Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Use and Function
Uploaded by
carlosperiivorraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Use and Function
Uploaded by
carlosperiivorraCopyright:
Available Formats
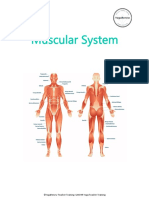
FUNCTION AND MOVEMENT
CALVES: The primary function of the calf muscles, or the "gemelos" in
Spanish, is to point the foot downward (plantarflexion) at the ankle joint. They
also assist in bending the knee joint. In everyday life, we use our calf muscles
for various activities, such as walking, running, climbing stairs, standing, and
even pushing the gas pedal in a car. These muscles play a crucial role in
supporting our body and facilitating movement in our lower limbs.
QUADRICEPS: The quadriceps are a group of four muscles in the front of the
thigh: the rectus femoris, the vastus lateralis, the vastus intermedius, and the
vastus medialis. Their main function is to extend the leg at the knee joint and
also assist in stabilizing the hip joint.
We use the quadriceps in many daily activities, such as walking, running,
climbing stairs, getting up from a chair, squatting, and various other tasks
involving leg movement. They are also crucial in sports like cycling, soccer,
and weightlifting. These muscles are essential for maintaining leg mobility and
strength.
HAMSTRINGS: The hamstrings are a group of muscles in the back of the
thigh, including the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus.
Their primary function is to flex the leg at the knee joint and extend the hip
joint. They also play a significant role in stabilizing the pelvis.
We use the hamstrings in daily activities like walking, running, climbing stairs,
and, in general, in any motion that involves bending the knee or extending the
hip. They are essential for maintaining leg flexibility and strength.
GLUTEUS: The gluteal muscles, commonly referred to as the glutes, have
several important functions. They are responsible for hip extension, which is
the movement of the thigh moving backward, and they also aid in thigh
abduction, which is moving the thigh away from the body. These muscles
provide stability and power to the hip and help us maintain an upright posture.
We use our glutes in various everyday activities, including standing up,
walking, climbing stairs, running, and even sitting down. These muscles play a
crucial role in maintaining our overall mobility and supporting the trunk and
pelvis during movement.
ABDOMINALS: The abdominal muscles, commonly referred to as the abs,
have the primary function of flexing the spine, which involves bending the
torso forward, and they also help stabilize the spine and pelvis. These
muscles are essential for maintaining posture, supporting the abdominal
organs, and assisting in various movements.
We use our abdominal muscles in everyday activities such as sitting up from a
lying position, bending forward to pick something up, and maintaining an
upright posture while standing or sitting. They also play a crucial role in core
stability during various physical activities and exercises.
LUMBARS: The lumbar muscles, or erector spinae muscles, are a group of
muscles along the lower spine. Their primary function is to extend and
straighten the spine. They also provide stability to the spine and help control
movements of the torso.
We use our lumbar muscles in various daily activities, including standing,
walking, sitting up straight, and lifting objects from the ground. These muscles
play a vital role in maintaining posture, supporting the lower back, and
facilitating movements that involve the spine and trunk.
PECTORALS: The pectoral muscles, often referred to as the pecs, are
located in the chest area and have the primary function of moving the arms
toward the body's midline, which is known as adduction. They also assist in
various movements of the shoulder joint.
We use our pectoral muscles in everyday activities such as pushing, pulling,
reaching, and hugging. These muscles are actively engaged in actions like
lifting objects, opening doors, and participating in sports or exercises that
involve arm and shoulder movements. They are essential for various upper
body movements and tasks.
DORSALS: The dorsal muscles, also known as the latissimus dorsi or lats,
have a primary function of shoulder adduction, extension, and internal
rotation. They help in moving the arms toward the back of the body and play a
crucial role in various shoulder and arm movements.
We use our dorsal muscles in daily activities that involve reaching, pulling, and
lifting, such as reaching for objects on high shelves, pulling doors or heavy
objects, and even activities like swimming or rowing. These muscles are
important for upper body mobility and strength.
