0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views5 pagesGENMATH1Q
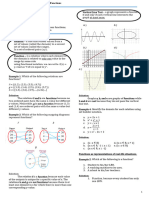
The document discusses key concepts in representing and evaluating functions. It defines functions as relations where each element of the domain corresponds to exactly one element in the range. Functions can be represented through tables, ordered pairs, graphs, or equations. The document also discusses evaluating functions by substituting values, and operations on functions such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, composition, and inverses. Rational functions are defined as the ratio of two polynomials.
Uploaded by
Venise RevillaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views5 pagesGENMATH1Q
The document discusses key concepts in representing and evaluating functions. It defines functions as relations where each element of the domain corresponds to exactly one element in the range. Functions can be represented through tables, ordered pairs, graphs, or equations. The document also discusses evaluating functions by substituting values, and operations on functions such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, composition, and inverses. Rational functions are defined as the ratio of two polynomials.
Uploaded by
Venise RevillaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd