RelationshipDocument12 pages02 Phase RelationshipDE DECADENo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Soil ClassificationDocument74 pagesChapter 1 - Soil ClassificationEyntan Iera100% (1)
- Lesson 2Document27 pagesLesson 2jrNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase ModelsDocument24 pages3 Phase Modelsfaroukm91No ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Unit 4 (Week 7 and 8) For Soil MechanicsDocument6 pagesMODULE 1 Unit 4 (Week 7 and 8) For Soil MechanicsMark Ruby OpawonNo ratings yet
- Three Phases in Soils - Composition, Properties and Particle Size AnalysisDocument25 pagesThree Phases in Soils - Composition, Properties and Particle Size AnalysisJannica Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Soil 1Document186 pagesChapter 2-Soil 1Ruth Sangalang-GabrilloNo ratings yet
- Phase Relation of Soils: Index Properties of Soil: Mass-Volume RelationshipDocument4 pagesPhase Relation of Soils: Index Properties of Soil: Mass-Volume RelationshipMarben Leynes-Cereno Agustin-ViernesNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering 1Document31 pagesGeotechnical Engineering 1Ranajit MajhiNo ratings yet
- Phase Relationships NotesDocument3 pagesPhase Relationships NotesFirat PulatNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document15 pagesCH 3omar TahaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Index PropertiesDocument78 pages2 - Index PropertiesKaranNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Chapter 3 Key RelationshipsDocument42 pagesSoil Mechanics Chapter 3 Key RelationshipsAbd El Rhman Mohamed50% (2)
- 02 Chapter 3 - Weight Volume RelationshipsDocument42 pages02 Chapter 3 - Weight Volume RelationshipsLeandrow BacolodNo ratings yet
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationFrom EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationGuilhem BourrieNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument112 pagesDatasheetStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Discontinued Tymphany LAT Products LAT500 001 PDFDocument2 pagesDiscontinued Tymphany LAT Products LAT500 001 PDFOgie FermoNo ratings yet
- Johnson Et Al.2006. Felidae PhylogenyDocument6 pagesJohnson Et Al.2006. Felidae Phylogenyaspergillus_jallNo ratings yet
- Trilon C Types TI enDocument11 pagesTrilon C Types TI enjuanfelipehincapieNo ratings yet
- Aiesha Edward Resume2Document2 pagesAiesha Edward Resume2api-491571342No ratings yet
- Make Every Day Count: George Eliot's inspirational poemDocument3 pagesMake Every Day Count: George Eliot's inspirational poemRUTUJA KALENo ratings yet
- Erowid LSD (Acid) Vault - ImagesDocument2 pagesErowid LSD (Acid) Vault - ImagesAdam BruhNo ratings yet
- Cereal Based Functional BeveragesDocument7 pagesCereal Based Functional BeveragesCorina ParicanazaNo ratings yet
- 2002 - Comparison of The Absorption of Micronized (Daflon 500 MG) and Nonmicronized 14c-Diosmin TabletsDocument9 pages2002 - Comparison of The Absorption of Micronized (Daflon 500 MG) and Nonmicronized 14c-Diosmin TabletsMai HuynhNo ratings yet
- TECHNICAL DATA SHEET of RUST CONVERTERDocument1 pageTECHNICAL DATA SHEET of RUST CONVERTERArmando AballeNo ratings yet
- A Project Report: Maya Engineering WorksDocument2 pagesA Project Report: Maya Engineering WorksVishwendra SinghNo ratings yet
- D 1123 - 99 Rdexmjmtotk - PDFDocument5 pagesD 1123 - 99 Rdexmjmtotk - PDFFrancisco GuerraNo ratings yet
- Esign IPS: Reducing Switching Losses in Portable DC/DC ConvertersDocument2 pagesEsign IPS: Reducing Switching Losses in Portable DC/DC ConvertersAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Starbucks BSC Project Analyzes Store PerformanceDocument8 pagesStarbucks BSC Project Analyzes Store Performanceandrea100% (1)
- S# Isin CFI Code (As Per New ISO) Security Name Security Symbol Sector Name Security Type StatusDocument25 pagesS# Isin CFI Code (As Per New ISO) Security Name Security Symbol Sector Name Security Type StatusahmedalishNo ratings yet
- Static DischargeDocument21 pagesStatic DischargeRRNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Breathing Exercise On Reducing Pain Perception and State Anxiety Among Primi ParturientsDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of Breathing Exercise On Reducing Pain Perception and State Anxiety Among Primi ParturientsPutra SpNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 4Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 4Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- GMP TD Ar FPL 11033Document1 pageGMP TD Ar FPL 11033Sammy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Yoga & Diet To Prevent DepressionDocument5 pagesYoga & Diet To Prevent DepressionDietician Mrunmayee DixitNo ratings yet
- Will The Real SMART Goals Please Stand Up?: Robert S. Rubin Saint Louis UniversityDocument2 pagesWill The Real SMART Goals Please Stand Up?: Robert S. Rubin Saint Louis UniversityKyoko TakayanagiNo ratings yet
- EWC661 TITLE: Dietary Habits During Term Time Among University Students. Background of StudyDocument4 pagesEWC661 TITLE: Dietary Habits During Term Time Among University Students. Background of StudyfarinaazmiNo ratings yet
- 2.factory Price - Alarm Accessories-Complete 20150325Document15 pages2.factory Price - Alarm Accessories-Complete 20150325FREE BUSINESS INTELLIGENCENo ratings yet
- Food Industry JTM2Document35 pagesFood Industry JTM2Jofin TMNo ratings yet
- Blue Bloods 1Document166 pagesBlue Bloods 1anastomaNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study of AcidizingDocument11 pagesAn Experimental Study of Acidizinggigi17No ratings yet