TRAPEZIUS: The trapezius muscles, commonly known as the traps, have a
multifaceted function. They are responsible for multiple movements involving
the scapula (shoulder blades) and provide support to the neck and upper
back. The upper portion of the trapezius elevates the scapula, the middle
portion retracts or squeezes the scapula toward the spine, and the lower
portion depresses the scapula.
We use the trapezius muscles in our daily activities whenever we move our
shoulders, lift objects, maintain proper posture, or tilt our head. These muscles
are involved in tasks such as shrugging, lifting heavy items, and even holding
a bag on your shoulder. They are vital for shoulder mobility and upper body
support.
DELTOIDS: The deltoid muscles, commonly referred to as the delts, have the
primary function of raising and rotating the arm at the shoulder joint. They
provide mobility and strength to the shoulder and play a crucial role in various
upper body movements.
We use our deltoid muscles in everyday activities that involve raising or
moving our arms, such as reaching for objects, lifting, throwing, and even
simple actions like waving or brushing our hair. These muscles are essential
for performing a wide range of tasks that require shoulder and arm movement.
BICEPS: The biceps, or biceps brachii, have the primary function of flexing
the forearm at the elbow joint and supinating the forearm (rotating the palm
upward). They also assist in various movements of the shoulder.
We use our biceps in daily activities such as lifting objects, bending the elbow
to bring food to our mouth, carrying bags, and performing tasks that involve
gripping and lifting. These muscles are crucial for many common actions that
require strength and control in the arms.
TRICEPS: The triceps, or triceps brachii, have the primary function of
extending the forearm at the elbow joint. They are responsible for
straightening the arm. Triceps also play a role in stabilizing the shoulder joint.
We use our triceps in everyday activities when extending the arm, such as
pushing open a door, pushing objects away from the body, or when performing
tasks that involve straightening the elbow. These muscles are vital for various
actions that require arm extension and control.
You might also like
- Healthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesFrom EverandHealthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesNo ratings yet
- Muscle GroupDocument2 pagesMuscle Groupsofiesantillan18No ratings yet
- Muscle GroupsDocument25 pagesMuscle GroupsRoxana LorenteNo ratings yet
- Group 2 PeDocument9 pagesGroup 2 PeDanielle FacturaNo ratings yet
- Natsci ReportDocument2 pagesNatsci ReportRaven Claire PelongcoNo ratings yet
- BiomechDocument2 pagesBiomechKisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Quick ReferenceDocument9 pagesMuscular System Quick ReferenceElena FlegkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 BiomechanicsDocument7 pagesChapter 8 BiomechanicsSakshamNo ratings yet
- The Human MusclesDocument7 pagesThe Human Musclesogboifavour41No ratings yet
- Pe 03 Unit 02Document8 pagesPe 03 Unit 02Eunice Lei YanitNo ratings yet
- Anterior 2Document4 pagesAnterior 2Trisha TamsiNo ratings yet
- PE Fitness ReviewerDocument6 pagesPE Fitness ReviewerMyles BeatrizNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument33 pagesANATOMYPhoebe LiasosNo ratings yet
- Muscle GroupsDocument6 pagesMuscle Groupsmedlej70No ratings yet
- Lower Limb MusclesDocument24 pagesLower Limb MusclesPrincess Aliah SolmeronNo ratings yet
- Chest Muscles Functions: Flexion AdductionDocument4 pagesChest Muscles Functions: Flexion Adductionxilina BacasnotNo ratings yet
- Analysis of MovementDocument18 pagesAnalysis of MovementEfren Jonicel Daguio Domingo50% (2)
- Aisyah Tasha Putri 3B AssignmentDocument4 pagesAisyah Tasha Putri 3B AssignmentLiaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of LEG TrainingDocument53 pagesAnatomy of LEG TrainingDiego Tzompa AcostaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Manuel, April Rose L. AR11FA2Document3 pagesMuscular System: Manuel, April Rose L. AR11FA2April ManuelNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Manuel, April Rose L. AR11FA2Document3 pagesMuscular System: Manuel, April Rose L. AR11FA2April ManuelNo ratings yet
- Human Body Major Muscle Regions-1Document4 pagesHuman Body Major Muscle Regions-1Chris Sevilla BurhamNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3 P.EDocument37 pagesLesson-3 P.ECandice SanchezNo ratings yet
- CatinfographicDocument2 pagesCatinfographicapi-296594804No ratings yet
- Leg EbookDocument13 pagesLeg EbookValmir Shala50% (2)
- The Process of The SquatDocument8 pagesThe Process of The SquatespositodominicNo ratings yet
- Skull Facial: Elevate The 1 and 2 Ribs)Document5 pagesSkull Facial: Elevate The 1 and 2 Ribs)Sara HamidiNo ratings yet
- PathFit 1Document28 pagesPathFit 1Alfred AbieraNo ratings yet
- The Functions of The Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesThe Functions of The Muscular SystemJOSHUA ABELLANOSANo ratings yet
- Shoulder JointDocument37 pagesShoulder JointquadpumperNo ratings yet
- HMS Term 2 ModuleDocument6 pagesHMS Term 2 ModuleSirupyEwe GamerNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 PathfitDocument3 pagesActivity 2 PathfitKhate MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Core Training-Group6Document43 pagesCore Training-Group6BlariousNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 PE 101Document14 pagesLecture 2 PE 101AyanoNo ratings yet
- Built by Science PDFDocument73 pagesBuilt by Science PDFHeidi Y. Matos GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument47 pagesMuscular SystemKrystal Kaye AczonNo ratings yet
- Unlock Your Hip Flexors For 2020Document2 pagesUnlock Your Hip Flexors For 2020Suthap KlomrodNo ratings yet
- Principal Muscles of The BodyDocument11 pagesPrincipal Muscles of The BodyleninuthupNo ratings yet
- Back TrainingDocument36 pagesBack TrainingAndrew SwartNo ratings yet
- The Seven Functional Human Movement PatternsDocument22 pagesThe Seven Functional Human Movement PatternsJudy Mae LazagaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PathfitDocument8 pagesReviewer PathfitRandom PersonNo ratings yet
- Guide To Fix Flat FeetDocument16 pagesGuide To Fix Flat FeetLenka AnastasovskiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 3Document3 pagesUnit 2 3Rm OtNo ratings yet
- Definition of FlexibilityDocument3 pagesDefinition of FlexibilityShayne GalvezNo ratings yet
- Definition of FlexibilityDocument3 pagesDefinition of FlexibilityShayne GalvezNo ratings yet
- Phed Group 1Document14 pagesPhed Group 1David Paul LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy VocabularyDocument15 pagesHuman Anatomy Vocabularyapi-551593542No ratings yet
- Hip and PelvisDocument59 pagesHip and PelvisIbNu OmErNo ratings yet
- Mobility Packet 1 1Document7 pagesMobility Packet 1 1yungohanNo ratings yet
- Starting Positions: Saba LatifDocument45 pagesStarting Positions: Saba LatifSaba LatifNo ratings yet
- Module-3-PE-1 PlainDocument15 pagesModule-3-PE-1 PlainClarrene LappayNo ratings yet
- Derived Position: Prepared by Sajida MazharDocument58 pagesDerived Position: Prepared by Sajida MazharAmbreena RasoolNo ratings yet
- Dead LiftsDocument8 pagesDead LiftsjwarswolvesNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Core Bped 1Document6 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Core Bped 1arold bodoNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment - Bones and Muscles in WalkingDocument2 pagesBiology Assignment - Bones and Muscles in WalkingSenal Malaka PremarathnaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Homework - Working Out INGLES 4Document2 pagesWeek 5 - Homework - Working Out INGLES 4Antonio Andres Duffoo MarroquinNo ratings yet
- 1st - Starting PositionsDocument23 pages1st - Starting PositionsSaira SolNo ratings yet
- Homework - Working OutDocument1 pageHomework - Working OutRhobert EchNo ratings yet
- Muscles NamingDocument17 pagesMuscles NamingAbraham MendezNo ratings yet
- Path FitDocument8 pagesPath FitRyza Cabullos IINo ratings yet
- 1217196105-Exercise Chart For TRXDocument2 pages1217196105-Exercise Chart For TRXMario CarrilhoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Cases For Finals: DR Alastair Brown ST1 Neurosurgery CXHDocument38 pagesMusculoskeletal Cases For Finals: DR Alastair Brown ST1 Neurosurgery CXHAravind RaviNo ratings yet
- Oah Elbow ExercisesDocument4 pagesOah Elbow ExercisesPratik KadamNo ratings yet
- Fracture Treatment ProtocolsDocument14 pagesFracture Treatment ProtocolsZikrul IdyaNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Physical Therapy ExercisesDocument14 pagesUpper Extremity Physical Therapy ExercisesShrutiNo ratings yet
- PE Final Quiz 2 - Attempt Review PDFDocument6 pagesPE Final Quiz 2 - Attempt Review PDFJOHNSON KORAINo ratings yet
- Booty X Body BoostDocument4 pagesBooty X Body BoostMr SNo ratings yet
- Joint MobilizationDocument42 pagesJoint MobilizationSérgio Xavier Silva100% (1)
- Comprehensive UL MM Table - Sheet1Document5 pagesComprehensive UL MM Table - Sheet1Teodora MunteanuNo ratings yet
- Toronto+Notes+2011+ +21.+orthopaedicsDocument46 pagesToronto+Notes+2011+ +21.+orthopaedicsChanique Cousins100% (1)
- Common Gait DeviationsDocument4 pagesCommon Gait Deviationsswimgrl54100% (2)
- ACL and PCL ReconstructionDocument25 pagesACL and PCL ReconstructionAli Aufar HutasuhutNo ratings yet
- Saromm FormDocument5 pagesSaromm FormCharlene KalawNo ratings yet
- Turnout For Dancers: Hip Anatomy and Factors Affecting TurnoutDocument7 pagesTurnout For Dancers: Hip Anatomy and Factors Affecting TurnoutsstavrosNo ratings yet
- Manual Muscle Testing Scoring SheetDocument1 pageManual Muscle Testing Scoring SheetjotiroyNo ratings yet
- Anatomia MSKDocument1,249 pagesAnatomia MSKArthemizio Lopes100% (1)
- Sports Medicine Protocol Patella Fracture ORIFDocument1 pageSports Medicine Protocol Patella Fracture ORIFJuwitaNo ratings yet
- Home Exercise Program: Created by Rick Rafael, DPT, OCS, CSCS Jun 8th, 2019Document2 pagesHome Exercise Program: Created by Rick Rafael, DPT, OCS, CSCS Jun 8th, 2019mayday247No ratings yet
- AnkleDocument54 pagesAnkleUmi ShakiraNo ratings yet
- Effects of Scapular Stabilization Exercise Training OnDocument12 pagesEffects of Scapular Stabilization Exercise Training OnNajoua SalomaoNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Grip Width and Hand Orientation On MDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Grip Width and Hand Orientation On MJesus TarabiniNo ratings yet
- Anterior Cruciate LigamentDocument26 pagesAnterior Cruciate LigamentAmandeep Singh100% (2)
- Common ErrorsDocument5 pagesCommon Errorsvikas guptaNo ratings yet
- Wrist Isometric Exercise ProgramDocument2 pagesWrist Isometric Exercise ProgramDarnell GNo ratings yet
- Gardner 1948Document14 pagesGardner 1948mitroisergiuNo ratings yet
- Joint Classification, Oesteokinematics and ArthrokinematicsDocument4 pagesJoint Classification, Oesteokinematics and ArthrokinematicsAminath YamaanyNo ratings yet
- Home Exercise Programs For Musculoskeletal and Sports InjuriesDocument265 pagesHome Exercise Programs For Musculoskeletal and Sports Injuriesvitor flenik100% (5)
- Tortora Aus1e ch09Document44 pagesTortora Aus1e ch09jonas hingcoNo ratings yet
- Special Arthrology of The ForelimbDocument37 pagesSpecial Arthrology of The ForelimbTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Acl - Rehab - Protocol After Knee OperationDocument37 pagesAcl - Rehab - Protocol After Knee OperationGinoNo ratings yet