Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PL20
Uploaded by
super95190Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PL20
Uploaded by
super95190Copyright:
Available Formats
y
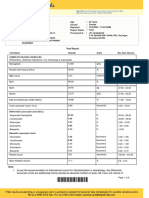
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
HEALTHKIND COMPLETE
HAEMATOLOGY
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Haemoglobin (Hb)
Total WBC Count / TLC 6.0 4.0 - 10.0 thou/µL
RBC Count 4.2 3.8 - 4.8 million/µL
PCV / Hematocrit 37.1 36.0 - 46.0 %
MCV 88.2 83.0 - 101.0 fL
MCH 28.7 27.0 - 32.0 pg
MCHC /dL
RDW (Red Cell Distribution Width) %
Neutrophils 68 40 - 80 %
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 1 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Lymphocytes %
Eosinophils %
Monocytes 03 02 - 10 %
Basophils 00 00 - 02 %
Absolute Neutrophil Count 4080 2000 - 7000 /µL
Absolute Lymphocyte Count 1620 1000 - 3000 /µL
Absolute Eosinophil Count 120 20 - 500 /µL
Absolute Monocyte Count 180 L 200 - 1000 /µL
Absolute Basophil Count L /µL
DLC Performed By EDTA Smear
Platelet Count
MPV (Mean Platelet Volume) H fL
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 2 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) H
BIOCHEMISTRY
Fasting Plasma Glucose H /dL
Impaired Fasting Glucose : 100 - 125
Diabetes : > 126
HbA1C (Glycosylated Hemoglobin)
HbA1c 8.2 H Non Diabetic : < 5.7 % %
Prediabetic Range : 5.7 - 6.4 %
Diabetic Range : >= 6.5 %
Goal of Therapy :<7.0 %
Action suggested :>8.0 %
Mean Plasma Glucose 188.6 H <116.0 mg/dL
Lipid Profile
Total Cholesterol v /dL
High Risk : >/= 240
Triglycerides 84 Desirable : < 150 mg/dL
High : 200 - 499
V
LDL Cholesterol (Calculated) /dL
Borderline High : 130 - 160
Very High : >/=190
HDL Cholesterol 40 Low : < 40 mg/dL
Optimal : 40 - 60
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 3 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
VLDL Cholesterol /dL
Total Cholesterol / HDL Ratio L
Av
Moderate Risk : 7.1 - 11.0
High Risk : > 11.0
LDL / HDL Ratio 1.6 0.5 - 3.0
Low Risk : 0.5 - 3.0
Moderate Risk : 3.1 - 6.0
High Risk : > 6.0
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 4 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Liver Function Test (LFT)
Bilirubin Total /dL
Bilirubin Direct /dL
Serum Bilirubin (Indirect) 0.20 <0.90 mg/dL
SGOT / AST 13 0 - 27 U/L
SGPT / ALT 11 0 - 33 U/L
AST / ALT Ratio 1.18
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) U/L
Total Protein /dL
Albumin 4.0 3.5 - 4.8 g/dL
Globulin /dL
Albumin/Globulin (A/G) Ratio /dL
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 5 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
SEROLOGY
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg) e e
Rapid Card
BIOCHEMISTRY
Blood Urea
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) 9.30 L 9.81 - 20.00 mg/dL
Urea 19.90 L 21.00 - 43.00 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.68 0.50 - 1.20 mg/dL
BUN Creatinine Ratio
Uric Acid 4.0 2.4 - 5.7 mg/dL
Electrolytes (Na/K/Cl)
Sodium
Potassium 4.4 3.5 - 5.1 mmol/L
Chloride 104 97 - 107 mmol/L
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 6 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Calcium /dL
Iron Studies
Sample: Serum
Iron 60 37 - 145 µg/dL
(UIBC) 410 H 110 - 370 µg/dL
Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity
Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC) 470 H 228 - 428 µg/dL
% Saturation 13 L 20 - 50 %
Thyroid Profile Total
Total T3 (Triiodothyronine) 1.22 0.80 - 2.00 ng/mL
Total T4 (Thyroxine) 9.87 5.10 - 14.10 µg/dL
TSH 3rd Generation 1.180 0.270 - 4.200 µIU/mL
Vitamin D 25 - Hydroxy 14.2 L Deficiency < 20 ng/mL
Sufficiency 30 - 100
Toxicity > 100
Vitamin B12 > 2000 H 191 - 663 pg/mL
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 7 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
CLINICAL PATHOLOGY
