Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet 3
Uploaded by
bodesaid2002Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet 3
Uploaded by
bodesaid2002Copyright:
Available Formats
Sheet 3
nd
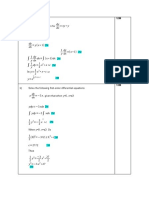
2 Order Differential Equations with variable coefficient
1) (1 + x) 2 y + (1 + x) y + y = 4 cos ln(1 + x)
2) y + y = 1 − cos ec x
3) y + 2(tan x) y + (1 + 2 tan 2 x) y = cos2 x ,where y = cos x is one of the solutions of
its corresponding homogeneous equation.
4) y − y = e −2 x sin e − x
15
5) (2 x + 1) y − 6 y + y = 8(2 x + 1)
2x + 1
6) ( x + 1) 2 y + ( x + 1) y = (2 x + 3)(2 x + 4)
7) xy − (2 x + 1) y + ( x + 1) y = ( x 2 + x − 1)e 2 x
8) x 2 y − x( x + 2) y + ( x + 2) y = 0
9) x 2 (ln x − 1) y − xy + y = 0
10) y + 2 y + y = (e x − 1) −2
1
11) (2 x + 1)( x + 1) y + 2 xy − 2 y = (2 x + 1) 2 , given that y1 = x and y2 =
are two
x +1
Linearly independent solutions of the corresponding homogenous equation.
12) y − 2 y + 2 y = e x (tan x + cot x)
13) ( x 2 − 2 x) y + (2 − x 2 ) y + 2( x − 1) y = 5 x 2 ( x − 2) 2 e x , given that yh = c1 x 2 + c2e x
14) y + y = cos ec3 x
15) If y = e m x is a particular solution of the equation: (2 x + 1) y + (4 x − 2) y − 8 y = 0 ,
Find the value of m and hence find the general solution.
16) (1 − x) y + xy − y = 0
2
17) y − y =
e − e−x
x
2
18) Show that the substitution t = reduces the equation: x 5 y + 2 x 4 y + 4 xy = 2 to
x
an equation with constant coefficients and hence find its solution.
You might also like
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- George F. Simmons Differential Equations With Applications and Historical Notes McGraw-Hill Science (1991) Solutions PDFDocument126 pagesGeorge F. Simmons Differential Equations With Applications and Historical Notes McGraw-Hill Science (1991) Solutions PDFEngineering Books45% (33)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Tut 1-1Document4 pagesTut 1-1Beauty SpotNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering Pune Ordinary Differential Equations and Multivariate Calculus Tutorial-1 (2019-2020)Document3 pagesCollege of Engineering Pune Ordinary Differential Equations and Multivariate Calculus Tutorial-1 (2019-2020)AlaiaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resolver Las Siguientes Ecuaciones Diferenciales LinealesDocument4 pagesEjercicios Resolver Las Siguientes Ecuaciones Diferenciales LinealesmariaNo ratings yet
- AOD Sheet SolDocument180 pagesAOD Sheet SolIshhuNo ratings yet
- Ma2020 2019 2 PDFDocument4 pagesMa2020 2019 2 PDFsusmithaNo ratings yet
- 8.E - Differential Equations (Exercises) - Mathematics LibreTextsDocument1 page8.E - Differential Equations (Exercises) - Mathematics LibreTextsRahel H.No ratings yet
- Answers To Final-2021Document9 pagesAnswers To Final-2021Enes ErtenNo ratings yet
- Math 2042 WorksheetDocument4 pagesMath 2042 WorksheetBiftu ShibbireNo ratings yet
- ODE MULTIVARIATE CALCULUSDocument2 pagesODE MULTIVARIATE CALCULUSRUTUJA MADHURENo ratings yet
- AnsSec3_7Document2 pagesAnsSec3_7Reginald AshongNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential Equations Segment Wise Questions From 1983 To 2011 Civil ServiceDocument6 pagesOrdinary Differential Equations Segment Wise Questions From 1983 To 2011 Civil ServiceNagendran KrishnamoorthiNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Document38 pagesDifferential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- FACULTY OF SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY AND HUMAN DEVELOPMENT UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIADocument2 pagesFACULTY OF SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY AND HUMAN DEVELOPMENT UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIAFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Problems On Two Dimensional Random VariableDocument15 pagesProblems On Two Dimensional Random VariableBRAHMA REDDY AAKUMAIIANo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - Additional Topics First Order ODE PDFDocument31 pagesDifferential Equations - Additional Topics First Order ODE PDFRicky Perez100% (1)
- D.E 6rd EditionDocument33 pagesD.E 6rd EditionkenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Chinthareddy Aman Reddy ae22b103No ratings yet
- Solve Elementary Differential EquationsDocument33 pagesSolve Elementary Differential EquationskenNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 LinearDocument18 pagesLecture1 LinearNguyễn Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- Problem A RioDocument28 pagesProblem A RioGerman Cordova MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Solve Elementary Differential EquationsDocument33 pagesSolve Elementary Differential EquationskenNo ratings yet
- ODE 2023 Tutorial 1 and 2Document2 pagesODE 2023 Tutorial 1 and 2Just EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Solve Elementary Differential EquationsDocument33 pagesSolve Elementary Differential Equationsken100% (2)
- 9 2012 Deqs Chap3a1Document113 pages9 2012 Deqs Chap3a1Steven BrownNo ratings yet
- CA2 TEE101 2021 AnswerDocument8 pagesCA2 TEE101 2021 AnswerSagilenNo ratings yet
- DE Lec 1-9Document9 pagesDE Lec 1-9Cheat CodeNo ratings yet
- 2A Unit 2 Lecture 2.1 To 2.6 Ordinary de of Order 1Document74 pages2A Unit 2 Lecture 2.1 To 2.6 Ordinary de of Order 1Arin SellsNo ratings yet
- W10 SolutionsDocument3 pagesW10 Solutionsjohn smitherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document45 pagesChapter 5api-3729261No ratings yet
- Tutorials 1Document1 pageTutorials 1Previnn BalaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech 2nd Semester Maths-II Question BankDocument8 pagesB.Tech 2nd Semester Maths-II Question BankAtul JanbandhuNo ratings yet
- First Order Ordinary Differential Equations (1 Order - ODE)Document3 pagesFirst Order Ordinary Differential Equations (1 Order - ODE)Naga MerahNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-Separation-of-Variables-ModuleDocument6 pagesChapter-2-Separation-of-Variables-ModuleMARK JAMES PUTOLANNo ratings yet
- Chap2-Second Order ODEsDocument16 pagesChap2-Second Order ODEsdanish91No ratings yet
- MA2201 - Tutorial Sheet 1Document6 pagesMA2201 - Tutorial Sheet 1Himanshu ChittuNo ratings yet
- Ans 2Document5 pagesAns 2teju1996coolNo ratings yet
- Math 202-102 Sec: 21 Solution Quiz 2Document2 pagesMath 202-102 Sec: 21 Solution Quiz 2AndreaMunozNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics FormulasDocument5 pagesEngineering Mathematics Formulasvenkata sridhar DhulipalaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 SolutionsDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 SolutionsAkshay NarasimhaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 1Document2 pagesProblem Sheet 3 1Sri KrishNo ratings yet
- 2233 mt1 S99sDocument5 pages2233 mt1 S99sAkoh C Josh ÜNo ratings yet
- Dasgal 3.5Document2 pagesDasgal 3.5renchindorj_md3753No ratings yet
- MAS 201 Spring 2021 (CD) Chapter 3 Higher-Order Differential EquationsDocument23 pagesMAS 201 Spring 2021 (CD) Chapter 3 Higher-Order Differential EquationsBlue horseNo ratings yet
- Deriv of Logs-1Document2 pagesDeriv of Logs-1psoohooNo ratings yet
- EContent 1 2023 06 07 09 59 44 Assignmentforslowlearner1pdf 2023 05 10 09 19 33Document2 pagesEContent 1 2023 06 07 09 59 44 Assignmentforslowlearner1pdf 2023 05 10 09 19 33Nitesh RajNo ratings yet
- Maths Mania #057 - Rational Expressions and PolynomialsDocument3 pagesMaths Mania #057 - Rational Expressions and PolynomialsTUSHAR JALANNo ratings yet
- MA 102 (Ordinary Differential Equations)Document3 pagesMA 102 (Ordinary Differential Equations)Lynx101No ratings yet
- Fe Tutorials Sem2Document8 pagesFe Tutorials Sem2narendasreNo ratings yet
- 4orca Share Media1664099245129 6979738120242220226Document5 pages4orca Share Media1664099245129 6979738120242220226Angelo GranadaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Besar Kalkulus IIIDocument50 pagesTugas Besar Kalkulus IIIKeisuke TakahiroNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Differential EquationsDocument12 pagesIntroduction to Differential EquationsWenaBacxNo ratings yet
- Linear differential equations solvedDocument5 pagesLinear differential equations solvedprakhar mishraNo ratings yet
- EJERCICIOS PROPUESTOS N° 3 LIMITES INDETERMINADOSDocument30 pagesEJERCICIOS PROPUESTOS N° 3 LIMITES INDETERMINADOSAlisson MartinezNo ratings yet
- First Order Differential EquationDocument15 pagesFirst Order Differential Equationdether acopiadoNo ratings yet
- 280hwalls19 PDFDocument69 pages280hwalls19 PDFArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- Exercises-Exact EquationsDocument4 pagesExercises-Exact EquationsJake GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 1st Order ODE and Its ApplicationsDocument76 pages1st Order ODE and Its ApplicationsMuhammad EhsanNo ratings yet