Urine Routine & Microscopic Examination
Colour Pale Yellow Pale Yellow
Appearance Clear Clear
Specific Gravity 1.010 1.003 - 1.035
pH 6.0 4.7 - 7.5
Chemical Examination
Glucose Not Detected Not Detected
Protein ect ect
Ketones Not Detected Not Detected
Blood Not Detected Not Detected
Bilirubin ect ect
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 8 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Urobilinogen
Nitrite ect ect
Microscopic Examination
Pus Cells 1-2 0-5 /hp
RBC Not Detected Not Detected /hp
Epithelial Cells 2-3 0-5 /hp
Casts Not Detected Not Detected /hp
Crystals ect ect /hpf
Bacteria ect ect /hpf
Remarks
Remarks
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 9 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Hemoglobin is the iron containing protein molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and returns carbon dioxide
from the tissues back to the lungs. Decrease in Hemoglobin levels results in anaemia and very high Hemoglobin levels results in hemochromatosis.
Hematocrit or Packed cell volume (PCV) is the proportion of blood volume occupied by red blood cells and is typically about three times the
Platelet Count
Platelets or thrombocytes are a cellular component of blood whose function is to stop bleeding by clumping or clotting blood vessel injuries. Low
platelet count, also known as Thrombocytopenia, can be either due to less production or increased destruction of platelets. High platelet count or
Thrombocytosis can be due to unregulated production, secondary to congenital, reactive or neoplastic conditions.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
measure of the size of the average RBC, MCH is a measure of the hemoglobin cointent of the average RBC and MCHC is the hemoglobin
concentration per RBC. The red cell distribution width (RDW) is a measure of the degree of variation in RBC size (anisocytosis) and is helpful in
distinguishing between some anemias. CBC examination is used as a screening tool to confirm a hematologic disorder, to establish or rule out a
and appropriate additional testing performed.
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 10 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level reflects the mean glucose concentration over the previous period (approximately 8-12 weeks) and provides a much
better indication of long-term glycemic control than blood and urinary glucose determinations. American Diabetes Association (ADA) include the use
of HbA1c to diagnose diabetes, using a cutpoint of 6.5%. The ADA recommends measurement of HbA1c 3-4 times per year for type 1 and poorly
controlled type 2 diabetic patients, and 2 times per year for well-controlled type 2 diabetic patients) to assess whether a patient's metabolic control
has remained continuously within the target range. Falsely low HbA1c results may be seen in conditions that shorten erythrocyte life span. and may
not reflect glycemic control in these cases accurately.
Total Cholesterol
Serum cholesterol is elevated in hereditary hyperlipoproteinemias and in other metabolic diseases. Moderate-to-markedly elevated values are also seen
in cholestatic liver disease. Increased levels are a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Low levels of cholesterol may be seen in disorders like
hyperthyroidism, malabsorption, and deficiencies of apolipoproteins.
Hyperlipidemia may be inherited or may be due to conditions like biliary obstruction, diabetes mellitus, nephrotic syndrome, renal failure,certain
metabolic disorders or drug induced.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is an important tool used to assess risk of developing coronary heart disease.Increased levels are seen in persons with
heart disease (CHD). Very low levels are seen in Tangier disease, cholestatic liver disease and in association with decreased hepatocyte function.
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 11 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
metabolism (eg, hereditary and neonatal jaundice). Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia is seen in newborn andd known as physiological jaundice.
Elevated unconjugated bilirubin in the neonatal period may result in brain damage (kernicterus).Crigler-Najjar syndromes type I and type II are also
associated with elevated levels of indirect bilirubin.Both conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin are increased in hepatitis and space-occupying lesions
of the liver; and obstructive lesions such as carcinoma of the head of the pancreas, common bile duct, or ampulla of Vater."
Bilirubin Direct
"Direct bilirubin is a measurement of conjugated bilirubin.Jaundice can occur as a result of increased bilirubin production (eg, hemolysis and ineffective
erythropoiesis), decreased bilirubin excretion (eg, obstruction and hepatitis), and abnormal bilirubin metabolism (eg, hereditary and neonatal jaundice).
Inherited disorders in which direct bilirubin levels are increased are seen in Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome,idiopathic neonatal hepatitis
and biliary atresia. The most commonly occurring form of jaundice of the newborn called physiological jaundiceis due to increase in levels of indirect
bilirubin.Both conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin are increased in hepatocellular diseases such as hepatitis and space-occupying lesions of the liver,
conditions affecting the liver along with ALT, though ALT levels are higher. The ALT:AST ratio which is normally <1 is reversed in these conditions
and becomes >1. AST levels are usually raised before clinical signs and symptoms of disease appear. AST and ALT also rise in primary or metastatic
SGPT / ALT
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 12 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
not exceed the upper limit of the reference interval in some cases.
syndrome).Hyperalbuminemia is seen in dehydration."
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 13 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
In case of negative results:
Please note that while rapid test is a sensitive and reliable screening test, it should not be used as a sole criterion for diagnosis. It is recommended to use
molecular testing (PCR) for confirmation.
In case of positive results:
The test has been performed on two different rapid technologies. Please note that while rapid test is a sensitive and reliable screening test, it should not
be used as a sole criterion for diagnosis. It is recommended to use molecular testing (PCR) for confirmation.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN) may be due to prerenal causes (cardiac decompensation, water depletion due to decreased intake
and excessive loss, increased protein catabolism, and high protein diet), renal causes (acute glomerulonephritis, chronic nephritis,
Creatinine
Serum creatinine is inversely correlated with glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Increased levels of Serum Creatinine is associated with renal dysfunction.
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 14 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Chloride
"Chloride (Cl) is the major extracellular anion and it has an important role in maintaining proper body water distribution, osmotic pressure, and
normalanion-cation balance in the extracellular fluid compartment. Chloride is increased in dehydration, renal tubular acidosis, acute renal failure,
metabolic acidosis associated with prolonged diarrhea and loss of sodium bicarbonate, diabetes insipidus, adrenocortical hyperfuction,salicylate
intoxication and with excessive infusion of isotonic saline or extremely high dietary intake of salt. Hyperchloremia acidosis may be a sign of severe
renal tubular pathology. Chloride is decreased inoverhydration, chronic respiratory acidosis, salt-losing nephritis, metabolic alkalosis, congestive heart
failure, Addisonian crisis, certain types of metabolic acidosis, persistent gastric secretion and prolonged vomiting, aldosteronism, bromide intoxication,
syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion,and conditions associated with expansion of extracellular fluid volume."
Serum Calcium levels are used to monitor and diagnose a wide range of diseases of bone, kidney, parathyroid gland, or gastrointestinal tract. Calcium
levels may also reflect abnormal vitamin D or protein levels. Hypocalcemia or low serum calcium levels is associated with absent or decreased function
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 15 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
Transferrin is the primary plasma iron transport protein but accounts for 25% to 30% saturation with iron. The additional amount of iron that can be
bound is the unsaturated iron-binding capacity (UIBC). The total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) can be indirectly determined using the sum of the serum
iron and UIBC. TIBC levels are usually low when serum Iron levels are high and vice versa.
Total T3 (Triiodothyronine)
Thyroid hormones, T3 and T4, which are secreted by the thyroid gland, regulate a number of developmental, metabolic, and neural activities throughout
the body. The thyroid gland synthesizes 2 hormones - T3 and T4. T3 production in the thyroid gland constitutes approximately 20% of the total
circulating T3, 80% being produced by peripheral conversion from T4. T3 is more potent biologically. Total T3 comprises of Free T3 and bound T3.
Bound T3 remains bound to carrier proteins like thyroid-binding globulin, prealbumin, and albumin). Only the free forms are metabolically active. In
hyperthyroidism, both T4 and T3 levels are usually elevated, but in some rare cases, only T3 elevation is also seen. In hypothyroidism T4 and T3
levels are both low. T3 levels are frequently low in sick or hospitalized euthyroid patients.
Total T4 (Thyroxine)
hypothyroidism.
TSH levels are elevated in primary hyporthyroidism and low in primary hyperthyroidism. Evaluation of TSH is useful in the differential diagnosis of
primary from secondary and tertiary hypothyroidism. In primary hypothyroidism, TSH levels are elevated, while in secondary and tertiary
14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 16 of 18
y
Sidhart Pathology (Siddharthnagar) Pathkind Diagnostic Pvt. Ltd.
Uska Road, Sidhartnagar, UP- 272207 Shop No 1, Dubey Complex, Bettihata, Gorakhpur - 273001
Report Status - Final
Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unit
FIRST TRIMESTER 0.100 - 2.500 µIU/mL
SECOND TRIMESTER 0.200 - 3.000 µIU/mL
THIRD TRIMESTER 0.300 - 3.000 µIU/mL
Vitamin D 25 - Hydroxy
The 25-hydroxy vitamin D test is used to detect bone weakness or other bone malfunctions or disorders that occur as a result of a vitamin D
deficiency.Those who are at high risk of having low levels of vitamin D include people who don’t get much exposure to the sun, older adult, people
with obesity, babies who are breastfed only, post gastric bypass surgery, Crohn’s disease and other intestinal malabsorption conditions.
Hypervitaminosis D usually occurs due to over intake of Vitamin D supplementation.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is necessary for hematopoiesis and normal neuronal function. It requires intrinsic factor (IF) for absorption. Vitamin B12 deficiency may
be due to lack of IF secretion by gastric mucosa (eg, gastrectomy, gastric atrophy) or intestinal malabsorption (eg, ileal resection, small intestinal
Urine routine examination and microscopy comprises of a set of screening tests that can detect some common diseases like urinary tract infections,
kidney disorders, liver problems, diabetes or other metabolic conditions. Physical characteristics (colour and appearance), chemical composition
** End of Report**
Dr Saurabh Nath Tripathi 14002020006592 Mrs. DUMMY PL20
age No: 17 of 18
age No: 18 of 18
You might also like
- Report of UsDocument7 pagesReport of UsMd Usman KhanNo ratings yet
- PL95Document8 pagesPL95Untold DarknessNo ratings yet
- PL95Document8 pagesPL95Ashutos MohantyNo ratings yet
- Pathkindlabs - Com:sites:default:files:2021-07:fever Panel BasicDocument7 pagesPathkindlabs - Com:sites:default:files:2021-07:fever Panel BasicVARUN REDDYNo ratings yet
- Fever Panel BasicDocument7 pagesFever Panel BasicMadNo ratings yet
- SHANTIDocument4 pagesSHANTINeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Report Status - Final Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval UnitDocument7 pagesReport Status - Final Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval UnitSiva MudunuriNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument5 pagesReportpateldrash2498No ratings yet
- LPL - Pasricha Diagnostics & Ultrasound ClinicDocument4 pagesLPL - Pasricha Diagnostics & Ultrasound ClinicJohnnieNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Covid-19 Health Checkup (Post Recovery)Document8 pagesDepartment of Hematology Covid-19 Health Checkup (Post Recovery)Geetika GuptaNo ratings yet
- LPLT12448 : LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Document6 pagesLPLT12448 : LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Kumar ManglamNo ratings yet
- (Reliable Diagnostic Laboratory Nepal Pvt. LTD.) Samakhushi-26, Kathmandu, Nepal, Phone: 014366073 9801612348Document1 page(Reliable Diagnostic Laboratory Nepal Pvt. LTD.) Samakhushi-26, Kathmandu, Nepal, Phone: 014366073 9801612348Abinash MandalNo ratings yet
- 01031134LB 2023 12 01Document2 pages01031134LB 2023 12 01shraddhaa129No ratings yet
- Life Healthcare - CC Gram-Ijarata Thana-Paliganj Paipura KAL Patna Lab II R K ESTATE Opposite IGIMS Raja Bazar Bailey Road Patna-800014Document5 pagesLife Healthcare - CC Gram-Ijarata Thana-Paliganj Paipura KAL Patna Lab II R K ESTATE Opposite IGIMS Raja Bazar Bailey Road Patna-800014Parth From class 7 ANo ratings yet
- RADHEDocument4 pagesRADHENeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report: M.D. (Path. & Bact.)Document13 pagesLaboratory Report: M.D. (Path. & Bact.)pateldrash2498No ratings yet
- Laboratory Report: Consultant PathologistDocument2 pagesLaboratory Report: Consultant Pathologisttafiki4253No ratings yet
- dfee0562-f38e-4bbe-b0fa-7eb727ea32eaDocument4 pagesdfee0562-f38e-4bbe-b0fa-7eb727ea32eaNirmal RajoriaNo ratings yet
- WP02Document9 pagesWP02lucky jainNo ratings yet
- 463938838Document8 pages463938838sumitthardak34No ratings yet
- Amit ReportDocument3 pagesAmit ReportXlramitNo ratings yet
- Investigation Bill With ReportDocument3 pagesInvestigation Bill With ReportDevesh KhandareNo ratings yet
- DR Lal Pathlabs: LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini Delhi 110085Document4 pagesDR Lal Pathlabs: LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini Delhi 110085Shubham BhadouriyaNo ratings yet
- 99f5fd85-4ee0-4756-afcf-49c54943d6afDocument12 pages99f5fd85-4ee0-4756-afcf-49c54943d6afprint emitraNo ratings yet
- LPL - PSC Rohini (DC Chowk) Shop No. 27, Ground Floor, SG Mall, Sect or - 9, DC Chowk, Rohini New Delhi - 110 DelhiDocument2 pagesLPL - PSC Rohini (DC Chowk) Shop No. 27, Ground Floor, SG Mall, Sect or - 9, DC Chowk, Rohini New Delhi - 110 DelhiSaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lab ResultDocument7 pagesLab ResultAanshika RaizadaNo ratings yet
- LPL - PSC Yamuna Vihar-2 B-4/122 Yamuna Vihar NR Bhajanpura Thana Cont: 011 22915901, 9811119729Document4 pagesLPL - PSC Yamuna Vihar-2 B-4/122 Yamuna Vihar NR Bhajanpura Thana Cont: 011 22915901, 9811119729Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 - 11 Apr Blood Urine TestDocument8 pages1 - 11 Apr Blood Urine Testguptarahul1992No ratings yet
- LPLT12451 : LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Document5 pagesLPLT12451 : LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Aarav MishraNo ratings yet
- Ha 2Document3 pagesHa 2Divyansh Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument5 pagesHematologyDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- All ServicesDocument3 pagesAll Servicesmohamed nasserNo ratings yet
- L89 - Ypl Diagnostics Ypl Diagnosticssamrat Hopping Mall, Garh Road, Pin Code No: 252002meerut Uttar MeerutDocument3 pagesL89 - Ypl Diagnostics Ypl Diagnosticssamrat Hopping Mall, Garh Road, Pin Code No: 252002meerut Uttar MeerutAyush Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Indian EconomyDocument10 pagesIndian Economyrajputdhruv100No ratings yet
- Indi Font Keyboad GuideDocument1 pageIndi Font Keyboad GuideJaydip GupteNo ratings yet
- CS1810457 Report 2Document1 pageCS1810457 Report 2giri00767098No ratings yet
- Department of Haematology: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument2 pagesDepartment of Haematology: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range Methodgsm2008No ratings yet
- 2 15 Apr Blood TestsDocument6 pages2 15 Apr Blood Testsguptarahul1992No ratings yet
- Q2ohrv4w3sib2vnjaa2m4iebDocument10 pagesQ2ohrv4w3sib2vnjaa2m4iebShalu SaharanNo ratings yet
- 3upneaa5qdckn2nonvdn0vouDocument7 pages3upneaa5qdckn2nonvdn0vouNitinNo ratings yet
- H5zx4fklv4ovtl2lopumlbu3Document9 pagesH5zx4fklv4ovtl2lopumlbu3roypalNo ratings yet
- Medical ReportsDocument5 pagesMedical Reportsritikapagraj01No ratings yet
- All ServicesDocument4 pagesAll Servicessamashawki123No ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWDocument4 pagesMedical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWdhavalNo ratings yet
- Report Status - Final Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval UnitDocument2 pagesReport Status - Final Test Name Result Biological Ref. Interval Unitsarvesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Kvo2rd2iirnhll0zct4myobjDocument10 pagesKvo2rd2iirnhll0zct4myobjmani bhushan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Jyoti Singh ReportsDocument5 pagesJyoti Singh ReportsRaghujyotisNo ratings yet
- Gpbxa1l2sjwh0xeblfzsz3zxDocument8 pagesGpbxa1l2sjwh0xeblfzsz3zxmani bhushan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Wvgrd5c40vivpeavmmpsf3cvDocument4 pagesWvgrd5c40vivpeavmmpsf3cvVishav Jindal100% (1)
- Medical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWDocument4 pagesMedical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWdhavalNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Mrs - Durva Shukla 29 Years / Female Maithili Ghadge 2011713370 177801575942 26-Apr-2020 / 12:24 R E P O R TDocument7 pagesBiochemistry: Mrs - Durva Shukla 29 Years / Female Maithili Ghadge 2011713370 177801575942 26-Apr-2020 / 12:24 R E P O R TSachin AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 41t3qpidtgztf1fevf4pneiyDocument4 pages41t3qpidtgztf1fevf4pneiyAdnan Rasheed ParimooNo ratings yet
- Hematology Test Name (Methodology) Result Flag Units Biological Reference IntervalDocument2 pagesHematology Test Name (Methodology) Result Flag Units Biological Reference IntervalMonu SahotaNo ratings yet
- PdfText PDFDocument10 pagesPdfText PDFshakila banuNo ratings yet
- Z021 PDFDocument2 pagesZ021 PDFAditya RudraNo ratings yet
- Shailesh 3Document2 pagesShailesh 3Shailesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Document5 pagesLPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Sneha RaiNo ratings yet
- 4700003265: Patient ID 47000838 Sid No Mumbai Branch Mr. DEENBANDHU (89579)Document9 pages4700003265: Patient ID 47000838 Sid No Mumbai Branch Mr. DEENBANDHU (89579)Deenbandhu SahaniNo ratings yet
- Movie Piracy in Ethiopian CinemaDocument22 pagesMovie Piracy in Ethiopian CinemaBehailu Shiferaw MihireteNo ratings yet
- Technology Management 1Document38 pagesTechnology Management 1Anu NileshNo ratings yet
- Mark Garside Resume May 2014Document3 pagesMark Garside Resume May 2014api-199955558No ratings yet
- Technical Specification For 33KV VCB BoardDocument7 pagesTechnical Specification For 33KV VCB BoardDipankar ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- in Strategic Management What Are The Problems With Maintaining A High Inventory As Experienced Previously With Apple?Document5 pagesin Strategic Management What Are The Problems With Maintaining A High Inventory As Experienced Previously With Apple?Priyanka MurthyNo ratings yet
- Shostack ModSec08 Experiences Threat Modeling at MicrosoftDocument11 pagesShostack ModSec08 Experiences Threat Modeling at MicrosoftwolfenicNo ratings yet
- Theories of International InvestmentDocument2 pagesTheories of International InvestmentSamish DhakalNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationLouis HilarioNo ratings yet
- Turn Around Coordinator Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesTurn Around Coordinator Job DescriptionMikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Elasticity and ForecastingDocument25 pagesChapter3 Elasticity and ForecastingGee JoeNo ratings yet
- Hamstring - WikipediaDocument21 pagesHamstring - WikipediaOmar MarwanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub - Bobs Refunding Ebook v3 PDFDocument65 pagesDokumen - Pub - Bobs Refunding Ebook v3 PDFJohn the First100% (3)
- Excon2019 ShowPreview02122019 PDFDocument492 pagesExcon2019 ShowPreview02122019 PDFSanjay KherNo ratings yet
- Cisco SDWAN Case Study Large Global WANDocument174 pagesCisco SDWAN Case Study Large Global WANroniegrokNo ratings yet
- 15.053/8 February 7, 2013: More Linear and Non-Linear Programming ModelsDocument42 pages15.053/8 February 7, 2013: More Linear and Non-Linear Programming ModelsShashank SinglaNo ratings yet
- GPS Spoofing (2002-2003)Document8 pagesGPS Spoofing (2002-2003)Roger JohnstonNo ratings yet
- 7400 IC SeriesDocument16 pages7400 IC SeriesRaj ZalariaNo ratings yet
- Ob NotesDocument8 pagesOb NotesRahul RajputNo ratings yet
- Washing Machine: Service ManualDocument66 pagesWashing Machine: Service ManualFernando AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Huawei R4815N1 DatasheetDocument2 pagesHuawei R4815N1 DatasheetBysNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Number System PDFDocument5 pagesAptitude Number System PDFharieswaranNo ratings yet
- Salads: 300 Salad Recipes For Rapid Weight Loss & Clean Eating (PDFDrive) PDFDocument1,092 pagesSalads: 300 Salad Recipes For Rapid Weight Loss & Clean Eating (PDFDrive) PDFDebora PanzarellaNo ratings yet
- 2021-03 Trophy LagerDocument11 pages2021-03 Trophy LagerAderayo OnipedeNo ratings yet
- FDA Approves First Gene Therapy, Betibeglogene Autotemcel (Zynteglo), For Beta-ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesFDA Approves First Gene Therapy, Betibeglogene Autotemcel (Zynteglo), For Beta-ThalassemiaGiorgi PopiashviliNo ratings yet
- Pivot TableDocument19 pagesPivot TablePrince AroraNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For SKPMG2 TSSP - Draft For Consultation 10.10.17Document5 pagesGuidelines For SKPMG2 TSSP - Draft For Consultation 10.10.17zqhnazNo ratings yet
- Agnes de MilleDocument3 pagesAgnes de MilleMarie-Maxence De RouckNo ratings yet
- Law of EvidenceDocument14 pagesLaw of EvidenceIsha ChavanNo ratings yet
- User Manual For Speed Control of BLDC Motor Using DspicDocument12 pagesUser Manual For Speed Control of BLDC Motor Using DspicTrung TrựcNo ratings yet
- Playful Homeschool Planner - FULLDocument13 pagesPlayful Homeschool Planner - FULLamandalecuyer88No ratings yet
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainFrom EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (95)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (61)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)